Similar presentations:
Teenage making good decisions
1.
making gooddecisions
2.
THETEENAGE
BRAIN
WHY DO TEENAGERS THINK AND ACT
DIFFERENTLY?
TEENAGERS ARE OFTEN ACCUSED OF
MAKING POOR DECISIONS AND EXCESSIVE
RISK-TAKING - HENCE THE HIGH NUMBER
OF CAR ACCIDENTS AMONG TEEN DRIVERS.
BUT DISCOVERIES IN BRAIN SCIENCE
SHOW THAT THERE IS A REASON FOR THIS
BEHAVIOUR.
3.
Do you know?For many years, scientists thought that the human brain was fully
mature before the teen years. They thought that a person's brain
growth was complete and the structure was more or less tixed by the
age of 3.
However, more recent research shows that although the brain reaches
its maximum size between the ages of 12 and 14, brain development is
not yet complete. In fact, certain regions of the brain continue to
develop into the early 20s.
4.
What is synapse?A key region of the brain that matures late is the
prefrontal cortex, located just behind the forehead.
This cortex acts as a control centre for thinking
ahead and calculating risks. This is the area of the
brain that might stop you from making a bad decision.
It communicates with the other sections of the brain
through connections called synapses. Scientists have
found that there is a growth in synapses during
adolescende.The brain automatically removes the
synapses that it doesn't need in order to make the
remaining ones more efficient, but because this
process starts at the back of the brain and moves
forward, the prefrontal cortex is reached last. As a
result, teenagers rely more on the back of the brain
when making decisions, whereas adults do more
processing in the prefrontal cortex and so are better
able to calculate risks.
5.
Meanwhile, two other parts of thebrain develop earlier, the nucleus
accumbens and the limbic system.
Teenagers rely more on the back of the brain
when making decisions, whereas adults do more
processing in the prefrontal cortex and so are
better able to
calculate risks.
Prefrontal cortex
Synapses
Nucleus accumbens
6.
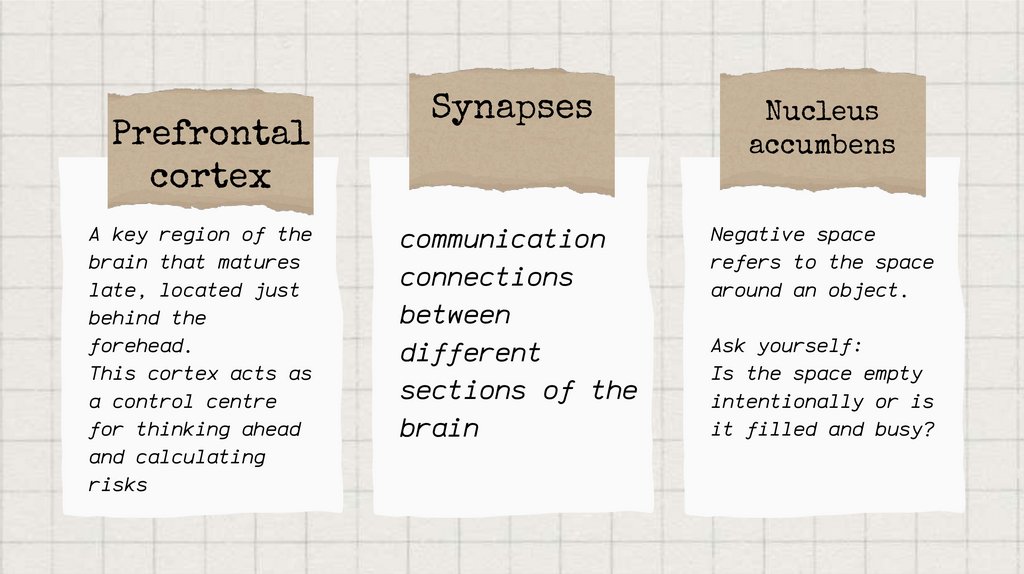
Prefrontalcortex
A key region of the
brain that matures
late, located just
behind the
forehead.
This cortex acts as
a control centre
for thinking ahead
and calculating
risks
Synapses
Nucleus
accumbens
communication
connections
between
different
sections of the
brain
Negative space
refers to the space
around an object.
Ask yourself:
Is the space empty
intentionally or is
it filled and busy?
7.
The nucleus accumbens isthe
with pleasure and reward
region of the brain
associated with pleasure
and reward while the
limbic system plays a
central
role in emotional
responses. The early
development of these two
areas explains why
emotions have a much
stronger influence in the
decision-making process
among teenagers.
8.
Together, these factorsmake it easier to
understand why
teenagers sometimes
make more impulsive
choices than adults.
They also suggest that
important life
decisions should be
made later in life, or
with the help of adult
advice.
9.
The good news is that teenagers do have thepotential, through choice and behaviour, to shape
their brain development. Scientists believe that
during the time the brain is removing synapses,
the cells and connections that are used survive,
while the ones that are not used die away. So if a
teenager is doing music, sports or academic
studies, those are the cells and connections that
will become part of the brain's operating system.
But unfortunately, if he or she is lying on the
sofa, watching TV and playing computer games,
those are the brain cells that will remain into
adulthood, meaning that what you do with your
teenage years could have an effect on the rest of
your life.
Just as important is that learning how the brain
develops can help teenagers be better equipped to
make more intelligent choices, motivating them to
take a moment before acting to consider the
consequences of their actions.
10.
the end!thank you for your attention










 psychology
psychology








