Similar presentations:
Agile Project Management Essentials. Part 1
1.
2.
Agile Project Management EssentialsPART 1
Become an Agile practitioner now and learn how efficiently to work within the team and provide
high results in short time
Lecturer: Arman Grigoryan
3.
Rules4.
What is a Project?•A project is an activity that:
• is temporary having a start and end date
•is unique
•brings about change
•has unknown elements, which therefore create risk
•has a definite start date and an expected completion date
•has a customer.
Generally, projects are formed to solve a
problem or take advantage of an opportunity.
5.
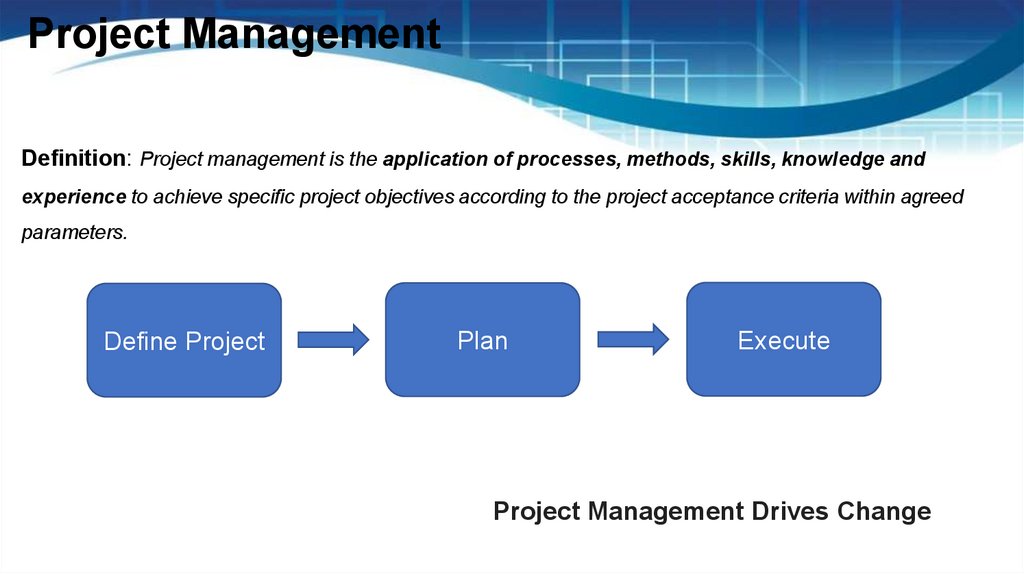
Project ManagementDefinition: Project management is the application of processes, methods, skills, knowledge and
experience to achieve specific project objectives according to the project acceptance criteria within agreed
parameters.
Define Project
Plan
Execute
Project Management Drives Change
6.
Project Manager•Manages resources, time, money, scope.
•A person with a diverse set of skills –
management, leadership, technical, conflict
management, and customer relationship.
•Manages risk
•Solves problems
7.
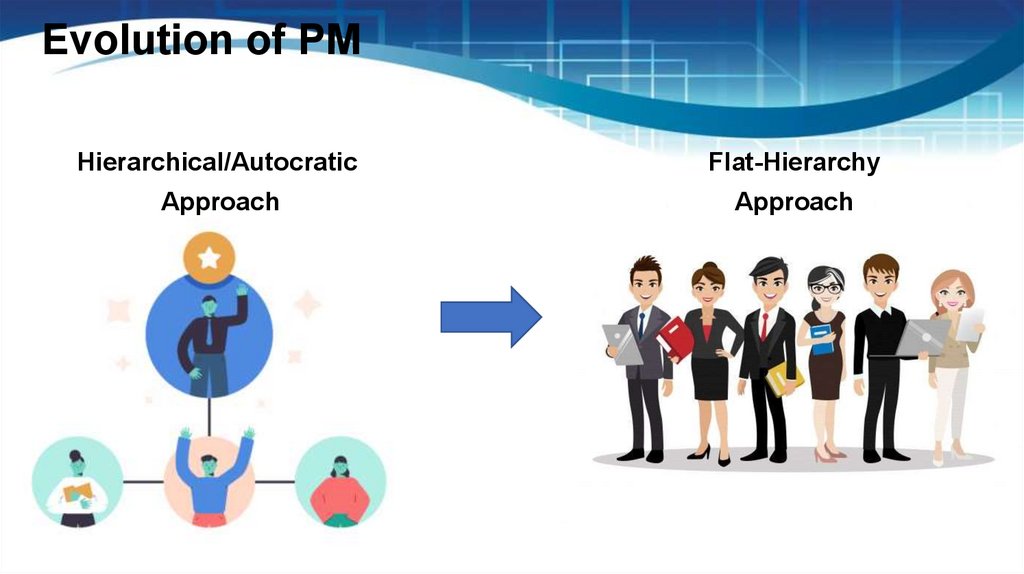
Evolution of PMHierarchical/Autocratic
Flat-Hierarchy
Approach
Approach
8.
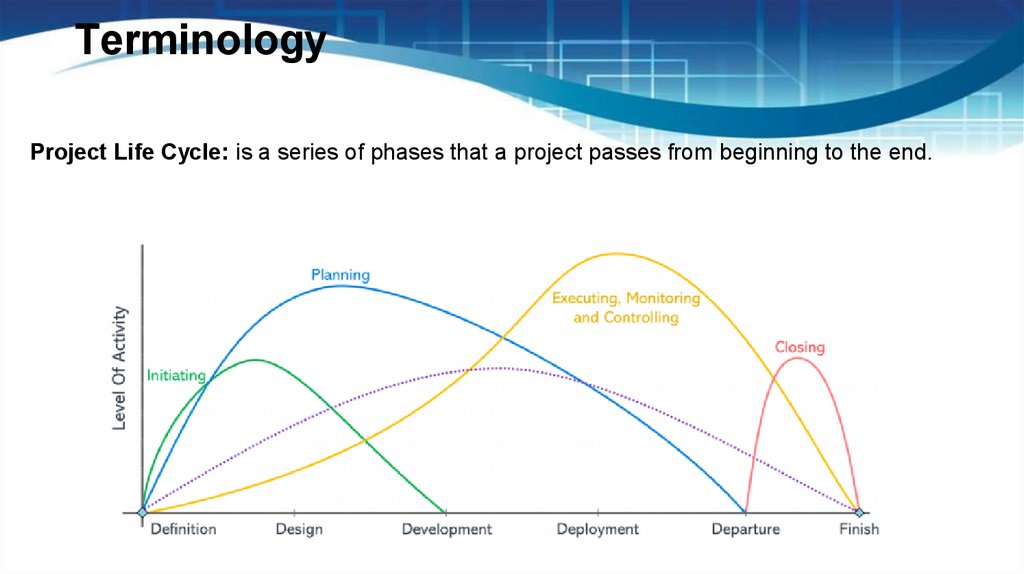
TerminologyProject Life Cycle: is a series of phases that a project passes from beginning to the end.
9.
TerminologyProject Life Cycle: is a series of phases that a project passes from beginning to the end.
10.
TerminologyProject Management Methodology is a collection of methods, practices, processes,
techniques, procedures, and rules.
Plan-Driven Approach
Agile Approach
11.
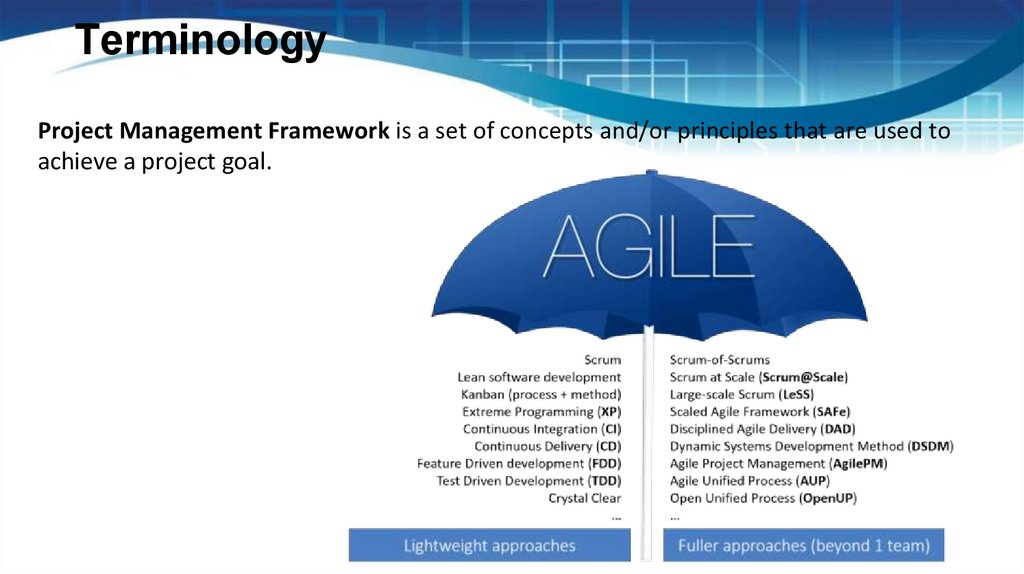
TerminologyProject Management Framework is a set of concepts and/or principles that are used to
achieve a project goal.
12.
Why do Projects fail?1. Poor project and program
management discipline
2. Lack of executive-level support
3. Wrong team members
4. Poor communication
5. No measures for evaluating the
success of the project
6. No risk management
7. Inability to manage change
13.
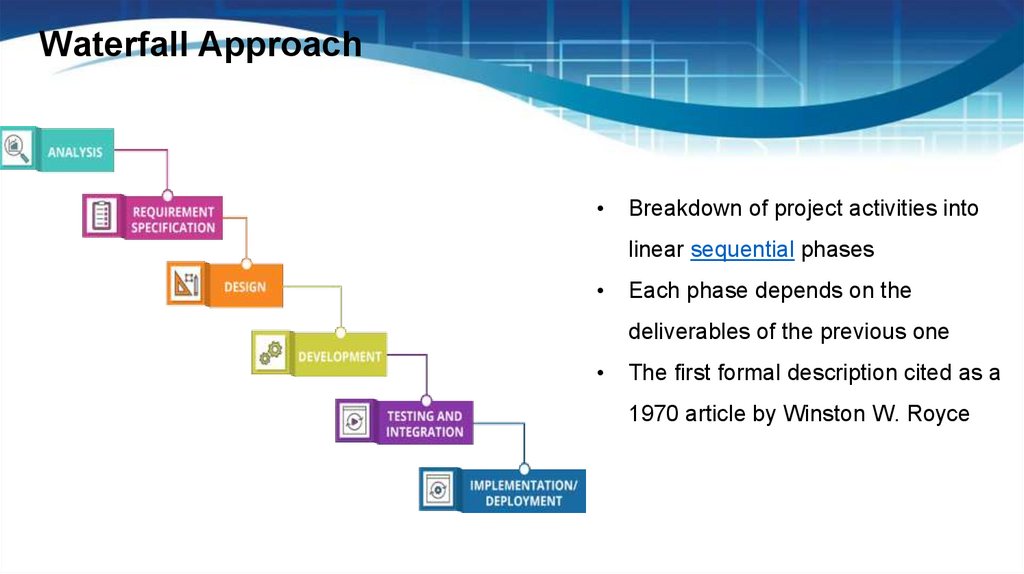
Waterfall ApproachBreakdown of project activities into
linear sequential phases
Each phase depends on the
deliverables of the previous one
The first formal description cited as a
1970 article by Winston W. Royce
14.
Application & UsageWaterfall assumptions
• Requirements are very well documented, clear and fixed.
• Product definition is stable.
• Technology is understood and is not dynamic.
• There are no ambiguous requirements.
• The project is short.
Usage Examples
• Public Money (Government, Funds etc.)
• Localization Projects ( Uber








































 management
management








