Similar presentations:
IT Project. Management
1.
Week #5IT Project
Management
Nini Grigoryan
International Black Sea University
Spring 2024
2.
Table of contents01
02
03
04
Importance of WBS
Work Breakdown Structure
WBS usage at different stages of the project
WBS example
3.
WBS - Work Breakdown StructureImagine building a complex jigsaw puzzle. You have hundreds of pieces,
each with a unique shape, and you want to create a beautiful, complete
picture. Now, think of a project as that puzzle. It has many different tasks,
team members, and moving parts. How do you make sure that all these
pieces come together seamlessly to create the desired result? This is where
a Work Breakdown Structure, or WBS, becomes essential in the world of
project management.
A Work Breakdown Structure is like the border pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. It
provides the framework and structure that allows you to organize and
understand the various elements of your project. In essence, it's the project
manager's guide to breaking down the project into manageable
components, understanding their relationships, and ensuring that nothing is
overlooked.
4.
The WBS is a critical tool in project management, and its importance cannotbe overstated. It serves as the foundation for project planning, execution,
and control. By dividing a project into smaller, more manageable pieces, the
WBS offers several key benefits:
1. Clarity and Structure: It provides a clear, visual representation of the
project's scope, helping both the project team and stakeholders understand
what needs to be done.
2. Effective Planning: It facilitates better planning by breaking the project into
smaller, actionable tasks, making it easier to allocate resources, estimate
costs, and set realistic schedules.
3. Improved Communication: The WBS enhances communication among
project stakeholders. It ensures everyone speaks the same language when
discussing project tasks and objectives.
4. Risk Management: It helps identify potential risks and bottlenecks in the
project, allowing for proactive risk management.
5.
6.within
Accountability: By assigning responsibility for each work package
the WBS, it ensures accountability among project team members
7.
Control and Monitoring: The WBS acts as a roadmap for project
progress. It simplifies tracking and control by providing a clear structure for
monitoring task completion.
In short, the Work Breakdown Structure is the cornerstone of effective project
management, guiding us through the complexity of projects to deliver successful
outcomes. In the following slides, we will explore what a WBS is, how to create
one, its components, and best practices for its use in project management."
6.
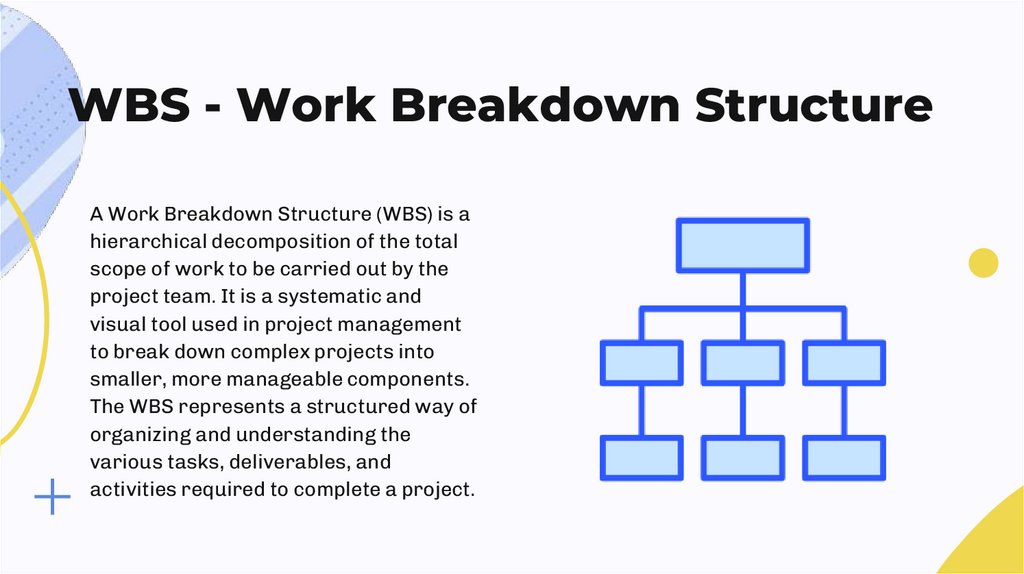
WBS - Work Breakdown StructureA Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a
hierarchical decomposition of the total
scope of work to be carried out by the
project team. It is a systematic and
visual tool used in project management
to break down complex projects into
smaller, more manageable components.
The WBS represents a structured way of
organizing and understanding the
various tasks, deliverables, and
activities required to complete a project.
7.
Hierarchy: It organizes project work into a structured hierarchy, with the top level
representing the entire project and lower levels breaking it down into progressively
smaller and more specific elements.
Decomposition: It involves the process of breaking down the project into discrete
work packages, sub-projects, or tasks. Each level of the hierarchy represents a more
detailed view of the project.
Scope: The WBS defines the scope of the project, including all the work that needs to
be done. It serves as a scope baseline against which project performance is
measured.
Visualization: It is typically presented as a visual diagram or chart, making it easier
for project stakeholders to grasp the project's structure and components.
Assignment of Responsibility: Work packages in the WBS are typically assigned to
specific team members or groups, clearly delineating who is responsible for each
task.
Control: It provides a framework for monitoring and controlling the project. By
breaking the project into smaller components, it allows for more precise tracking of
progress, resource allocation, and cost management.
8.
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is composed of several key components thathelp project managers organize and manage project work effectively. These
components include Work Packages, Control Accounts, and Planning Packages:
Work Packages:
Definition: Work Packages are the smallest, most detailed elements within a WBS.
They represent individual tasks, activities, or components of a project that can be
assigned to a specific team member or a group.
Characteristics: Work Packages are typically defined to a level where they can
be easily managed and tracked. They should be specific, measurable, achievable,
relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Responsibility: Each Work Package is assigned to a responsible team member,
making it clear who is accountable for its completion.
Duration and Resources: Work Packages specify the estimated duration,
required resources, and any dependencies associated with the task.
Examples: In an IT project, Work Packages could include tasks like "Software
Development," "System Testing," "User Training," or "Hardware Installation."
9.
Control Accounts:Definition: Control Accounts are intermediate-level components in the WBS
hierarchy. They group related Work Packages together and provide a higherlevel view of project work.
Characteristics: Control Accounts summarize related Work Packages, making
it easier to manage and control a set of related activities. They are often used
to manage project budgets and schedules.
Responsibility: Control Accounts may have a control account manager who is
responsible for ensuring that the Work Packages under the control account
are completed on time and within budget.
Monitoring and Reporting: Control Accounts are often associated with
performance metrics and reporting. They allow project managers to monitor
the progress of a group of related Work Packages more efficiently.
Examples: In a construction project, a Control Account could be "Foundation
Construction," which encompasses various Work Packages related to pouring
concrete, reinforcing, and inspecting the foundation.
10.
Planning Packages:Definition: Planning Packages represent work that is not yet fully defined but is
included in the project plan for planning purposes. They are a way to account
for work that requires additional information before being fully detailed as
Work Packages.
Characteristics: Planning Packages are typically used in the early stages of
project planning when specific tasks are not yet well-defined. They serve as
placeholders for future Work Packages.
Information Gathering: Project teams may use Planning Packages to gather
more details and refine the scope before breaking down the work into specific
tasks.
Status Tracking: While a Planning Package is in use, it may be monitored for
progress, and once details are available, it can be converted into specific Work
Packages.
Examples: In an architectural design project, a Planning Package might
represent "Site Survey and Assessment," which is initially defined broadly but is
later refined into specific Work Packages once the survey is complete.
11.
Let's create a simplified example of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) for a hypotheticalproject - "Organizing a Charity Fundraising Event." In this scenario, we'll start with the toplevel project and break it down into progressively smaller components:
Project: Organizing a Charity Fundraising Event
Level 1: Project Phases
Phase 1: Planning and Preparation
Phase 2: Marketing and Promotion
Phase 3: Event Execution
Phase 4: Post-Event Evaluation
12.
Level 2: Phase 1 - Planning and PreparationTask 1.1: Define Event Goals and Objectives
Task 1.2: Assemble Planning Team
Task 1.3: Develop Budget
Task 1.4: Secure Venue
Task 1.5: Create Event Schedule
13.
Level 2: Phase 2 - Marketing and PromotionTask 2.1: Design Event Branding
Task 2.2: Create Marketing Materials
Task 2.3: Social Media Promotion
Task 2.4: Contact Local Media for Coverage
Task 2.5: Launch Ticket Sales Campaign
14.
Level 2: Phase 3 - Event ExecutionTask 3.1: Set Up Venue
Task 3.2: Coordinate Catering
Task 3.3: Manage Registration and Check-In
Task 3.4: Conduct Raffle Draw
Task 3.5: Entertainment and Speakers
Task 3.6: Silent Auction
Task 3.7: Manage Volunteers
15.
Level 2: Phase 4 - Post-Event EvaluationTask 4.1: Collect Attendee Feedback
Task 4.2: Evaluate Budget vs. Actuals
Task 4.3: Generate Post-Event Report
Task 4.4: Thank You Letters to Sponsors and Attendees
16.
Level 3: Task 3.1 - Set Up VenueSubtask 3.1.1: Arrange Seating
Subtask 3.1.2: Decorations
Subtask 3.1.3: Audio-Visual Setup
Subtask 3.1.4: Safety Inspections
17.
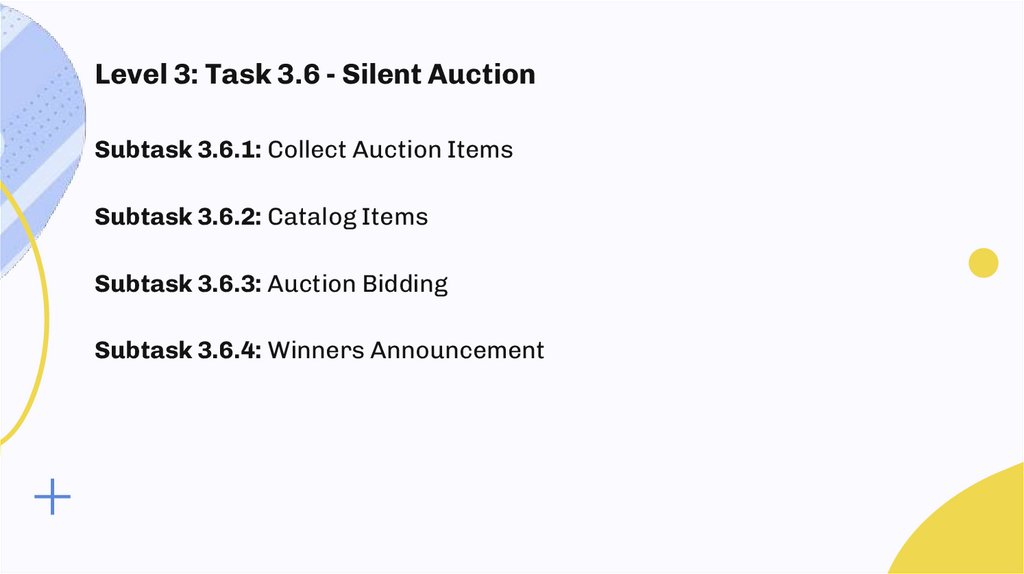
Level 3: Task 3.6 - Silent AuctionSubtask 3.6.1: Collect Auction Items
Subtask 3.6.2: Catalog Items
Subtask 3.6.3: Auction Bidding
Subtask 3.6.4: Winners Announcement
18.
Here's how a WBS is used at different stagesof the project:
Initiation:
Project Definition: During project initiation,
the WBS helps define the project's scope by
breaking it down into smaller, manageable
components. It provides a clear understanding
of what the project will entail.
Objective Alignment: The WBS helps align
project objectives with the organization's
strategic goals by detailing how the project will
contribute to those objectives.
19.
Planning:Task Identification: In the planning phase, the WBS
is expanded and refined to include all the tasks and
work packages necessary for project completion.
Each task is assigned a unique identifier and a
responsible party.
Resource Allocation: The WBS assists in allocating
resources (human, financial, and material) by
providing a basis for estimating resource
requirements for each work package.
Project Schedule: Work packages in the WBS are
used to create a detailed project schedule. The
dependencies between work packages help
establish the project's critical path.
Budgeting: By assigning cost estimates to work
packages, the WBS serves as a foundation for
creating and managing the project budget.
20.
Execution:Task Management: The WBS is used to guide the
execution phase, providing a roadmap for project
teams to carry out their assigned tasks and work
packages.
Resource Management: It helps manage resources
efficiently, ensuring that the right people and
materials are available at the right time for each
task.
Communication: The WBS is used to facilitate
effective communication among team members and
stakeholders by providing a structured framework
for discussing project progress and issues.
21.
Closure:Project Evaluation: During project closure, the WBS
can be used to evaluate the project's success
against the original objectives and scope outlined in
the WBS.
Documentation: It aids in documenting project
completion by comparing the status of work
packages against the final project outcomes.
Lessons Learned: The WBS can be used to identify
lessons learned for future projects, as it provides a
structured view of what went well and what could be
improved.
In summary, a Work Breakdown Structure plays a crucial role throughout the project
lifecycle, from initiation to closure. It guides project management activities, facilitates
communication, supports scope management, helps manage resources, and provides a
framework for evaluation and improvement. It's a dynamic tool that evolves and adapts as
the project progresses, ensuring that the project remains on track and aligned with its goals.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
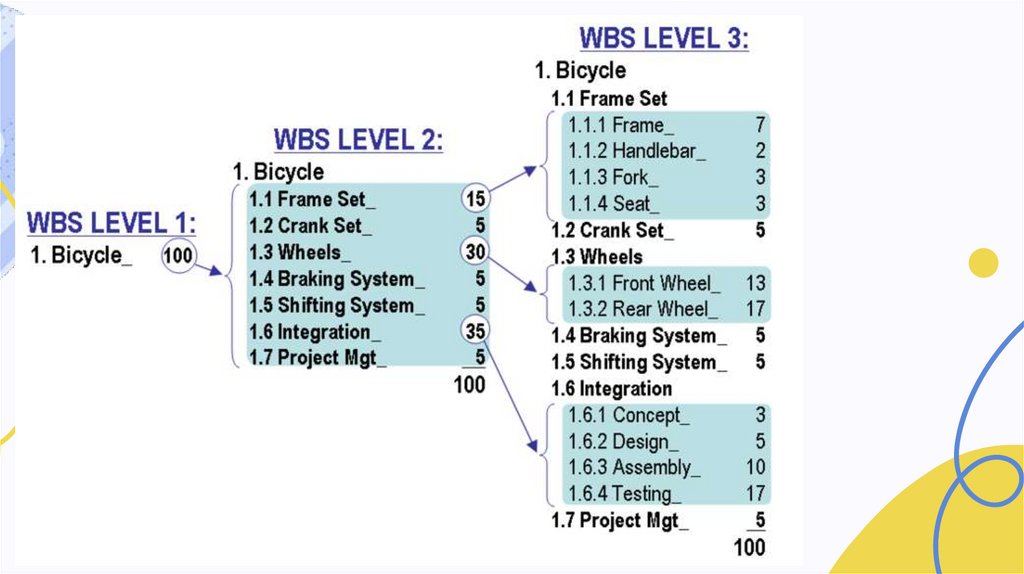
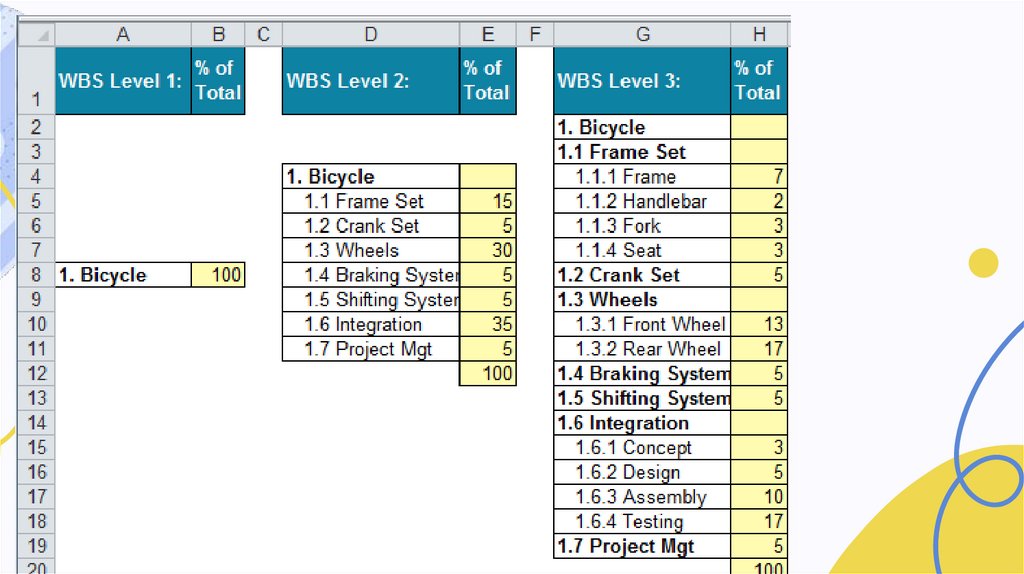
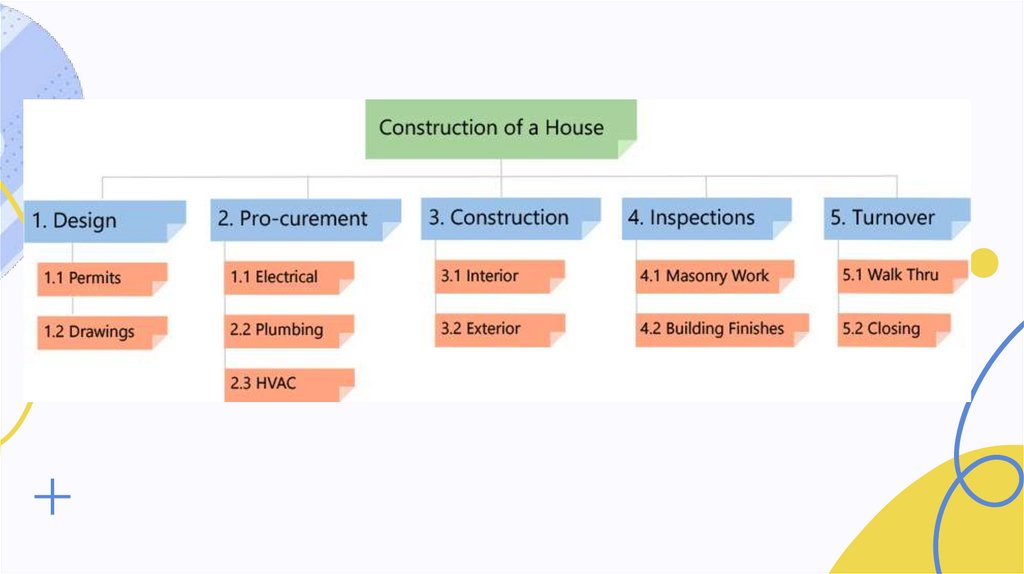
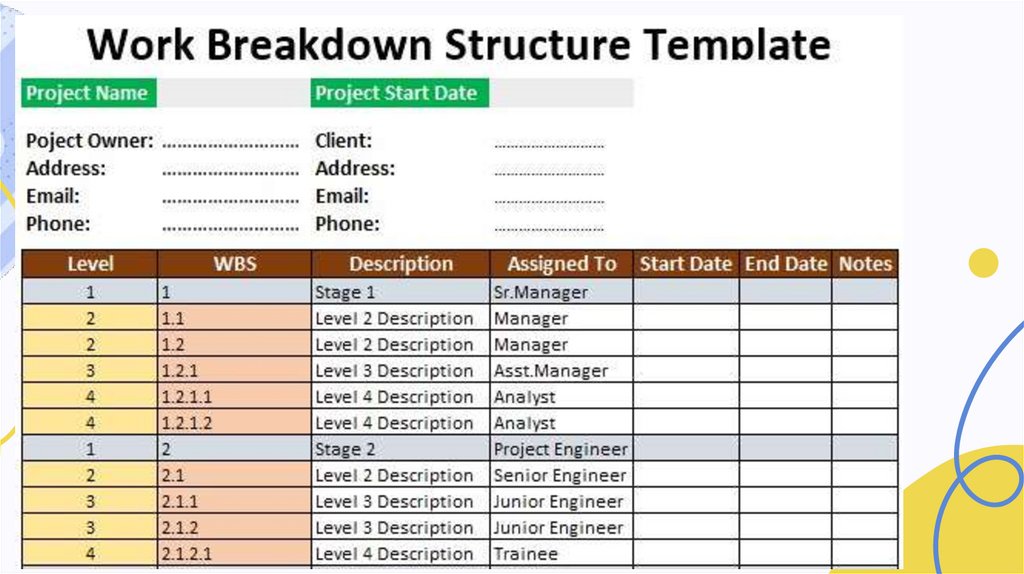
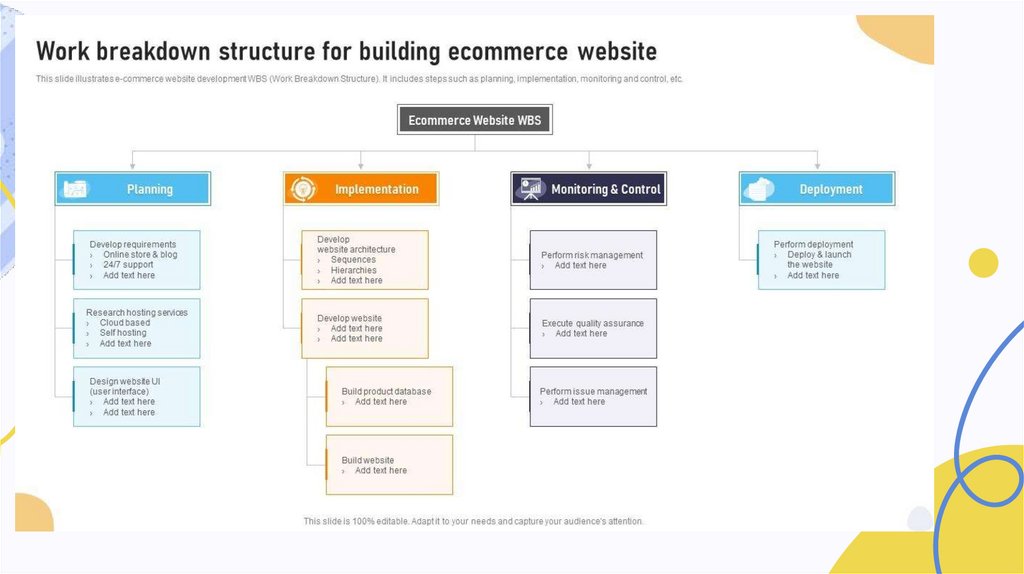
Class Activity:Create WBS for the given
example






















 management
management








