Similar presentations:
Organisation of Tourism and Hospitality Industry
1.
Topic:Organisation of Tourism and
Hospitality Industry
2.
My Journey so far – a colorful career!Professor/Researcher at
Anant National University,
India
Head of department on
LWP
University of Africa, Nigeria
Academic
Non-Academic
Vice President
International Tourism
Studies Association
Nigeria:
University of
Africa
India:
DU, IITTM, LPU,
Amity, Noida
Executive Member
Indian Ocean
Islands Association
Associate Editor
International
Journal of
Tourism Cities
Mauritius:
UOM, UTM,
MIE. Amity
UK:
University of
Nottingham
Expert Member
ICOMOS
Tourism Member
Planet Happiness, Australia
3.
Mauritius and India in World Map4.
University of Technology, Mauritius4
5.
6.
More about me – Google me you will get me! – Dr Vanessa GB Gowreesunkar• Research Gate: Vanessa
Gowreesunkar
• LinkedIn: Dr Vanessa GB
Gowreesunkar
• Academia: Vanessa GB Gowreesunkar
• ORCID No.:0000-0001-5934-6872
• SCOPUS ID: 57189264587
• Video:https://flipgrid.com/encytmm
Publications: 95+
Book Chapters: 20+
Editorship: 7
7.
Published by EmeraldBook Link
https://www.emerald.com/insight/publication/
doi/10.1108/9781800715110
8.
9.
Definition of Tourism• Mathieson and Wall (1982):
• Tourism is the temporary movement of people to destinations outside their
normal places of work and residence, the activities undertaken during their stay
in those destinations, and the facilities created to cater to their needs.
• Macintosh and Goeldner (1986):
• Tourism is the sum of the phenomena and relationships arising from the
interaction of tourists, business suppliers, host governments and host
communities in the process of attracting and hosting these tourists and other
visitors
• Jenkin and Lickorish (1997):
• Tourism is the sum of the phenomena and relationships arising from the travel
and stay of non-residents, in so far as they do not lead to permanent residence
and are not connected with any earning activity
10.
Geographical Components of Tourism• Climate: sunshine, clouds, snow, rain
• Animal Life: wildlife, zoos, hunting, fishing
• Settlement features: cities, monuments
• Culture: Ways of life, traditions, arts, craft
11.
• A tourism destination predominantly consists of avariety of tourism resources that have potential to
attract tourists. Some examples are:
• Sea, sun and sand destination like Mauritius, Maldives,
Seychelles;
• Wildlife, forest, nature reserve and safari destinations
like Uganda
• Mountains, lakes, rivers like Lake Tanganyika in Burundi
• Cultural assets in the form of the built environment
(monuments, old cities) – For example the Red Fort in
India
• Living heritage expressed in customs, songs, dance, art
and handicrafts – For example the Aborigines of
Australia
• Museums that reflect the local cultural heritage or a
wider global heritage – For example, Mandela House in
Soweto ,South Africa
• Besides the above mentioned tourism assets, the
component of a tourism destination equally comprises a
variety of stakeholders nurturing a wide range of both
compatible and conflicting interests
12.
13.
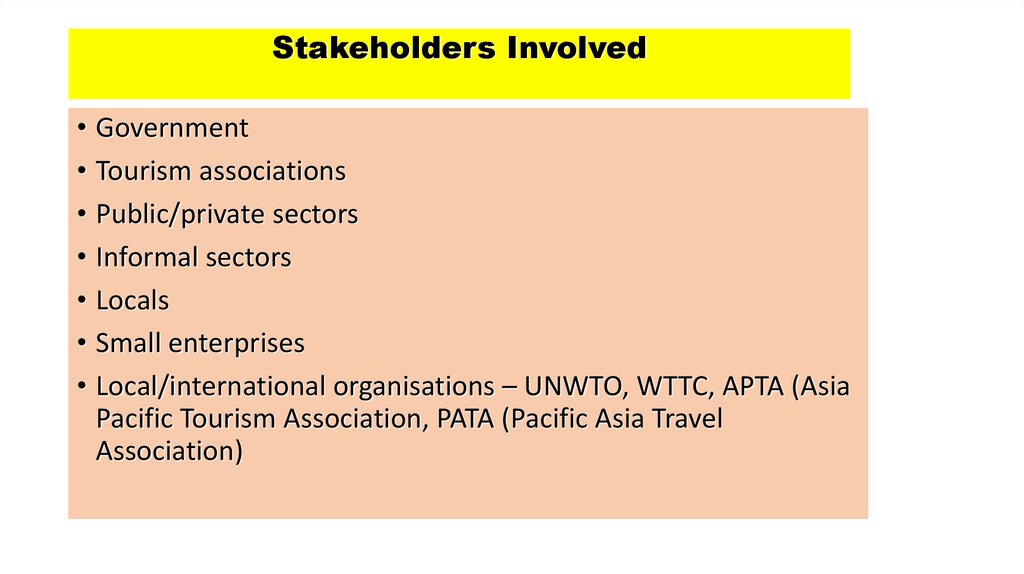
Stakeholders Involved• Government
• Tourism associations
• Public/private sectors
• Informal sectors
• Locals
• Small enterprises
• Local/international organisations – UNWTO, WTTC, APTA (Asia
Pacific Tourism Association, PATA (Pacific Asia Travel
Association)
14.
Tourism and Hospitality: An Inexorable LinkTeaser
In small group, discuss how tourism
and hospitality are inexorably
linked.
Hints to guide your mind:
1 Is tourism a stand-alone industry?
2 Hospitality can survive all alone?
3 Tourism needs hospitality or
hospitality need tourism?
15.
• Main points about tourism:• Tourism arises out of a movement of people to, and
their stay in, various places or destinations outside
their normal living environment.
• Tourism gives rise to activities that are distinct from
residents and working populations of the places
through which they travel and stay.
• The movement to the destination is temporary with
minimum and maximum length of stay stipulated.
• The purpose is stated.
16.
Main Points about Hospitality?• An exchange which takes place within an intermediate
time frame which reflects the close temporal
connection between production and consumption
• A concern with producing and supplying certain
physical products namely accommodation, food and
drink
• A combination of tangibles and intangible elements
• Tangibles….food, drink, furniture , accommodation
• Intangibles…image, atmosphere, customer care, service
level
• An activity entered into a voluntary basis by parties
involved.
• Involvement in a relationship which may be economic,
social or psychological in nature.
17.
• Hospitality in Tourism• - There is a demand for a range of activities viz
attractions, facilities
• - There is a demand for accommodation
• - There is a demand for F&B
18.
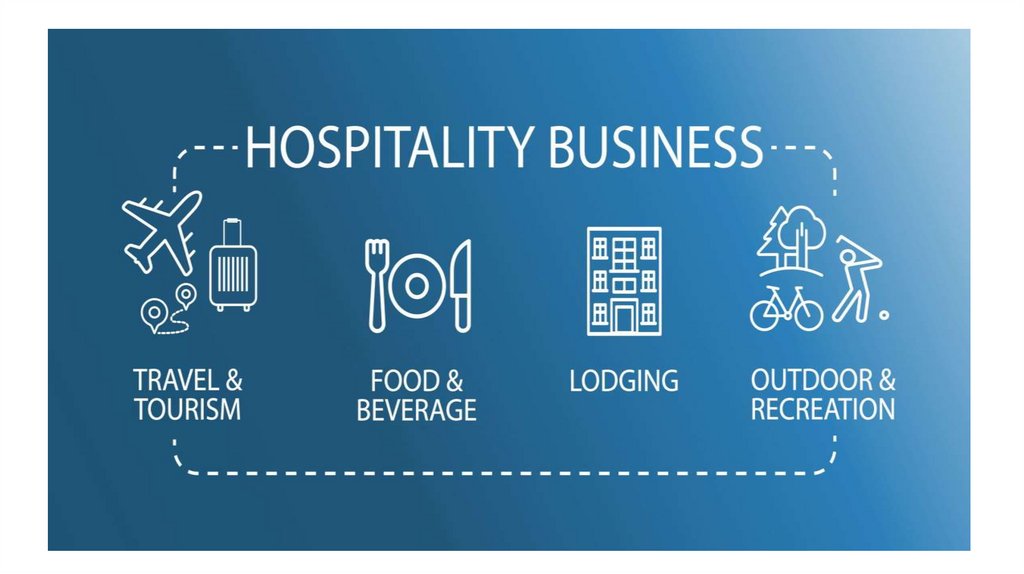
Tourism and Hospitality19.
The Hospitality IndustryThe hospitality industry consists of the following:
- Hotels
- Restaurants
- Leisure and Sport
- Gaming
- Pubs and clubs
- Education and training
- Meetings and facilities
- Caterers
- Cruise lines
- Other accommodations
20.
Hospitality in tourismWatch a
video
https://youtu.be/Q7tTV5Ki5KU
21.
How is the Hospitality and Tourism Industryorganized?
22.
23.
24.
How tourism industry worksRegulatory framework
Influences
on demand
DEMAND
Domestic and
international
tourists
TRAVEL
SUPPLY
Tourist
destinations
and facilities
Tourism intermediaries
Tourism
impacts
25.
International tourism industry structureThe 8 Sectors of the Tourism Industry:
https://prezi.com/aggbbi8nlahq/the-8-sectors-of-the-tourismindustry/
May 20, 2023
25
26.
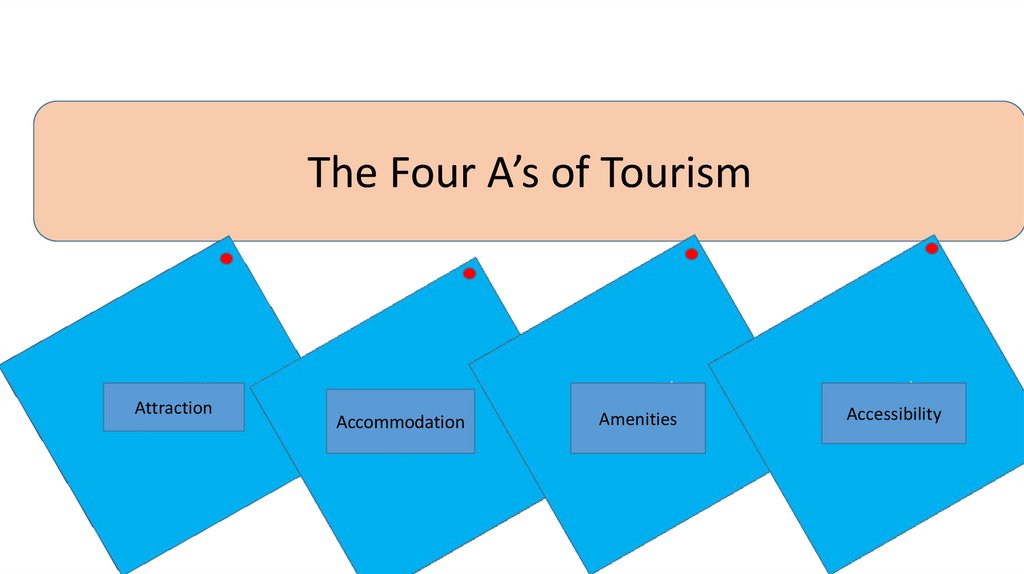
The Four A’s of TourismAttraction
Accommodation
Amenities
Accessibility
27.
The Four A’s of Tourism – explained!• Attractions: These may be natural or artificial features or events that
provide the initial motivation to visit. Eg the great china wall, Mount
Everest, aborigines of Australia, safari park in Africa, Disney Land in
Florida, Hawaii Island, the Glaciers of Alp, Niagara Falls, Grand Canyon
in the US, The city of Agra in India,, the Aapravaasi Ghat in Mauritius
• Accommodation: hotels, guest houses, inns, airbnb
• Amenities: These are the support services or facilities required by a
tourist at the destination.
• Accessibility: Mans by which tourists can reach the area where
attractions are located. E.g planes, ships, ferry, train, scenic drives,
explorer buses, cycles
28.
The A’s RedefinedAttractions (natural, man-made, artificial, purpose built, heritage, special
events)
• Accessibility (entire transportation system comprising of routes, terminals
and vehicles)
• Amenities (accommodation and catering facilities, retailing, other tourist
services)
• Available packages (pre-arranged packages by intermediaries and
principals)
• Activities (all activities available at the destination and what consumers
will do during their visit)
• Ancillary services (services used by tourists such as telecommunications,
post, newsagents, hospitals, etc)
(Source:Cooper, Fletcher, Shepherd and Wanhill, 1998)
29.
Linkages with United Nations Sustainable Development Goals(SDGs)
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a collection of 17 global
goals set by the United Nations Development . Tourism can contribute to
the following SDGs:
• 1- End poverty
• 5 – Achieve gender equality and empower women and girls
• 8 - promote sustained inclusive and economic growth
• 10 – reduce inequality within and among countries
• 12 – ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
• 14 – conserve and sustainably use oceans
• 15 – Sustainable use of land resources
• 16 – peaceful, inclusive societies for sustainable development
30.
• Before COVID-19• Travel and tourism was a booming business
• Ongoing MICE
• Increasing number of leisure travelers
• Tourism operators capitalizing on resources – overtourism,
exploitation of resources, commercialization of culture etc
• After COVID-19
• A paradigm shift driven by survival, revival, renewal strategies
• Competition or collaboration?
• Finally…… a blessing or a blight?
( Source: Gowreesunkar et al, 2019)
31.
The pain points:• WTTC estimates 75 million travel tourism jobs are at risk globally due
to COVID-19 pandemic
• UNWTO reports that International tourism will go down by 20-30%
during 2020 and there will be a decline in international receipt of
around 300 to 400 billion dollars
• Around 96% of all worldwide destinations have introduced travel
restrictions in response to the pandemic,
• About 43% (90 destinations) have completely or partially closed their
borders, About 21% (44 destinations) have introduced travel bans to
passengers coming from certain destinations that have been affected
by COVID-19
• About 27% (56 destinations) have suspended all or partially
international flights into the destination
32.
The Gain points• COVID-19 has given a breathing space to tourism resources in many
countries. Eg. India, Africa, islands…etc
• Destinations which recently suffered from overtourism are now restored.
Residents of Venice have reported that the sea is now blue again and they
can see fish swimming.
• In India, reports show that the Ganga river is cleaner now. In Africa, places
like Table Mountain in Cape Town and the Masai Mara in Kenya are now
having some breathing space.
• Elephants, lions, gorillas of the zoo are also having a break from public and
over- visitation.
• The Covid Crisis has also prompted creativity. Grounded business travellers
are realising virtual business meetings.
• Conferences are re-organising for virtual sessions. Arts and cultural events
are turning to live streaming to connect with audiences.
33.
Post Covid-19 - Critical Success Factors of Tourism• Visibility
• Marketability
• Profitability
• Sustainability
• Technology
• Security
Driven by
Collaboration
NOT
Competition
34.
Tourism Management Strategies Post pandemic• Incentives from Government – pro tourism policies to support tourism entrepreneurs, airlines and other
businesses
• Support to Organisations like NITHM to conduct research on post COVID,
• Re-education and re-training/training of tourism is required - tourists and tourism operators to come up with
new business models
• Workforce to be trained and re-skilled
• Follow guidelines from UNWTO, WTTC, GSTC (Global Sustainable Tourism Council) and seek advice
• Certification with international tourism organizations to make products holistically sustainable – products to be
credible and certified for re-assurance of travellers
• Destinations are called upon to set up a tourism recovery committee
• We have to forget competition and embrace collaboration
• Join hands with stakeholders, partners even rivals …objective is survival of the industry
• New policies based on health and safety - health protocol is needed
• Bank to bail out industry with credit stimulus to facilitate recovery
• Development of new tourism product based on health and safety protocol; New travel itinerary and
diversification
• Develop products that are holistically sustainable and how to add value - marketing of a corona free
destinations to boast travel confidence
• New business model should be rolling not based on a rigid plan ;adaptive strategies
• Awareness and sensitization for responsible tourism
• Re-think Re –invent Re-orientate Re-educate
35.
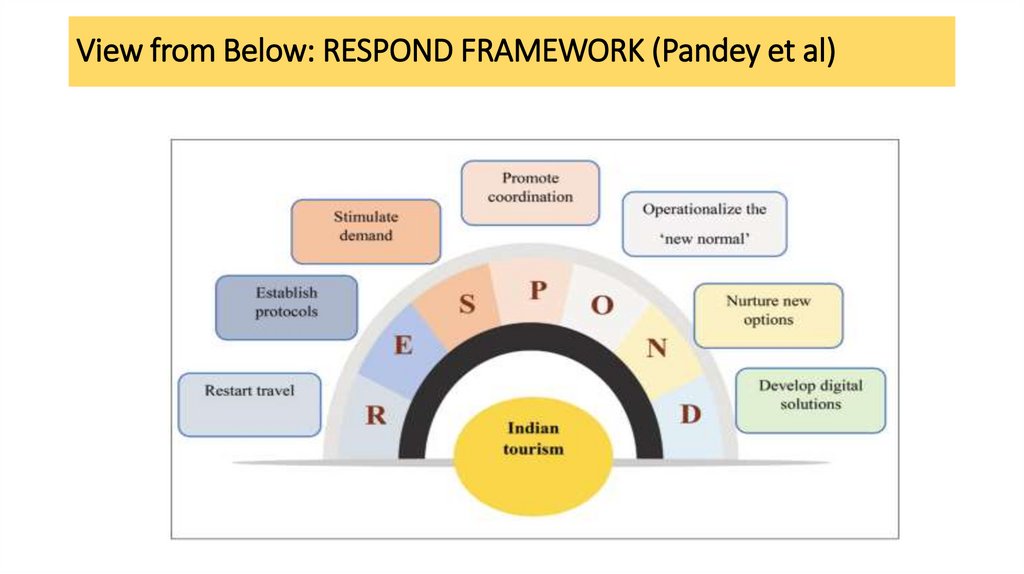
View from Below: RESPOND FRAMEWORK (Pandey et al)36.
Reflections• COVID-19 is a radical wake-up call for humanity and this pandemic
has taught us a great lesson – the world is a global village and we all
depend on each other ….
• The organization of the tourism industry shuld be driven by
collaboration and NOT competition
• Information, Precaution and Medication
• As tourism professionals, it is our duty to be at the forefront and give
assurance about our industry.
• Hundreds of thousands of livelihoods depend on it
• If we don't do it, who else will?
37.
Mauritius Sega Dance38.
Destination Discovery – Indiahttps://www.youtube.com/watch
?v=8493u5yFwr0
39.
Short Video on Tourism Potential40.
Dragon Boat Festival in ChinaDr GB Gowreesunkar
40
41.
My Contact DetailsDr Vanessa GB Gowreesunkar
Mail: gvanessaa@gmail.com
Whatsap : +23057191719
Research Gate: Vanessa Gowreesunkar
Academia: Vanessa GB Gowreesunkar
ORCID No.:0000-0001-5934-6872
LinkedIn: Dr Vanessa GB Gowreesunkar
YouTube: Vanessa Gowreesunkar
SCOPUS ID: 57189264587


































 management
management geography
geography








