Similar presentations:
Economic responsibilities
1.
2.
3.
• Carroll’s four part definition of CSR wasoriginally stated as:
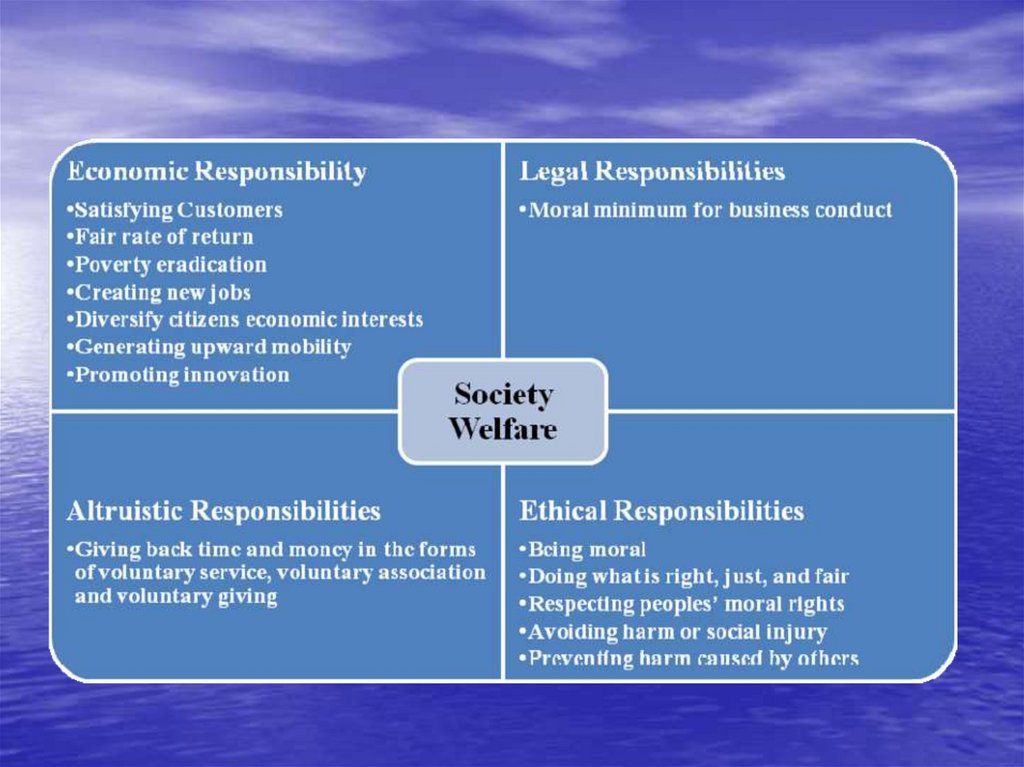
• Corporate
social
encompasses the
responsibility
– Economic,
– Legal,
– Ethical and
– Discretionary (philanthropic) expectations
4.
• Economic responsibilities5.
... In its origins, society views businessorganizations as institutions that will
produce and sell the goods and services
society needs and desires…
6.
• Profits are necessary both to rewardinvestor/owners and also for business
growth
7.
• Virtually all economic systems of the worldrecognize the vital importance to the
societies of businesses making profits.
8.
Those firms that are not successful in theireconomic or financial sphere go out of
business and any other responsibilities
that may be incumbent upon them
become moot considerations. ….
9.
• Therefore, the economic responsibility is abaseline requirement that must be met in
a competitive business world and so
economic responsibility is a critical part of
corporate social responsibility”.
https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/businessfuncdn/chapt
er/article-carrolls-corporate-social-responsibility-pyramid/
10.
• Legal responsibilities11.
• They articulate fundamental notions of fairbusiness practices as established by
lawmakers at federal, state and local
levels.
12.
While meeting these legal responsibilities,important expectations of business include
their….
13.
• Ethical responsibilities14.
• … Part of the ethical expectation is thatbusinesses will be responsive to the
“spirit” of the law, not just the letter of the
law. ….
15.
• … Ethical responsibilities embrace thoseactivities,
standards,
policies,
and
practices that are expected or prohibited
by society even though they are not
codified into law. …
16.
• The distinction between legal and ethicalexpectations can often be tricky. ….
17.
• Legal expectations certainly are based onethical premises….
18.
– Performing in a manner consistent withexpectations of societal mores and ethical
norms
– Recognizing and respecting new or evolving
ethical/moral norms adopted by society
– Preventing ethical norms from being
compromised in order to achieve business
goals
19.
– Being good corporate citizens by doing whatis expected morally or ethically
– Recognizing that business integrity and ethical
behaviour go beyond mere compliance with
laws and regulations
20.
• …in addition to society’s expectationsregarding ethical performance, there are
also the great, universal principles of
moral philosophy such as rights, justice,
and utilitarianism that also should inform
and guide company decisions and
practices.
21.
• Philanthropic responsibilities22.
• Certainly, the quantity and nature of theseactivities are voluntary or discretionary.
23.
• They want to do what is right for society.24.
• To fulfill its perceived philanthropicresponsibilities, companies engage in a
variety of giving forms. ….
25.
• an altruistic motivation … To enhance oraugment the company’s reputation and
not necessarily for noble or self-sacrificing
reasons. …
26.
• The primary difference between theethical and philanthropic categories in the
four part model is …
27.
• The philanthropic responsibility is morediscretionary or voluntary on business’s
part.
28.
• The four part CSR definition forms aconceptual framework that includes the
economic, legal, ethical, and philanthropic
or discretionary expectations
29.
As time passes what exactly each of thesefour categories means may change or
evolve as well.
30.
31.
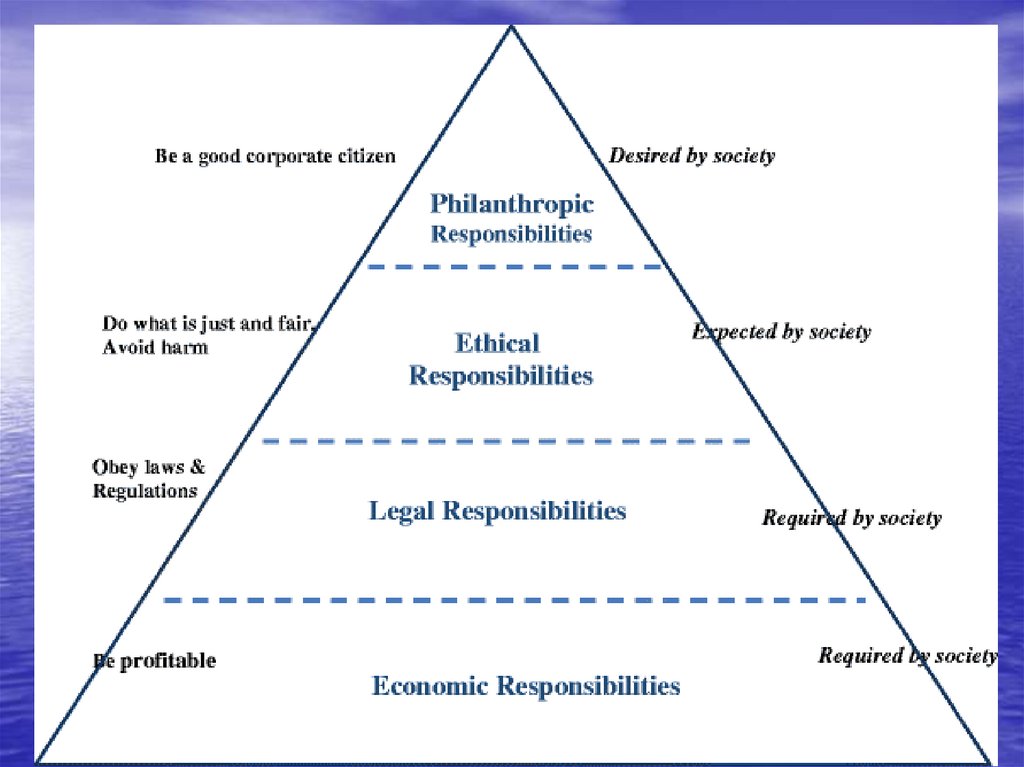
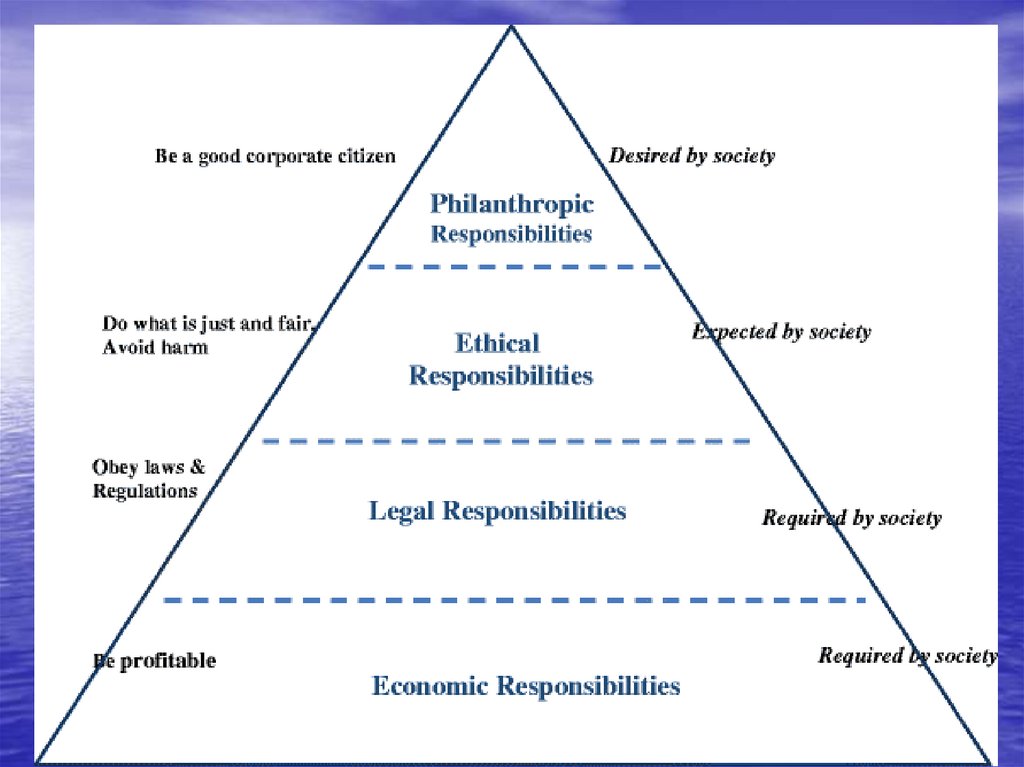
• The pyramid of CSR32.
• The pyramid was selected as a geometricdesign because it is simple, intuitive, and
built to withstand the test of time.
33.
The infrastructure of CSR is built uponthe premise of an economically sound and
sustainable business.
34.
• Society is conveying the message tobusiness that it is expected to obey the
law and comply with regulations..
35.
• A legal infrastructure is imperative toprovide a foundation
business growth.
for
legitimate
36.
• Business is expected to operate in anethical fashion.
37.
The pyramid is built in a fashion thatreflects the fundamental roles played and
expected by business in society.
38.
• The CSR pyramid holds that firms shouldengage in decisions, actions, policies and
practices that simultaneously fulfill the
four component parts.
39.
• The pyramid should not be interpreted tomean that business is expected to fulfill its
social responsibilities in some sequential,
hierarchical fashion, starting at the base.
40.
• Economicand legal responsibilities
are required; ethical and philanthropic
responsibilities are expected and desired.
41.
• EconomicResponsibilities + Legal
responsibilities + Ethical Responsibilities +
Philanthropic Responsibilities = Total
Corporate Social Responsibility.
42.
• The CSR driven firm should strive to makea profit, obey the law, engage in ethical
practices and be a good corporate citizen.
43.
• The pyramid is a sustainable stakeholderframework
44.
• Economicdramatically
employees …
responsibilities
most
impact shareholders and
45.
• Ethicalresponsibilities
affect
all
stakeholder groups. Shareholder lawsuits
are an expanding category. When an
examination of the ethical issues business
faces today is considered, they typically
involve employees, customers, and the
environment.
46.
• Finally, philanthropic responsibilities mostaffect the community and nonprofit
organizations, but also employees because
some research has concluded that a
company’s employees’
morale and
engagement is significantly related to its
philanthropic involvement.
47.
• Thepyramid should be seen as
sustainable in that these responsibilities
represent long term obligations that
overarch into future generations of
stakeholders as well.
48.
• A consideration of stakeholders andsustainability, today, is inseparable from
CSR.














































 economics
economics