Similar presentations:
Vegetative propagation
1.
Vegetative propagation2.
Lesson objectivesTo compare methods of vegetative
propagation in plants.
3.
VEGETATIVE PROPOGATIONRoot, stem and leaves are called
vegetative organs in plants.
• When they give rise to new plants
this process is called vegetative
propagation.
• It is seen mostly in flowering
plants.
4.
TYPES OFVEGETATIVE PROPOGATION
1) Natural propagation:
1-Tuber
2-Stolons and runners
3-Rhizome
4-Bulb
2) Nrtificial propagation:
1-Cutting
2-Stem grafting.
5.
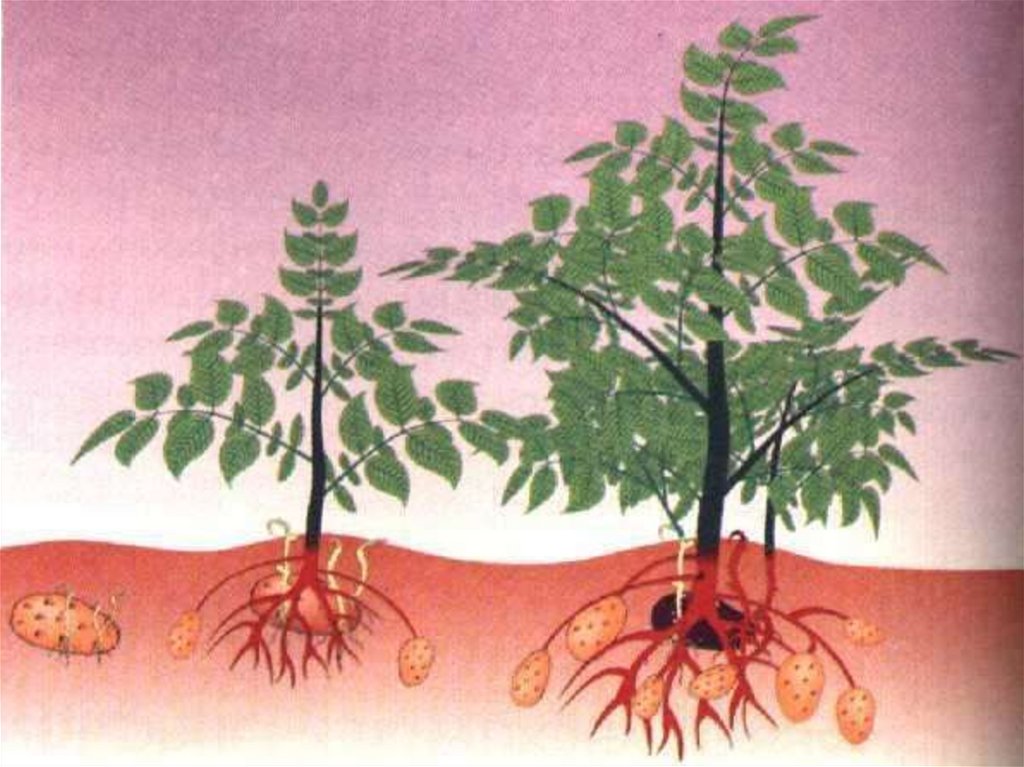
TuberTubers are underground stem (potato) or
root (batata).
6.
7.
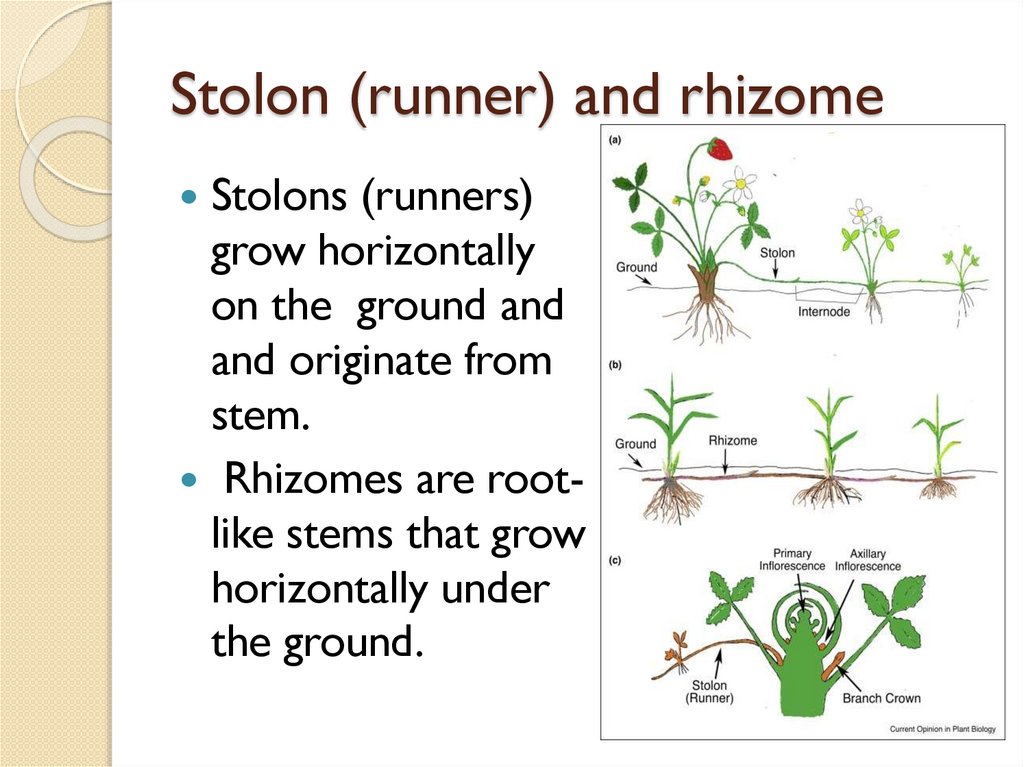
Stolon (runner) and rhizomeStolons (runners)
grow horizontally
on the ground and
and originate from
stem.
Rhizomes are rootlike stems that grow
horizontally under
the ground.
8.
9.
10.
BulbBulb is a modified shoot.
Has reduced stem , root, bulbs, scaly
leaves and leaves with food storage.
Found under the ground.
11.
12.
13.
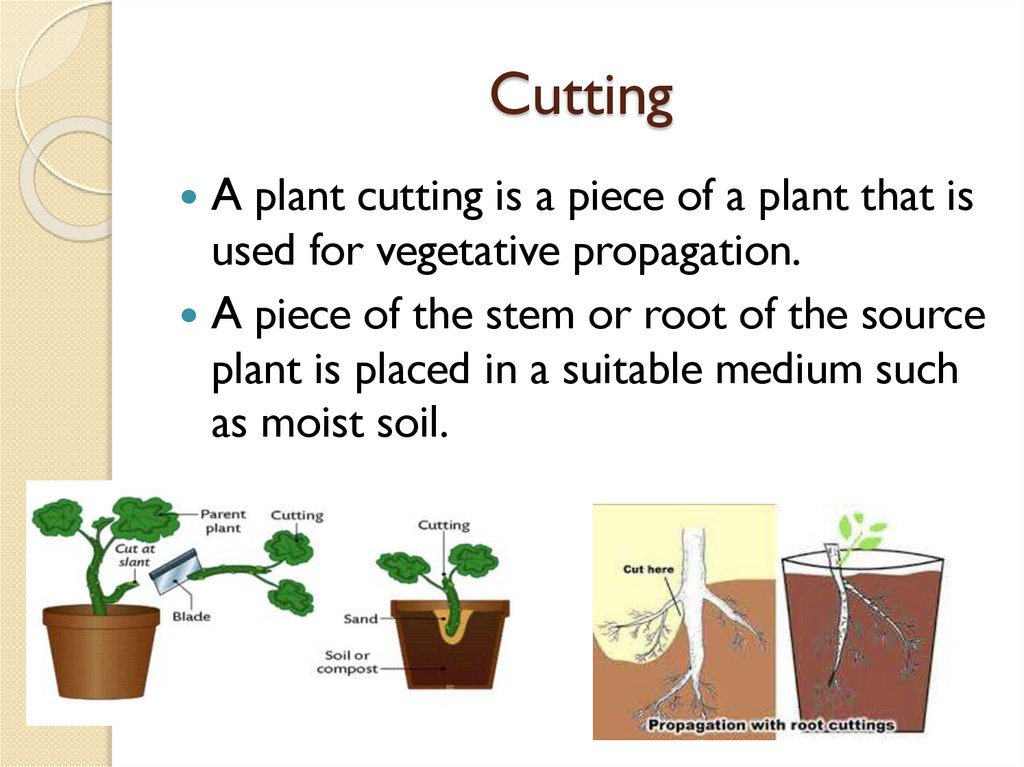
CuttingA plant cutting is a piece of a plant that is
used for vegetative propagation.
A piece of the stem or root of the source
plant is placed in a suitable medium such
as moist soil.
14.
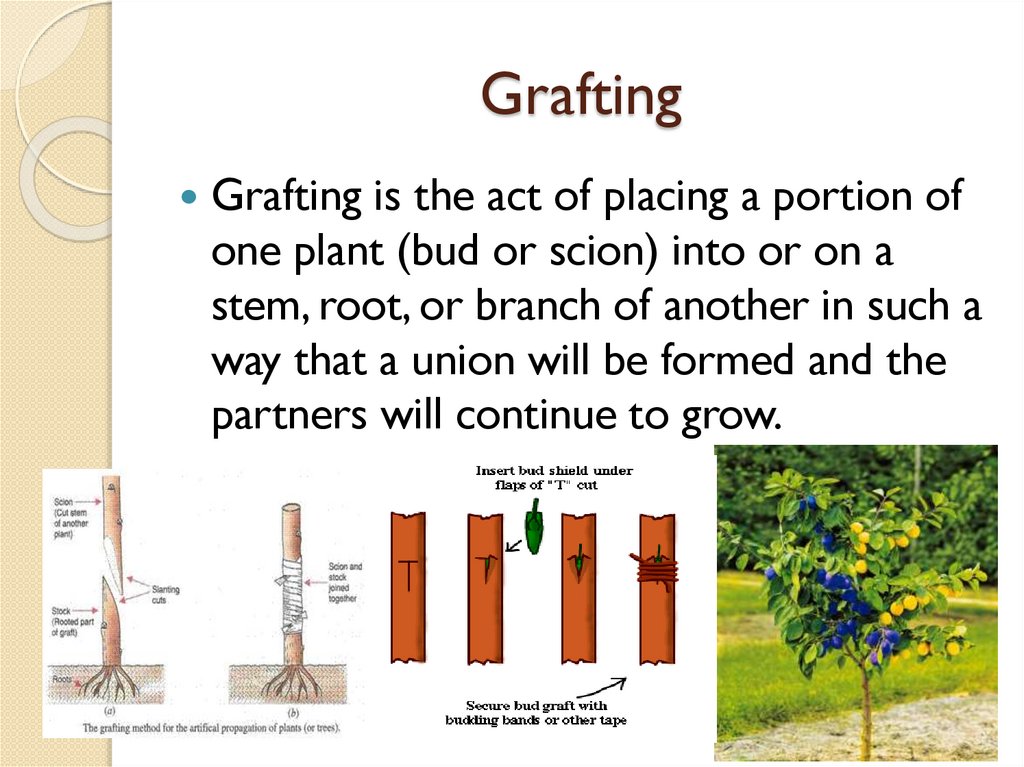
GraftingGrafting is the act of placing a portion of
one plant (bud or scion) into or on a
stem, root, or branch of another in such a
way that a union will be formed and the
partners will continue to grow.
15.
16.
Let’s do activity on p.11917.
HomeworkRead p. 118-119
Answer to literacy questions on p 119
New words













 english
english








