Similar presentations:
Working Capital Inventory Control. Seminar 10
1.
Working CapitalInventory Control
Seminar 10
5FNCE001C Financial Management 2022-2023
2.
Today• Inventory control
• Objectives
• Costs of low inventory levels
• Economic order quantity (EOQ)
• Re-order level (ROL)
• Inventory management systems
3.
Inventory control: Objectives• Inventory is a major investment for many companies. Manufacturing
companies can easily be carrying inventory equivalent to between 50% and
100% of the revenue of the business. It is therefore essential to reduce the
levels of inventory held to the necessary minimum.
• Keeping inventory levels high is expensive owing to:
• foregone interest from tying up capital in inventory
• holding costs:
• storage
• stores administration
• risk of theft/damage/obsolescence
4.
Inventory control: Objectives5.
Inventory controlCost of low inventory levels
• If inventory levels are kept too low, the business faces alternative problems:
• stockouts:
• lost contribution
• production stoppages
• emergency orders
• high re-order/setup costs
• lost quantity discounts.
• The objective of good inventory management is therefore to determine:
• the optimum re-order level – how many items are left in inventory when the next order is placed,
and
• the optimum re-order quantity – how many items should be ordered when the order is placed for
all material inventory items.
• In practice, this means striking a balance between holding costs on the one hand and
stockout and re-order costs on the other.
6.
Inventory controlCost of low inventory levels
• The balancing act between liquidity (keeping inventory levels low) and
profitability (maintaining high inventory levels, although this does require extra
funding which impacts profitability negatively), which might also be a trade-off
between holding costs and stockout/re-order costs, is key to any discussion on
inventory management
• Other key terms associated with inventory management include:
• lead time – the lag between when an order is placed, and the item is delivered
• buffer inventory – the basic level of inventory kept for emergencies. A buffer is required
because both demand and lead-time will fluctuate, and predictions can only be based on
best estimates.
• Ensure you can distinguish between the various terms used: re-order level, reorder quantity, lead-time and buffer inventory.
7.
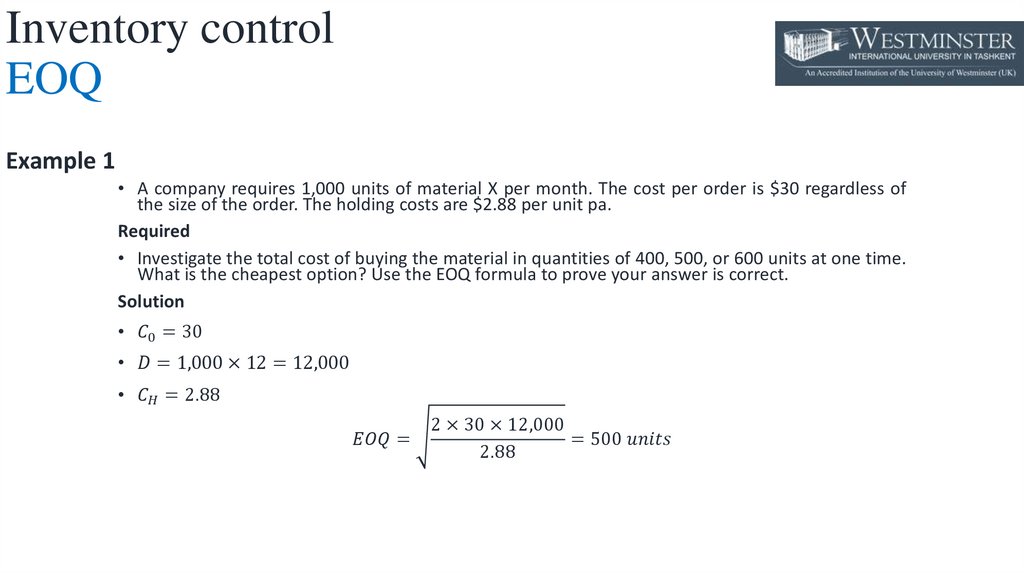
Inventory controlEOQ
• For businesses that do not use just in time (JIT) inventory management systems (discussed in more
detail below), there is an optimum order quantity for inventory items, known as the EOQ.
• The aim of the EOQ model is to minimize the total cost of holding and ordering inventory
• To minimize the total cost of holding and ordering inventory, it is necessary to balance the relevant
costs. These are:
• the variable costs of holding the inventory
• the fixed costs of placing the order
• The model assumes that it costs a certain amount to hold a unit of inventory for a year (referred to
as CH in the formula). Therefore, as the average level of inventory increases, so too will the total
annual holding costs have incurred.
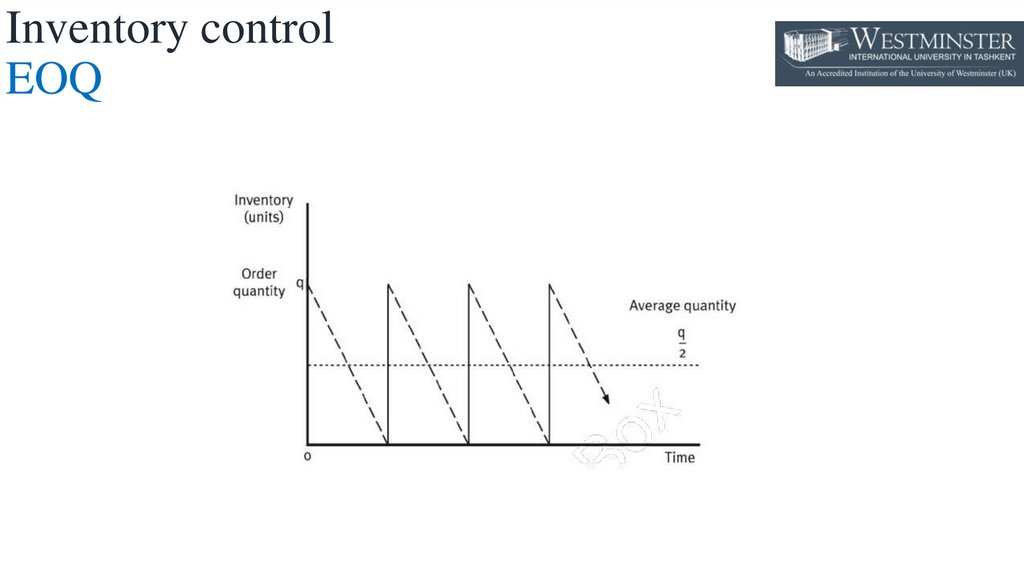
• Because of the assumption that demand per period is known and is constant (see right), conclusions
can be drawn over the average inventory level in relationship to the order quantity
• When new batches or items of inventory are purchased or made at periodic intervals, the inventory
levels are assumed to exhibit the following pattern over time.
8.
Inventory controlEOQ
9.
Inventory controlEOQ
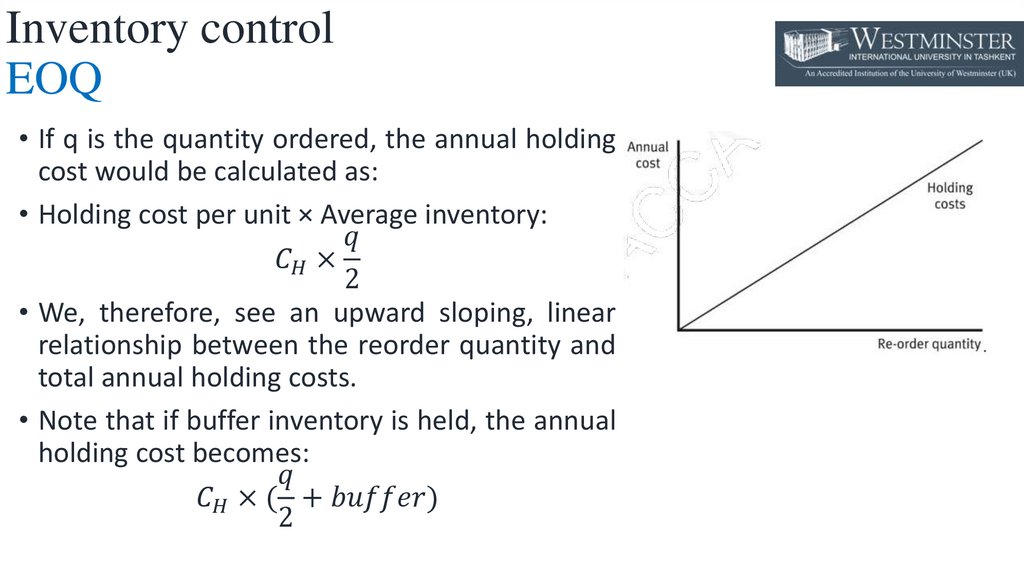
• If q is the quantity ordered, the annual holding
cost would be calculated as:
• Holding cost per unit × Average inventory:


















 finance
finance management
management








