Similar presentations:
Heredity and variability
1.
HEREDITY ANDVARIABILITY
2.
Lesson objectivesTo investigate hereditary and non-
hereditary traits in human.
To give examples for discrete and
continuous variability
3.
WHY DO WE LOOK SIMILARTO OUR RELATIVIES AND
LOOK DIFFERENT TO
OTHERS?
4.
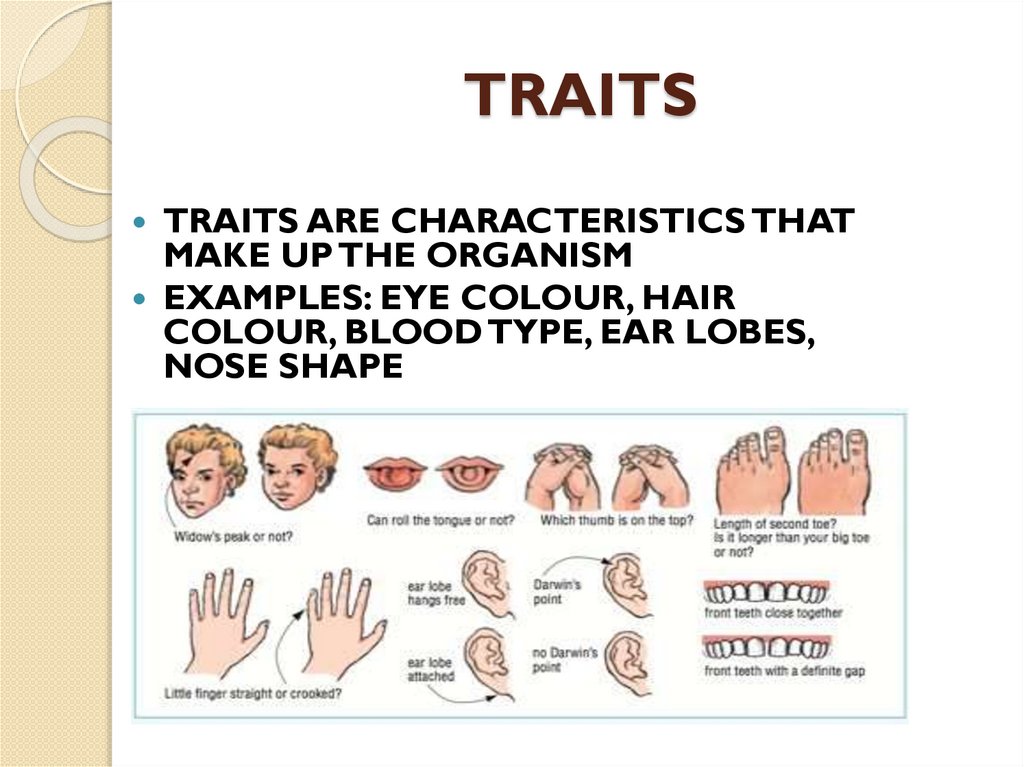
TRAITSTRAITS ARE CHARACTERISTICS THAT
MAKE UP THE ORGANISM
EXAMPLES: EYE COLOUR, HAIR
COLOUR, BLOOD TYPE, EAR LOBES,
NOSE SHAPE
5.
THERE ARE TWO TYPES OFTRAITS
INHERITED (НАСЛЕДСТВЕННЫЙ)
ACQUIRED (ПРЕОБРЕТЕННЫЙ)
6.
INHERITED TRAITSINHERITED TRAITS ARE THE TRAITS THAT
CAN PASS FROM PARENTS TO OFFSPRING
Ex: brown eyes, free ear lobes, stripes on a tiger,
long neck in giraffe, flower scent.
7.
AQUIRED TRAITSTHE TRAITS THAT CAN NOT BE INHERITED AND ARE GOT
THROUGHOUT THE LIFE ARE CALLED AQUIRED TRAITS.
EXAMPLES: KNOWLEDGE, SKILLS, IDEAS, MEMORIES.
8.
VariationVariation is any difference
between organisms of the same
species.
9.
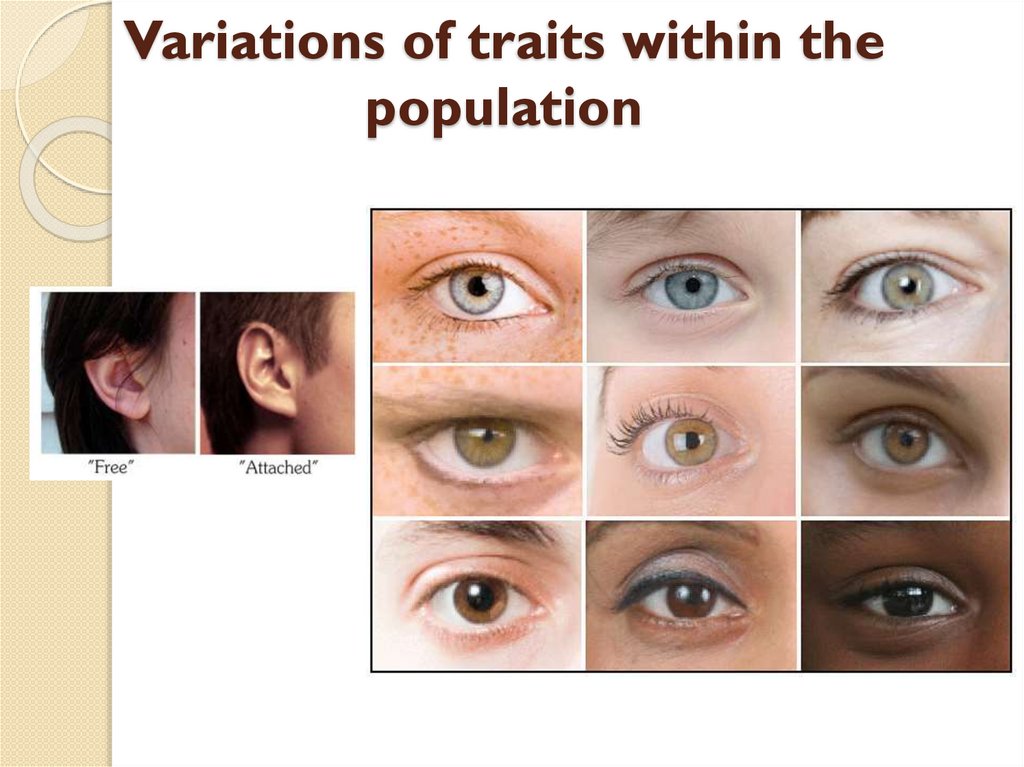
Variations of traits within thepopulation
10.
Skin color variation11.
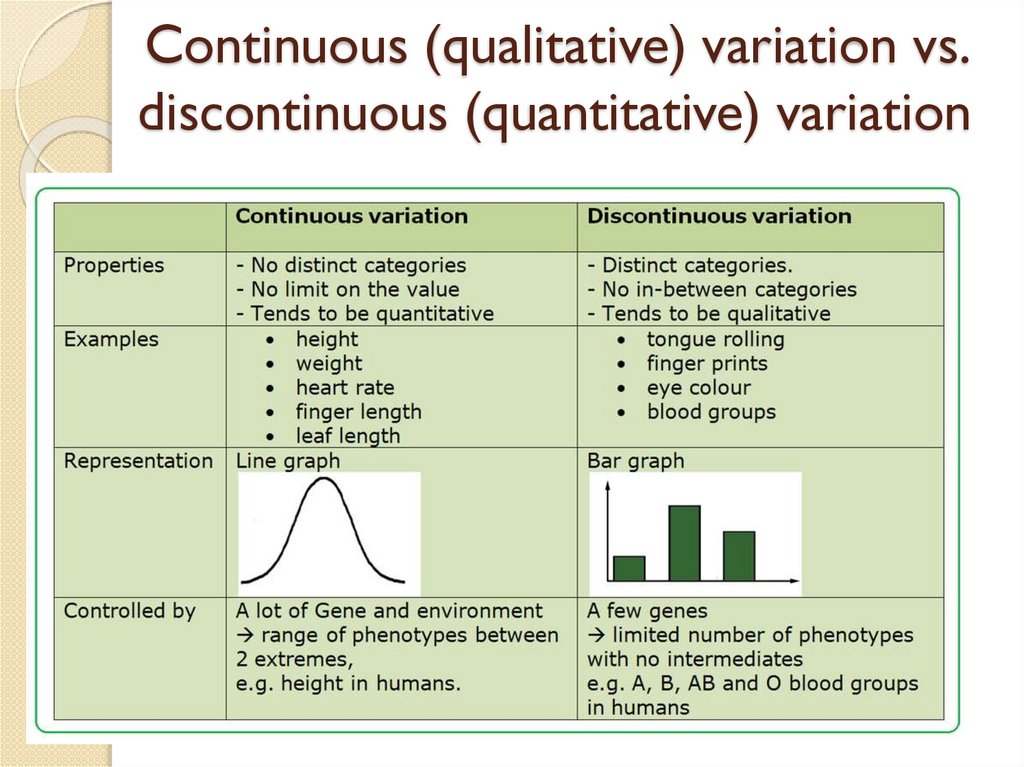
Types of variationsContinuous (qualitative)
2. Discontinuous (quantitative)
1.
12.
Continuous (qualitative) variation vs.discontinuous (quantitative) variation
13.
Let’s do activity on p.10914.
HomeworkRead p. 108-109
Answer to literacy questions on p 109
New words











 biology
biology








