Similar presentations:
Flexible Project Management Methodologies. Lecture 6. Managing IT Project Quality
1.
Flexible Project ManagementMethodologies
Lecture 6
Managing IT Project Quality
Krivulina Irena Gennadievna
Associate Professor
2. Управление качеством проекта (Quality Management)
Quality refers to:products, services, processes , systems
Quality – the degree of conformity of own(not
assigned) characteristics to the requirements
Characteristic – distinctive property
Requirement – a need or expectation that is
documented, generally accepted, or mandatory
3. Definition of quality
Quality is defined as:• Compliance with requirements (specifications)
• Conformity of applicability (fitness for use)
Two aspects of quality in IT projects:
• Quality of the project execution
• Product quality project
A triplet of project success:
Timing
Price
Quality
4. Warning, not inspection
Warning, not inspection – the cost of noncompliance is higher than the cost of warningand security
• Quality must be planned!
• Increased importance of planning and quality
assurance rather than control, because,
unlike a permanent activity, a project product
is created once
• The more innovative the project, the higher
the importance of quality management
5. Quality management processes
• Plan Quality Management(Планирование качества)
• Perform Quality Assurance
(Обеспечение качества)
• Control Quality
(Контроль качества)
6. Планирование качества (Plan Quality Management)
Defining those quality standards, to whichthe project must comply and the definition
of actions to ensure these standards
Process result – document
«Quality Management Plan», which
describes, how the project team will
implement the quality policy during the
project execution
7. Quality policy
Политика качества (Quality Policy) of theperforming organization is determined by the top
management of the organization , often fixed in
regulatory documents
Duty of the project manager – ensure that the
project complies with the organization’s quality
policy
In the absence of a formalized quality policy for
the organization, the project team must develop
one for their project
8. Standards and regulations
Standard and Regulations in the subjectarea of the project determine the project
quality policy
Standard
• Describes a generally accepted approach,
best practice, recommendations
• Recommends execution
• Regulation
(law, instruction, order)
obliges to fulfill
9. Benchmarking, Design of experiments
Сравнение (Benchmarking) – comparison ofyour project and its product with similar previous
ones in order to develop ideas for the necessary
quality standards
Эксперименты (Design of Experiments) to
determine which factors and how affect various
parameters of the system. Usually applied to a
product.
A computer model of the project can be
considered as an “experiment” of the project
10. Quality control diagrams
Диаграммы(Flowcharts)
show
the
relationship of various elements of the system
and the logical actions necessary to achieve
goals. Most common:
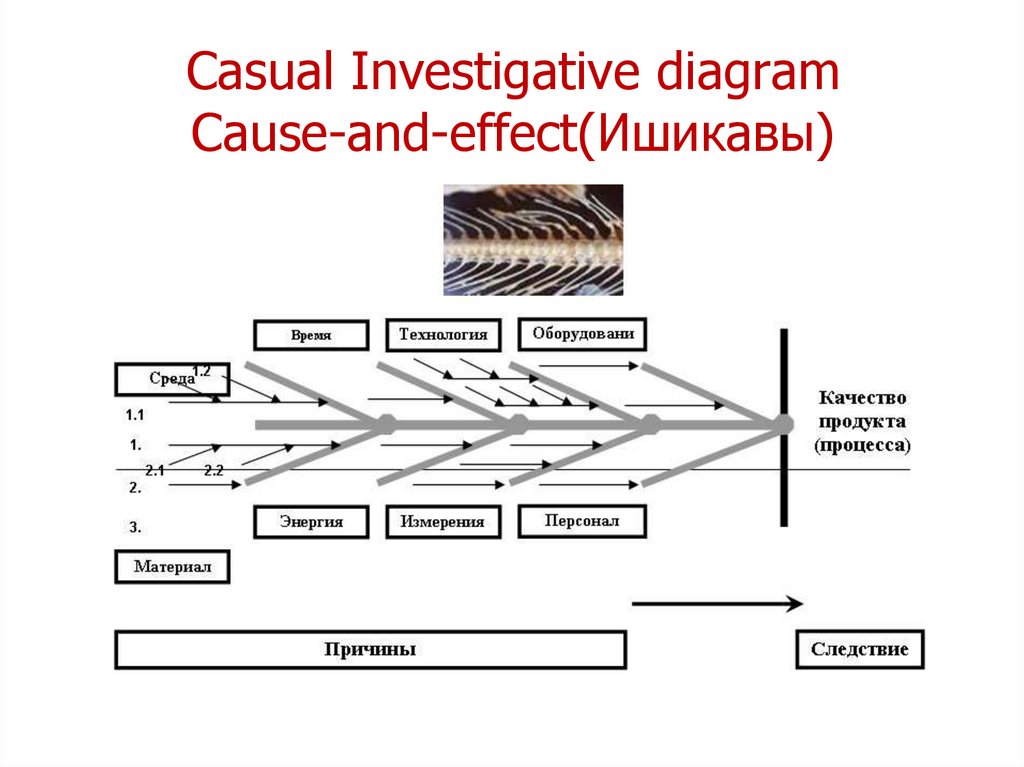
• Casual-Investigative diagram
(Причинно-следственные
диаграммы)
Ishikawa
diagrams (also called fishbone diagrams, herringbone
diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, or Fishikawa) are
casual diagrams that show the potential causes of a
specific event
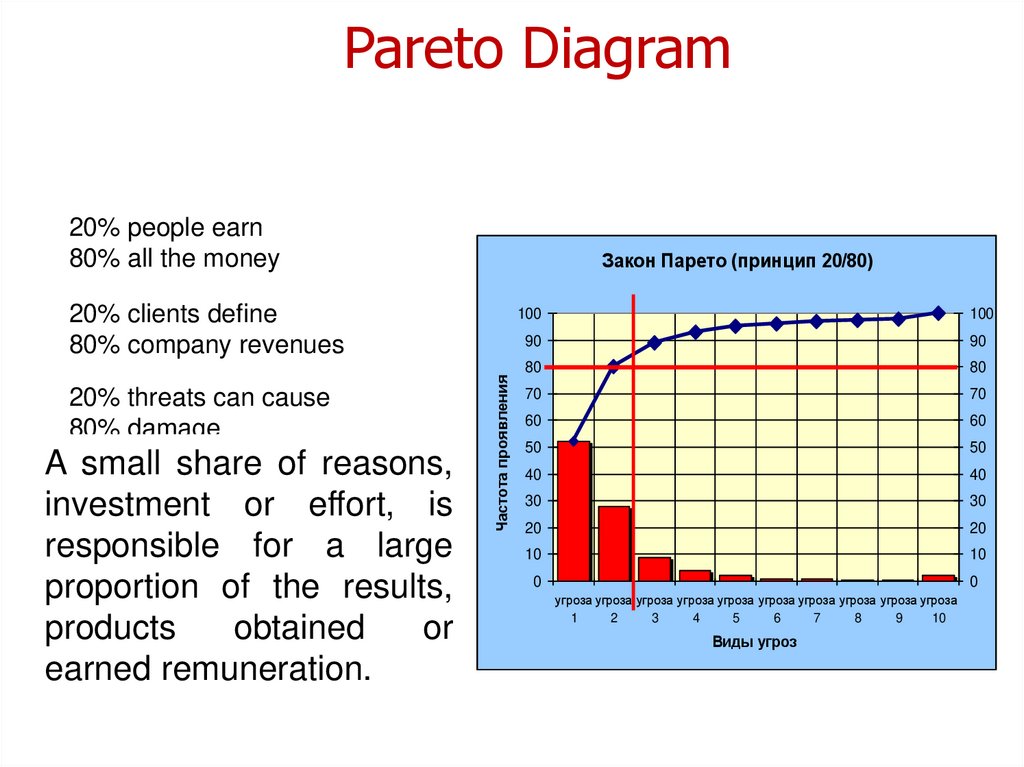
Pareto diagram
Process flowcharts
11. Casual Investigative diagram Cause-and-effect(Ишикавы)
12. Cause-and effect diagram
13.
Pareto Diagram20% people earn
80% all the money
Закон Парето (принцип 20/80)
20% threats can cause
80% damage
A small share of reasons,
investment or effort, is
responsible for a large
proportion of the results,
products
obtained
or
earned remuneration.
Частота проявления
20% clients define
80% company revenues
100
100
90
90
80
80
70
70
60
60
50
50
40
40
30
30
20
20
10
10
0
0
угроза угроза угроза угроза угроза угроза угроза угроза угроза угроза
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Виды угроз
14. Стоимость качества (Cost Quality) is the cost of all efforts to achieve the required quality level
Compliance cost• Planning
• Staff training
• Provision and control
• Quality specialists
• Tests, audits
• Research, reviews...
Nonconformity cost
• Waste
• Alterations
• New research
• Warranty service
• Return of products
• Complaints
15. План управления качеством (Quality Management Plan)
The quality management plan defines the selected qualitypolicy and how to implement it in the project.
• In ISO 9001 terms it describes the quality system of
the project: «organizational structures, responsibilities,
procedures, processes and resources, necessary to
ensure quality management»
• Is an integral part and input for the development of
the Project Plan
• Can be formal or informal, depending on the needs of
the project
16. Operational definitions
Операционныехарактеристики
(Operational
Definitions) – describe in a specific (technical) form,
what and how will be measured to ensure quality.
Often called metrics.
For example, not enough to say, that meeting deadlines
will be an indicator of the quality management (need to
indicate, should each operation start as planned, or just
finish on time, are all operations monitored, or just some
results (milestones), if so, which ones...
17. Обеспечение качества (Perform Quality Assurance)
Perform Quality Assurance – this is theexecution of all systematic actions planned in the
quality system to ensure that the project will
meet the required quality standards
Main process object – the system of quality
itself
Before development the development of a series
of standards ISO 9000 activity, which is related to
quality planning was considered as a part of
quality assurance
Performed by the relevant part of an organization
18. Process inputs (Perform Quality Assurance)
Quality management plan defines standardsand procedures, used for quality assurance
• Operating characteristics
• Describe in detail,what should be measured and
how (metrics) for quality assurance
• Quality control measurement results in the
form, suitable for analysis and comparison with
the required quality standards
19. Quality audits
Quality planning methods and tools – herethey are used to measure the state of execution
Quality audits serve the purpose:
• Periodic
review of quality management
activities to confirm their correctness and
effectiveness
• Measure the status of performance and identify
necessary corrective actions
• Identify ineffective and uneconomical rules,
processes and procedures used in the project
• Identify lessons for future projects
20. Control Quality
Control Quality is to control the specific results of theproject in order to compare them with the required
quality standards and find ways to eliminate the causes
of unsatisfactory. Includes quality control of both
product and project management.
Work results:
• What is completed, and what not and how much
• Actual budget expenditures
• To what extent quality standards are achieved
21.
Approaches to quality improvement• TQM - Total Quality Management
• 6 sigma
• Approach «Кайдзен»
22.
First principle TQM«customer orientation»
• Mental inclusion of the consumer inside the company
• The main goal of each employee – consumer satisfaction
• The concept is completely opposite to the concept
«product out»
• Japanese proverb says: «Buyer - God!»
23.
Approach «Кайдзен»The principle of permanent, continuous improvement
Corporate
culture
and
management mechanisms,
encouraging employees to
suggest improvements and
implement
them
in
operational mode.
24. Takeaways
Project Management:• Goal – content, timing, cost
• Do what, when and how much
• Tagline ( Слоган) – RIGHT (ПРАВИЛЬНО)
Quality management:
• Goal – process efficiency and product applicability
• Do the right thing (Делать как надо)
• Tagline (Слоган) - GOOD (ХОРОШО)
25.
Lecture 6 – what we learn?Quality definition
Quality management processes
Quality Policy
Standards and Requlations
Diagram (Ishikava, Pareto)
Quality management Plan
Operational definitions
Quality Assurance
Quality Control
26.
Thank you for attention!Questions?
Continuation will follow…






















 informatics
informatics management
management








