Similar presentations:
Epistemology, gnosolgy. Cognition and creativity (lecture 5)
1.
Handouts• Lecture №5 Epistemology, gnosolgy.
Cognition and creativity
• Philosophy
• 3 credits
• PhD
Yerkin Massanov
2.
Issues of lecture:• 1. The philosophy of science,
cognition;
• 2. Function and types of MS;
• 3. Thomas Kuhn: “Scientific
revolutions”.
3.
The main concepts of previouslecture:
• 1. Which branch of philosophy studies
being?
• 2. What are the main questions of
Ontology?
• 3. Examples for Ontology of Kazakh
people?
4.
Previous-lectures:Education and Methodolgy of Ph-y develop in each
periods. Key finding
1)Lecture –synonymous of philosophy is sciences;
2)Ancient Chinese ph-y – based on ethical ph-y
3)Ancient Indian ph-y – mythological-cosmological
ph-y;
4)Ancient Greece ph-y – first foundation of scientific
rational, objective and logical methodology;
5)Medieval ph-y – Western-Christianity and EastIslamic religion;
6)Renaissance ph-y – rebirth of Antique: Ancient
Greece ph-y;
5.
BEING:• Term used mostly for describing widely;
• Substance, basis of life;
• The problem of being is studied by such
philosophical discipline as ontology;
• synonyms of meaning, “existence” ;
• Virtues of human;
6.
Definition:Being one of the fundamental concept
philosophy which describe widely meaning
of life.
For instance: Being of Kazakh people –
which includes of all virtues and values of
nation: freedom and peace, tolerance,
striving for objectivity and justice,
Positive and optimistic philosophy for the
future etc.
7.
Previous L. Keys for understandingof Philosophy
Synonyms for Philosophy –
science.
Ph-y - through combination
all subjects describing world
(Picture of world).
8.
The 3 historical types of outlook:1.Mythology - system of legends;
2.Religion – based on faith and
believe;
3.Philosophy – close to the
science and rational, theoretical
way of knowledge
9.
W.-6. Discussion for Seminar (1 p.)Who is the author of
“The black square”?
How impact to the way of
thinking or cognition?
(with Internet-5 without I.-10 marks)
10.
Essay “The Black square” by KazimirMalevich:
Why this is not square?
BS is not black?
What is the meaning of BS?
Cubism-traditional thinking?
11.
1. The philosophy of scienceis a branch of ph-y that studies the concept,
possibility and methodology of science.
There are also more special sections of
the ph-y of science, for example, the
philosophy of: mathematics, physics,
chemistry, biology, medicine, psychology and
IT etc.
12.
Epistemology (Greek- “knowledge” or“understanding” or “acquaintance”)
Epistemology is a philosophical and
methodological discipline that explores
scientific knowledge, its structure, structure,
functioning and development.
13.
Gnosology (Greek - Cognition,reasoning, teaching)
the doctrine of cognition, is a branch of
philosophy that studies the possibilities of
understanding the world by man, the
structure of cognitive activity, the forms of
knowledge in its relation to reality, the
criteria for the truth and reliability of
knowledge, its nature and boundaries.
14.
In philosophy, there are two mainviewpoints on the process of cognition:
Gnosticism & Agnosticism;
A-gnosticism (Knowlable);
A-theism (belief existence of God)
Ir-rational.
15.
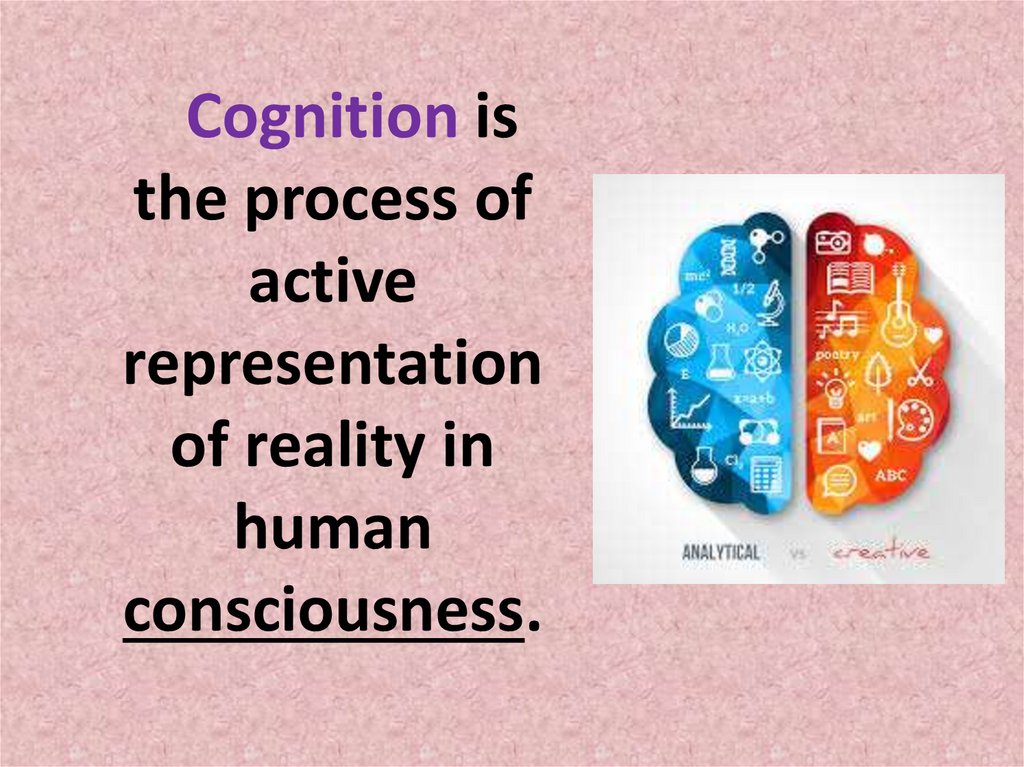
Cognition isthe process of
active
representation
of reality in
human
consciousness.
16.
The philosophical categories ofscience mostly based on material and
non material dualism:
Practical and Theoretical ;
Realistic and transcendental;
Dialectical and Metaphysical;
Rational and irrational.
17.
3 types of methodology science:1. The general methodology of science
studies the problems of all areas of research
(Universal);
2. The Specific m-y of science explores the
methodological problems of individual
sciences or their small groups (Physics,
Chemistry);
• 3. Concrete m-y of science concentrate to
the temporary issues (Economical crises).
18.
Function of methodology science helps:1. To understand clear scientific issues;
2. Interpretation of results science as a
worldviews (Evolutionism);
3. To do strategies development of science;
4. Stimulates the development of S.;
5. Concrete instruments to solve the tasks;
6. Through description process
recommendation;
7. Analysis and improve of the structure of
activity including motivation, goals,
objectives etc.
19.
Week-6 Book for seminar discussion:Thomas Kuhn: “The structure of scientific
revolutions”.
Published in 1962 y.
The author focuses on the
laws of the development of
science, which radically change
the way of scientific thinking.
20.
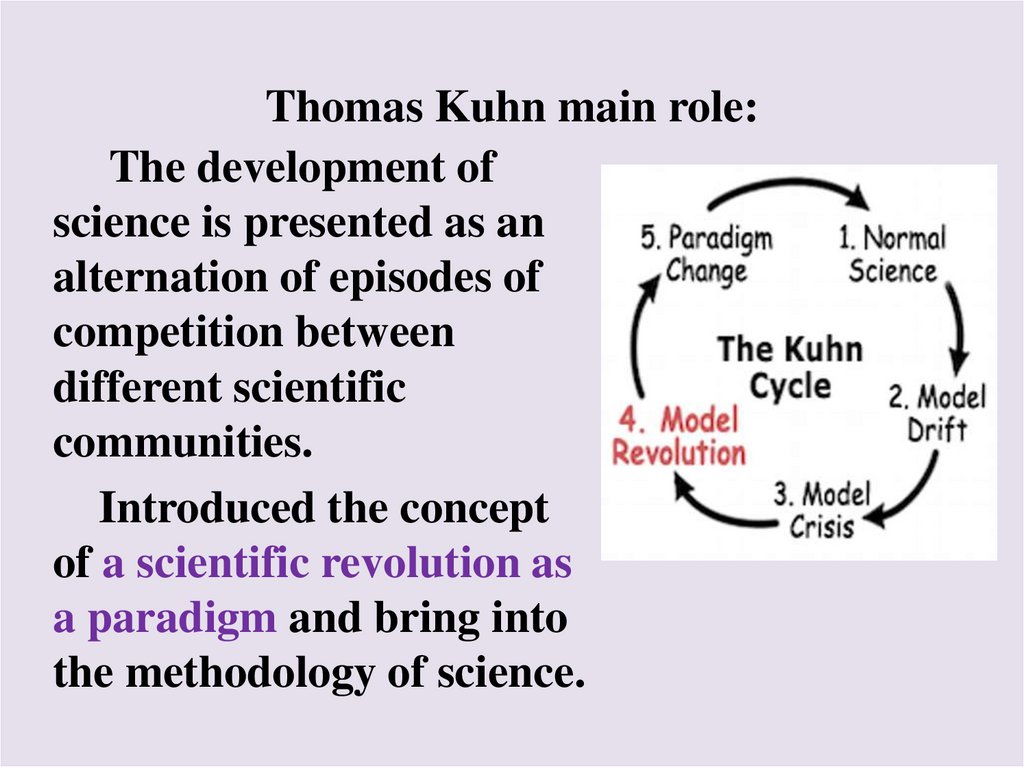
Thomas Kuhn main role:The development of
science is presented as an
alternation of episodes of
competition between
different scientific
communities.
Introduced the concept
of a scientific revolution as
a paradigm and bring into
the methodology of science.
21.
Supporters of gnosticism(usually materialists)
optimistically consider presence
and future knowledge. In their
view, the world is knowable, and
the person has a potentially
limitless possibilities of cognition.
22.
Agnostics do not believe inthe possibility of either man to
explore the world or in the
knowable of the world or they
allow a limited possibility of
human cognition.
Among agnostics the most
famous is Immanuel Kant.
23.
Kant put forward a consistent(последовательный) theory of
agnosticism, which provides:
24.
the person has limited cognitiveabilities (owing to limited cognitive
abilities of the mind);
the world itself is unknowable, that
is, people will be able to cognize
outside of the objects and
phenomena, but never know the
inner essence of these objects and
phenomena, that is, “things in
themselves”.
25.
Agnostics-idealists believe thatcognition is a self-employed
activity of an ideal reason.
26.
Materialists believe thatcognition is a process, in which
the matter is studying itself
through its reflectivity –
consciousness (отражательную
способность).
27.
Principles of cognitionModern gnoseology in the
majority stands on positions of
gnosticism and is based on the
following principles:
1) Dialectics;
2) Relativism;
3) Historicism.
28.
1) Dialectics, which impliesthe need dialectically (i.e. in
terms of development)
approach to the problem of
cognition and knowledge, to
use the laws, categories,
principles of dialectics;
29.
2) Historicism, whichconsiders all things and
phenomena in the context of
their historical emergence and
formation;
30.
In conclusion:Epistemology:
- one of the branches of philosophy,
which studies cognitions;
- cognition: agnostism-gnostism or
unknowable – knowable;
- philosophical knowledge combine all
scientific methodology and give more
objectivity and relative concepts.
31.
№5 Discussion for seminar:1. Compare. Explain: Gnosticism
and Agnosticism, scientism?
2. Interpretation. Thomas Kuhn: “The
structure of scientific revolutions”.
3. Analyze: Scientific Innovations of
modern Kazakhstan (Askar Jumadildaev
etc.)?
(at less 2-3 pages in copybook)
32.
• Essay – interpretation:• Muhammad Yunus.
“BUILDING SOCIAL
BUSINESS”.
• The role of Humanism.
Humanistic values on management
in organization?
• Cognition and creativity in
social research?
• Realization of Social business in
Kazakhstan?
(1-2 pages in copybook)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TB7-TX-qoqg
33.
Forms to writing answer:• Introduction/ Defenition…
• Basic ideas…
• Examples/In my opinion…
• Conclusion...
34.
• Abstract (Referat) –at less 5-7 pages in copybook:
• 1) Title
• 2) Content
• 3) Introduction
• 4) Basic ideas and examples
• 5) Conclusion (1 page)
• 6) Literature or reference (3 book or
article)
35.
Self-studies Choose one
1 Self-studies (15-more marks, deadline Week-6)
QAZAQ PHILOSOPHY – topics for Articles, YouTube, Wikipedia
Choose one of them or acceptable own related with Qazaq ph-y:
1. Chokan Valihanov: "Notes on judicial reform“;
2. Abay Kunanbayuly: "Biy rules" or poems;
3. Abay Kunanbayulu: “Kara sozderi” or “Abay zholy”;
4. Mashhur Zhusip Kopeiuly philosophy;
5. Arystanbaba as a Qazaq spiritual center;
6. Koja Axmet Yassaui: “Diuani xikmet” philosophy;
7. Korkyt ata: philosophical analyze;
8. Beket ata or Shopan ata, Zhusuip Balasagun: “Kutty bilik” philosophy;
9. Enlightenments philosophy of Kazakh Intelligence?
10. Compare: Qazaq and Russian ph-y (Slavianfils and Westernization R.)?
11. Philosohy of Zar-zaman periods?
12. Philosophical Thoughts of Akyn-Zhyraus and Beys Kazakhstan?
13. Philosophy of Modern and Independent Qazaqstan: “Mangilik el” ideas;
14. Modernization of Qazaqstan: “Ruhani jangyru”
15. Shakarim Kudaiberdiulu: “Ush anyk” (Three truth);
































 philosophy
philosophy








