Similar presentations:
Word formation
1. WORD FORMATION
Derivation2. Derivative structure
• A derivational base• A derivational affix
• A derivational pattern
3. A derivational base
• A derivational base = a morphological stem(computer- computer – ize)
• A derivational base = a word form
(known- un-known)
- A derivational base = a word group
(narrow-mind- narrow-mind-ed)
4. Derivational affixes
Depend on• Etymological
• Phonological
• Structural-semantic
properties of derivational bases
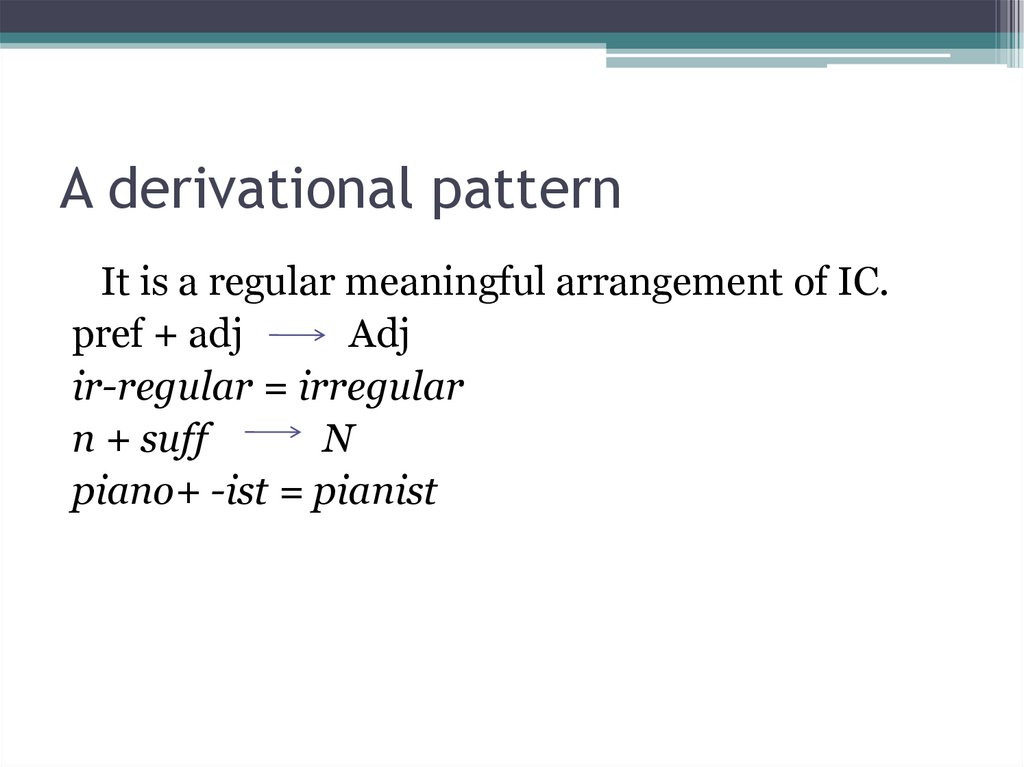
5. A derivational pattern
It is a regular meaningful arrangement of IC.pref + adj
Adj
ir-regular = irregular
n + suff
N
piano+ -ist = pianist
6. Major types of word-formation
• Conversion (zero derivation)• Affixation
• Composition (compounding)
7. Minor types of word-formation
• Back-formation• Shortening
• Blending
• Extension of proper names
• Others
8. Affixation
• Prefixation• Suffixation
9. Conversion
Conversion is a morphological way of wordformation resulting in a change of a word’sparadigm.
Hand n. – hand v.
Cut v. – cut n.
10. Conversion
Conversion is very active in nouns for verbformation
Doctor – to doctor
Shop – to shop
Conversion is very active in verbs to form nouns
To catch – a catch
To smile – a smile
11. Composition (compounding)
Word composition (word compounding) is auniversal way of deriving new words.
Word composition is a kind of word-formation
based on combining two derivational bases.
12. Composition
Derivational bases may have different degrees ofcomplexity:
- simple: snow+man
- derived: shoe+(make+er)
- compound: water+(boat+man)
But most English compounds have two simple
bases (or, from the point of view of
morphological analysis, two roots).
13. Classification of compounds
• According to the structure- compounds proper
- derivational compounds (derivational
compound nouns, derivational compound
adjectives and derivational compound verbs)
14. Classification of compounds
• According to the part of speech they belong to- nouns
- adjectives
15. Classification of compounds
• According to semantic features- endocentric (subordinative)
- exocentric
- coordinative (copulative)
16. Classification of compounds
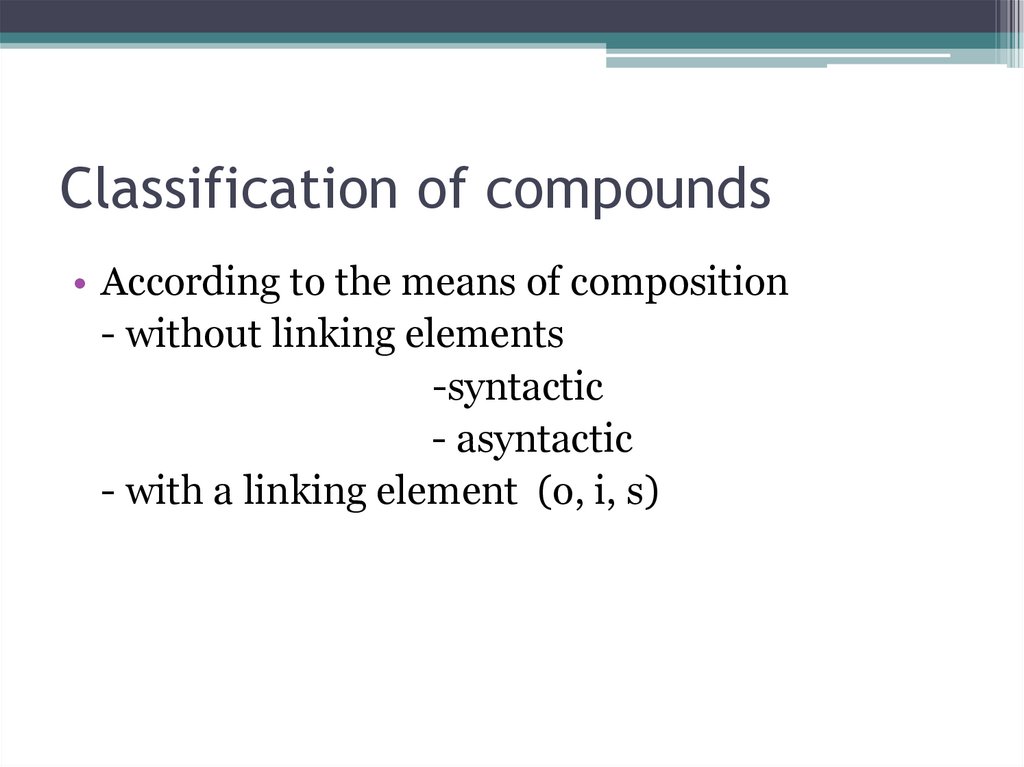
• According to the means of composition- without linking elements
-syntactic
- asyntactic
- with a linking element (o, i, s)
17. Classification of compounds
• According to the part-of-speech meaning of theirderivational bases
- nominal
- nominal-verbal
- nominal-adjectival
- adjectival-nominal
- adverbial-verbal
- verbal-adverbial + conversion















 english
english