Similar presentations:
Process Design. Increasing Plant Capacity. Process Trouble Shooting
1. Why did we waste your time with this course??
Terry A. RingChE
2. Where are M&E Balances used in the Chemical Industry? Process Design Increasing Plant Capacity Process Trouble Shooting
Where are M&E Balancesused in the Chemical
Industry?
Process Design
Increasing Plant Capacity
Process Trouble Shooting
3. Where is Design used in Industry?
• De Novo Designs• Known Plants but different location or
larger size
• Plant Improvement
– Debottlenecking Plant
– Increase Plant Capacity
– Increase Plant Efficiency
– Decrease Costs
– Pollution Minimization
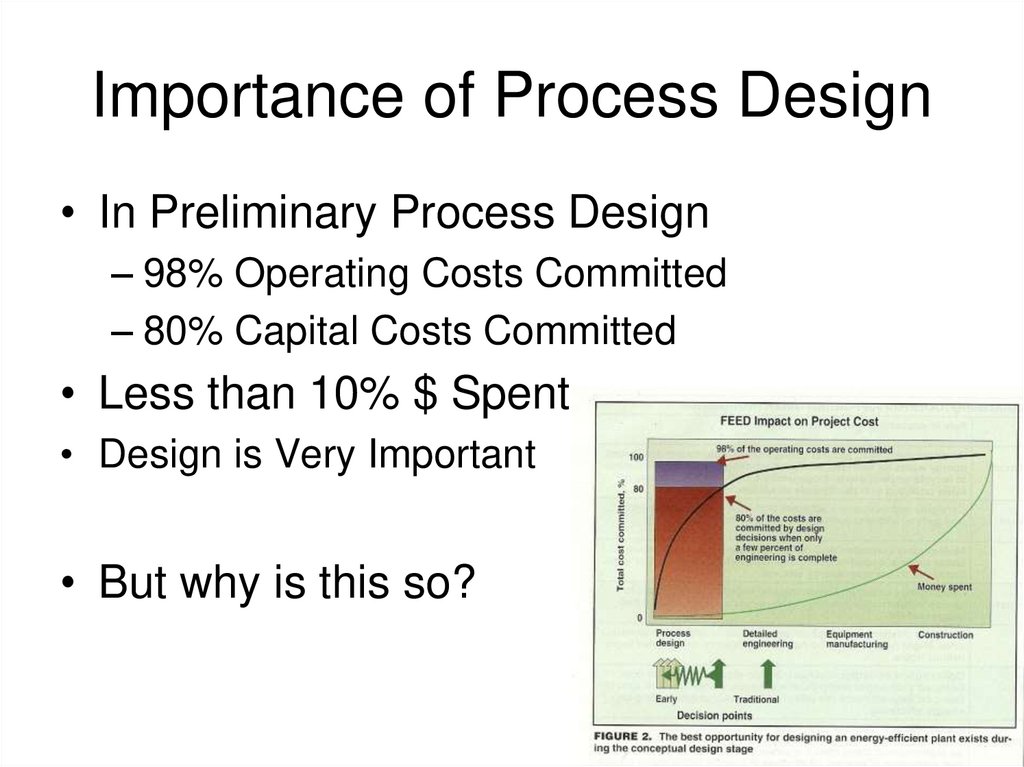
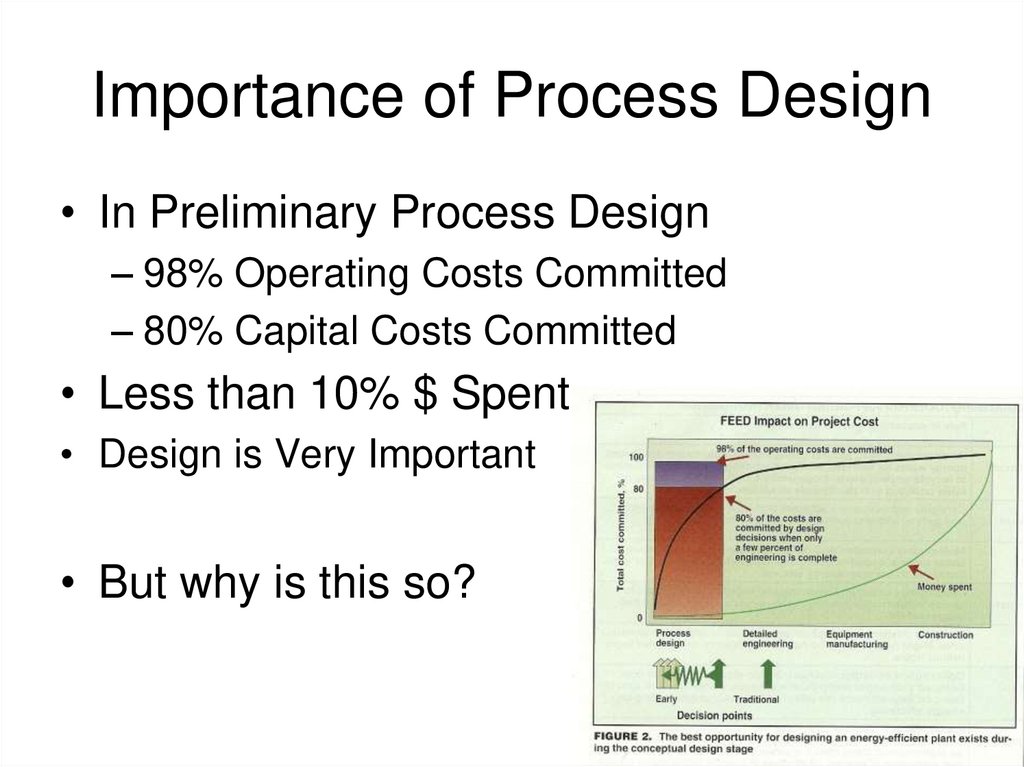
4. Importance of Process Design
• In Preliminary Process Design– 98% Operating Costs Committed
– 80% Capital Costs Committed
• Less than 10% $ Spent
• Design is Very Important
• But why is this so?
5. How is Design Practiced
Process Conception
Preliminary Design
– Process Concepts
– Process Economics
Management decision to go forward
Intermediate Design
– P&ID’s
– Ask vendors for prices major pieces of equipment
• Reactor, Separators, HX, Utilities, tank farms
– Process Economics
Management decision to go forward
Detailed Design
– Mechanical Engineering
• Equipment + Supports
– Where are all the nuts and bolts
–
–
–
–
Piping elevation
Electrical/Power Engineering
Utilities
Process Economics
Management decision to go forward
6. Process Creation
• Chemical Reaction Routes• Preliminary Database
– MSDS – (Health and safety info.)
• Raw Materials
• Reaction Products and Intermediates
– Thermo/phys properties (Expts and Predictions)
• Heats of Formation
• VLE data, solubilities, etc.
– Chemical Prices (Chemical Market Reporter)
7. Operating costs
• Selection of Raw Materials• Selection of Reaction Path to Product
• Determine Gross Profitability of Process
• Examples
– Vinyl Chloride Manufacture (part of PVC plant)
• Example in your book
– Octane Manufacture (part of refinery)
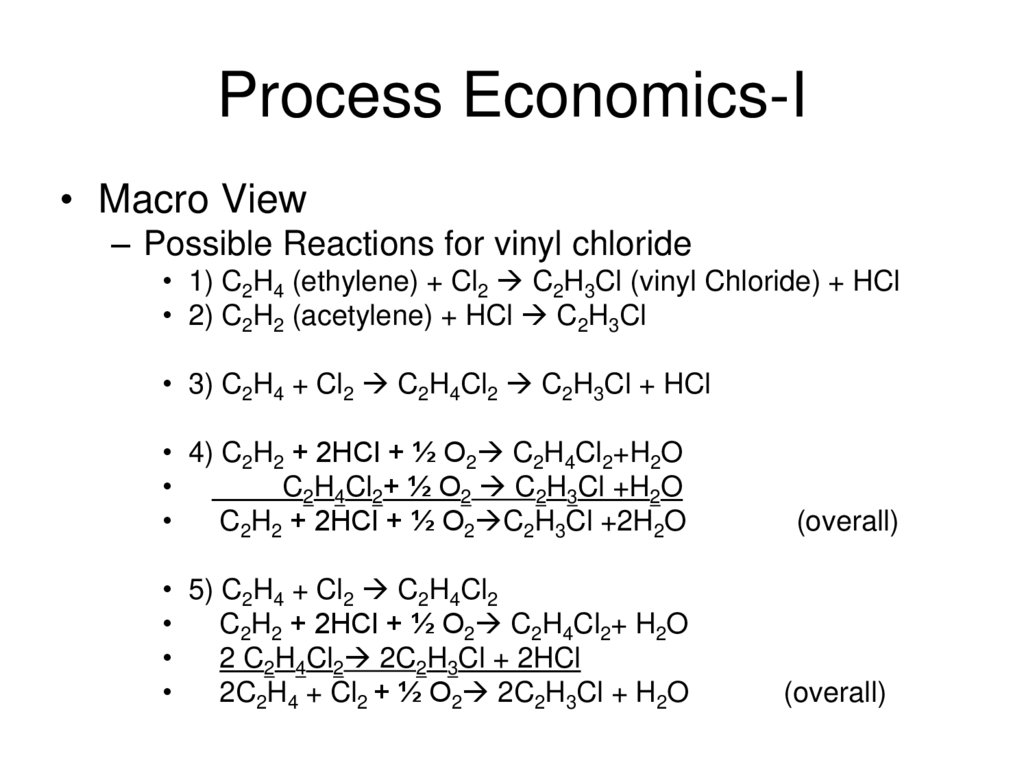
8. Process Economics-I
• Macro View– Possible Reactions for vinyl chloride
• 1) C2H4 (ethylene) + Cl2 C2H3Cl (vinyl Chloride) + HCl
• 2) C2H2 (acetylene) + HCl C2H3Cl
• 3) C2H4 + Cl2 C2H4Cl2 C2H3Cl + HCl
• 4) C2H2 + 2HCl + ½ O2 C2H4Cl2+H2O
C2H4Cl2+ ½ O2 C2H3Cl +H2O
C2H2 + 2HCl + ½ O2 C2H3Cl +2H2O
(overall)
• 5) C2H4 + Cl2 C2H4Cl2
C2H2 + 2HCl + ½ O2 C2H4Cl2+ H2O
2 C2H4Cl2 2C2H3Cl + 2HCl
2C2H4 + Cl2 + ½ O2 2C2H3Cl + H2O
(overall)
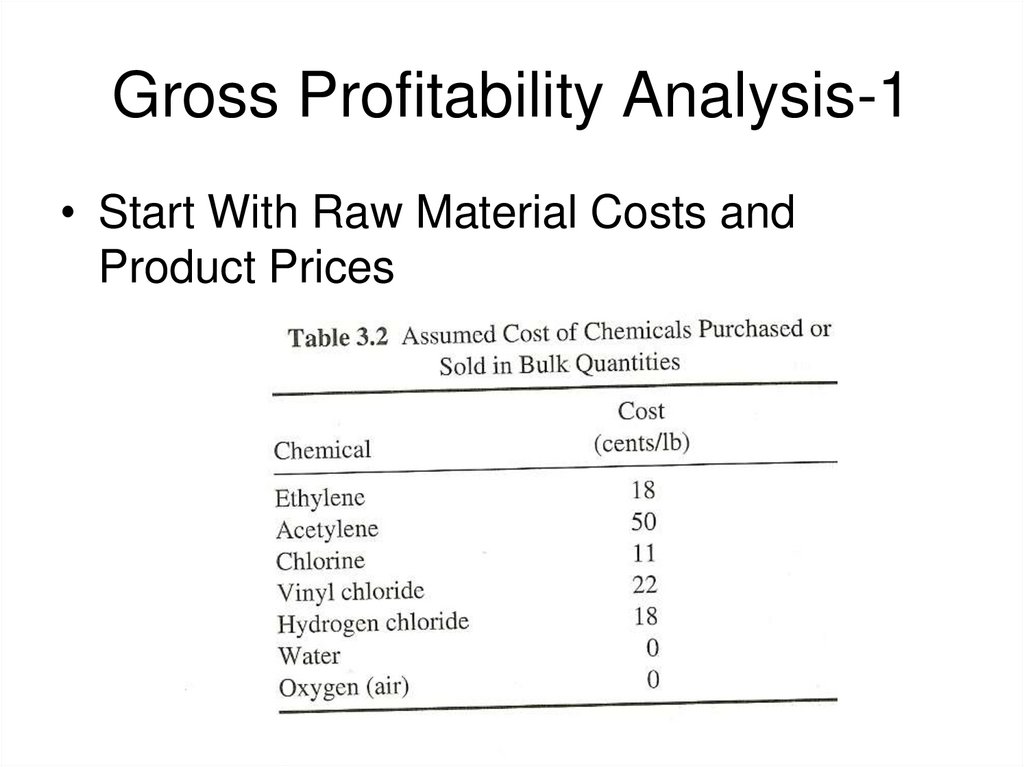
9. Gross Profitability Analysis-1
• Start With Raw Material Costs andProduct Prices
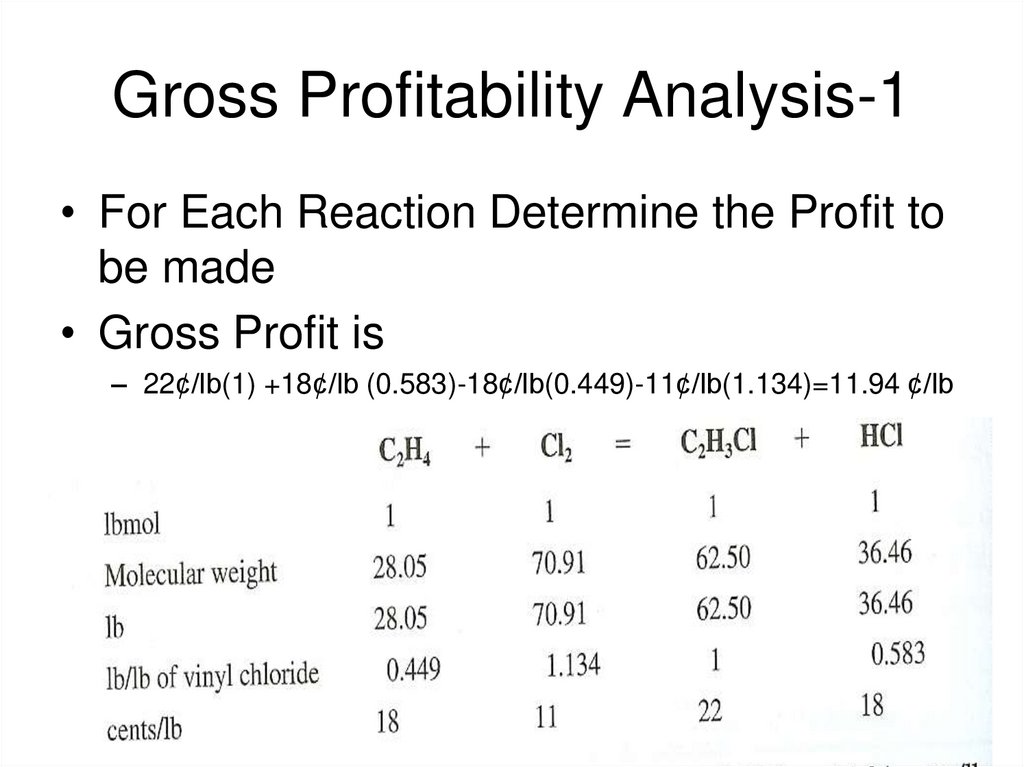
10. Gross Profitability Analysis-1
• For Each Reaction Determine the Profit tobe made
• Gross Profit is
– 22¢/lb(1) +18¢/lb (0.583)-18¢/lb(0.449)-11¢/lb(1.134)=11.94 ¢/lb
11. Gross Profitability Analysis-2
• Overview of Various Reactions• Reaction 3 is most profitable!
• How much do we make? Market Volume?
http://nexant.ecnext.com/coms2/summary_0255-3041_ITM
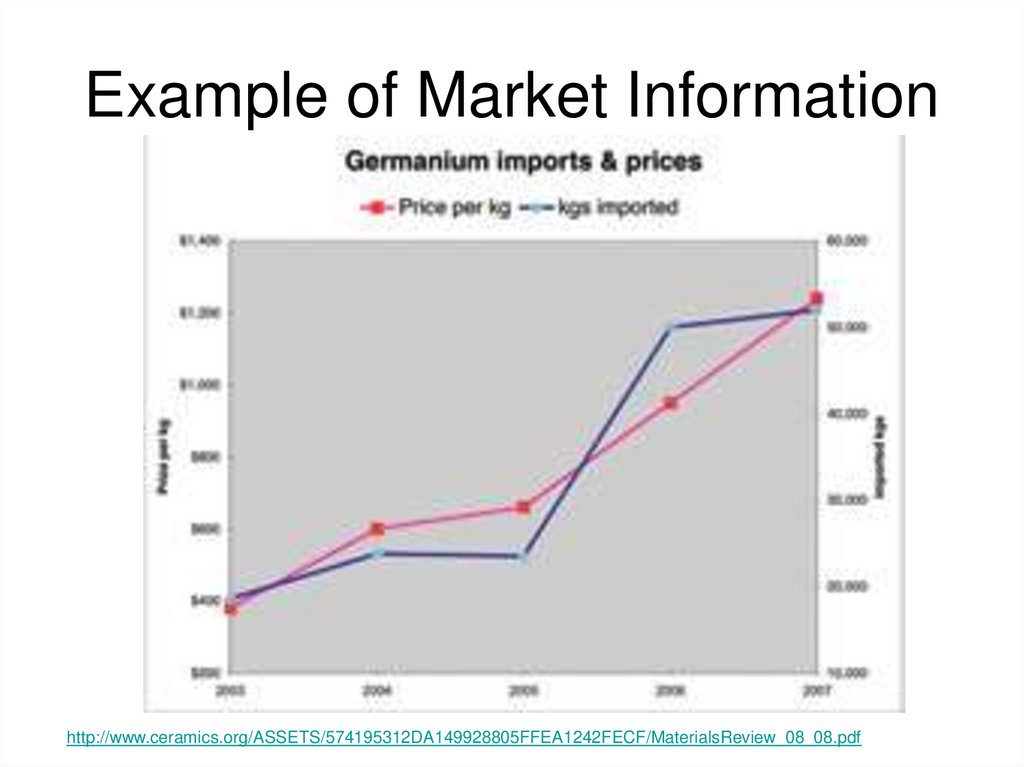
12. Example of Market Information
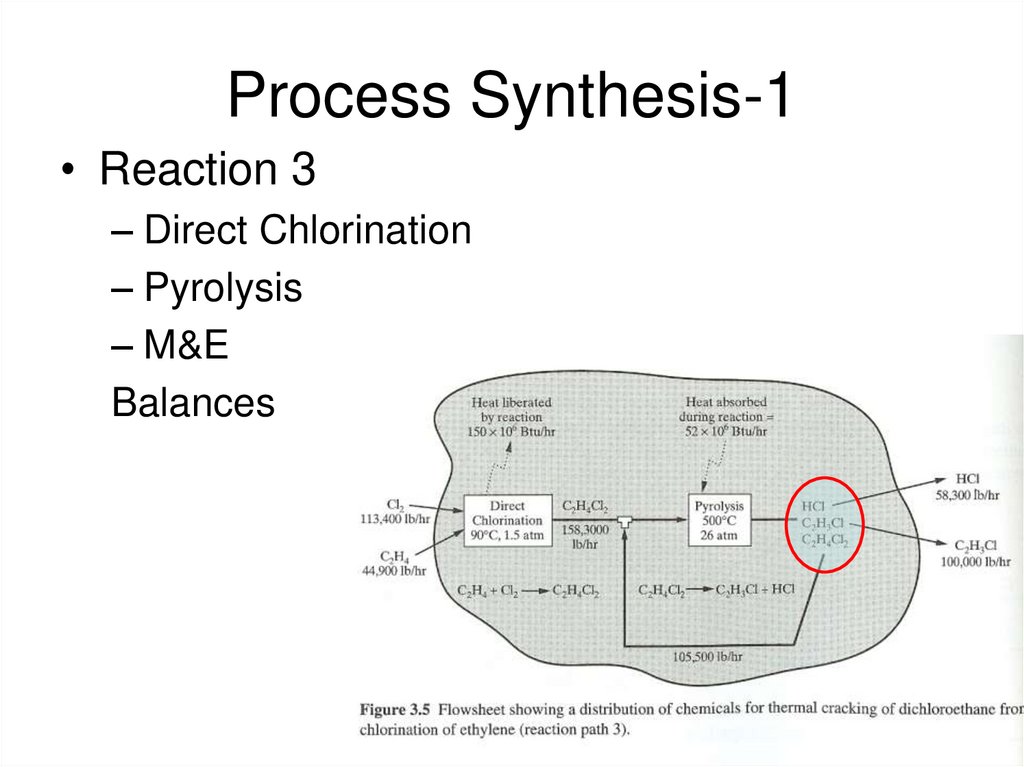
http://www.ceramics.org/ASSETS/574195312DA149928805FFEA1242FECF/MaterialsReview_08_08.pdf13. Process Synthesis-1
• Reaction 3– Direct Chlorination
– Pyrolysis
– M&E
Balances
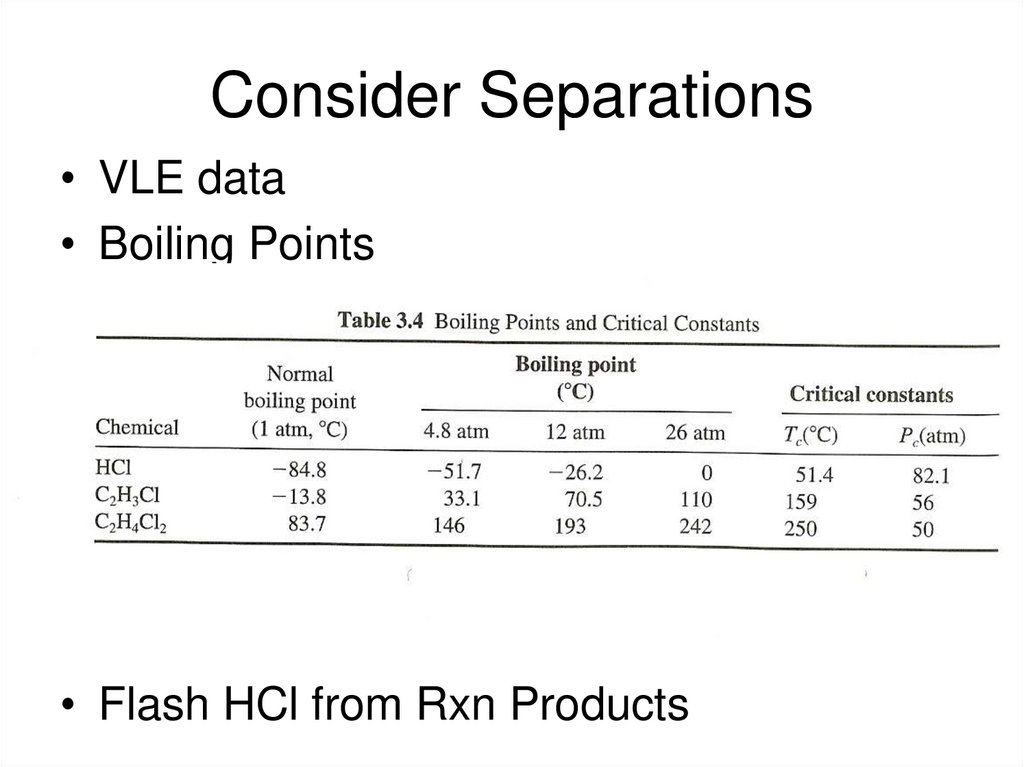
14. Consider Separations
• VLE data• Boiling Points
• Flash HCl from Rxn Products
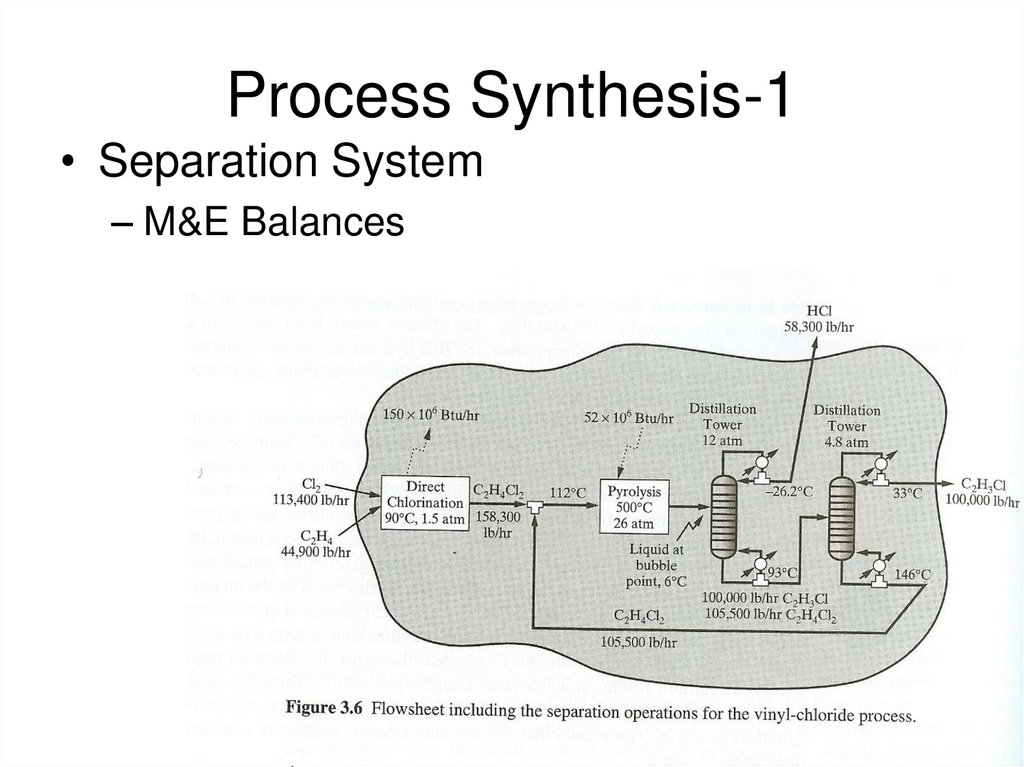
15. Process Synthesis-1
• Separation System– M&E Balances
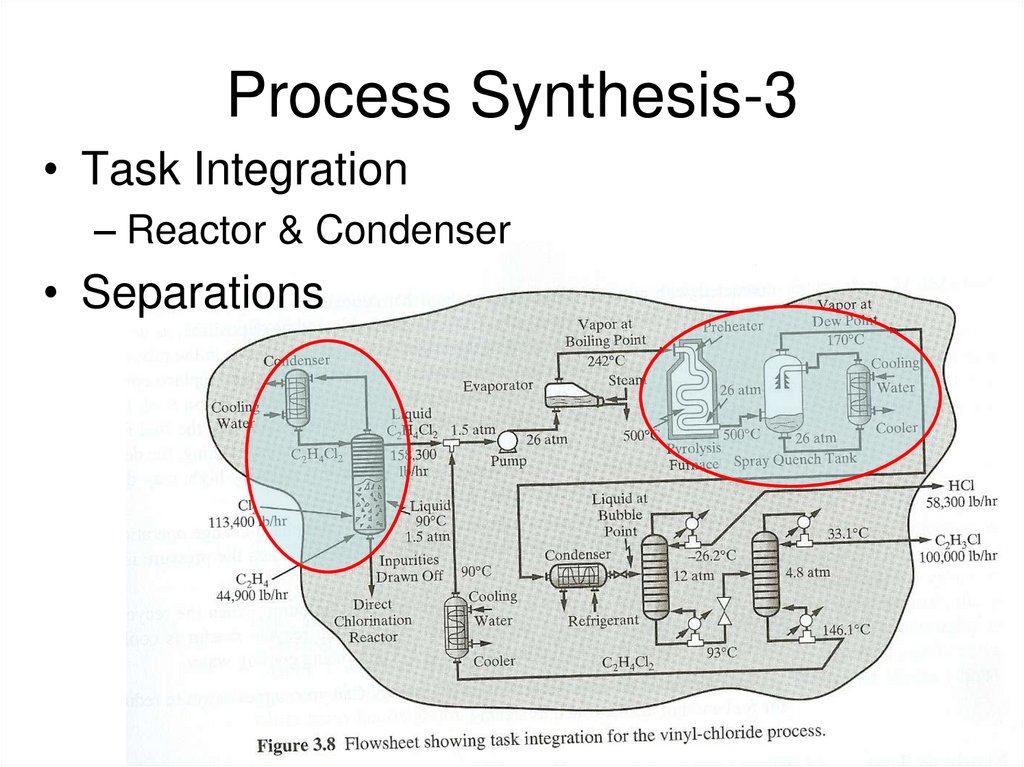
16. Process Synthesis-3
• Task Integration– Reactor & Condenser
• Separations
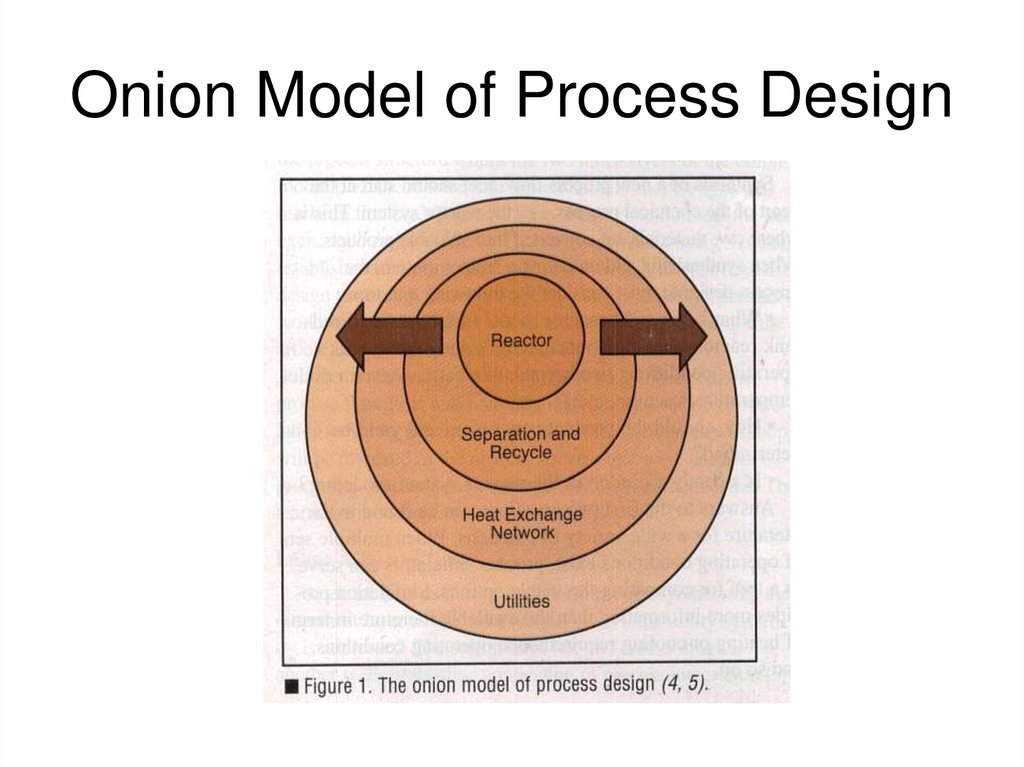
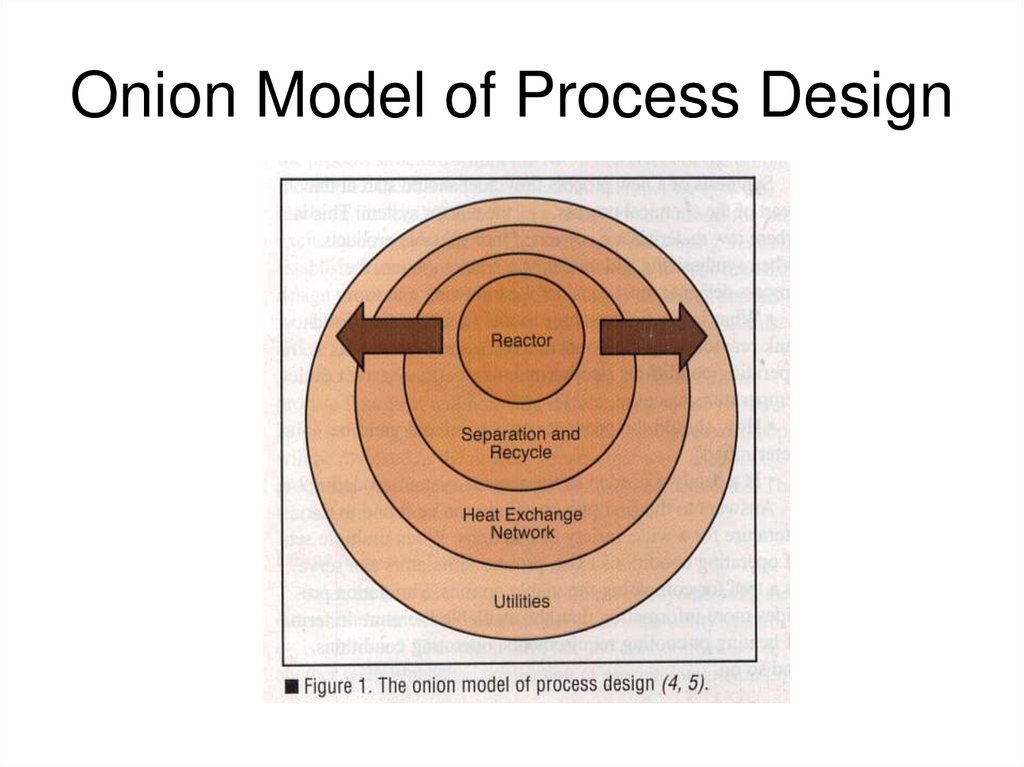
17. Onion Model of Process Design
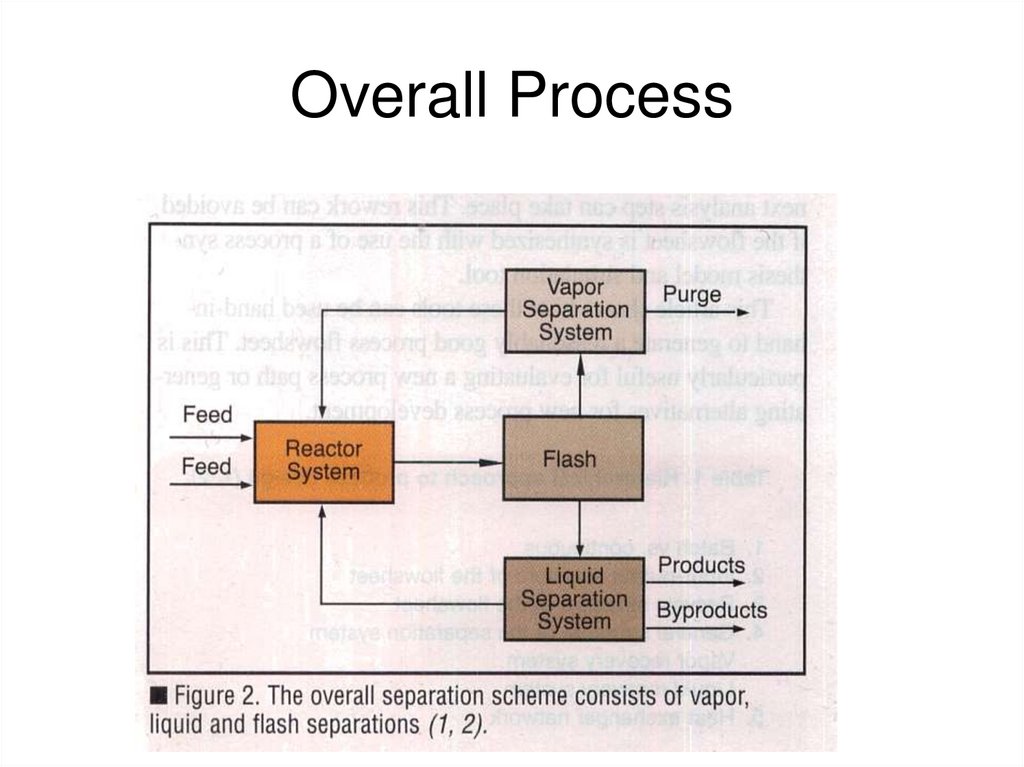
18. Overall Process
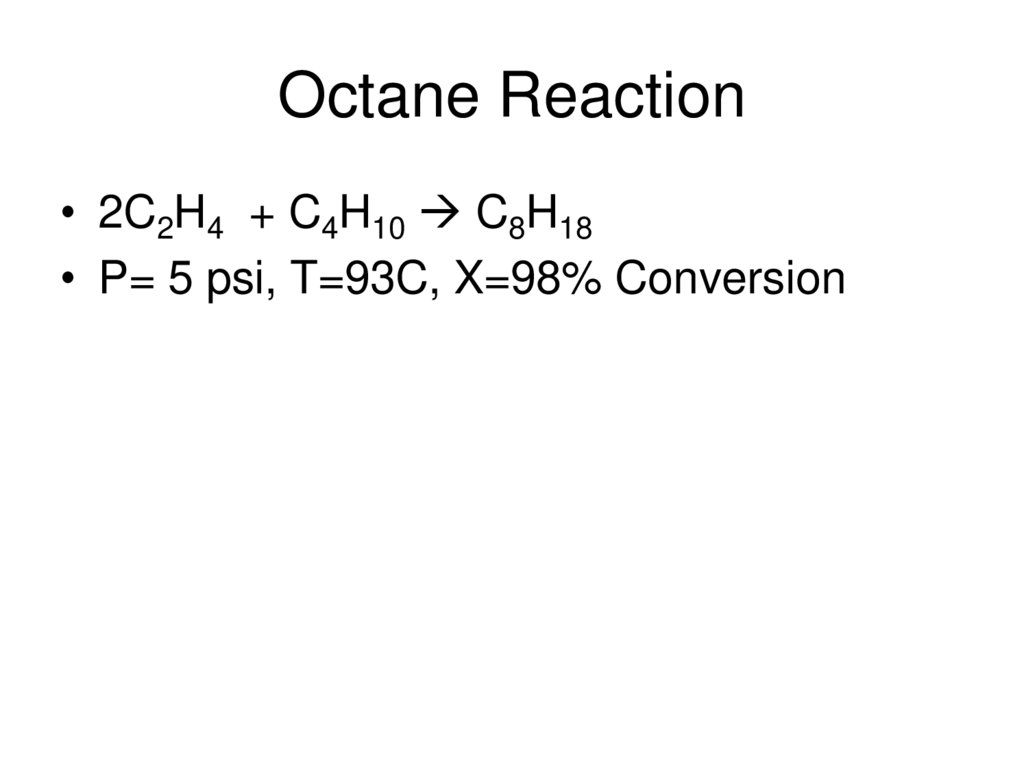
19. Octane Reaction
• 2C2H4 + C4H10 C8H18• P= 5 psi, T=93C, X=98% Conversion
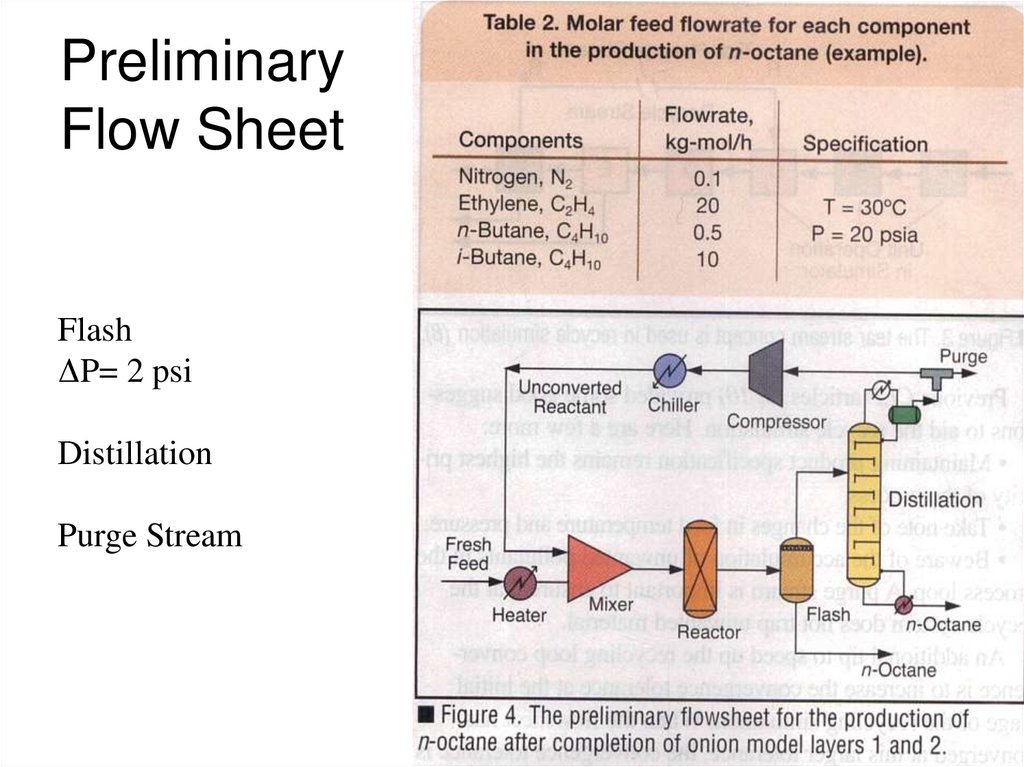
20. Preliminary Flow Sheet
FlashΔP= 2 psi
Distillation
Purge Stream
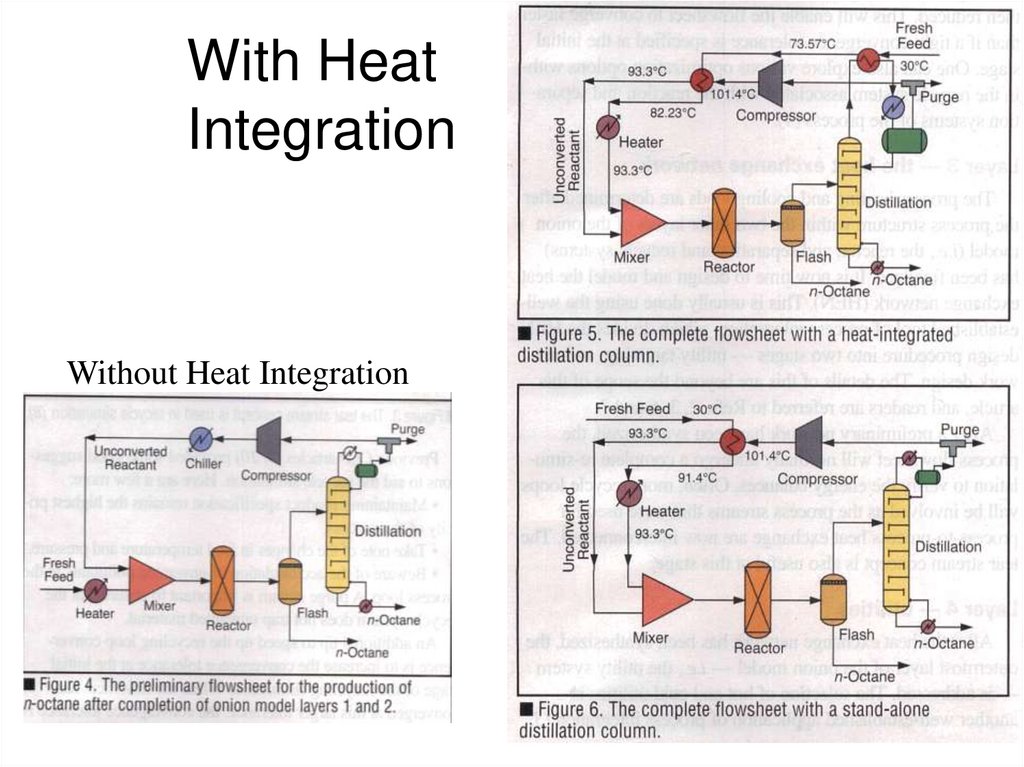
21. With Heat Integration
Without Heat Integration22. What else can be done?
• Where is the heat duty for the Flash vesselcoming from?
– Heat Exchanger coupling reactor feed to
reactor product.
• Do we really need the flash vessel?
– Let distillation column do all the separation.
• Reactor heat duty
– Exo or Endo reaction?
– Where does it come from?
23. Onion Model of Process Design
24. Many M&E Balances
Many M&E Balances• All Done by Hand????
• No!!!
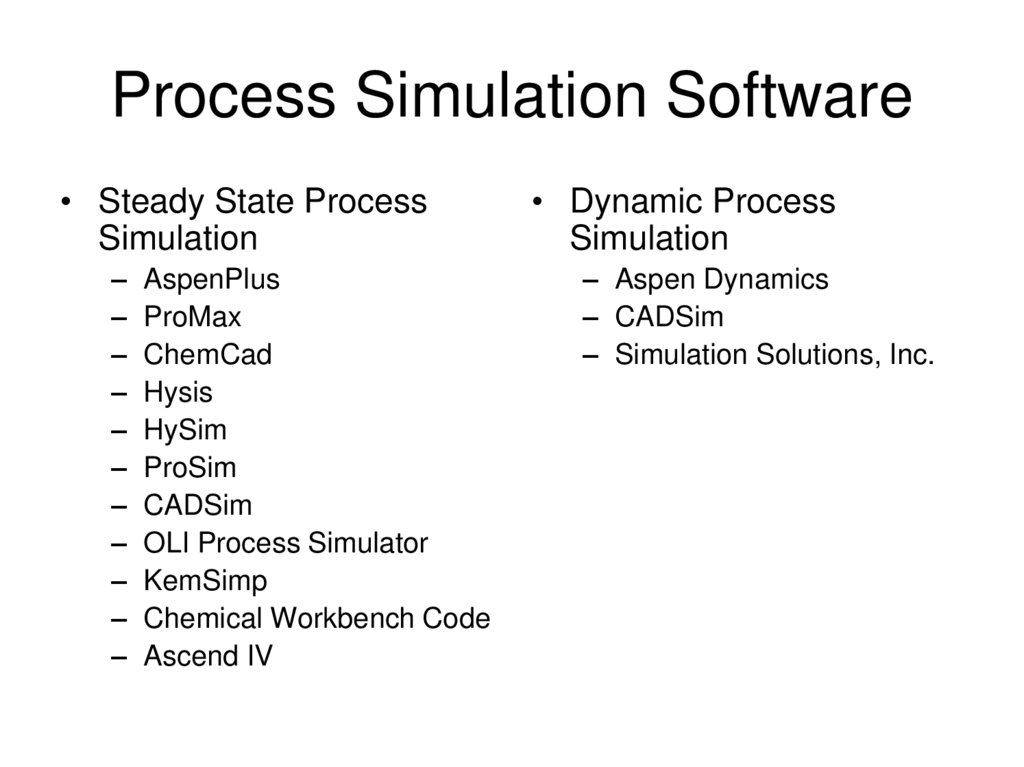
25. Process Simulation Software
• Steady State ProcessSimulation
– AspenPlus
– ProMax
– ChemCad
– Hysis
– HySim
– ProSim
– CADSim
– OLI Process Simulator
– KemSimp
– Chemical Workbench Code
– Ascend IV
• Dynamic Process
Simulation
– Aspen Dynamics
– CADSim
– Simulation Solutions, Inc.
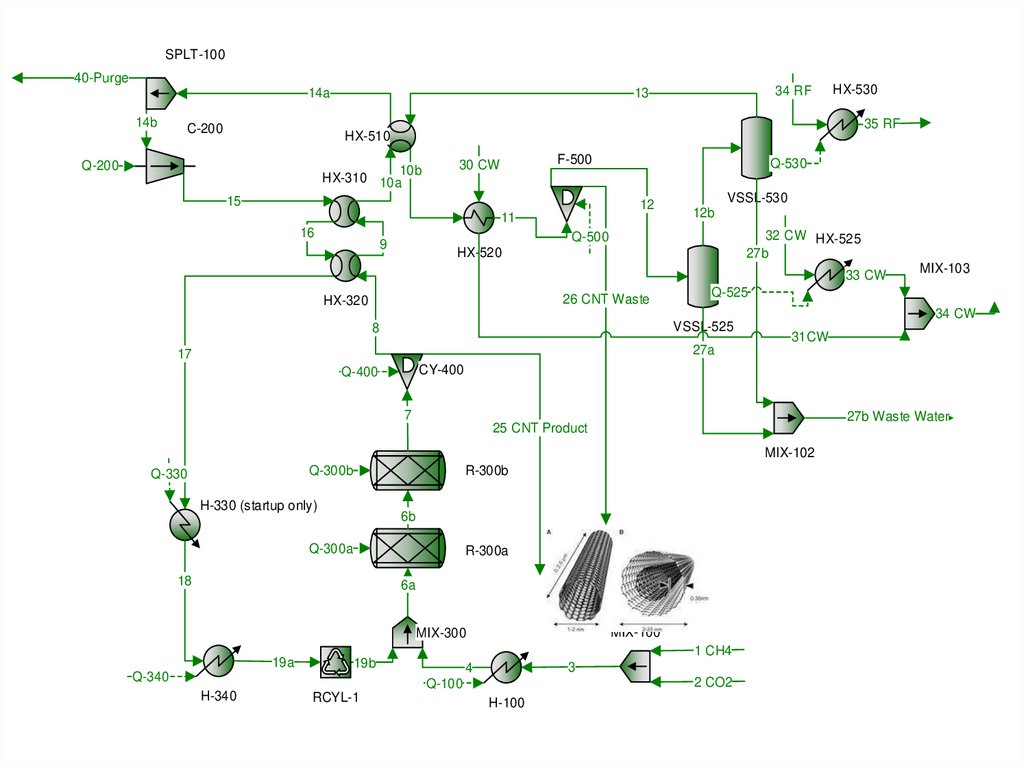
26.
SPLT-10040-Purge
14a
14b
C-200
34 RF
13
HX-530
35 RF
HX-510
Q-200
10b
HX-310 10a
F-500
30 CW
15
Q-530
12
11
16
VSSL-530
12b
32 CW HX-525
27b
Q-500
9
HX-520
33 CW
26 CNT Waste
HX-320
MIX-103
Q-525
34 CW
VSSL-525
8
31CW
27a
17
CY-400
Q-400
7
27b Waste Water
25 CNT Product
MIX-102
Q-300b
Q-330
R-300b
H-330 (startup only)
6b
Q-300a
R-300a
18
6a
MIX-100
MIX-300
19a
1 CH4
19b
Q-340
3
4
2 CO2
Q-100
H-340
RCYL-1
H-100
27. Importance of Process Design
• In Preliminary Process Design– 98% Operating Costs Committed
– 80% Capital Costs Committed
• Less than 10% $ Spent
• Design is Very Important
• But why is this so?
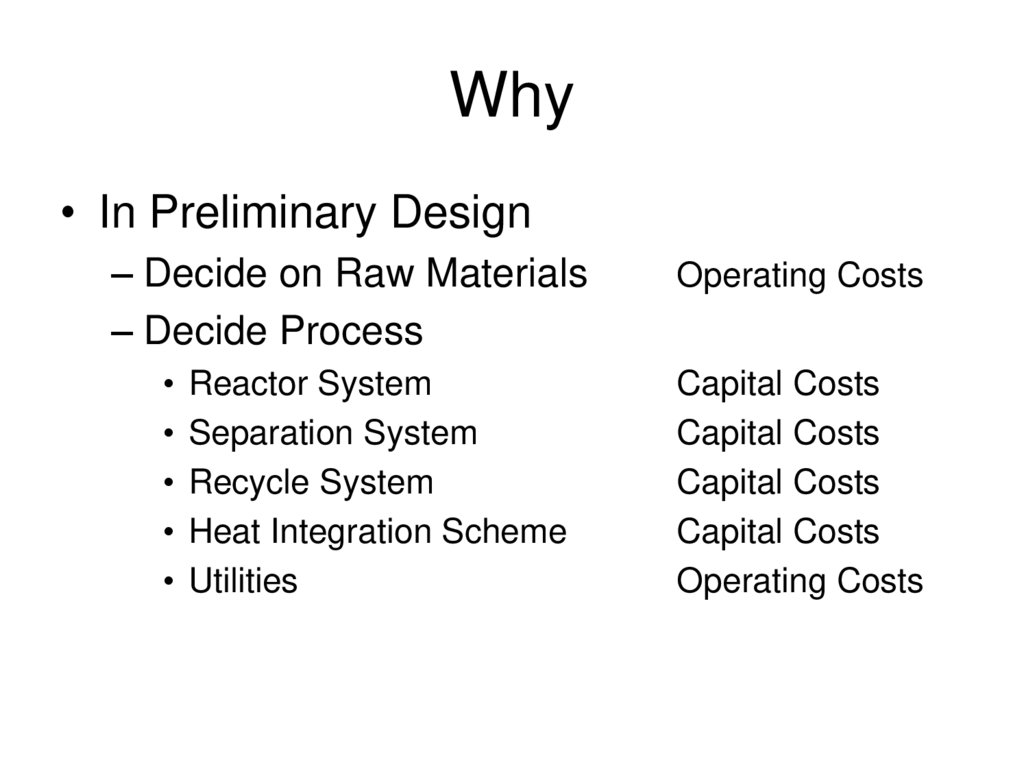
28. Why
• In Preliminary Design– Decide on Raw Materials
– Decide Process
Operating Costs
• Reactor System
• Separation System
• Recycle System
• Heat Integration Scheme
• Utilities
Capital Costs
Capital Costs
Capital Costs
Capital Costs
Operating Costs









 chemistry
chemistry industry
industry

