Similar presentations:
The Constitution
1. The Constitution
Paula Childs2. Vocabulary:
• Opinion• Legislation
• Living Document
• Repealed
• Overturned
3. Preamble
• The introduction to the Constitution is calledthe Preamble.
• The Preamble begins with the phrase “We the
people…”
• What does that mean?
• Why was the Constitution written?
• Who does the Constitution regulate?
4. Amendment
• Is a change in the Constitution• There have been 27 amendments to the
Constitution.
• The first 10 amendments are called the Bill of
Rights.
5. The Branches of Government
• There are three branches of government:1. The legislative - which makes the laws
2. The executive - which enforces the laws or
make sure the laws are carried out
3. The judicial - which judges the laws or
explains the laws and makes sure they are fair
6. Legislative Branch
• The legislative branch is called Congress and ismade up of two Houses (parts):
• The House of Representatives
• Senate.
7. The House of Representatives
• States with the largest populations have themost representatives in the House.
• House members must be at least 25 years old
or older to serve.
• House members are elected to a two year
term.
• There are 435 members in the House of
Representatives.
8. The Senate
• The Senate is the other part of the Congress• There are two senators for each state, which
means of course there are 100 Senators.
• Senators must be at least 30 years old.
• Senators are elected to a six year term.
9. The Executive Branch
• The executive branch is headed by thepresident.
• The president is the commander-in-chief of
the armed forces.
10. The President
• The president is elected to a four year term.• The president can only serve two terms.
• The president must be a citizen by birth
• The president must be at least 35 years old.
11. The Judicial Branch
• The Judicial Branch of the federal governmentis headed by the Supreme Court.
• Supreme Court justices are nominated by the
president and approved by the Senate.
• There are 9 Supreme Court justices, who are
appointed for life.
• Judicial Review
12. Whos Your Moma…
13.
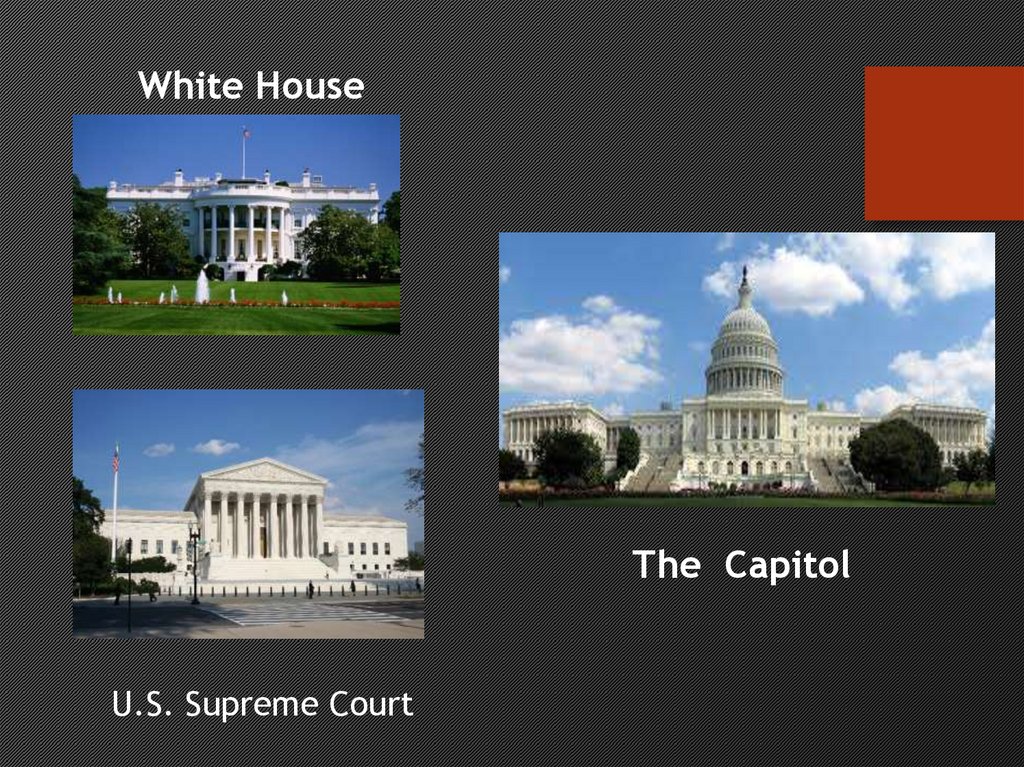
White HouseThe Capitol
U.S. Supreme Court
14. Who’s Your Moma
• Act?• Brown v. Board of Education?
• Executive Order 9981?
15. Checks and Balances
• The framers of the Constitution established asystem of checks and balances to prevent any
branch government from getting too powerful.
• Example: Congress has the right to pass bills
into law, but the president can veto them,
which means the bill does not become a law.
16. Federalism
• The power of government is also split betweenthe states and the federal government.
• This is called Federalism.
• If the Constitution does not have a law, the
states can do what they want.
• State law cannot contradict federal law, or a
Supreme Court Opinion. They must be follow
by the letter.
17. Dual Sovereignty
• Dual Sovereignty means that whatever thefederal government does not make a law
about, the states can act however they
choose.
• That is why there is different state laws
regarding the age of drinking alcohol, driving,
the death penalty, and many more.















 law
law








