Similar presentations:
Surgical instruments & tools
1.
Surgical Instruments & ToolsMade by Mi k h ay l ov a M. V .
Gro u p 2 6 MC/ C
T h e t e ac h er: S t o y an ova L. V .
2.
DefinitionSURGICAL INSTRUMENTS ARE
TOOLS OR DEVICES THAT
PERFORM SUCH FUNCTIONS
AS CUTTING, DISSECTING,
GRASPING, HOLDING,
RETRACTING, OR SUTURING.
3.
Properties of surgical instrumentsprecisely manufactured tools;
must be resisted physical and chemical effects,
body fluids, secretions, cleaning agents and
sterilization;
4.
This instruments are generally made of:Stainless steel;
Other metals (titanium, chromium, vanadium, and
molybdenum).
5.
ClassificationBasic categories of surgical instruments include specialized implements for
the following functions:
cutting, grinding, and dissecting
clamping and occluding
grasping and holding
retracting and exposing
suturing and stapling
others (dilating or enlarging, viewing, suction)
6.
Сutting, grinding, and dissecting instrumentshave sharp edges or tips;
used to dissect, incise, separate, or excise tissue.
7.
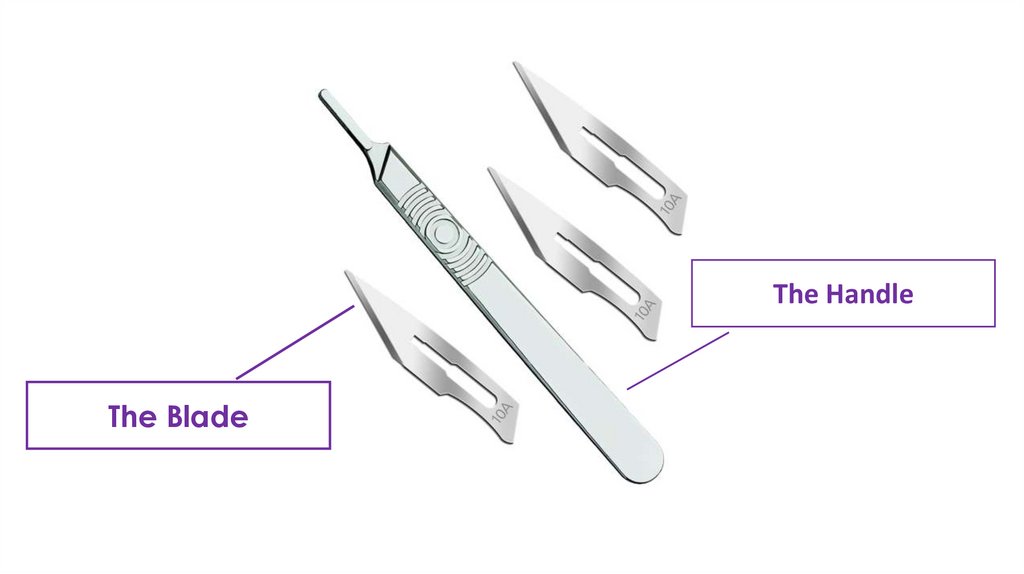
Scalpel (surgical blade)used for cutting skin and tissue
handle and blade (fixed (conventional scalpel) or
separated)
manufacturers for these medical instruments include
Ansell, Aspen Surgical, Dynarex, McKesson, Miltex,
Robbins Instruments, and Swann-Morton.
8.
The HandleThe Blade
9.
Types of blades10
11
12
15
20
10.
ScissorsIris scissors are a type of scissors with short blades that was originally developed
for ophthalmic surgery.
Metzenbaum scissors designed for cutting delicate tissue and blunt dissection.
Mayo scissors are a type of surgical scissor, often used in the cutting of fascia.
Tenotomy Scissors are used for delicate dissection and cutting, commonly in
ophthalmologic, neurological, and plastic surgery procedures
Bandage/Dressing Scissors are angled tip scissors, with a blunt tip on the
bottom blade, which helps in cutting bandages without gouging the skin.
11.
IrisMetzenbaum
Mayo
Tenotomy
Bandage
12.
Bone cutter&sawA bone cutter and saw is a surgical instrument used to
cut or remove bones.
13.
RaspsSurgical rasps are used in operations in the specialised
field of final prosthetics.
14.
Clamping & Occludingused to compress blood vessels or hollow organs for
hemostasis or to prevent spillage of contents.
15.
Kelly Hemostatis used to clamp larger vessels and tissue;
available in short and long sizes;
curved or straight.
16.
Mosquito HemostatThe jaw contains transverse striations (good for the occlusion of
small vessels)
17.
Grasping and holdingused to grasp and hold tissue or blood vessels that may be in the
way during a surgical procedure.
18.
ForcepsTweezer style
Scissors style
19.
Tweezer Stylepick-ups;
thumb forceps;
tissue forceps;
dressing forceps.
20.
Thumb forcepsare used to grasp tough tissue (fascia, breast).
21.
Adson pick upsare either smooth: used to grasp delicate tissue;
with teeth: used to grasp the skin.
22.
Mayo-Hegar needle holdersare used to hold needles.
23.
Scissor Style24.
Babcockis used to grasp delicate tissue (intestine, fallopian tube, ovary).
available in short and long sizes.
25.
Kocher (Rochester-Ochsner)is used to grasp heavy tissue.
26.
Retracting and Exposingused to hold back or retract organs or tissue to gain
exposure to the operative site.
27.
Deaver retractoris used to retract deep abdominal or chest incisions.
28.
Richardson retractoris used to retract deep abdominal or chest incisions.
29.
An Army-Navy retractoris used to retract shallow or superficial incisions.
30.
Skin Hooksused for holding back the edges of skin during intranasal and
pharyngeal procedures.
31.
Suturing & StaplingNeedles
are typically made of steel;
come in different sizes;
have sharp or blunt tips;
straight or curved.
Sutures
used to hold together the edges of a wound or surgical incision.
32.
Sutureabsorbable;
non Absorbable.
33.
ViewingSurgeons can examine body cavities, hallow organs, or structures
with viewing instruments
34.
SpeculumsNasal
Vaginal
Rectum
35.
Endoscopesrigid;
flexible.
36.
TypesGastrointestinal tract esophagus, stomach, and duodenum
(esophagogastroduodenoscopy), small intestine (enteroscopy), large
intestine/colon (colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy), bile duct, rectum (rectoscopy),
and anus (anoscopy).
Respiratory tract: Nose (rhinoscopy), lower respiratory tract (bronchoscopy).
Ear: Otoscopy
Urinary tract: Cystoscopy
Female reproductive tract (gynoscopy): Cervix (colposcopy), uterus
(hysteroscopy), fallopian tubes (falloposcopy).
Abdominal or pelvic cavity (laparoscopy), interior of a joint (arthroscopy),
organs of the chest (thoracoscopy and mediastinoscopy).
37.
SuctionsIn surgery suction can be used to remove blood from the area
being operated on to allow surgeons to view and work on the area
38.
Dilating or enlargingused to induce dilation, that is, to expand an opening or passage such as
the cervix, urethra, esophagus.





































 medicine
medicine








