Similar presentations:
Animal locomotion
1.
ANIMAL LOCOMOTION2.
Lesson objectivesTo compare organs of locomotion in
invertebrates and vertebrates.
3.
LocomotionIt is movement during which organisms
change its location.
4.
There mechanisms of locomotion inanimals:
Amoeboid
2. Ciliary and flagellar
3. Mascular
1.
5.
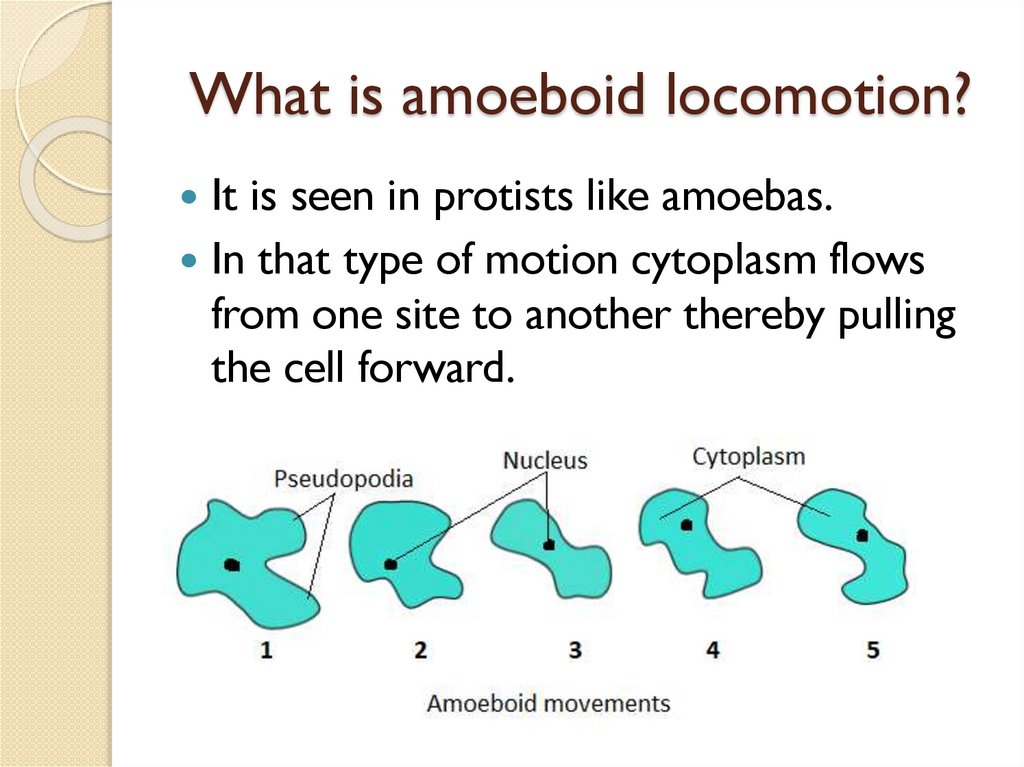
What is amoeboid locomotion?It is seen in protists like amoebas.
In that type of motion cytoplasm flows
from one site to another thereby pulling
the cell forward.
6.
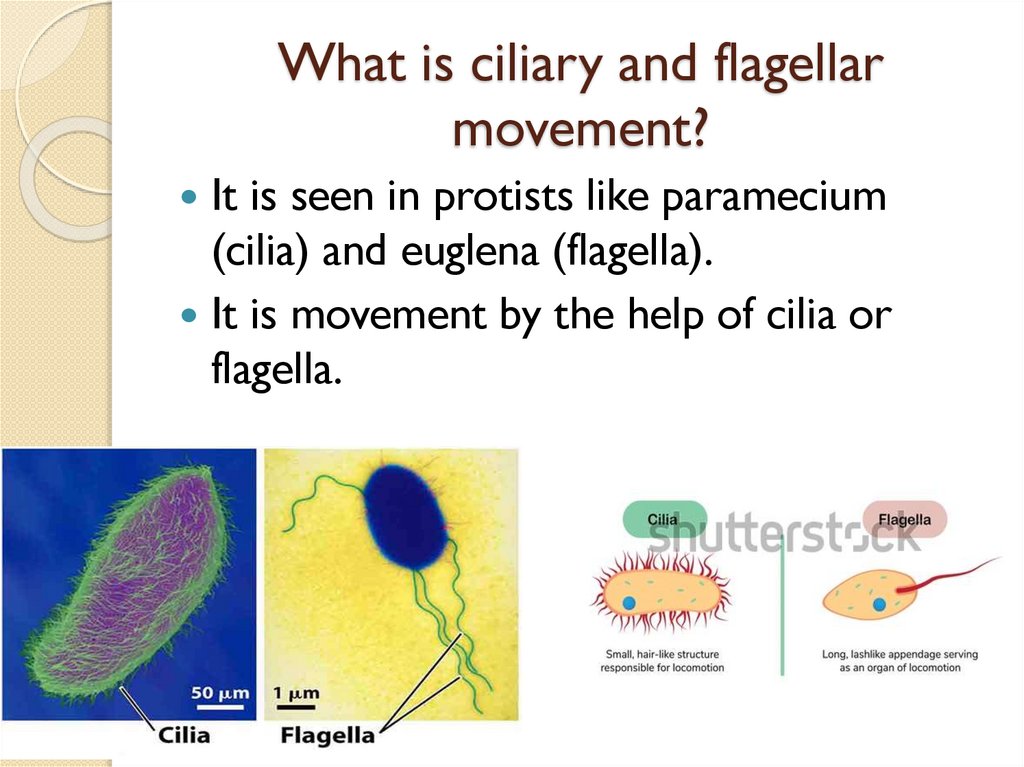
What is ciliary and flagellarmovement?
It is seen in protists like paramecium
(cilia) and euglena (flagella).
It is movement by the help of cilia or
flagella.
7.
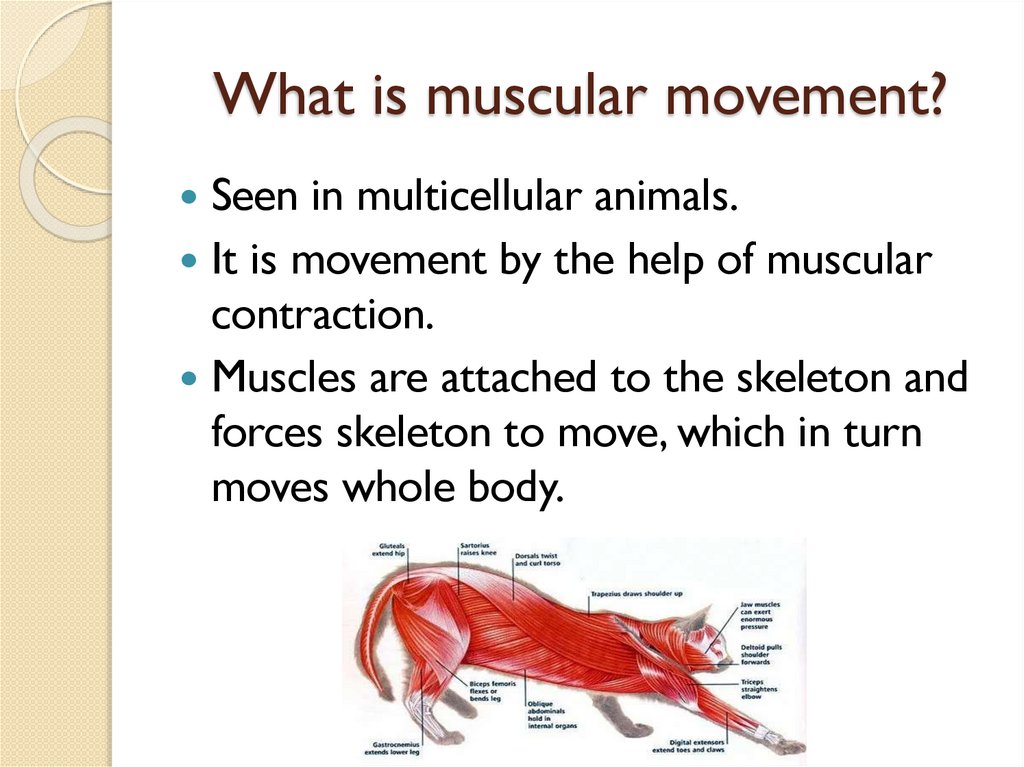
What is muscular movement?Seen in multicellular animals.
It is movement by the help of muscular
contraction.
Muscles are attached to the skeleton and
forces skeleton to move, which in turn
moves whole body.
8.
Types of skeleton:Hydrostatic skeleton
2. Exoskeleton
3. Endoskeleton
1.
9.
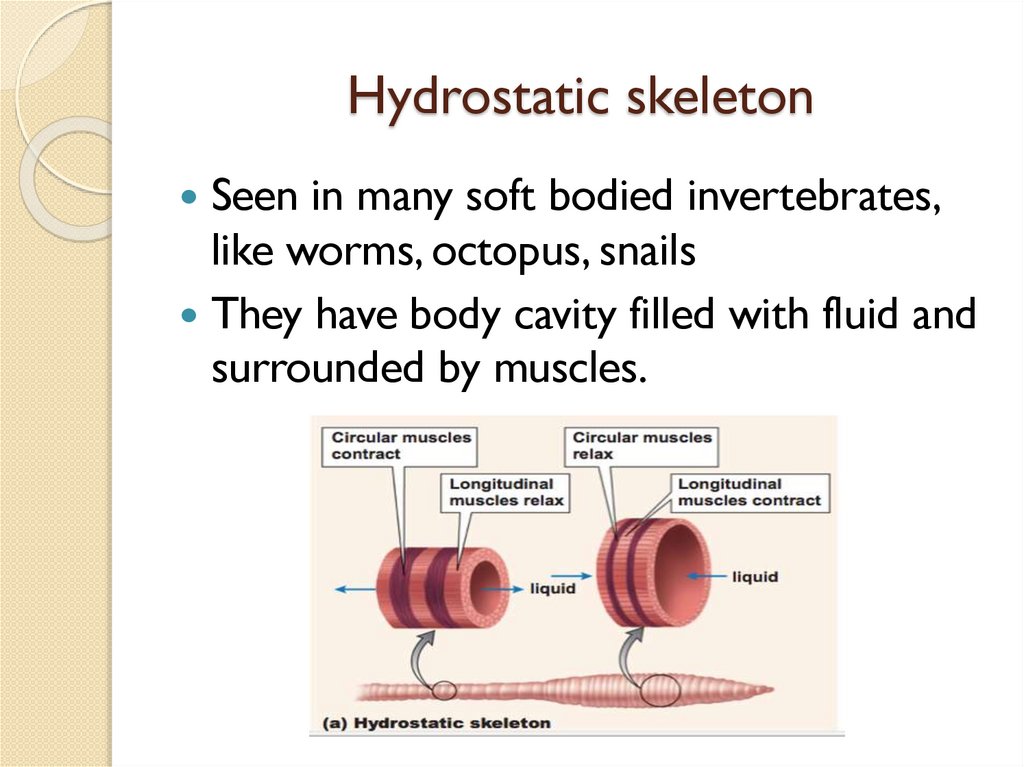
Hydrostatic skeletonSeen in many soft bodied invertebrates,
like worms, octopus, snails
They have body cavity filled with fluid and
surrounded by muscles.
10.
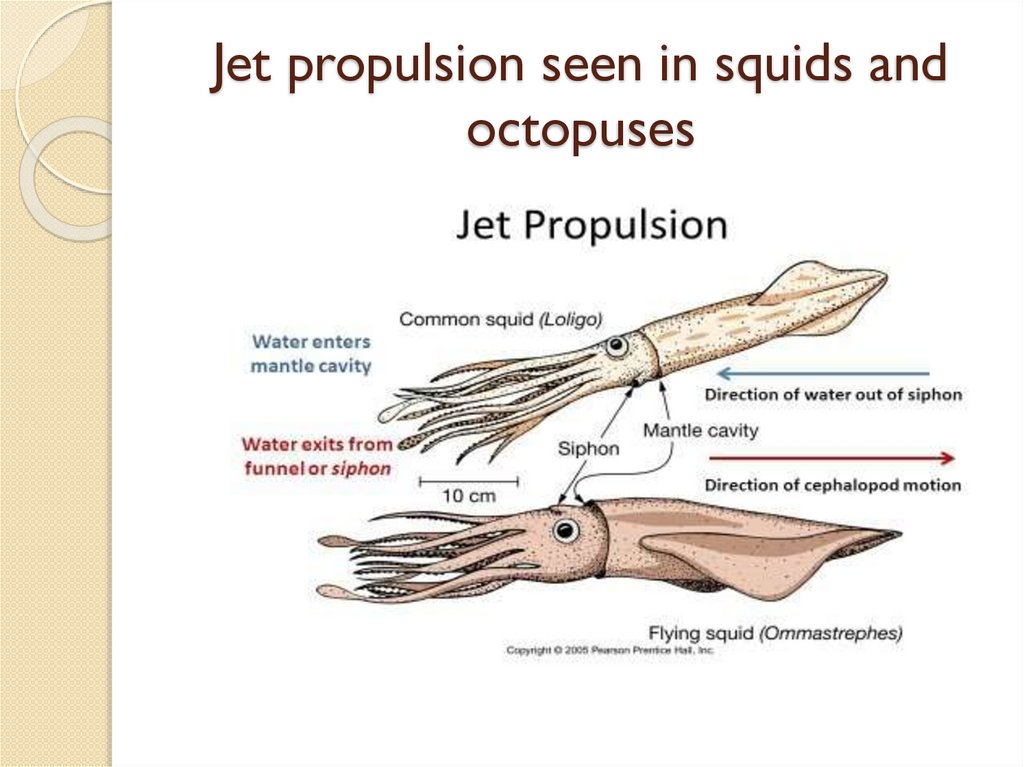
Jet propulsion seen in squids andoctopuses
11.
ExoskeletonSeen in arthropods
(crustaceans,
spiders and
insects).
It is hard, nonliving
and covers outside
surface of the body.
Muscles are
attached to
internal surface of
exoskeleton
12.
Crustaceans have 4-5 pairs of legsSpiders have 4 pairs of legs
Insects have 3 pairs of legs (+1 or 2
Pairs of wings)
13.
EndoskeletonSeen in vertebrates
It is living, made up of bones, found inside
of body.
Muscles are attached on outer surface of
endoskeleton.
14.
Organs of movement in vertebrates:Fins in fishes to swim
Wings in birds to fly
All terrestrial animals have 2 or 4 legs to
walk.
15.
Let’s do activity on p8516.
HomeworkRead p.84-85
Literacy on p. 85
New words











 biology
biology