Similar presentations:
Trends in periodic table
1.
Trends in periodic table2.
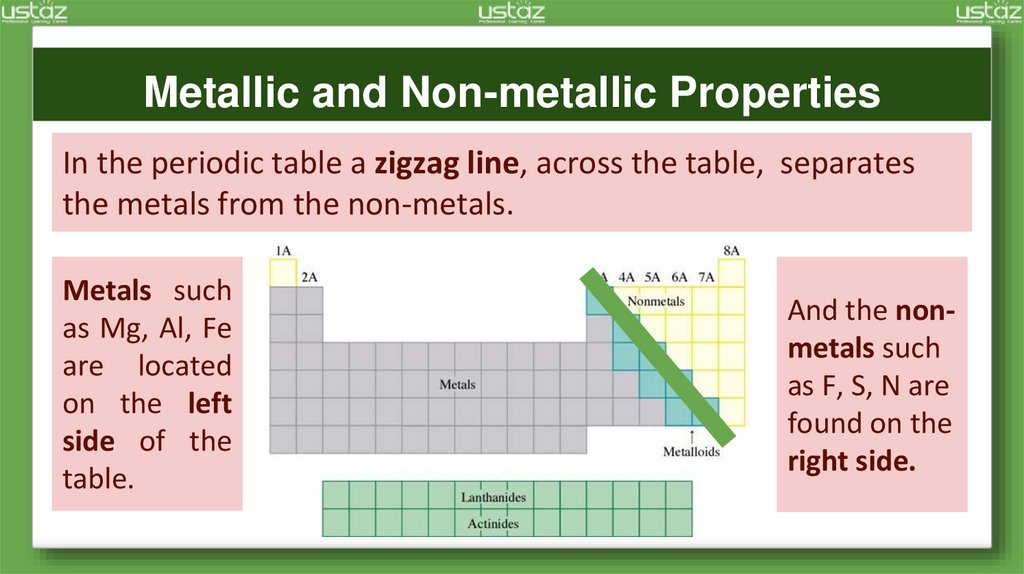
Metallic and Non-metallic PropertiesIn the periodic table a zigzag line, across the table, separates
the metals from the non-metals.
Metals such
as Mg, Al, Fe
are located
on the left
side of the
table.
And the nonmetals such
as F, S, N are
found on the
right side.
3.
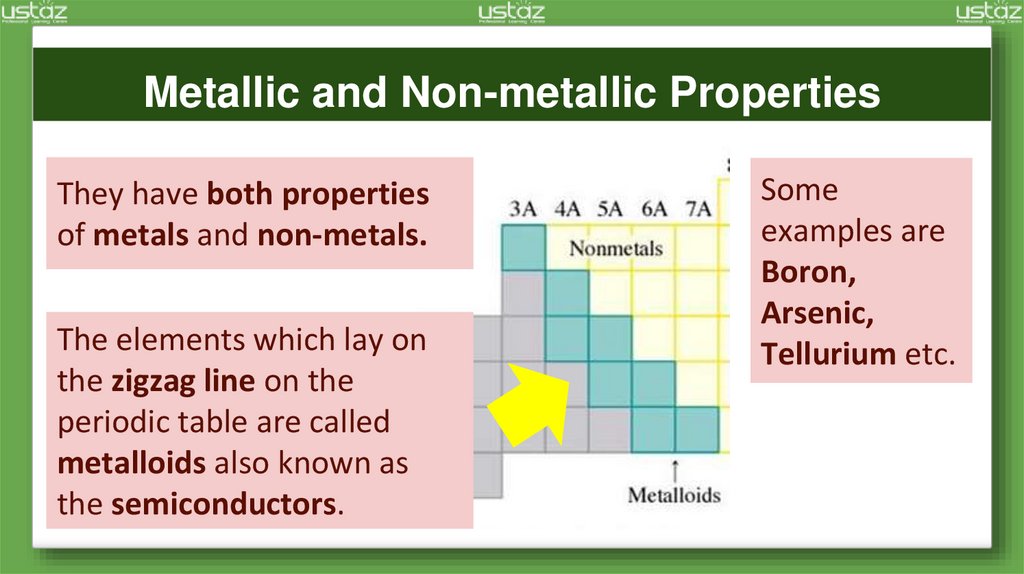
Metallic and Non-metallic PropertiesThey have both properties
of metals and non-metals.
The elements which lay on
the zigzag line on the
periodic table are called
metalloids also known as
the semiconductors.
Some
examples are
Boron,
Arsenic,
Tellurium etc.
4.
Metallic and Non-metallic CharacterFluorine is
most
active
nonmetals
Francium
is most
active
metals
5.
Metallic and Non-metallic Character6.
Metallic and Non-metallic Character7.
ElectronegativityThe ability of an atom in a
MOLECULE to attract shared
electrons to itself.
Electronegativity does not
have any unit
8.
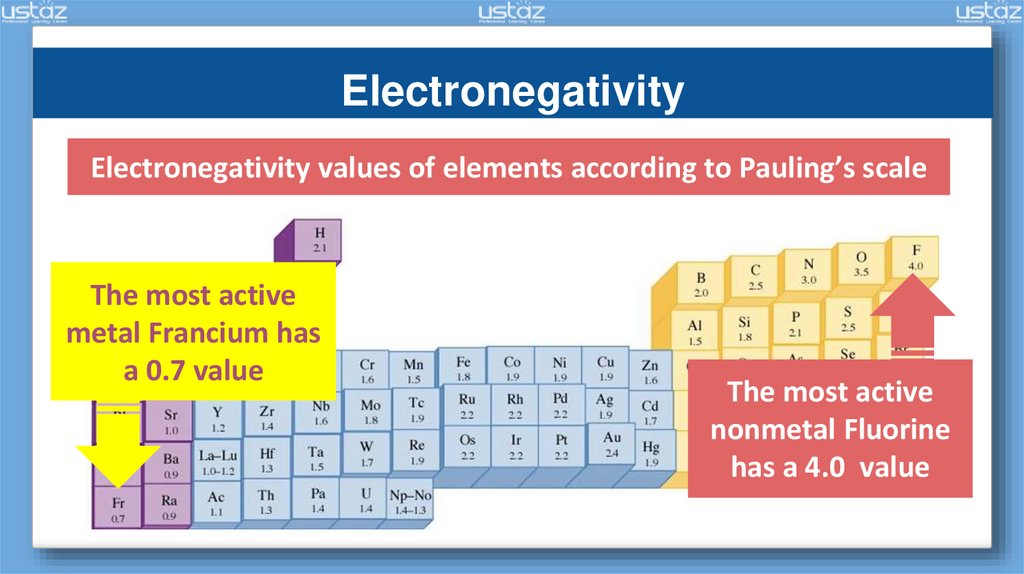
ElectronegativityElectronegativity values of elements according to Pauling’s scale
The most active
metal Francium has
a 0.7 value
The most active
nonmetal Fluorine
has a 4.0 value
9.
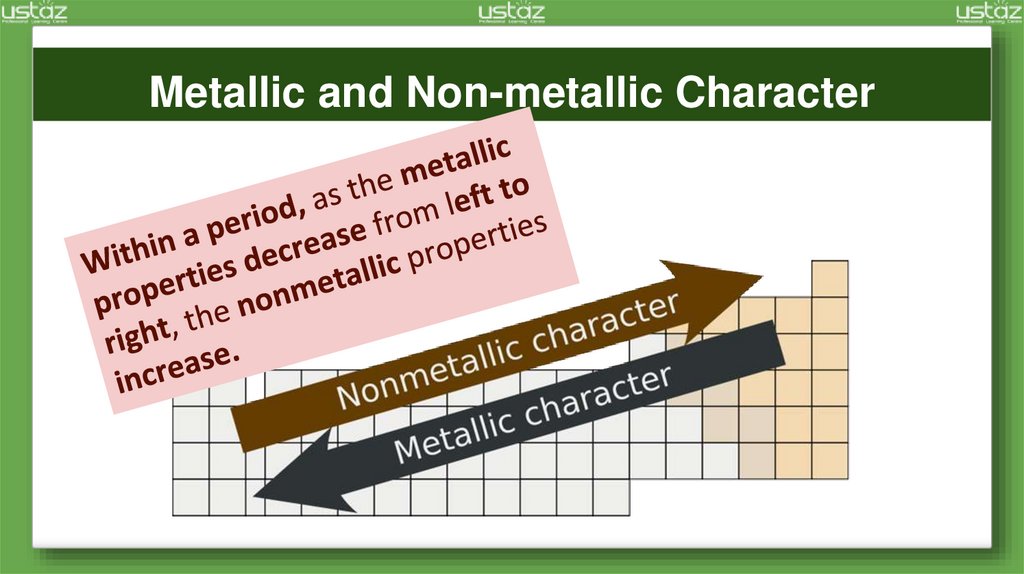
ElectronegativityFrom left to right across a period
of elements, electronegativity
increases.
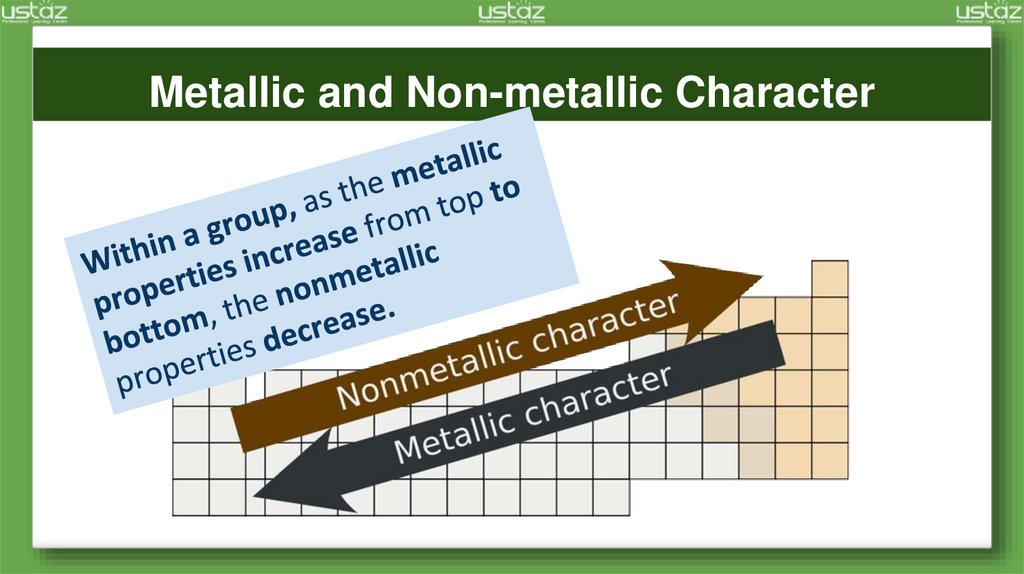
From top
to bottom
down a
group,
electrone
gativity
decreases
.
10.
Atomic radiusAtomic radius is the distance
from the nucleus to the
outermost stable electron
11.
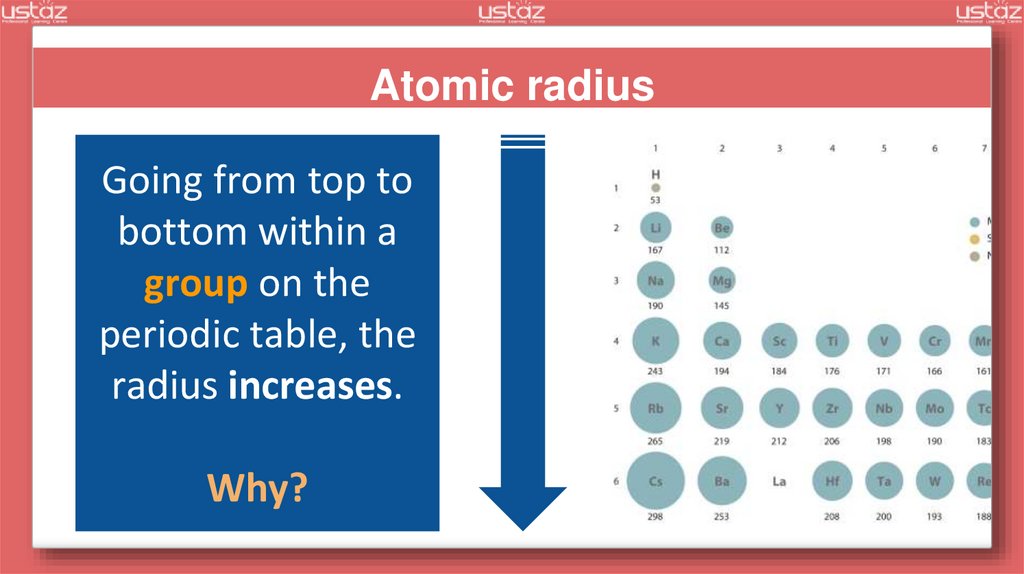
Atomic radiusGoing from top to
bottom within a
group on the
periodic table, the
radius increases.
Why?
12.
Atomic radiusAs you move down
the periodic table,
elements have more
protons and forms
an electron shell, so
atoms become
larger.
13.
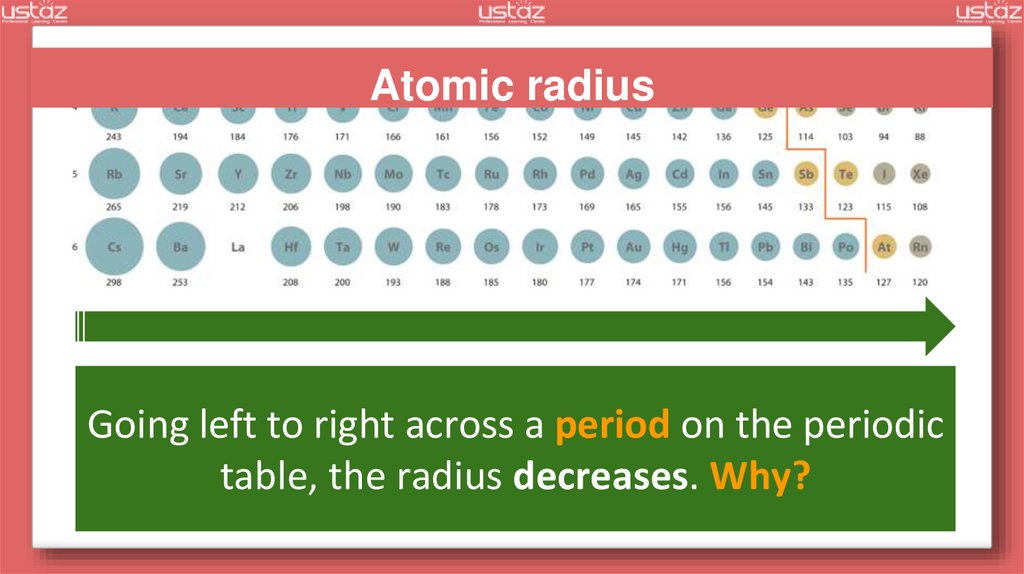
Atomic radiusGoing left to right across a period on the periodic
table, the radius decreases. Why?
14.
Atomic radiusAs you move across a row of the periodic table, there are more
protons and electrons. Electrons are held more closely to the
nucleus, so the overall size of the atom decreases.
15.
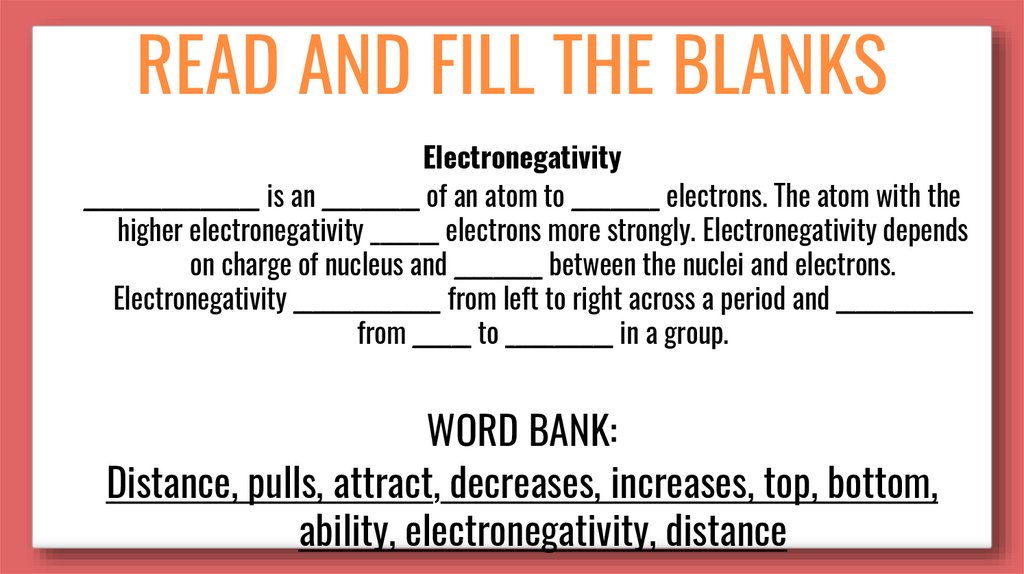
READ AND FILL THE BLANKSElectronegativity
__________________ is an __________ of an atom to _________ electrons. The atom with the
higher electronegativity _______ electrons more strongly. Electronegativity depends
on charge of nucleus and _________ between the nuclei and electrons.
Electronegativity _______________ from left to right across a period and ______________
from ______ to ___________ in a group.
WORD BANK:
Distance, pulls, attract, decreases, increases, top, bottom,
ability, electronegativity, distance
16.
Metallic and Nonmetallic PropertiesAbout 80% of the elements in the periodic table are metals. Only the eleven elements,
H, C, N, O, P, S, Se, F, Cl, Br, I and __________are ________________. However B, Si, Ge,
As, Sb, Te, Po and At are _______________. Metallic ________________ increase from top
to bottom and from right to left in a periodic table. Nonmetallic properties _________
from bottom to top and from left to right in a periodic table.
WORD BANK:
Metalloids, nonmetals, noble gases, properties, increase
17.
Atomic Radius___________________ is the distance between the nucleus and the ________________. It affects
the melting point, boiling point, _______________ of elements and the ability of losing
or gaining electrons by atoms. Two factors affect the atomic radius of elements:
number of energy levels and nuclear charge. Atomic radius increases from top to
________ within a group, and it decreases from _____ to right across a period in the
periodic table.
WORD BANK:
Density, outer shell, atomic radius , bottom, left









 chemistry
chemistry








