Similar presentations:
The structure of the atom
1. The structure of the atom
2. The main provisions of the atomic and molecular doctrine
Substances are made up ofmolecules, and molecules are
made up of atoms.
A molecule is the smallest particle
of a substance that retains the
composition and properties of a
given substance, physically
indivisible.
Atom - the smallest particle of
matter, chemically
indivisible.With physical
phenomena, the composition of
substances does not change, with
chemical phenomena it changes,
from some substances others are
obtained.
Molecules and atoms are in
constant, chaotic motion.
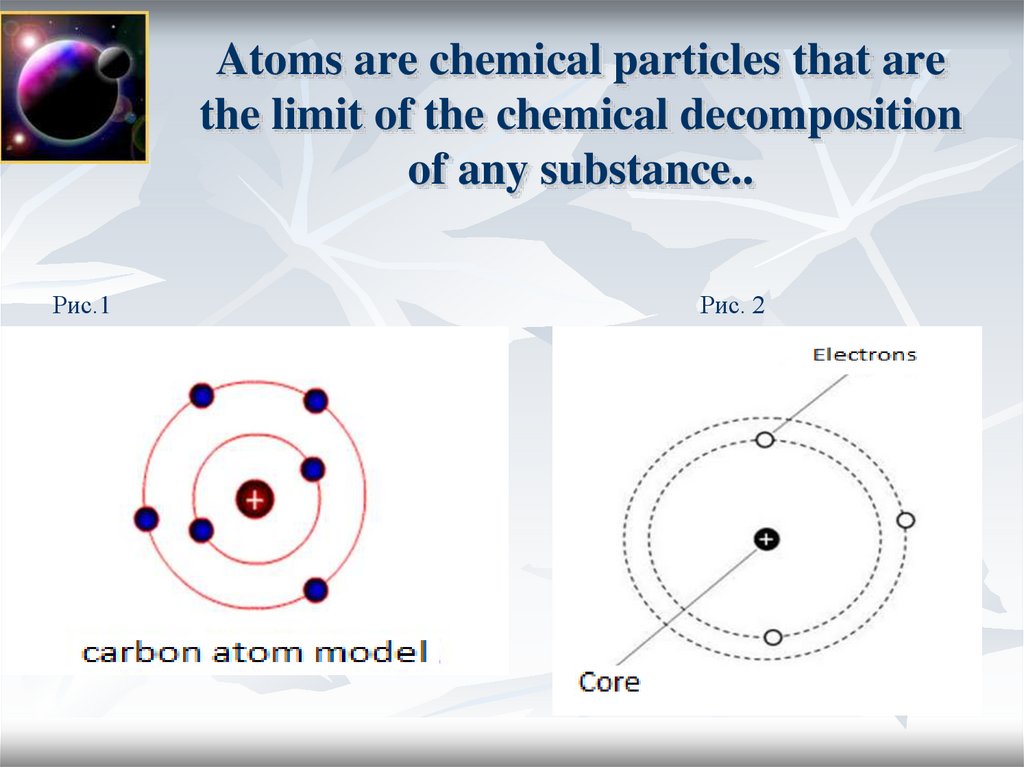
3. Atoms are chemical particles that are the limit of the chemical decomposition of any substance..
Рис.1Рис. 2
4.
5. The structure of the atom
АтомЯдро
состоит из нуклонов
Протон(p+)
p+ = Z
Нейтрон(n0)
n0 = A – Z
Электронная
оболочка
Состоит из электронов
Электрон(e-)
е- = Z
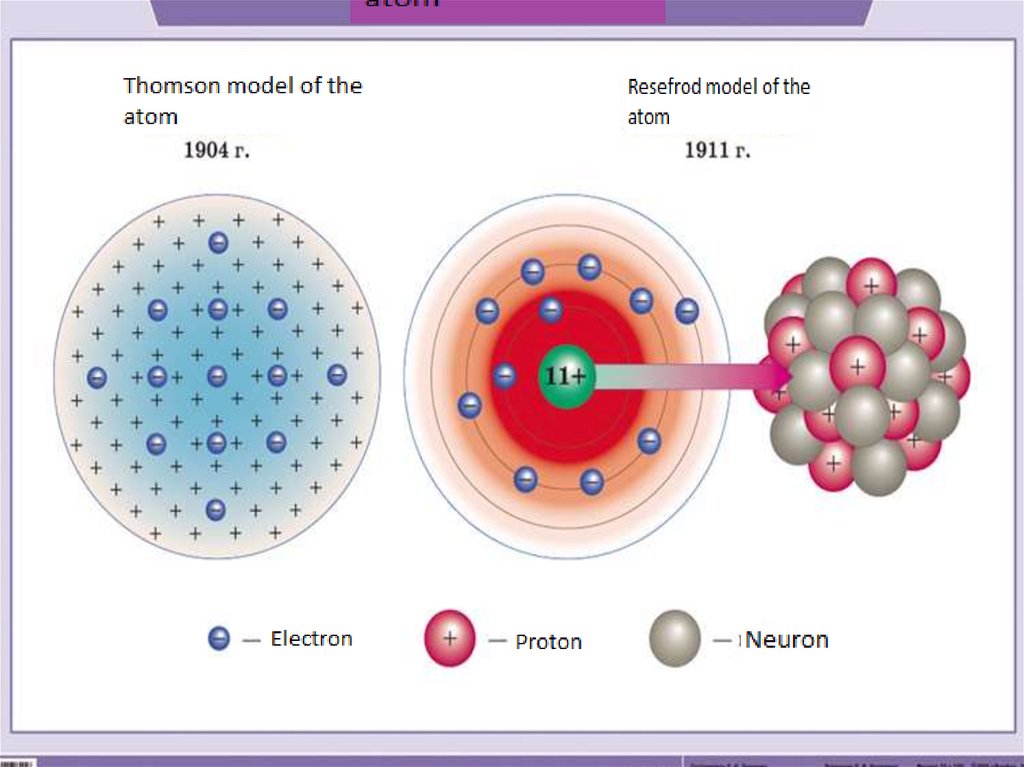
6. Planetary model of the atom
An atom is a microparticle that has the shape of a sphere.An atom is a complex system consisting of a nucleus and
electrons.
The nucleus is located in the center of the atom and has a very
small size, but almost all the mass of the atom is concentrated
in the nucleus.
The nucleus has a positive charge, the value of which is
determined by the number of protons in it.
Electrons move around the nucleus, have a negligible mass
and size, and have a negative charge.
An atom is a neutral particle, so the number of protons and
electrons in an atom is the same.
The serial number of the element shows: the position of the
element in the periodic system, the number of protons and
electrons.
7.
Four quantum numbers are used to describe the position ofelectrons in an atom:
1)
2)
3)
4)
1) The main quantum number n determines the energy level
to which the given orbit corresponds and its distance from
the nucleus.
2) Orbital, secondary or azimuthal quantum number l
characterizes the moment of momentum of the electron
relative to the center of the orbit.
3) The magnetic quantum number m determines the position
of the plane of the electron orbit in space.
4) The spin quantum number s determines the direction of
rotation of the electron, it can take only two values: 1/2 and 1/2.
8.
The structure of the electron shell of the atomAn atomic orbital is the state of an electron in an atom.
Each orbital corresponds to an electron cloud.
The orbitals of real atoms in the ground (unexcited) state are
of four types: s, p, d, and f.
An electron cloud is a part of space in which an electron
can be found with a probability of 90 (or more) percent.
9.
The order in which electrons fill the orbitals of an atom isdetermined by three laws of nature:
1. The principle of least energy - electrons fill the orbitals
in order of increasing energy of the orbitals.
2. Pauli's principle - there cannot be more than two electrons
in one orbital.
3. Hund's rule - within the sublevel, electrons first fill free
orbitals (one at a time), and only after that they form electron
pairs.
10.
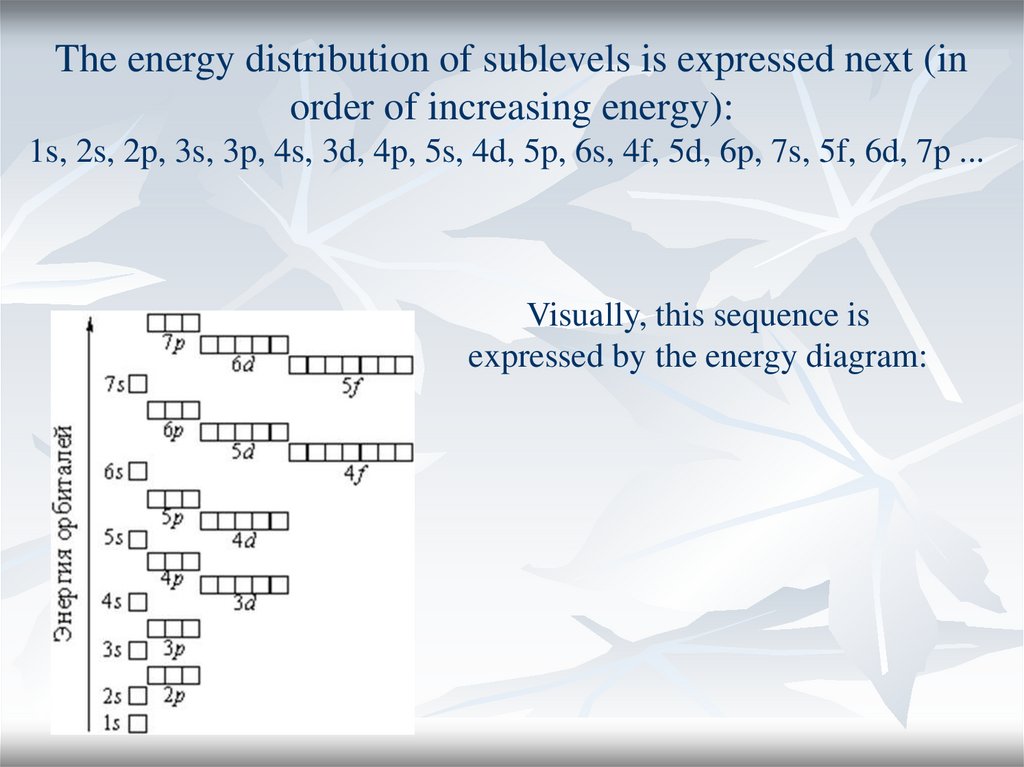
The energy distribution of sublevels is expressed next (inorder of increasing energy):
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f, 6d, 7p ...
Visually, this sequence is
expressed by the energy diagram:
11. 1. the substance consists of a huge number of particles (atoms and molecules), between which there are gaps; 2. a molecule of a
1. THE SUBSTANCE CONSISTS OF A HUGE NUMBER OF PARTICLES(ATOMS AND MOLECULES), BETWEEN WHICH THERE ARE GAPS;
2. A MOLECULE OF A SUBSTANCE CONSISTS OF ATOMS OF ONE OR
MORE CHEMICAL ELEMENTS;
3. THE ATOMS OF ONE CHEMICAL ELEMENT ARE THE SAME, THE
MOLECULES OF ONE SUBSTANCE ARE THE SAME;
4. WITH AN INCREASE IN BODY TEMPERATURE, THE GAPS BETWEEN
THE PARTICLES INCREASE;
5.MOLECULES AND ATOMS ARE VERY SMALL, THEY CAN BE
PHOTOGRAPHED WITH AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE;
12. 1. Substances consist of atoms, ions, molecules and crystals; 2. atoms have a complex structure, a certain type of atoms is
conclusion1. SUBSTANCES CONSIST OF ATOMS, IONS, MOLECULES AND
CRYSTALS;
2. ATOMS HAVE A COMPLEX STRUCTURE, A CERTAIN TYPE OF ATOMS
IS CALLED CHEMICAL ELEMENTS;
3. CHEMICAL ELEMENTS DIFFER IN PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL
PROPERTIES;
4. ATOMS, INTERACTING WITH EACH OTHER, FORM COMPOUNDS SIMPLE AND COMPLEX SUBSTANCES;
5. PARTICLES OF A SUBSTANCE ARE IN CONTINUOUS CHAOTIC
MOTION AND, DEPENDING ON THE ENERGY, CAN GIVE THE
SUBSTANCE ONE OR ANOTHER STATE OF AGGREGATION;
6. SUBSTANCES DIFFER FROM EACH OTHER IN PHYSICAL AND
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES.









 chemistry
chemistry








