Similar presentations:
Writing a paragraph
1.
Writing aparagraph
2.
02What is a
paragraph?
a group of sentences that supports one
central, unified idea.
3.
03Topic Sentence
First support sentence
Explanation or expansion
Examples, illustration or supporting
evidence
Second support sentence
Third support sentence
Concluding sentence
Parts of a
paragraph
4.
04Topic
Sentence
1. [Usually] the very first sentence
2. States both the topic and the
controlling idea
3. Neither too general nor too specific
4. One paragraph = one idea
5. Helps the reader to predict the content
of the paragraph
5.
053 support sentences
Expand on the
topic sentence
Facts, details,
and examples
Presented in a
systematic way
6.
06Concluding sentence
Re-states the idea in the topic sentence using
different words (make use of synonyms)
7.
How do I makemy ideas flow in a
paragraph?
• Use signal words to support your logic
To sequence your ideas:
first(ly), second(ly), third(ly), next, then, after
this, last(ly), finally, accordingly, meanwhile
To introduce an example or illustration:
Transition signals
are ALWAYS
SEPARATED by
commas
07
for example, such as, for instance, to
demonstrate, namely, in particular, specifically
To signal a conclusion:
thus, therefore, ultimately, in conclusion/to
conclude, in brief, indeed, in short, in summary
8.
Checklist for writing a paragraph1. Is the topic sentence clear and relevant?
2. Do the facts, details, and examples
explain/develop
the topic sentence?
Step 1 – Write the
topic sentence
3. Is there enough support?
Step 2 – Brainstorm
4. Is the material presented in a systematic way?
Step 3 – Plan
5. Does one sentence lead smoothly to the next?
Step 4 – Write the first draft
Step 5 – Revise and edit
Step 6 – Check grammar, spelling, and punctuation
Step 7 – Write the final draft
Step 8 – Proofread your paragraph
08
9.
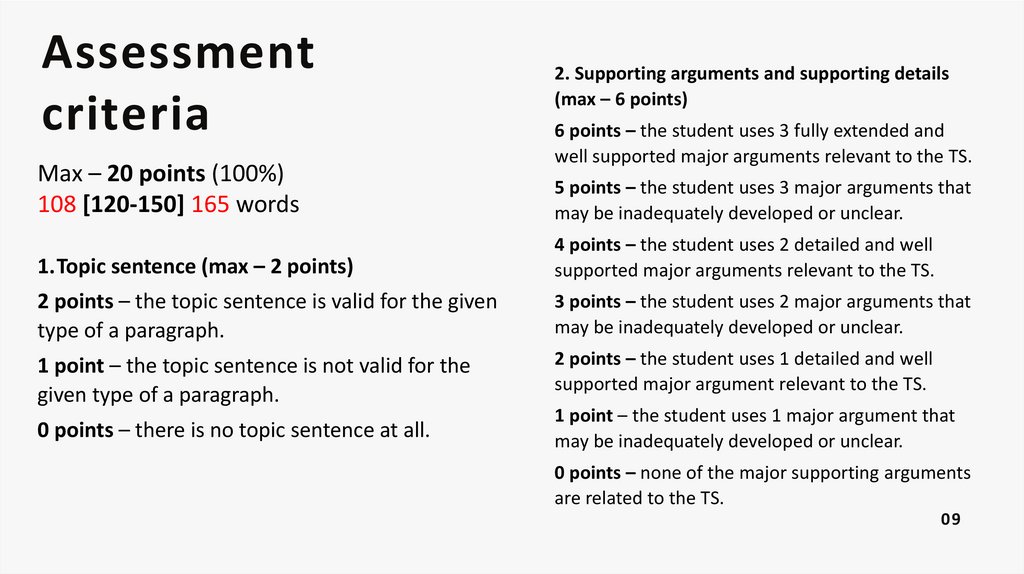
Assessmentcriteria
Max – 20 points (100%)
108 [120-150] 165 words
2. Supporting arguments and supporting details
(max – 6 points)
6 points – the student uses 3 fully extended and
well supported major arguments relevant to the TS.
5 points – the student uses 3 major arguments that
may be inadequately developed or unclear.
1.Topic sentence (max – 2 points)
4 points – the student uses 2 detailed and well
supported major arguments relevant to the TS.
2 points – the topic sentence is valid for the given
type of a paragraph.
3 points – the student uses 2 major arguments that
may be inadequately developed or unclear.
1 point – the topic sentence is not valid for the
given type of a paragraph.
2 points – the student uses 1 detailed and well
supported major argument relevant to the TS.
0 points – there is no topic sentence at all.
1 point – the student uses 1 major argument that
may be inadequately developed or unclear.
0 points – none of the major supporting arguments
are related to the TS.
09
10.
Assessmentcriteria
3. Transitions (max – 2 points)
2 points – the student uses transitions
appropriately.
1 point – 1-2 transitions are used
inappropriately.
0 points – the student does not use
transitions at all.
4. Concluding sentence (max – 2
points)
2 points – the student summarises
the major supporting arguments of
the paragraph.
1 point – the concluding sentence
does not summarise the content of
the paragraph adequately.
0 points – there is no concluding
sentence at all.
10
11.
Assessmentcriteria
5. Grammar (max – 3 points)
3 points – the student uses a variety of complex
grammar structures but may make 1 minor
grammar mistake.
2 points – the student uses a mix of simple and
complex grammar structures but may make 2
grammar mistakes.
1 point – the student uses elementary grammar
structures and may make 3 grammar mistakes.
6. Vocabulary (max – 3 points)
3 points – the student uses a wide range of
vocabulary including 4-5 active vocabulary items
and makes no lexical mistakes.
2 points – the student uses basic vocabulary, 2-3
active vocabulary items and makes 1-2 lexical
mistakes.
1 point – the student uses a limited range of
vocabulary, fails to use any active vocabulary items
and makes more than 3 lexical mistakes.
0 points – the student uses an extremely limited
range of vocabulary, numerous lexical mistakes
impede communication.
0 points – the student uses elementary grammar
structures and makes numerous grammar mistakes
which may impede communication.
11
12.
Assessmentcriteria
7. Register (max – 1 point)
1 point – appropriate register.
0 points – inappropriate register.
8. Spelling and punctuation (max – 1 point)
1 point – the student makes no more than 1
spelling mistake and/ or no more than 1
punctuation mistake.
0 point - the student makes more than 1
spelling mistake and/ or no more than 2
punctuation mistakes.
12
13.
Task 1Step 1. Read the sentences and decide which sentence is the best topic sentence.
Step 2. Decide what is wrong with the other sentences. They may be too general, or
they may be too specific.
The best topic
sentence
Too general
Too specific
a. Hybrid automobiles are more economical to operate than
gasoline-powered cars.
b. The new hybrid automobiles are very popular.
c. Hybrid cars have good fuel economy because a computer
under the hood decides to run the electric motor, the small
gasoline engine, or the two together.
d. The new hybrid automobiles are popular because of their
fuel economy.
13
14.
Step 1. Read the sentences and decide which sentence is the best topic sentence.Step 2. Decide what is wrong with the other sentences. They may be too general, or
they may be too specific.
The best topic sentence
Too general
Too specific
a. The history of astronomy is interesting.
b. Ice age people recorded the appearance of new
moons by making scratches in animal bones.
c. For example, Stonehenge in Britain, built 3500
years ago to track the movement of the sun.
d. Ancient people observed and recorded lunar
and solar events in different ways.
14
15.
Task 2. Read the following scrambled paragraphs and decide whichsentence is the topic sentence.
__ a. Another important change was that people had the freedom to live and
work wherever they wanted.
__ b. The earliest significant change was for farming families, who were no
longer isolated.
__ c. The final major change brought by the automobile was the building of
superhighways, suburbs, huge shopping centers, and theme parks such as
Disney World in Florida.
__ d. The automobile revolutionized the way of life in the United States.
__ e. The automobile enabled them to drive to towns and cities comfortably
and conveniently.
__ f. In fact, people could work in a busy metropolitan city and live home to the
quiet suburbs.
15
16.
Task 2. Read the following scrambled paragraphs and decide whichsentence is the topic sentence.
__ a. A notes function lets you make quick notes to yourself.
__ b. Other capabilities include word processing, spreadsheets, and e-mail.
__ c. A voice recorder that uses a built-in microphone and speaker works like a
tape recorder.
__ d. Basic tools include a calendar to keep track of your appointments, an
address and phone number book, to-do lists, and a calculator.
__ e. MP3 playback lets you listen to digital music files, and a picture viewer
lets you look at digital photos.
__ f. Most personal digital assistants (PDAs) have tools for basic tasks as well as
for multimedia functions.
__ g. A few models also include a built-in digital camera and keyboard.
16
17.
Task 3Step 1. Read Paragraphs A and B about red-light running. Notice the different specific
supporting details that have been added to Paragraph B.
Step 2. Locate the topic sentence in Paragraph B. Circle the topic and underline the
controlling idea.
Step 3. Which supporting sentences in Paragraph B contain the kinds of details listed
below? Give the sentence numbers of each kind.
An example: _
A statistic: _
A quotation: _
17
18.
1819.
Descriptive paragraphTopic Sentence identifies the phenomenon to be described. The controlling idea should
give an overall impression of the place/object/person you are describing.
Support Sentences give an organised description of its parts, functions, and/or
characteristics.
Concluding Sentence restates the idea in the TS.
Strong sensory details:
• Sight
• Hearing
• Touch
• Smell
• Taste
21
20.
Descriptive paragraph• Useful transitional words and phrases:
in the foreground, in the middle distance, in the background, in the far distance, next to,
near, up, down, between, above, below, on top of, beneath, left, right, centre, front,
back, middle, in the interior, on the exterior, on the inside, on the outside, surrounding
• Vivid vocabulary, colourful adjectives and a lot of descriptive details.
20
21.
Descriptive paragraphA Place to Relax
My favourite place to relax is a small café down the street where I live. This café is on a
small side street and as soon as you see it, you feel like going in. There are three
windows on either side of the door, and each window has a small window box with
brightly coloured flowers. There is a small wooden door that opens into the café, and as
soon as you go in, you can see a dozen small tables all around the room. I always like to
sit at a small table in the corner near the front windows. From here, I can look at the
artwork on the walls and at the pretty green plants hanging from the ceiling. With a
strong cup of coffee and a good book, I feel very happy and relaxed in my favourite
place.
21
22.
Descriptive paragraphA Place to Relax
My home library is a perfect place to relax. When you first enter the room, the dark
blue walls draw you in and make you feel at peace. A bookcase filled from top to bottom
stands at the far end of the room inviting anyone to come and grab a book. Next to this
majestic, red bookcase is the leather couch. It is well-worn so that it feels comfortable
the minute you sit down. It is perfect for resting or reading or day dreaming. The cosy
armchair is across from the couch and by the window. Behind the armchair is a lush fern
in a terra cotta planter. In between the couch and the armchair is round wooden coffee
table. On the floor is a faded Persian rug. When it’s time for some piece and quit at
home, the library is the only room that I want to be in.
22
23.
Discussion in groupsBeing a HSE student.
What is it like to study at the HSE?
• Formulate the topic sentence
• Think about the 3 support sentences
• Formulate the concluding sentence
23
24.
Home assignmentWrite a paragraph (29.11):
Describe a place that is a good tourist destination.
• Formulate the topic sentence
• Write 3 support sentences
• Formulate the concluding sentence
Use the topical vocabulary from Unit 2 (Sightseeing)
24






















 informatics
informatics








