Similar presentations:
Economics. Chapter 12. Lesson 3: Poverty and the distribution of income
1.
2.
Lesson 3: Poverty and the
distribution of income
Grade 12
Ms. Maya Zanhour
3.
OBJECTIVESDefine poverty
Discuss the distribution of income
List reasons for income inequality
Understand the role of the government to
fight poverty
• List and define anti-poverty programs
• Analyze to which extent the government
should support those in poverty
4.
POVERTY• One of the most difficult problems in any
economy
• It is a relative measure that depends on
prices, standard of living and income that
others earn.
• Definition: people are classified as living in
poverty if their incomes fall below a
predetermined level, or threshold
5.
POVERTY• Definition: people are classified as living in
poverty if their incomes fall below a
predetermined level, or threshold
The poverty threshold id the benchmark used to evaluate the income
that people receive. If they receive an income below the determined
threshold they are considered in poverty.
6.
LET’S WATCH THIS VIDEO AND TAKENOTES
7.
REASONS FOR INCOME INEQUALITYEducation
Wealth
Tax law changes
Decline of the role of unions
More service jobs
Advances in technology
Monopoly power
Discrimination
Changing family structure
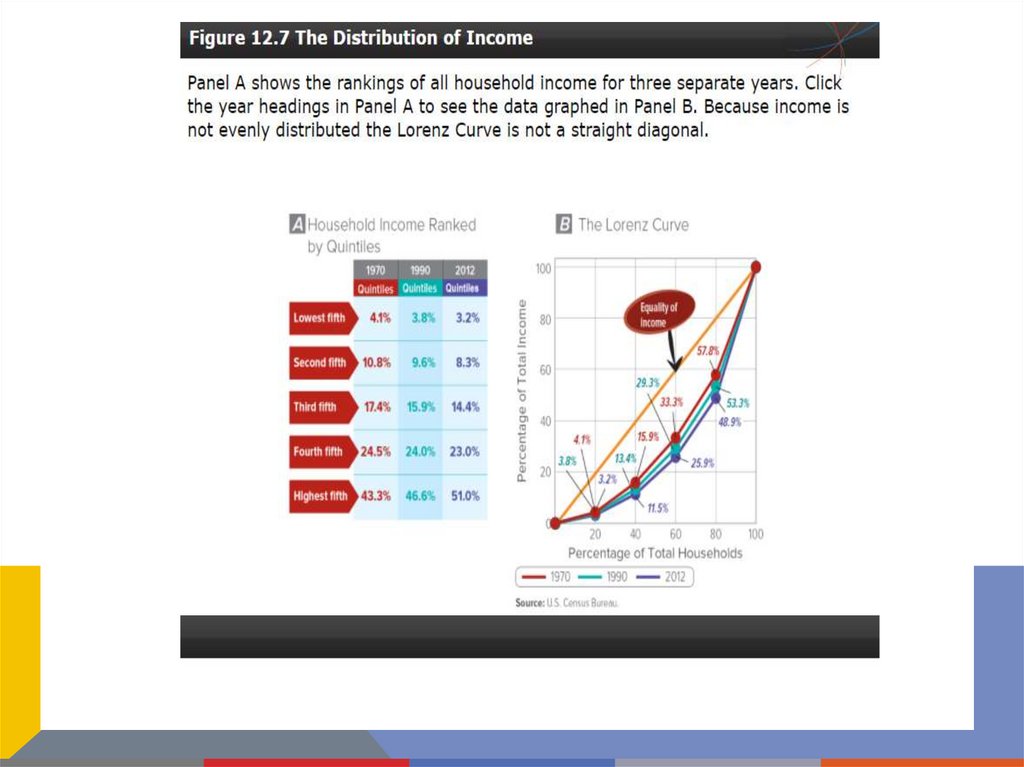
Mobility between quintiles
8.
QUINTILES: IN STATISTICSAny of five equal groups into which a
population can be divided according to the
distribution of values of a particular variable
9.
10.
11.
1. An enterprise zone, is a designatedgeographical area free of local, state, and
federal tax laws as well as other operating
restrictions.
Thus, for any company located in a free
enterprise zone, operating costs are
dramatically reduced.
12.
2. The residents of a designated enterprise zonewill from a factory being built. The factory
becomes the major employer in the area,
providing otherwise unavailable jobs.
3. Local store owners benefit when nearby
residents have jobs—and therefore income to
purchase goods from the stores.
4. The factory purchases some of its supplies from
local businesses which have located in the area
to be close to their customers.
13.
ANTIPOVERTY PROGRAMS1. Income assistance:
• Temporary assistance for needy families
• Supplemental security income for disabled and old people
2. General assistance:
• supplemental nutrition assistance or Food Stamps
• Medicaid
3. Social services:
• Child abuse prevention, foster care, and job training.
4. Workfare program
• Welfare recipients work for their benefits
14.
ANTIPOVERTY PROGRAMS1. Income assistance:
• Temporary assistance for needy families
• Supplemental security income for disabled and old people
2. General assistance:
• supplemental nutrition assistance or Food Stamps
• Medicaid
3. Social services:
• Child abuse prevention, foster care, and job training.
4. Workfare program
• Welfare recipients work for their benefits
15.
DISCUSS1. To which extent should the government help people who
are in poverty?







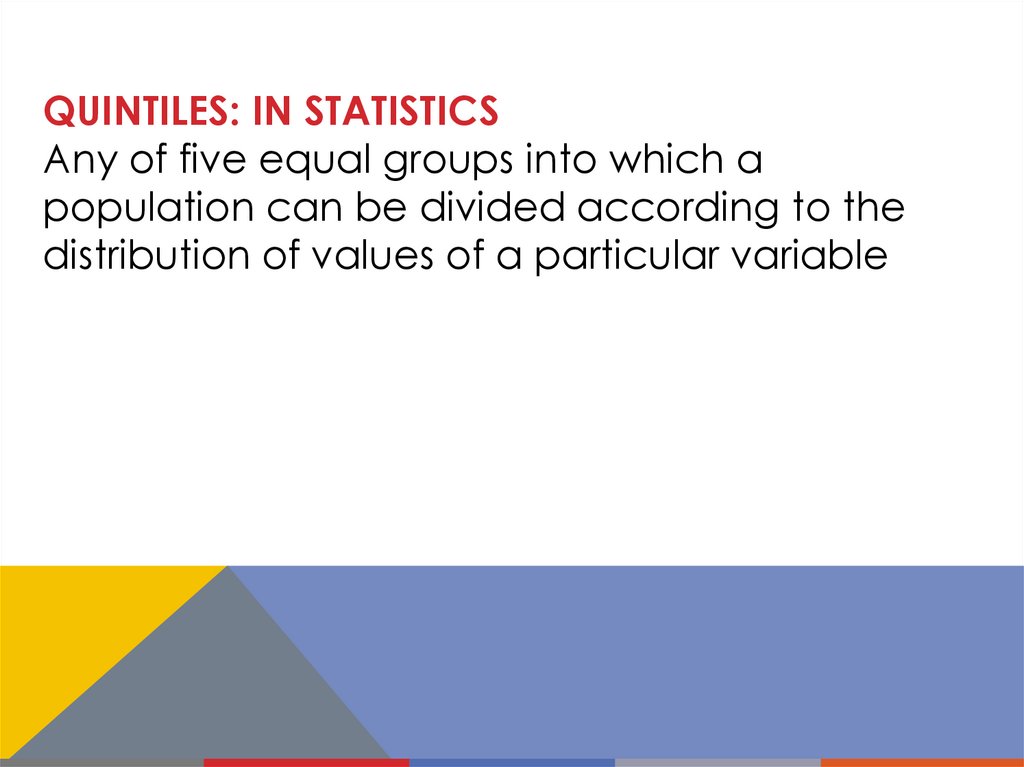







 economics
economics








