Similar presentations:
Philosophy of motion
1.
Philosophy of motionThis Presentation is made as a part of the PhD thesis “Conceptualization
Of Motion in English Phraseological Worldview” by Diana Shidlovskaya
2.
What exactly ismotion?
The answer has changed
over time...
3.
Motion as change.Does it exist?
Parmenides of
Elea (512 BC)
NO
Zeno of Elea (495 -430 BC)
4.
Parmenides and Zeno of EleaParmenides:
The world is One Being → stationary
“Ex nihilo nihil fit” (eng. Nothing comes
from nothing)
“There is a way which is and a way
which is not” (a way of truth and a way
of opinion) and that, “There is not, nor
will there be, anything other than what is
since indeed Destiny has fettered it to
remain whole and immovable.”
Zeno’s paradoxes of motion:
Achilles and the tortoise
Arrow paradox
Dichotomy paradox
5.
Motion as change.Does it exist?
YES
Democritus (460 BC - 370 BC)
Heraclitus (535 BC -475BC)
6.
Democritus and HeraclitusDemocritus - considered the first scholar
who formulated the atomic theory.
❏ All things are made of atoms, small
invisible particles.
❏ Depending of the state of an object
atoms move differently.
CONCLUSION: If everything consists of
constantly moving atoms → everything
moves
Heraclitus:
“Everything changes and nothing
remains still ... and ... you cannot step
twice into the same stream.”
7.
Aristotelian theory of motionEntelechy — The complete realisation and final form of some potential concept or
function.
Two types of physical motion: natural and unnatural (violent motion)
● Every object has its natural state:
EX: a thrown stone falls down because it seeks its natural place — earth.
● Natural motion is the motion that an object does naturally — without being forced
● Unnatural motion is caused by the outer forces. Once the force is removed so does the
motion.
● Heavier objects fall faster (stones falls faster than a feather)
8.
Aristotleis wrong!
9.
Galileo Galilei vs Aristotle10.
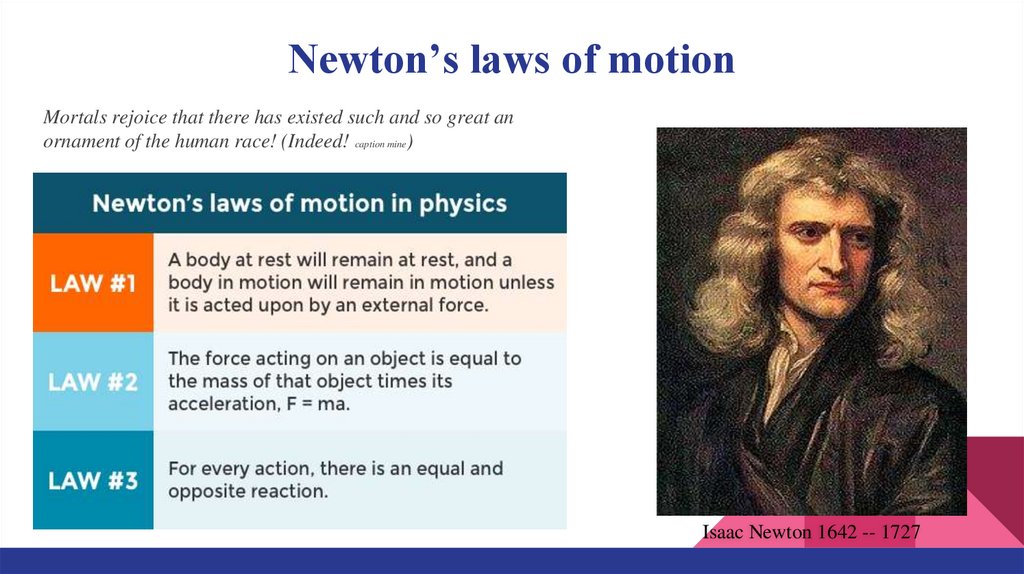
Newton’s laws of motionMortals rejoice that there has existed such and so great an
ornament of the human race! (Indeed! caption mine)
Isaac Newton 1642 -- 1727
11.
Marxist theory of motionMotion is defined as any change in the position or state.
❖ Motion is the mode of existence of matter and its chief properly
(including time and space)
❖ There are 5 types of motion:
➢ mechanical
➢ physical
➢ chemical
➢ biological
➢ social
❖ Motion is contradictory in nature
12.
Most Important Discoveries of the 20th Century❏ The birth of of quantum physics (Max Planck)
❏ Explanation of Brownian motion and photoelectric
effect (Albert Einstein)
❏ Theory of Relativity (special and general)
❏ Planetary model of the atom and discovery of
proton (Ernest Rutherford)
❏ Emergence of different theories of Universe
origins, etc.
13.
14.
What does it come down to?“The important thing is not to stop questioning. Curiosity has its
own reason for existing. One cannot help but be in awe when he
contemplates the mysteries of eternity, of life, of the marvelous
structure of reality. It is enough if one tries merely to comprehend a
little of this mystery every day.”
Max Planck











 philosophy
philosophy








