Similar presentations:
The Travel and Tourism Industry in Perspective
1. HOSP 100 - INTRODUCTION TO THE HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY
1HOSP 100 INTRODUCTION TO THE
HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY
LECTURER: PANAYIOTOU
GEORGE
2. CHAPTER 1: The Travel and Tourism Industry in Perspective
2What is Hospitality?
• The reception and entertainment of guests,
visitors and strangers with liberality and good
will
Traveler
• Any person visiting a country, other than that
in which he/she usually resides, for a period of
at least 24 hours.
Excursionist
• Persons traveling for pleasure for a period of
less than 24 hours.
3. Reasons for Travel
3Internal (“push”)
factors
Health
Curiosity
Sports
Religion
Pleasure
External (“pull”)
factors
Culture
History
Geography
Wildlife
Climate
Architecture
Shopping
4. Why people travel more?
4“Travel is an attractive leisure time
activity”
More Leisure Time
40 hours per week, 5 days a week
More Disposable Income
Credit Cards
Travel now – pay later
Bank interest
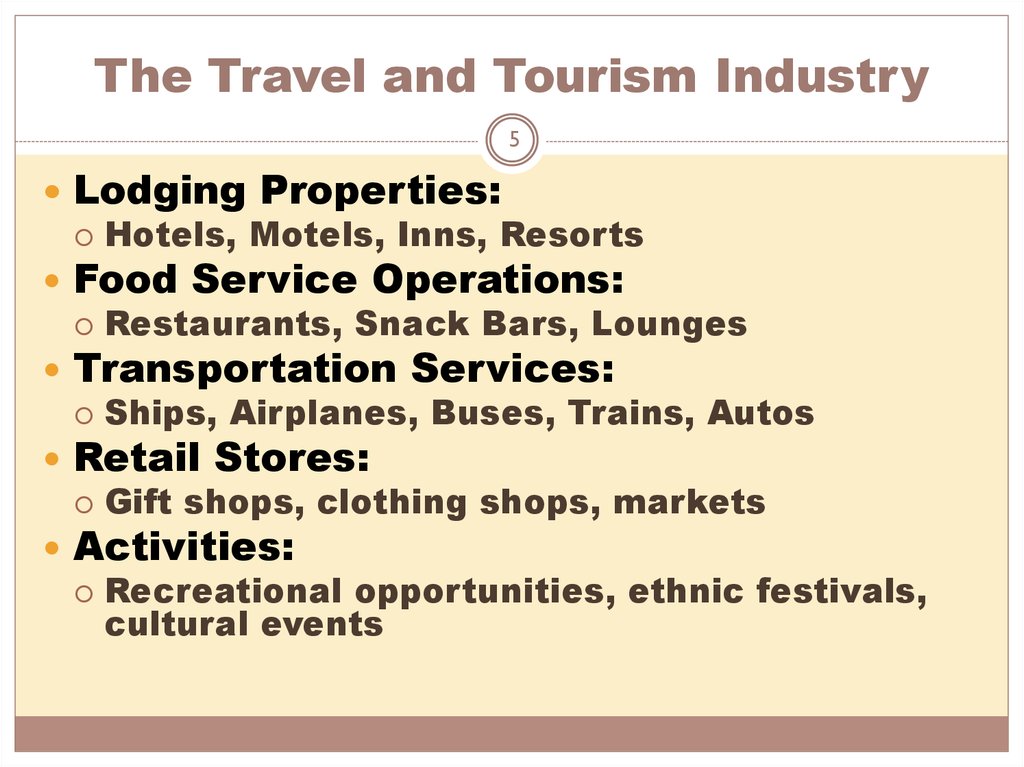
5. The Travel and Tourism Industry
5Lodging Properties:
Hotels, Motels, Inns, Resorts
Food Service Operations:
Restaurants, Snack Bars, Lounges
Transportation Services:
Ships, Airplanes, Buses, Trains, Autos
Retail Stores:
Gift shops, clothing shops, markets
Activities:
Recreational opportunities, ethnic festivals,
cultural events
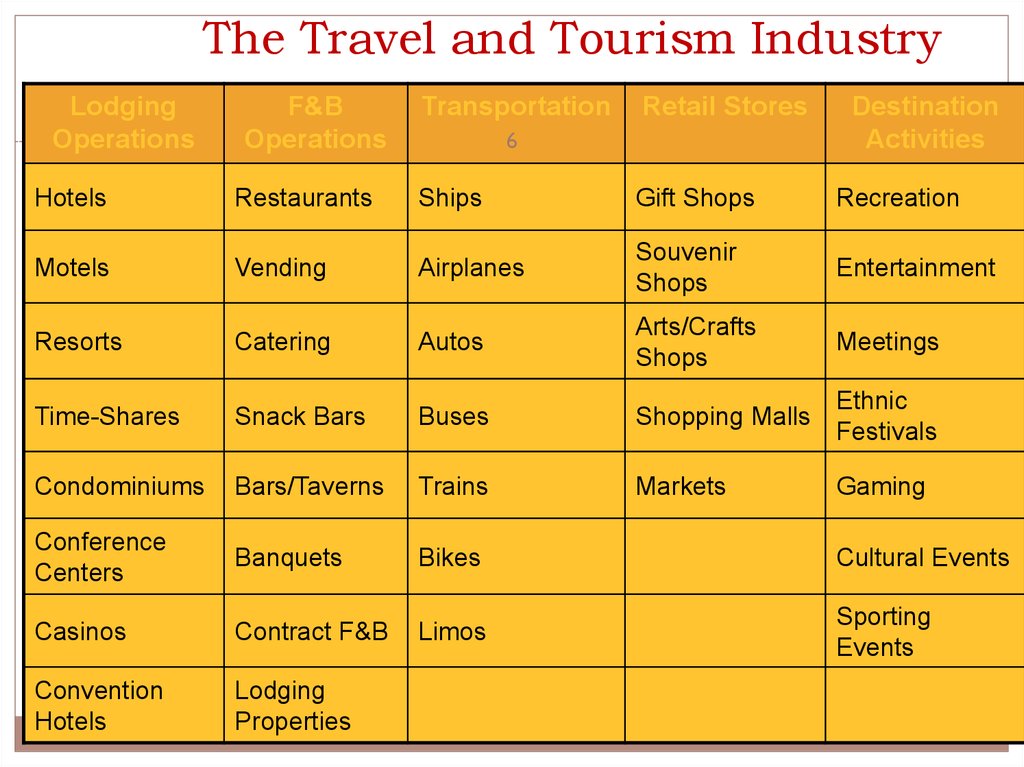
6. The Travel and Tourism Industry
LodgingOperations
F&B
Operations
Transportation
Retail Stores
6
Destination
Activities
Hotels
Restaurants
Ships
Gift Shops
Recreation
Motels
Vending
Airplanes
Souvenir
Shops
Entertainment
Resorts
Catering
Autos
Arts/Crafts
Shops
Meetings
Time-Shares
Snack Bars
Buses
Shopping Malls
Ethnic
Festivals
Condominiums
Bars/Taverns
Trains
Markets
Gaming
Conference
Centers
Banquets
Bikes
Cultural Events
Casinos
Contract F&B
Limos
Sporting
Events
Convention
Hotels
Lodging
Properties
7.
7Hoshi Hotel -Japan
Founded 718- Worlds
oldest operating hotel-by
the same family
8.
MGM GRAND – 5005 ROOMS8
9. Las Vegas Strip - Dusk
910.
The Grand Hyatt, Shanghai China is thetallest hotel in the world.
10
11.
1112.
Yotel'sGatwick
12
13.
1314.
Pod-U-Like: A fibreglass unit at The Capsule Inn Osaka.14
15.
1516.
Tree House Hotel in France16
17.
Ariau Amazon Towers Hotel- the worlds largestcommercial treehouse hotel-8 treetop wooden towers
with 268 treetop rooms 17
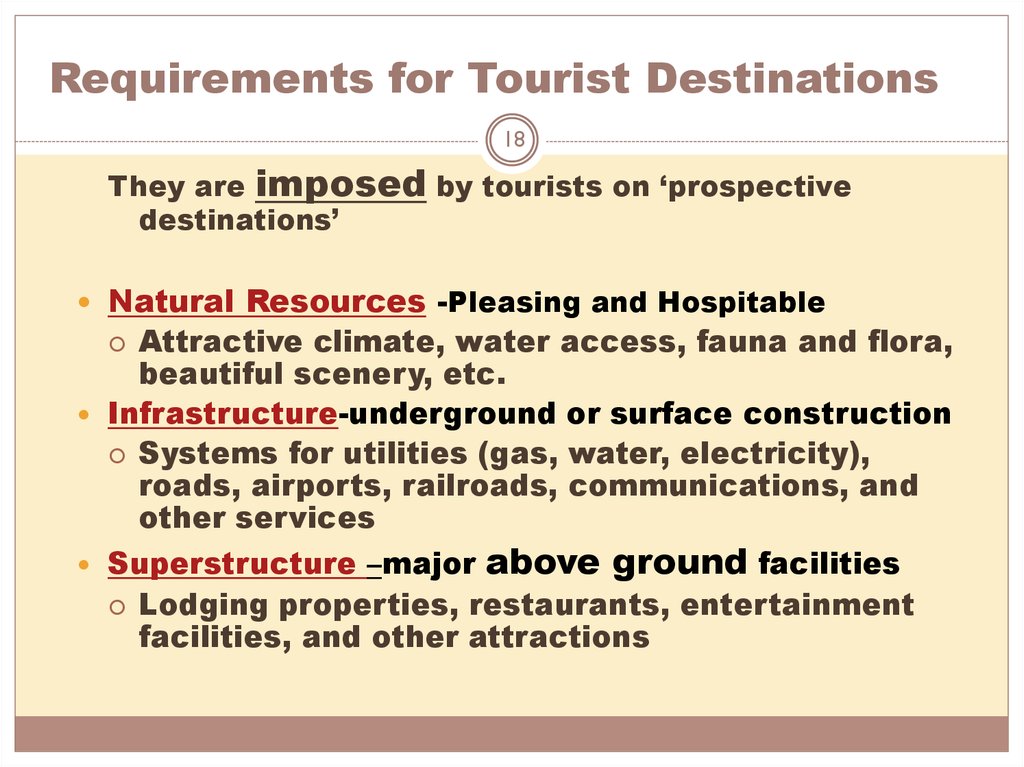
18. Requirements for Tourist Destinations
18They are imposed by tourists on ‘prospective
destinations’
Natural Resources -Pleasing and Hospitable
Attractive climate, water access, fauna and flora,
beautiful scenery, etc.
Infrastructure-underground or surface construction
Systems for utilities (gas, water, electricity),
roads, airports, railroads, communications, and
other services
Superstructure –major
above ground facilities
Lodging properties, restaurants, entertainment
facilities, and other attractions
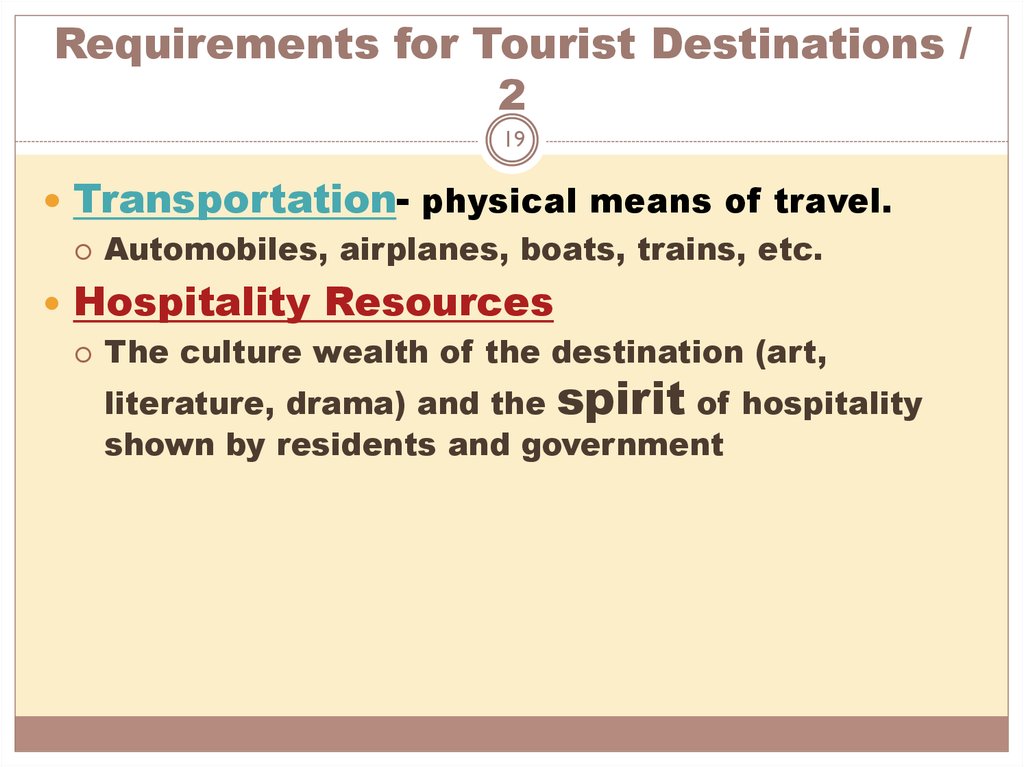
19. Requirements for Tourist Destinations / 2
19Transportation- physical means of travel.
Automobiles, airplanes, boats, trains, etc.
Hospitality Resources
The culture wealth of the destination (art,
literature, drama) and the spirit of hospitality
shown by residents and government
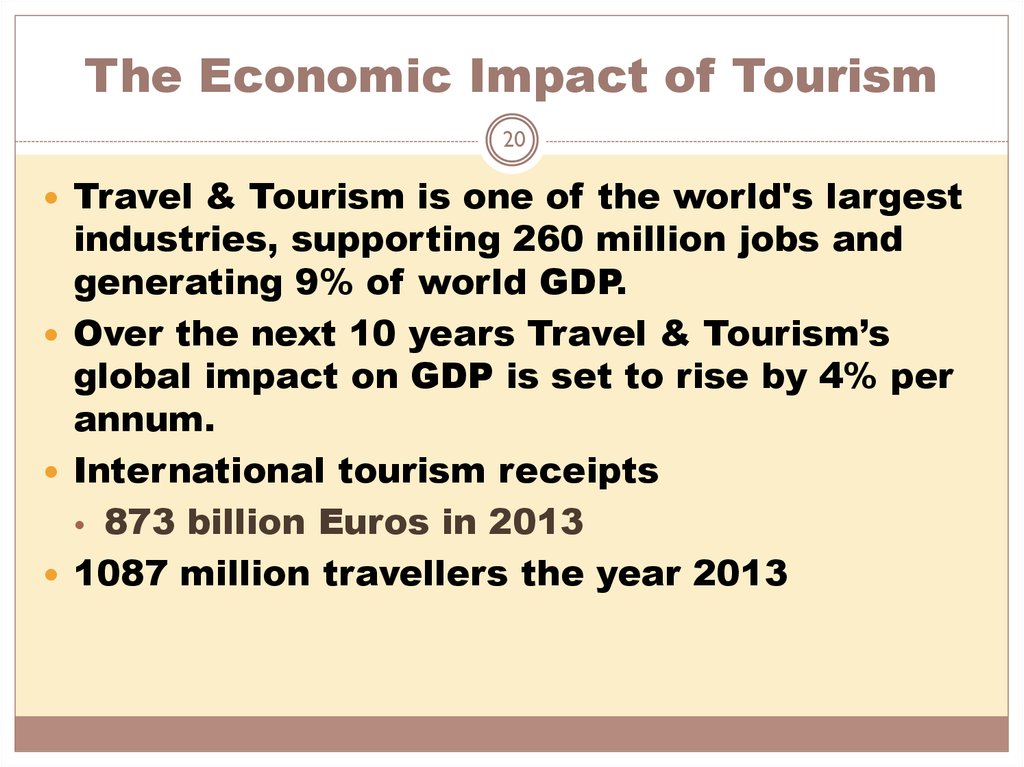
20. The Economic Impact of Tourism
20Travel & Tourism is one of the world's largest
industries, supporting 260 million jobs and
generating 9% of world GDP.
Over the next 10 years Travel & Tourism’s
global impact on GDP is set to rise by 4% per
annum.
International tourism receipts
• 873 billion Euros in 2013
1087 million travellers the year 2013
21. Ripple Effect and Globalization
21“Ripple Effect”
The
indirect financial benefits that local
business (outside the hospitality industry)
enjoy because of tourism
Globalisation
The increasing ease of international travel
and to the world-wide expansion of major
corporations
Hilton, McDonalds, Pizza Hut, Holiday Inn.
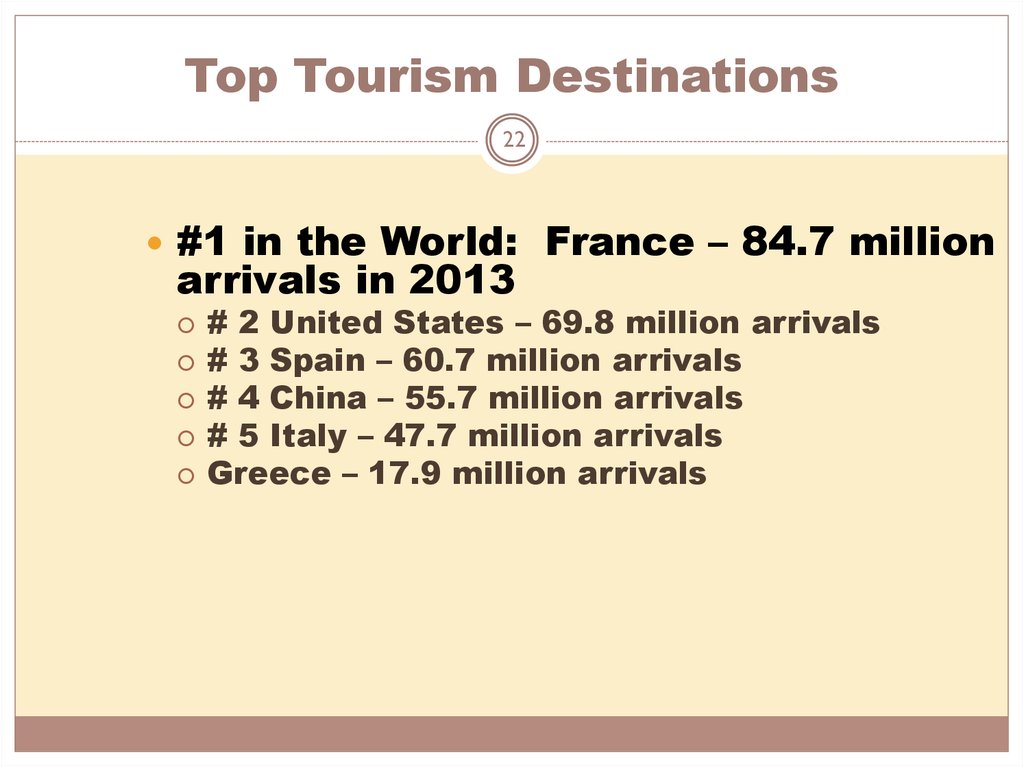
22. Top Tourism Destinations
22#1 in the World: France – 84.7 million
arrivals in 2013
# 2 United States – 69.8 million arrivals
# 3 Spain – 60.7 million arrivals
# 4 China – 55.7 million arrivals
# 5 Italy – 47.7 million arrivals
Greece – 17.9 million arrivals
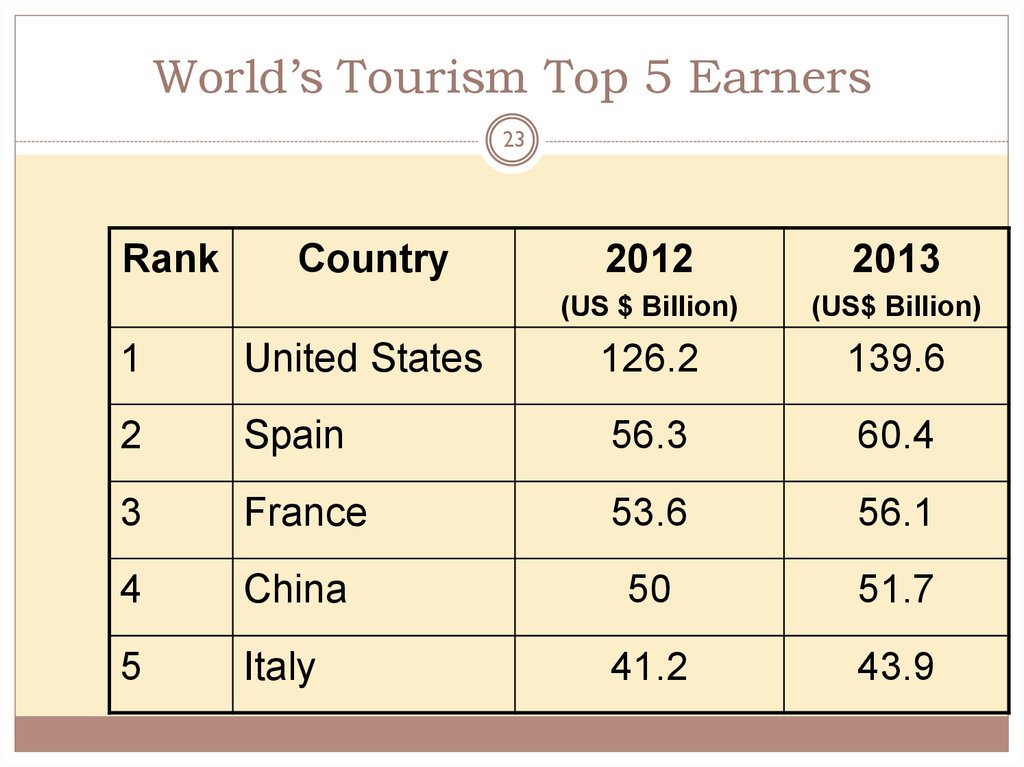
23. World’s Tourism Top 5 Earners
23Rank
Country
2012
2013
(US $ Billion)
(US$ Billion)
1
United States
126.2
139.6
2
Spain
56.3
60.4
3
France
53.6
56.1
4
China
50
51.7
5
Italy
41.2
43.9
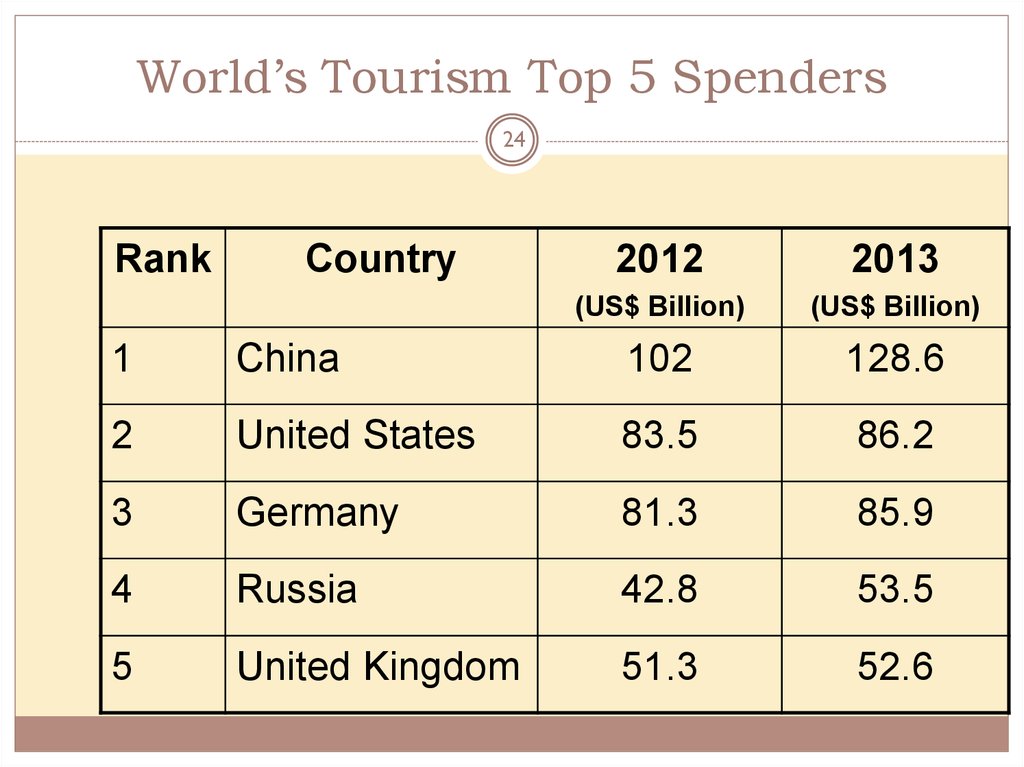
24. World’s Tourism Top 5 Spenders
24Rank
Country
2012
2013
(US$ Billion)
(US$ Billion)
1
China
102
128.6
2
United States
83.5
86.2
3
Germany
81.3
85.9
4
Russia
42.8
53.5
5
United Kingdom
51.3
52.6
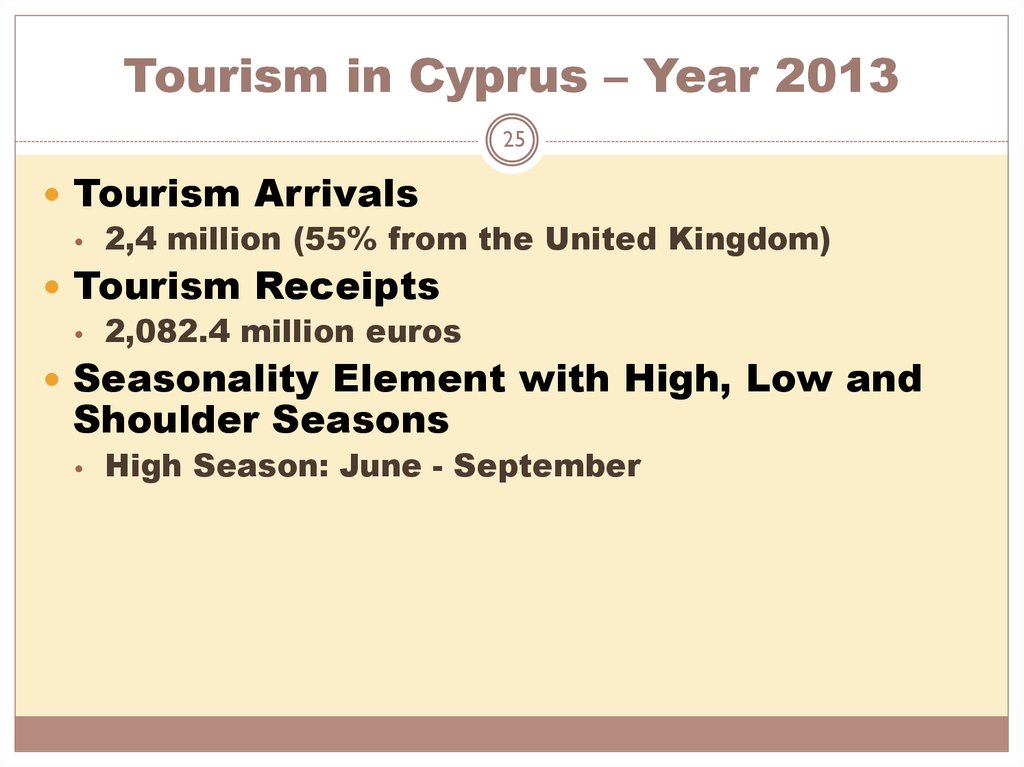
25. Tourism in Cyprus – Year 2013
25Tourism Arrivals
• 2,4 million (55% from the United Kingdom)
Tourism Receipts
• 2,082.4 million euros
Seasonality Element with High, Low and
Shoulder Seasons
High Season: June - September
26. What influence travel to and from the United States?
26TO
Strength of the US$
Stronger the dollar less the tourist traveling to the
USA
FROM
Threat of terrorism
Travel advisories
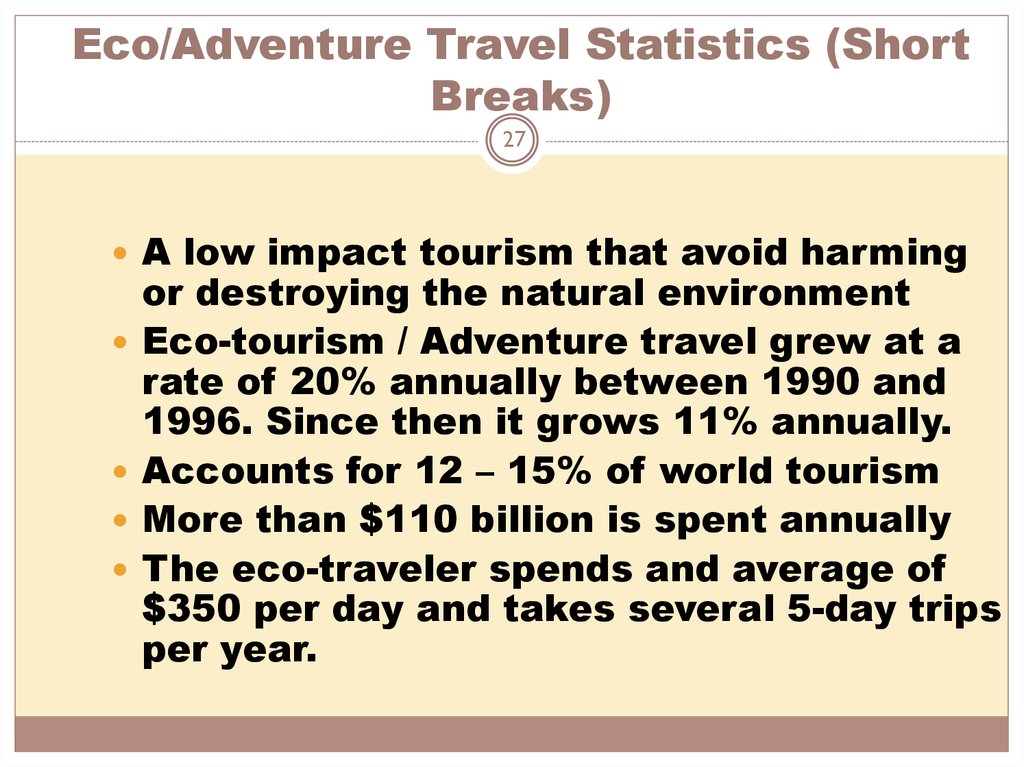
27. Eco/Adventure Travel Statistics (Short Breaks)
27A low impact tourism that avoid harming
or destroying the natural environment
Eco-tourism / Adventure travel grew at a
rate of 20% annually between 1990 and
1996. Since then it grows 11% annually.
Accounts for 12 – 15% of world tourism
More than $110 billion is spent annually
The eco-traveler spends and average of
$350 per day and takes several 5-day trips
per year.

















 business
business








