Similar presentations:
Inflation
1.
INFLATIONPrepared by Shlyakhtitskaya Anna
Second year student
Institute of Finance Economics and Management
Ek-b-18-6o group
2.
WHAT IS INFLATION?This is a general increase in prices in the country over a long period. When people talk
about inflation, they often mean the depreciation of money: for the same amount, after a
while you can buy less goods. With inflation, the cost of all goods does not necessarily
increase; some may even fall in price, but overall, the price level in the country is growing.
3.
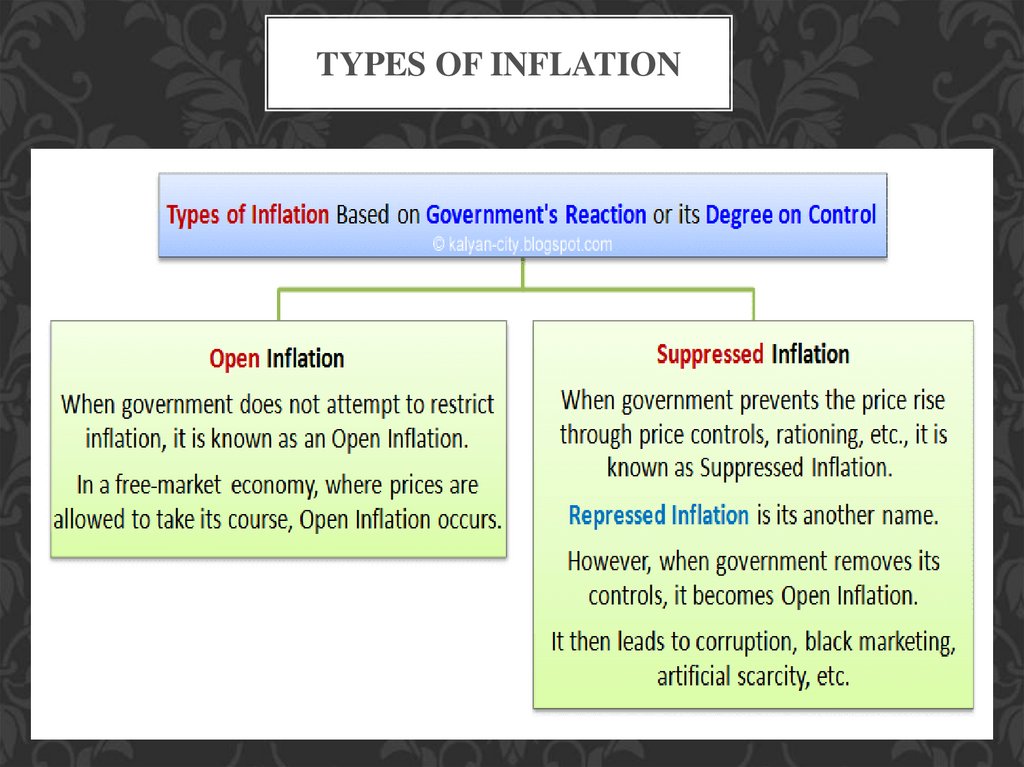
TYPES OF INFLATION4.
TYPES OF INFLATION5.
TYPES OF INFLATION6.
Most of the reasons are somehow related to the amount and availabilityof money for the economy. Such factors are called monetary. Inflation
accelerates when there is more free money in the economy.
CAUSES OF OCCURRENCE
interest on loans is reduced
taxes are reduced
production volumes are falling
budget spending is rising
salary is growing
7.
Prices even depend on how citizens themselves evaluate inflation.Economists use the term inflationary expectations - when buyers are
constantly waiting for price increases, are procured for the future
and create rush demand, which really increases the cost of goods.
Then manufacturers predict high inflation, start raising prices in
advance to offset future costs.
8.
In Russia, Rosstat considers inflation. To do this, every month,statistics look at how prices for goods and services that are included in
the consumer basket change. A consumer basket is a set of
approximately 700 goods and services, ranging from food to
smartphones and cars.
MEASUREMENT
Price changes are observed in all regions, and then they calculate the
average inflation rate for the country. A similar calculation technique is
used by statistics in other countries.
9.
COMPONENTSThe depreciation of money occurs for two reasons: due to inflation of
demand and costs.
Demand for inflation occurs when the
amount of money earned by the
population is higher than the value of
goods and services produced by all
these people. As a result, prices begin
to rise in order to balance supply and
demand.
Supply inflation begins when the cost of
goods and services increases - for
example, due to rising tariffs. To
maintain profitability, manufacturers are
raising prices.
10.
CONSEQUENCES OF INFLATIONModerate inflation is needed for the development of the economy: if
prices do not rise or even fall, it becomes unprofitable to produce new
goods. Economists call the annual increase in prices by 1-2%
acceptable. When this indicator exceeds 10% per year, and inflation
turns from moderate to galloping, it negatively affects the economy.
11.
The state is trying to regulate inflation. If you need to speed itup, state sign prints more money. At the same time, the
Central Bank lowers the key rate - the percentage at which
the state provides loans to commercial banks. They, in turn,
can lend to the population and entrepreneurs at a low rate.
WHO AND HOW HOLDS
BACK PRICES
If you need to slow inflation, the national sign prints less money, and the
Central Bank raises the key rate. Banks do not borrow from the state, but
attract citizens to open deposits. People stop spending and carry money
on deposits. Loan rates are rising. Money turnover decreases, prices and
demand for goods fall.
12.
INFLATION IN RUSSIA FOR 2020In March 2020, the inflation rate in Russia amounted to 0.55%, which is 0.22 more than
in February 2020 and 0.23 more than in March 2019. Along with this, inflation since
the beginning of 2020 amounted to 1.29%, and on an annualized basis - 2.55%. In
2020, Russia takes 1st place in terms of inflation in the world.
13.
THANK YOU FORATTENTION












 finance
finance








