Similar presentations:
Assets, Depreciation, Liabilities and Balance sheet
1.
Assets, Depreciation,Liabilities and
Balance sheet
1
2.
Balance SheetBalance Sheet is a report
on the financial condition
of the company at a
certain date. Date of the
report can be any, but
usually it's the end of the
month, quarter or fiscal
year.
2
3.
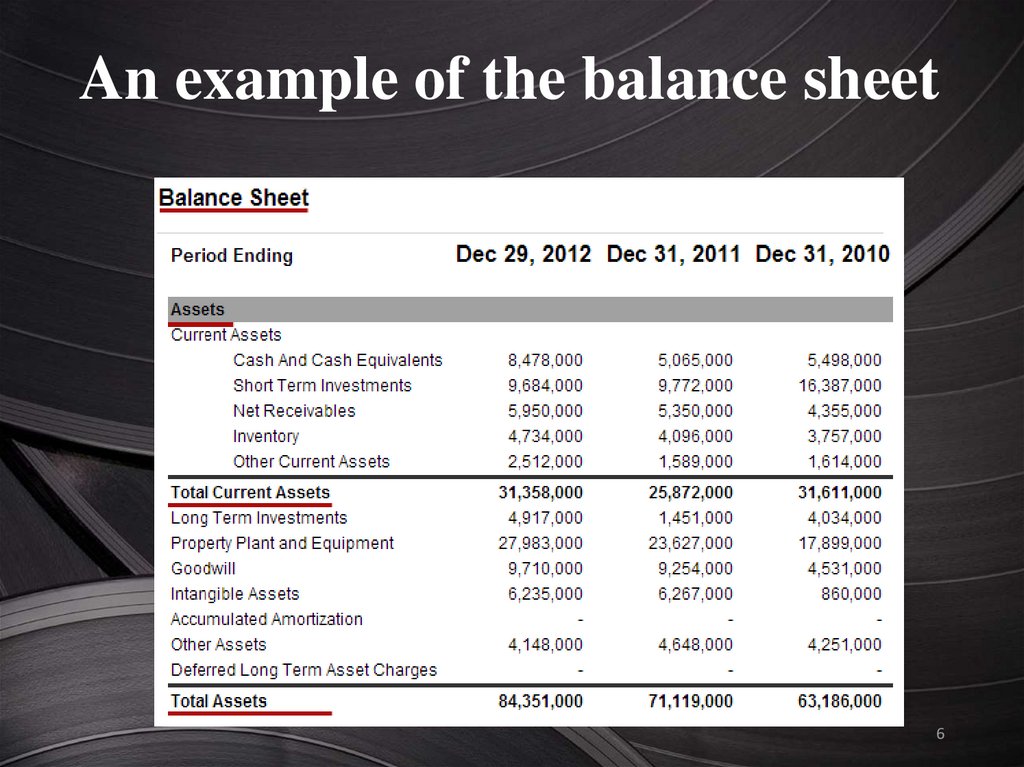
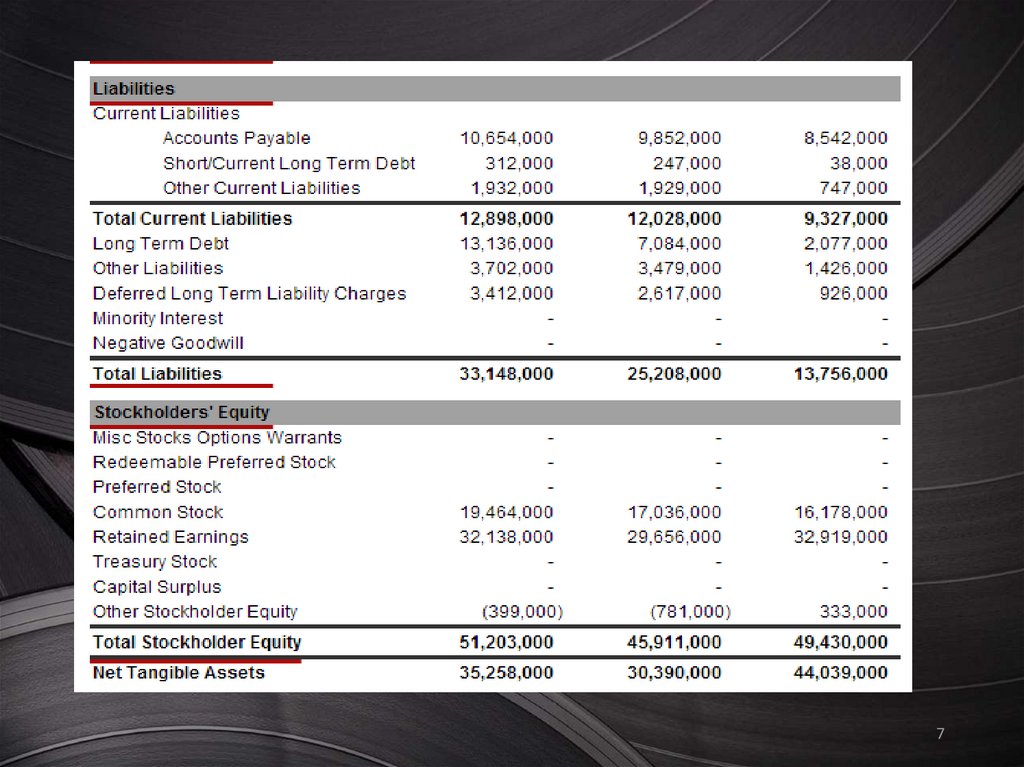
Сomposition of the balanceThe balance includes assets and
liabilities, the results of which are.
3
4.
Assets in the balance sheet arearranged in descending order of
degree of liquidity.
4
5.
Liabilities that in international practice consists ofliabilities and Stockholders’ Equity, are displayed as
follows:
Liabilities are presented by descending of their
requirements (repayment);
Article equity are placed after the commitment.
5
6.
An example of the balance sheet6
7.
78.
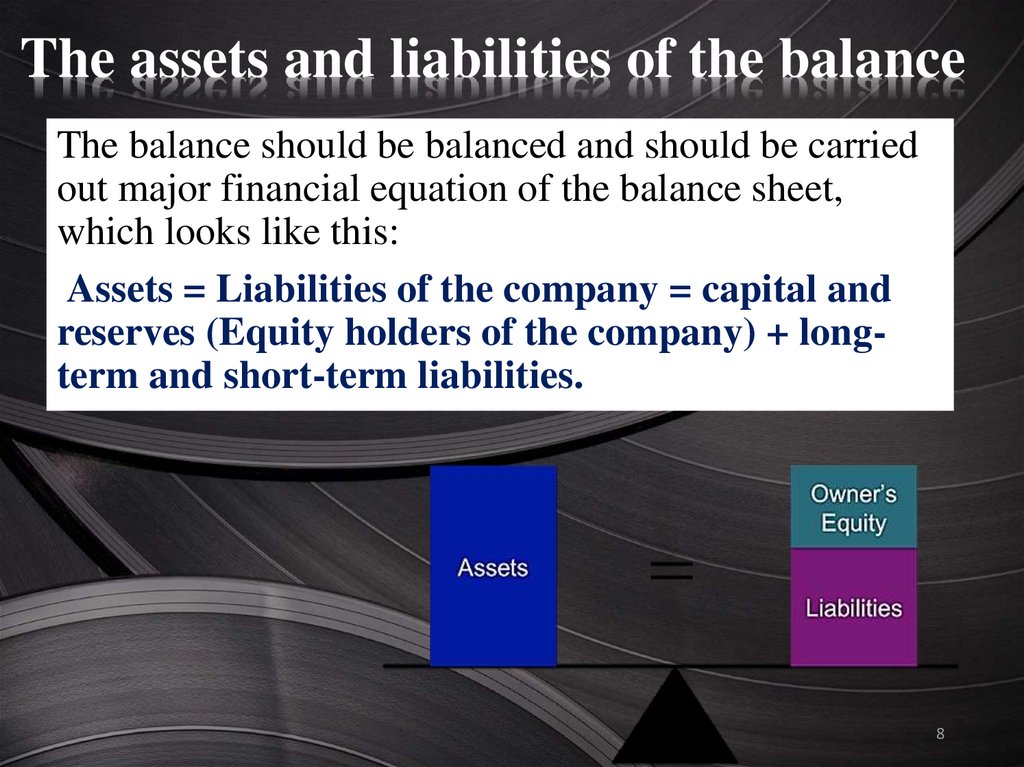
The assets and liabilities of the balanceThe balance should be balanced and should be carried
out major financial equation of the balance sheet,
which looks like this:
Assets = Liabilities of the company = capital and
reserves (Equity holders of the company) + longterm and short-term liabilities.
8
9.
Stockholders' EquityStockholders' Equity is the main source of
financing of the enterprise. . It represents the
aggregate amount of investments of shareholders
and net profit.
9
10.
The composition of the company'sown capital balance comprises:
Preferred
Stock
Common
Stock
Capital
Surplus
Retained
Earnings
Other
Stockholder
Equity
10
11.
Monetary and nonmonetary balance sheet itemsBalance Sheet Items are divided into:
Monetary
Nonmonetary
11
12.
FOR MONETARY ITEMS OTHER THANCASH AND SECURITIES ARE ALSO:
Receivables
Accounts
payable
Bonds issued
Lease
obligations
Deferred tax
assets and
liabilities
Accrued
expenses and
deferred
income
12
13.
All the rest - it's nonmonetary items.That is, stocks of
goods and raw
materials are noncash items.
13
14.
The size of the monetary and nonmonetary items in the balance sheetrestated for the changes in the
exchange rate
14












 english
english








