Similar presentations:
Topic 1. Introduction
1.
TOPIC 1INTRODUCTION
Click to add text TO FINANCE
Elena Rogova, Professor, erogova@hse.ru
10.01.2022
TOPIC 1 – KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
1
2.
1-1KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
Elena Rogova, Professor, erogova@hse.ru
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
2
3.
WHAT IS FINANCE?• Finance is the study of how and under what
terms savings (money) are allocated between
lenders and borrowers.
– Finance is distinct from economics in that it
addresses not only how resources are allocated
but also under what terms and through what
channels
• Financial contracts or securities occur whenever
funds are transferred from issuer to buyer.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
3
4.
REAL VERSUS FINANCIAL ASSETS• Real assets are tangible things owned by
persons and businesses
–
–
–
–
Residential structures and property
Major appliances and automobiles
Office towers, factories, mines
Machinery and equipment
• Financial assets are what one individual has lent to
another
– Consumer credit
loans
– Mortgages
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
4
5.
FINANCE EXAMPLES• Investing personal money in stocks, bonds, or guaranteed
investment certificates (GICs)
• Borrowing money from institutional investors by issuing bonds
on behalf of a public company
• Lending money to people by providing them a mortgage to
buy a house with
• Using Excel spreadsheets to build a budget and financial
model for a corporation
• Saving personal money in a high-interest savings account
• Developing a forecast for government spending and revenue
collection
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
5
6.
FINANCE: EXAMPLES (1)• If you receive $1 million today, then what decision would you
make regarding consumption and investment? Suppose you
spend (consume)
$100,000 now. This leaves you with $900,000. You can
postpone consumption to future time periods by investing
the $900,000 today.
• On the other hand, what if you have $20,000 but need to
consume $30,000. You can borrow the
$10,000 and pay it back in a future period along with the
interest.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
6
7.
FINANCE: EXAMPLES (1)• If you receive $1 million today, then what decision would you
make regarding consumption and investment?
• Suppose you spend (consume) $100,000 now. This leaves you
with $900,000. You can postpone consumption to future time
periods by investing the $900,000 today.
• On the other hand, what if you have $20,000 but need to
consume $30,000. You can borrow the $10,000 and pay it
back in a future period along with the interest.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
7
8.
FINANCE: EXAMPLES (2)• A firm must spend $100 million for the required assets if a proposed
project is approved. Important issues are:
• Should the project be accepted or rejected?
• What do investors demand as a (minimum acceptable) project rate of
return?
• What are the project’s forecasted future cash flows?
• How risky are these forecasted cash flows?
• Where will the $100 million come from, i.e., what mix of equity and debt
financing should be used?
• If a firm has $200 million of cash flow, but needs reinvest $100 million, what
should be done with the remaining $100 million of cash?
10.01.2022
Pay it out as a dividend or repurchase some stock?
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
8
9.
FINANCE: EXAMPLES (3)• A mutual fund manager that manages a fund with
$10 billion portfolio receives an additional $100
million in cash from new investors.
• Which stocks or bonds to purchase?
• How will any proposed new investments affect the
expected return and risk of the overall portfolio?
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
9
10.
GENERAL AREAS OF FINANCE• Financial Markets and Institutions: banks,
insurance companies, savings and loans, and
credits unions
• Investments: determining the values, risks, and returns
of financial assets (stocks, bonds) and the optimal mix
of securities to be held in a portfolio of investments
• Financial Services: how to invest money (home
purchase, financial stability, budgeting)
• Managerial (Business) Finance: firms’ decisions
about their cash flows (plant expansion, credit terms,
• inventory, cash on hand, earnings, dividends,…)
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
10
11.
FINANCE DISCIPLINES• Public finance is about the taxing and spending
activities of the government. Focus is on microeconomic
functions of government – policies that affect overall
unemployment or price levels are left for
macroeconomics. Scope of public finance is unclear –
government has role in many activities, but focus will be
on taxes and spending.
• Corporate finance is every decision that a business
makes has financial implications, and any decision which
affects the finances of a business.
• Personal Finance is managing your personal budget,
money and investment.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
11
12.
FINANCE THEORY• Finance Theory is the study of the behavior of
individuals in the inter-temporal allocation (over time)
of their resources in an uncertain environment, and the
study of the function of economic institutions and
markets in making these allocations possible.
• Financial theory consists of:
the set of concepts that help to organize one’s thinking
about how to allocate resources over time;
the set of quantitative models used to help evaluate
alternatives, make decisions, and implement them. These
concepts and models apply at all levels and scales of
decision making.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
12
13.
BASIC TENET OF FINANCE• The existence of economic organizations (e.g. firms
and governments) facilitates the satisfaction of
people’s consumption preferences.
• Two features: The costs and benefits of financial
decisions are
1) Spread out over time
2) Usually not known with certainty in advance by
either the decision makers or anybody else.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
13
14.
THE VALUE CREATION FUNCTION OF FINANCE• The practice of finance exists for the creation of value
• Financial contracting brings about the substitution of
real wealth (i.e. real business assets) for financial
wealth (i.e. securities)
• Investing in financial securities has better attributes
than in real assets.
• Value is created in the real assets held by businesses,
and then transmitted into the value of financial
wealth issued by businesses and held by investors.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
14
15.
BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE10.01.2022
Risk and Return
Time value of Money
Cash is King
Financial Markets Efficiency
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
15
16.
BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE: RISK AND RETURN• The higher is the risk of investments, the higher is the
return that investors require
Practical implications
Financial assets valuation,
Capital
investments projects
Companies valuation,
Credit ratings assignment etc.
10.01.2022
decision-making,
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
16
17.
THREE TYPES OF RISK• Autonomous risk
related to a specific project
or business unit
• Corporate risk
related to a whole company
A
B
C
Y
X
N
• Market risk
Related to a market portfolio
of securities (stocks and bonds)
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
17
18.
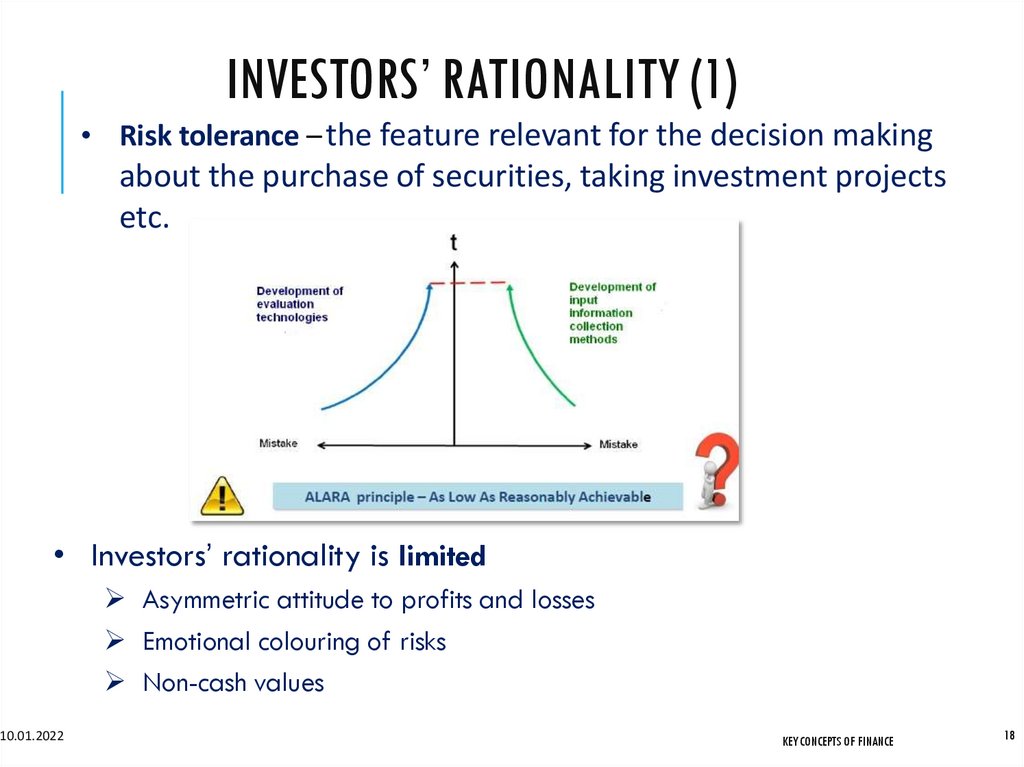
INVESTORS’ RATIONALITY (1)• Risk tolerance – the feature relevant for the decision making
about the purchase of securities, taking investment projects
etc.
• Investors’ rationality is limited
Asymmetric attitude to profits and losses
Emotional colouring of risks
Non-cash values
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
18
19.
TEST 1• You can choose between two games
(1) You throw a dice and got $60 if 6 appears
OR
(2)You throw a dice and got $10 regardless which number
appears
(2)Which game would you choose?
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
19
20.
TEST 1• You can choose between two games
(1) You throw a dice and got $60 if 6 appears
OR
(2) You throw a dice and got $10 regardless which number appears
• Which game would you choose?
Test 1 (modified)
(1) You throw a dice and got $60,000 if 6 appears
OR
(2)You throw a dice and got $10,000 regardless which number
appears
• Which game would you choose now?
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
20
21.
RISK TOLERANCE• If you prefer the first game, you are a RISKTAKER
• It you choose the second one, you are a RISKAVERTER
– Risk aversion is a typical feature of rational investors
• If you are indifferent to your choice, you are
RISK-NEUTRAL
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
21
22.
BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE: TIMEVALUE OF MONEY
• One ruble in your pocket today has more value
than the right to get this one ruble in a couple of
days
Practical implications of the concept
• Interest rates term structure,
• Financial assets valuation,
• Business valuation etc.
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
22
23.
10.01.202223
24.
10.01.2022KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE 24
25.
TEST 2• You have won in a competition and now can choose a
prize:
(1) 5,000 rubles now
OR
(2) 10,000 rubles in a year
• Which prize would you choose?
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
25
26.
TEST 2• You have won in a competition and now can choose a prize:
(1) 5,000 rubles now
OR
(2) 10,000 rubles in a year
• Which prize would you choose?
Test 2 (modified)
• You have won in a competition and now can choose a prize:
(1) 5,000,000 rubles now
OR
(2) 10,000,000 rubles in a year
• Which prize would you choose now?
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
26
27.
INVESTORS’ RATIONALITY (2)• Investors’ rationality can be limited by:
– Asymmetric attitude
to big and small amounts of money
– Asymmetric attitude
to close and far future
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
27
28.
BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE: PRIORITY TO CASHFLOWS (CASH IS KING)
• CASH can be immediately used for consumption or business
objectives
• Accountancy-based indicators do not fully reflect cash flows:
Accruals policy
Non-cash profits and losses
Practical implications of the concept
Financial reporting standards,
Performance indicators of companies and their divisions
Capital investments decision making and financial assets valuation
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
28
29.
INVESTORS’ RATIONALITY (3)Investors’ rationality is limited by:
– The historical belief in “paper-fixed” financial results
got on the base of accountancy
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
29
30.
BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCE:FINANCIAL MARKETS EFFICIENCY
Efficient markets hypothesis by E. Fama (EMH)
At the efficient capital market, all the information available is fully
reflected in stock prices
That’s why the new information immediately changes stock prices –market
signals should be considered by decision-takers
• Financial markets data provides the fair asset pricing
Practical implications of the concept
Investors relations
Mergers and
acquisitions Dividend
payments Personal
investments
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
30
31.
INVESTORS’ RATIONALITY (4)• Investors’ rationality is limited by:
– Lack of information
asymmetric access to information for different
players
– Subjective attitude to market signals
emotional colouring
– Costly information processing and limited
ability to interpret the information
10.01.2022
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
31





























 finance
finance








