Similar presentations:
Surgical knots
1.
SURGICAL KNOTS2.
Surgical treatment (treatment using the surgical method of treatment) - a methodof treating diseases by disconnecting and connecting tissues during a surgical
operation.
TISSUES CONNECTION
Bloodless methods
- with a metal staples
- with a patch
- with a surgical glue
Bloody methods
- continuous suture
- separate suture
3.
4.
5.
6.
SURGICAL SUTURE – CONNECTION OF THEWOUND EDGES WITH A SUTURE MATERIAL
External sutures
- a skin
- A mucous membranes
Internal sutures
- During a surgical
treatment
7.
SUTURES CAN BE:Continuous
Separate
8.
LIGATURELigature is a thread applied o a blood vessel or ANY
OTHER hollow organ to narrow its internal space.
9.
10.
THE MOST IMPORTANT THINGIS NOT MEMORIZING
OF NUMEROUS KNOTS AND ITS STRUCTURE,
BUT UNDERSTANDING
THE MAIN PRINCIPLES OF ITS FORMATION!
11.
assistantExternal thread
A far half of the
operating field
A wound
A near half of the
operating field
Internal thread
operator
12.
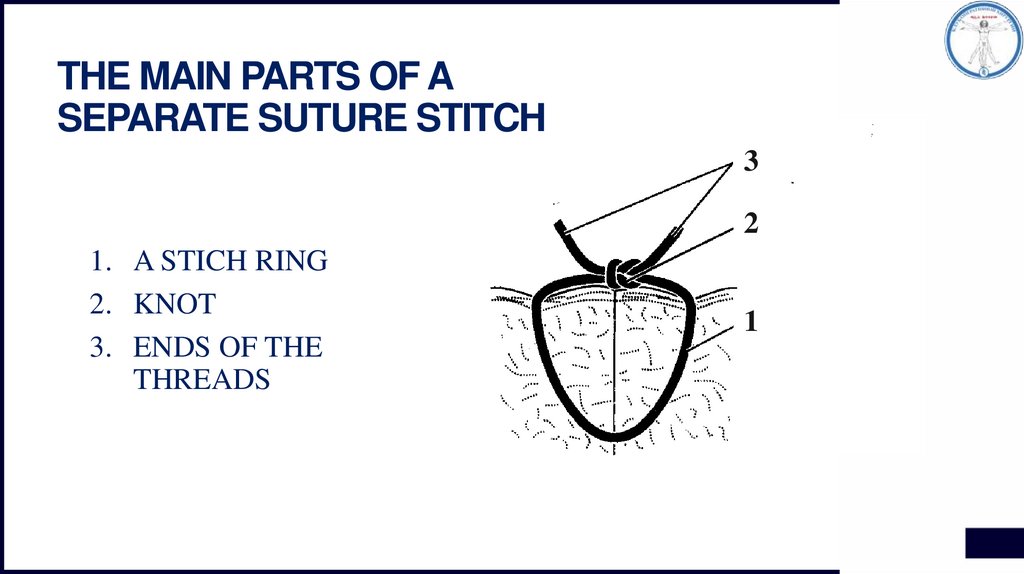
THE MAIN PARTS OF ASEPARATE SUTURE STITCH
3
2
1. A STICH RING
2. KNOT
3. ENDS OF THE
THREADS
1
13.
Second semi-knotEvery surgical knot consist of AT
LEAST TWO loops
A single weave of threads is called
a SEMI-KNOT
A LOOP – stitch ring completed by a
semi-knot
First semi-knot
Second loop
First loop
14.
CLASSIFICATIONOF LOOPS
15.
1 . BY AMOUNT OF INTERWEAVING INTHE LOOP
Single
Double
Triple
16.
Be careful!17.
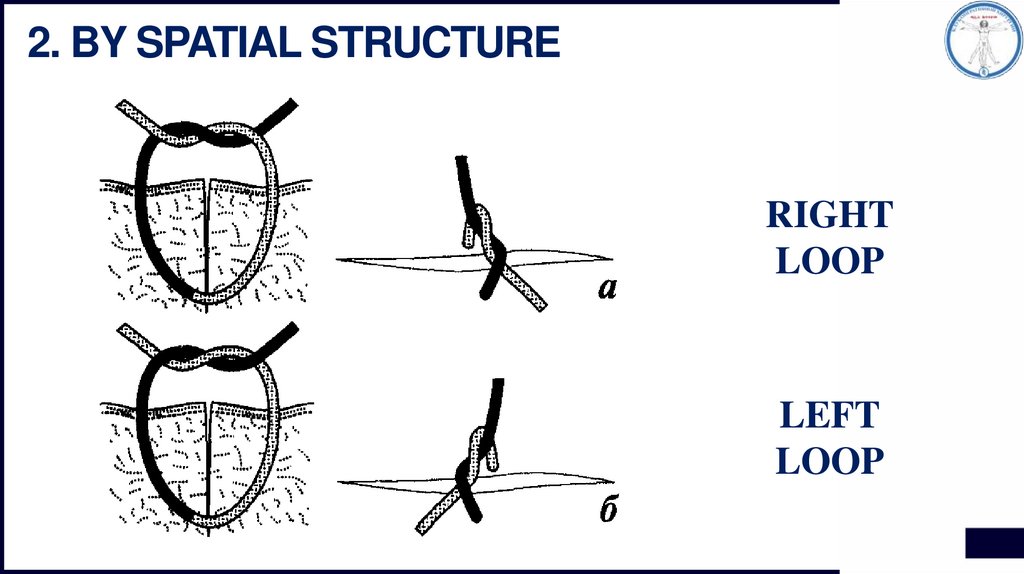
2. BY SPATIAL STRUCTURERIGHT
LOOP
LEFT
LOOP
18.
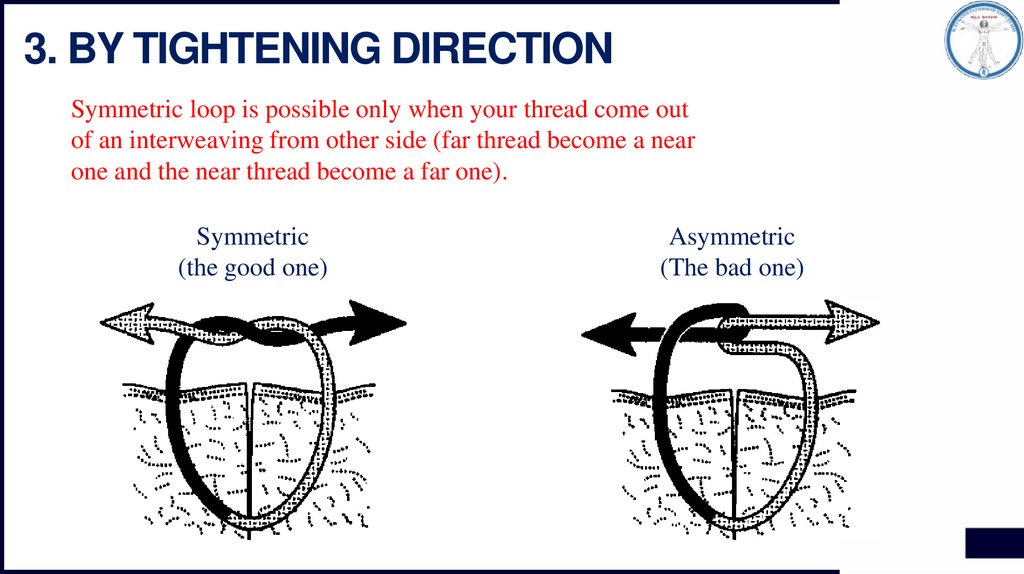
3. BY TIGHTENING DIRECTIONSymmetric loop is possible only when your thread come out
of an interweaving from other side (far thread become a near
one and the near thread become a far one).
Symmetric
(the good one)
Asymmetric
(The bad one)
19.
KNOTSCLASSIFICATION
20.
1. BY AMOUNT OF LOOPS• Amount of loops starts from TWO and more;
• After 3th-4th loop knot strength almost doesn’t increase.
«Sea»
knot
Double
«Sea»
knot
Triple
«Sea»
knot
20
21.
2. BY AMOUNT OF INTERWEAVING IN LOOPS1) Simple – a knots consist of loops only with single interweaving;
2) Complex – we can meet a loop with double interweaving;
a) Equal – amount of interweaving is similar to every loop– “academic” knot;
b) Unequal – amount of interweavings in loops is not similar – “a surgical”
knot.
An “academic”
knot
A “surgical” knot
A “sea” knot.
21
22.
3. BY AMOUNT OF STITCH RINGSI. One-ring knots;
II. Two-ring knots – A Barkov knot;
III. Three-ring knots.
A Barkov knot
22
23.
4. BY SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF THE LOOPSI. Parallel – the loops are alternating (right-left-right-left)
II. Crossed – all the loops are right or left.
III.Mixed – loops can both alternate and match (right-left-left)
A “sea” knot
A “woman” knot.
23
24.
5. BY TIGHTENING DIRECTIONI. Symmetric – all the loops are tightened in right direction;
II. Asymmetric – there a loops tightened not right.
1) Sliding – ALL the loops are tightened not right:
A. Simple sliding;
B. Sliding blocked – a «Parisian» knot.
2) Turned – good loops at start, bad loops at the end;
3) Offset – bad loops at start, but good loops at the end.
A «Parisian» knot
Sliding knot
Turned knot
Offset loop
24
25.
EXAM1. Theoretic part
An examination, during which the examinee must answer theoretical
questions, as well as form the knots given by the examiner, to test
the understanding of the principles of knot formation.
The answering process shouldn’t exceed 10 minutes.
2. Practical part
You must braid 30 mm of a “tale” consist of simple knots
for 30 seconds.
Type of thread – caprone, size 2/0.
In case of “window” existing (like on the photo), the
measuring is carried from beginning to this window.
25
26.
THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION!Жить на белом свете - значит
постоянно бороться и постоянно
побеждать. - Николай Пирогов
Living this life means a constant
struggling and constant winning.
- Nikolay Pirogov























 medicine
medicine