Similar presentations:
Globalization and Related concepts
1. Global Issues: Week 2
Globalizationand
Related concepts
Readings:
1) Karns, Margaret P. and Karen A. Mingst (2004) “The
Challenges of Global Governance”,
2) Falk, Richard A. (2015) Horizons of Global Governance, in
Critical perspectives on the crisis of global governance:
reimagining the future.
2. Outline
Globalisation and Global Issuesconceptualisation
theoretical perspectives
Global Governance and IOs
3.
Your global issuesClimate change (global warming, polution, envirnonment) 30 –
Poverty (6) - water issues – Unemployment (3) – US-China relations
- Refugee crisis, migration (4) – Hunger crisis, food security (5) Corruption (4) – The North-South issue (imperialist-opressed
countries) (4) – Terrorism (4) - Overconsumptions - Freedom of
speech – Capitalism – Woman's rights and gender equality (8) Increasing inequalities (3) - Russian war in Ukraine (5) – Lack of
education (3) – Survival of multilateralism (2) - Energy security –
Russian Imperialism and terrorism - Overpopulation- Animal
Rights – Pandemic deseases (3) - Biodiversity loss - Mental health Far-right sentiments in Europe – Dependence on technologies –
Discrimination of LGBT people (3)
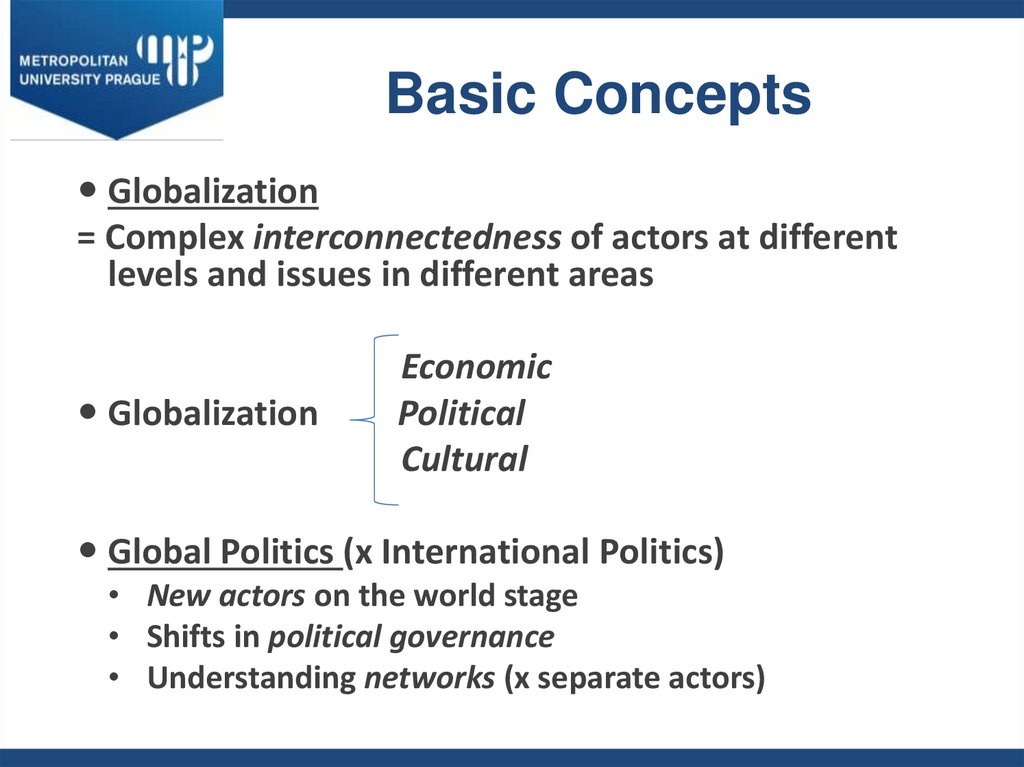
4. Basic Concepts
Globalization= Complex interconnectedness of actors at different
levels and issues in different areas
Globalization
Economic
Political
Cultural
Global Politics (x International Politics)
• New actors on the world stage
• Shifts in political governance
• Understanding networks (x separate actors)
5. Globalisation Theories
Understanding global politicsTheoretical responses
Skepticism – Realism: states are still the most
important players
Support – (Neo) Liberalism: free market economy
and removal of barriers in free movement of people,
goods, capital, ideas etc.
Critiques – (Neo)Marxism, Feminism, Postcolonialism: divides in the global system, inequality,
systematic injustice
6. Global studies
Globalization as a dependent variable – causes• Transportation – free movement of people,
goods etc.
• Communication – free movement of ideas,
human thought
• Technical innovations – trade cooperation –
pressure for coordination – emergence of new
institutions
• Neoliberal market economy - progressing
development of economic integration
7. Globalization as an independent variable – effects
Positive+ Trade - access to
products and technologies
+ access to information
+ competition based
market
+ communication and
cultural exchange
+ dissemination of norms
Negative
-lack of regulation
-exploitation of workers
-extensive production and
consumption
-power shifted to
corporations
-environmental
degradation
-cultural assimilation
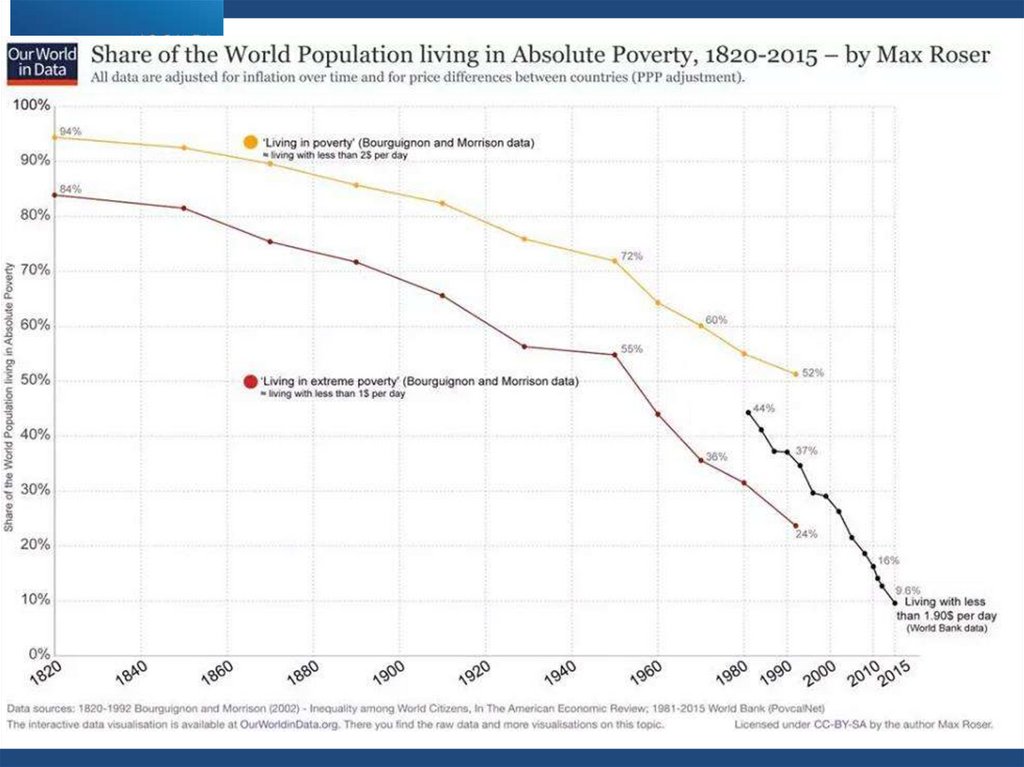
8. Global Issues: Inequality
Critical argument:„due to globalization, the
rich are getting richer
while the poor are getting
poorer!“
→ assess the argument
9.
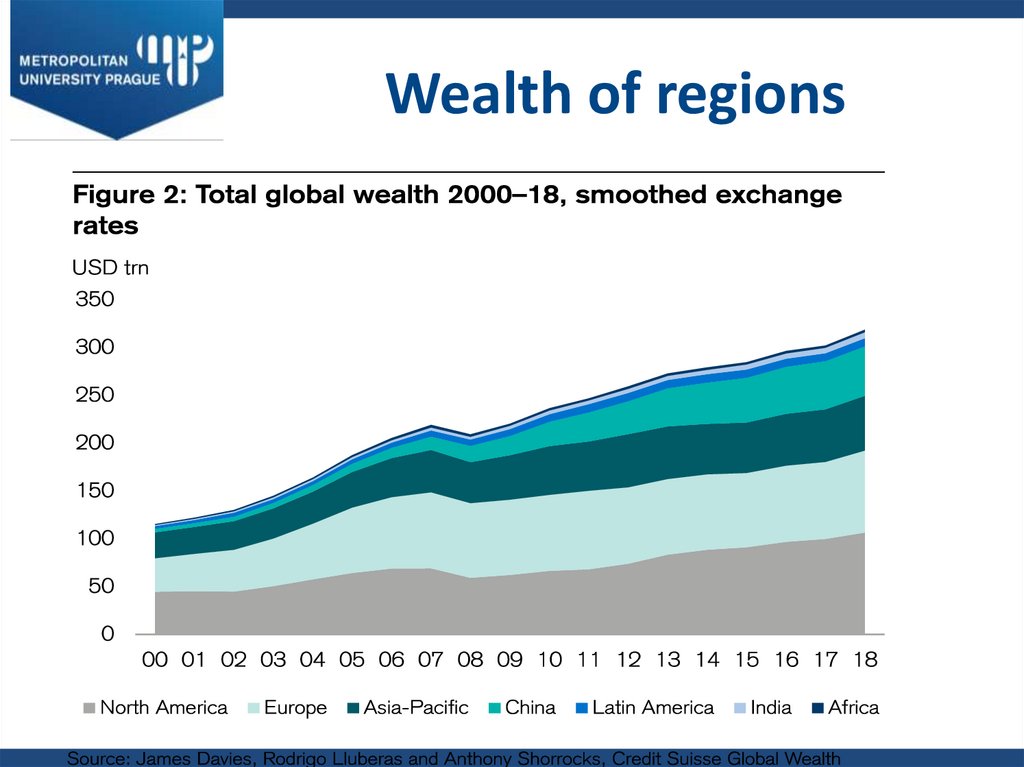
10. Wealth of regions
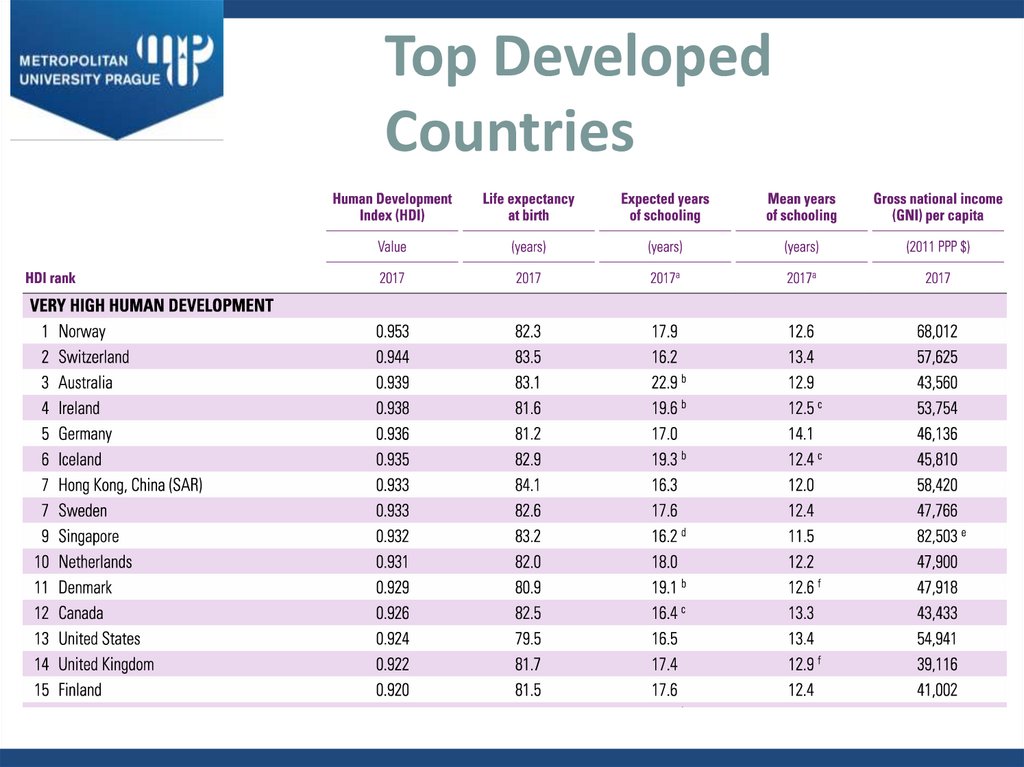
11. Top Developed Countries
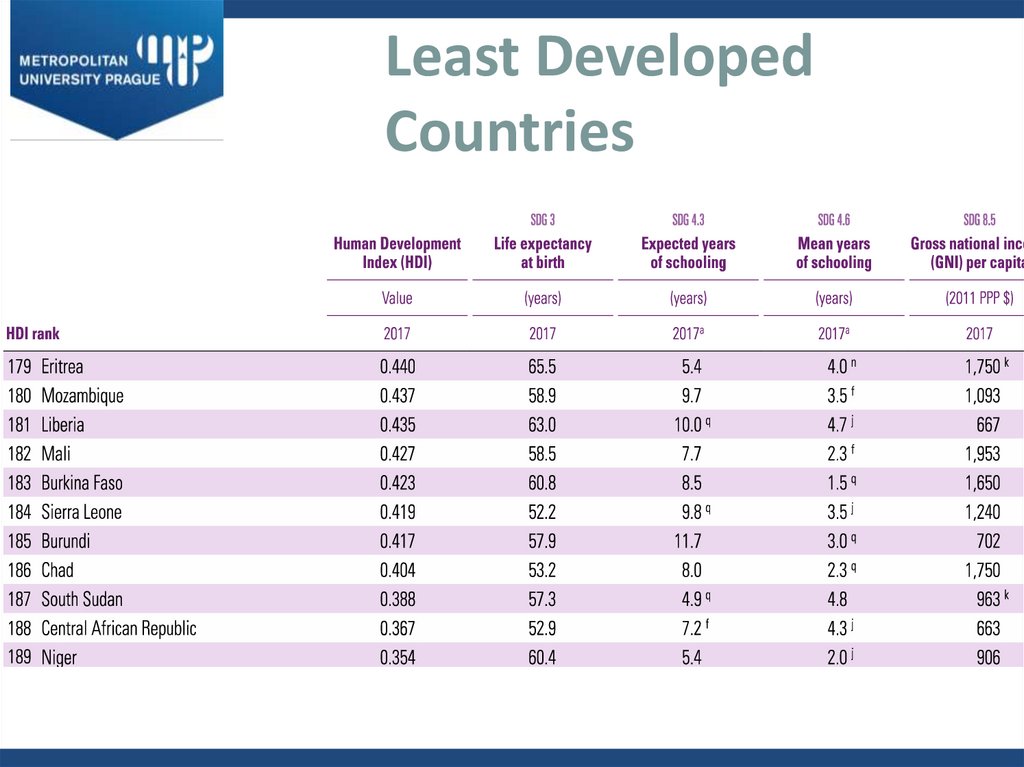
12. Least Developed Countries
13. Inequality based on GINI
14. Global issues in progress
Positive progress:Poverty
Life expectancy
Access to education
Inter-state conflicts
Constant issues:
Inequality
Global
Regional
Intra-state
New challenges:
Environment (increase in
pollution,
deforestation…)
Migration and internal
displacement
Regional spillover of
conflicts
Various forms of
trafficking
Spread of diseases
15.
Your global issuesClimate change (global warming, polution, envirnonment) 30 –
Poverty (6) - water issues – Unemployment (3) – US-China relations
- Refugee crisis, migration (4) – Hunger crisis, food security (5) Corruption (4) – The North-South issue (imperialist-opressed
countries) (4) – Terrorism (4) - Overconsumptions - Freedom of
speech – Capitalism – Woman's rights and gender equality (8) Increasing inequalities (3) - Russian war in Ukraine (5) – Lack of
education (3) – Survival of multilateralism (2) - Energy security –
Russian Imperialism and terrorism - Overpopulation- Animal
Rights – Pandemic deseases (3) - Biodiversity loss - Mental health Far-right sentiments in Europe – Dependence on technologies –
Discrimination of LGBT people (3)
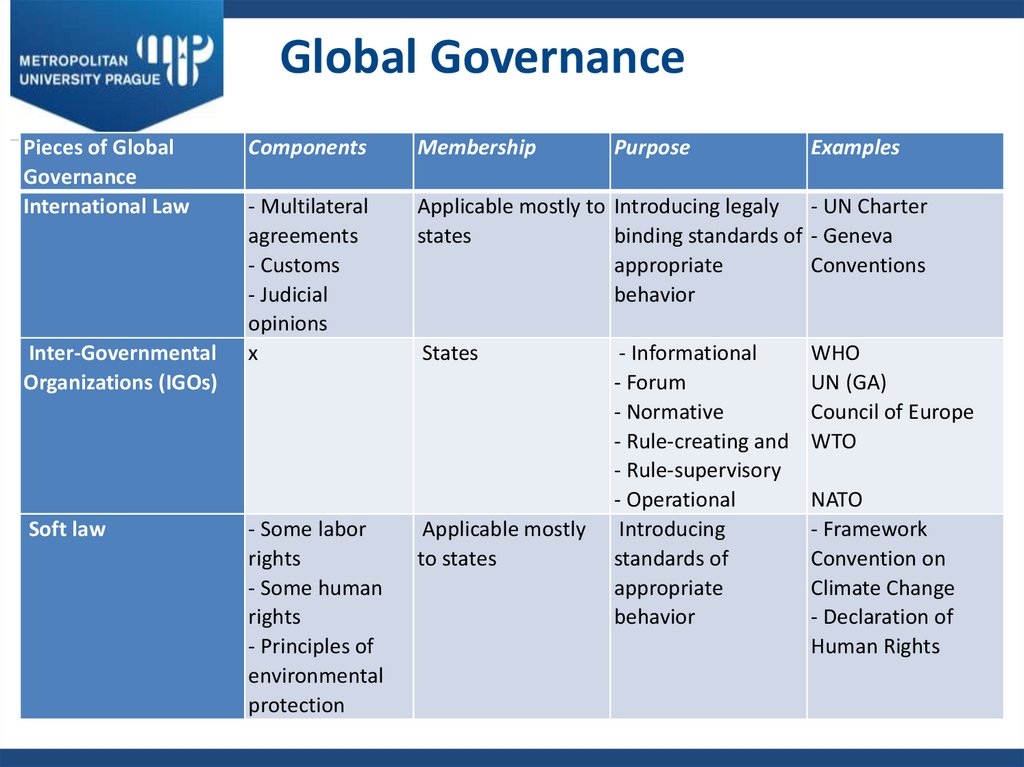
16. Global Governance
Pieces of GlobalGovernance
International Law
Inter-Governmental
Organizations (IGOs)
Soft law
Components
Membership
- Multilateral
agreements
- Customs
- Judicial
opinions
x
Applicable mostly to Introducing legaly - UN Charter
states
binding standards of - Geneva
appropriate
Conventions
behavior
- Some labor
rights
- Some human
rights
- Principles of
environmental
protection
States
Applicable mostly
to states
Purpose
- Informational
- Forum
- Normative
- Rule-creating and
- Rule-supervisory
- Operational
Introducing
standards of
appropriate
behavior
Examples
WHO
UN (GA)
Council of Europe
WTO
NATO
- Framework
Convention on
Climate Change
- Declaration of
Human Rights
17. Global Governance
Pieces of GlobalGovernance
Non-Governmental
Organizations
Components
Membership
Purpose
Examples
x
Individuals, activist
groups, nongovernmental
entities
- Advocacy
- Information
gathering and
dissemination
- Humanitarian
assistance
Managing an adhoc issues out of
the existing
structures
Amnesty International
Green Peace
Human Rights Watch
Enforcement of
existing rules
ICJ, ICC
ECJ, ECHR
Ad-hoc Arrangements Groups of States States
Tribunals
Individuals
Conferences
Global Conferences
x
States
(NGOs, Individuals)
International Courts
Int. Courts
Regional Courts
Jurisdiction over
states or over
individuals
International Regimes Prinicples,
States, IGOs, NGOs, Complex
norms, rules,
Courts, Individuals governance of a
decision-making
single issue
structures
(e.g. prohibition)
ICRC
G8
Non-Aligned
movement
ICTY, ICTR
Earth Summit
- Prohibition of
Genocide
- Nuclear NonProliferation
18.
19. Next week (3):
UN at CrossroadsReading: Fassbender
Homework (deadline 31. October midnight):
name and explain an issue, where the UN
contradicts interests of your country´s (or its
government) interests.













 policy
policy








