Similar presentations:
Introduction. System of International Relations after the collapse of the USSR. Topic 1
1.
Topic 1. Introduction. System of International Relations after thecollapse of the USSR.
The plan of the lecture:
Methodology of scientific research in social sciences
Defining system of international relations (IRs)
Brief overview of the history of system of IRs
Contemporary system of IRs
2.
Methodology of scientific research in social sciencesIn simple terms, a method is a way that you use
to understand or investigate something. For
example, when you write an essay, you may use
method of content-analysis, that is , you read a
book or article, analyze it (its content), and
decide whether it fits your topic of study. Or you
may just do copy+paste method but it is illegal.
What is
method?
3.
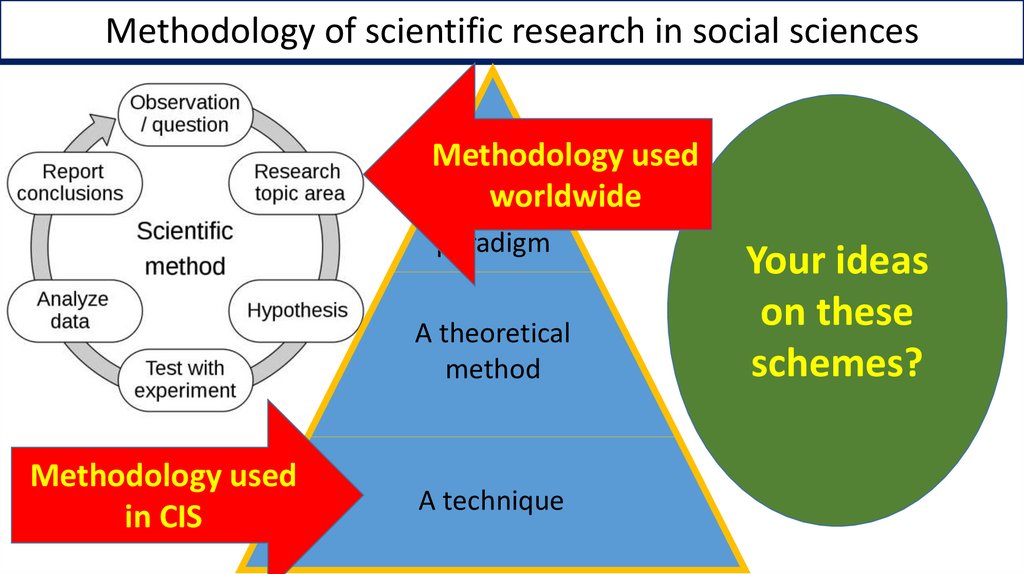
Methodology of scientific research in social sciencesMethodology used
Aworldwide
paradigm
A theoretical
method
Methodology used
in CIS
A technique
Your ideas
on these
schemes?
4.
Methodology of scientific research in social sciencesA paradigm ??
Can you give examples of
paradigms in IR?
A very broad set of
ideas, thoughts,
Political liberalism/idealism/institutionalism
believes, which try
to explain the
Political realism (now neorealism)
international reality.
To some extent,Marxism (now neo-Marxism)
Critical theory (post-theories – feminism,
paradigm = theory
postcolonialism, sometimes neo-Marxism)
5.
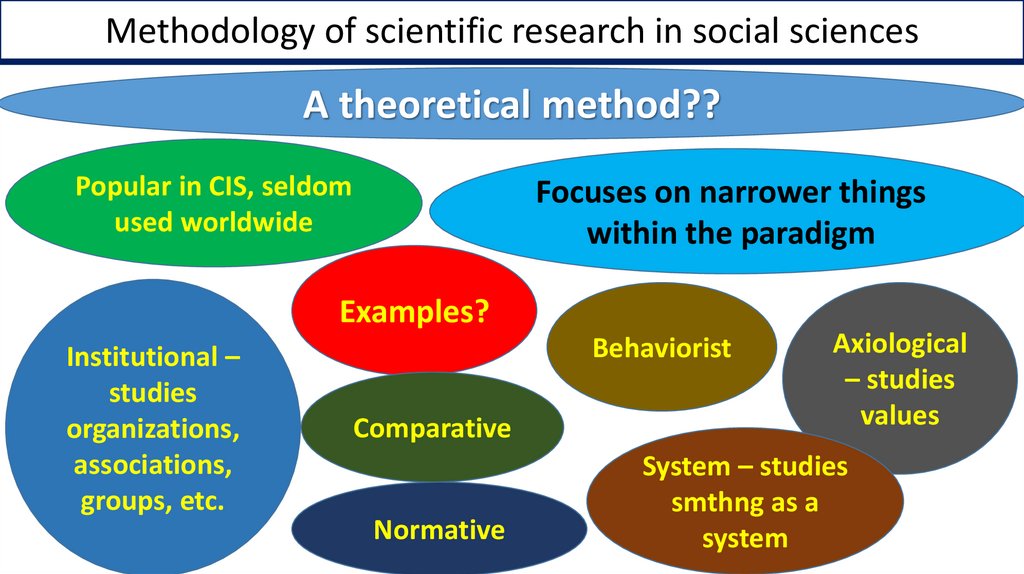
Methodology of scientific research in social sciencesA theoretical method??
Popular in CIS, seldom
used worldwide
Focuses on narrower things
within the paradigm
Examples?
Institutional –
studies
organizations,
associations,
groups, etc.
Behaviorist
Comparative
Normative
Axiological
– studies
values
System – studies
smthng as a
system
6.
Methodology of scientific research in social sciencesA technique??
Examples?
ASWOT
technique is a practical or empirical method for
collecting data.
Experiment
Survey
(interviewing)
Contentanalysis
Induction\Deduction
Survey
(questionnaire)
Observation
7.
Topic 1. Introduction. System of International Relations after thecollapse of the USSR.
System of international relations refers to the set of
economic,
cultural,
humanitarian,
security,
political
What is the
connections between state and non-state actors (TNCs,
system
of
global media, terrorist groups) based on treaties, regimes,
international
international
organizations, forums, summits and other
types of connection.
relations? Your
ideas?
8.
System of international relationsHow many systems
of international
relations do you
know in the history
of IR? What are
they?
1648. Ends the Thirty
Years’ War in Europe.
9.
System of international relationsVersailles-Washington system of international relations (1919-1939).
What else do you Key points:
1. Ended the World War I;
know
about
the
2. European empires were collapsed (Austria-Hungary, Russia);
system
ofwas broken – Germany must stay restricted in
3. Balance
of power
territorial claims, military power and economic growth;
international
4. France
and
Great
Britain
dominated
in
European
and
colonial
affairs;
relations? Which is
5. New “alien” communist state emerged – the USSR;
the next?
6. Germany wished vengeance.
Hint: What peace treaties
7. The League of Nations – the first multilateral
did endorganization.
the WWI?
10.
System of international relationsYalta-Potsdam system of international relations 1945-1991.
Key points:
1. Bipolar system: two great powers emerged: the USA and the USSR. They
created two blocks of their supporters: capitalist and socialist;
2. Both blocks were institutionalized: NATO (1949) and the Warsaw Pact (1955);
3. The League of Nations collapsed. The United Nations Organization (UNO)
emerged;
4. The “Cold war” – tough competition between two great powers and two
blocks in economy, security, culture, ideology, politics;
5. Constant local conflicts – proxy wars of theHint:
USA and
USSR
in picture
the regions
whatthe
does
this
(Korea, Vietnam, Cuba,
etc.);
symbolize? The end of what
6. Indisputable value of human life -> human rights, ethnic, gender, race
event?
equality (The Universal Declaration of Human Rights 1948).
7. De-colonization;
How many
8. systems
Acknowledgement
didn’t we that war is awful tool to
be used
in international politics;
mention:
one,
two,
three, more?
9.
Treaties,
pacts, agreements formed the
Your ideas? system.
11.
System of international relationsScholars don’t have common consent about the post-YaltaPotsdam. Contemporary system of international relations does
not have
even name.
Some call it “Post-Westphalian”, some –
Yalta-Potsdam
system
just collapsed
“Contemporary”,
in 1991some
after – “Post-bipolar” or “Post-Cold war
Some
identify it as “multipolar”.
the USSRera”.
broken
down.
Anyway, let’s figure it out.
What’s now?
OR
Is there any system? Or
do we live in anarchy?
?
12.
Contemporary system of international relationsIt can be divided into 3 or more stages:
2009-2014(?) –
2001-2008
(?) – Crimea
– accession
(in
economic
and
1991- 2014-2021
discourse)toor annexationfinancial
(in
2001 – Russian attempts
cooperate
and American
against discourse)
to rise of
problems,
the US European
(by)
Russia,
new
threat:
rising
contradictions,
non-state actors,
“unipolar
serious
international
problems
in
the
regime
of
continued
moment”.
strategic
terrorism
arms control. contradictions.
13.
Contemporary system of international relationsThe “Unipolar moment”, “The end of history”
(1992), “The clash of civilizations” (1993).
FrancisCharles
Fukuyama
(American(American
political scientist)
Krauthammer
political
Samuel
Huntington
(American
political
(1952).
His idea: communism
failed
in after
the Cold
columnist)
1950-2018. His
idea:
the
scientist)
His
idea:
war, as
its 1927-2008.
leading
the
USSR
broke
down.
collapse
of thepower
USSR,
the
USAFukuyama
remained
the
was
conflicts
Thewrong.
history
stopped
developing,
asinternational
conflicts
and
onlyFurther
super power
in thein
world.
Not any
relations
would
occur
between
contradiction
the only
drivingcivilizations,
force.
Liberal
statewere
was
equal
in economy,
military
democracies,
onHe
behalf
of the
won the
race.
cultural
influence,
ideology,
political
notpower,
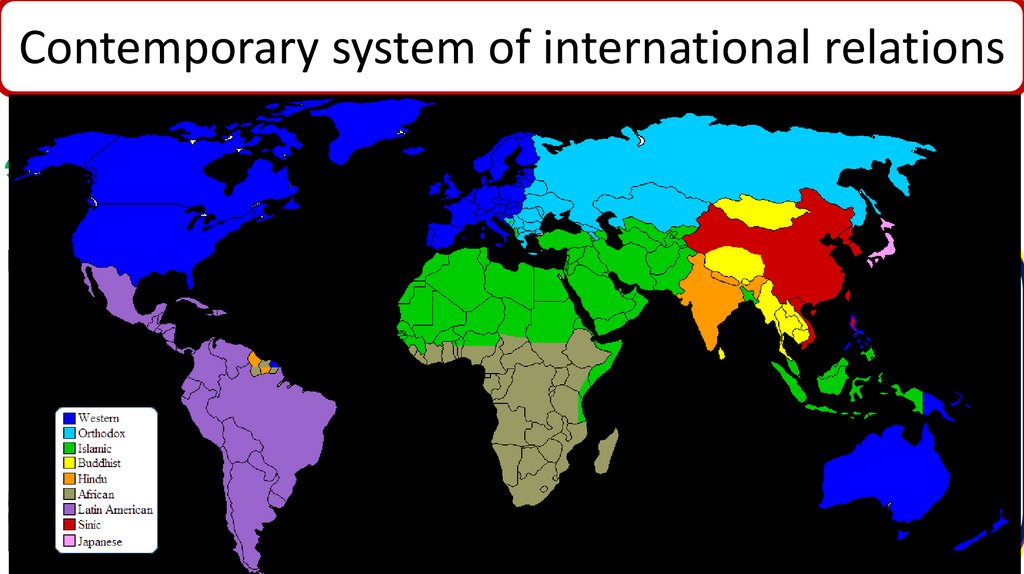
states.
offered
9 USA,
civilizations:
The world
became Islamic,
more
liberal
and identical
influence.
Western,
Orthodox,
Buddhist,
Hindu,
because
“new states”
– CIS, Russia,
Eastern
TheLatin
world
was UNIPOLAR,
ONE
pole
African,
American,
Sinic,i.e.,
Japanese.
Europeexisted,
– declared
that democracies.
was the USA.
14.
Contemporary system of international relationsScientific discourse in 2000’s
2002
2008
The
Russia
USA
AlexeyHaass
Bogaturov
(Russian
political
scientist)
Richard
(American
diplomat)
1951.
His idea:
1954. His
idea:Since
pluralist
of
non-polar
world.
manyunipolarity
non-state actors
international
relations.
It means that
the pole
is
become influential
in international
relations
(TNCs,
concentrated
in the
USAterrorist
and G7.groups,
Literally,
it
global
media, social
media,
NGOs),
unites
liberal
democracies
capitalist
states
are not
the only
actors anyand
more.
That’s why
the pole is absent.
The power
is dispersed
among
economies.
However,
they are
more than
one.
many-many
with
leader orworld.
leaders.
That’s whyparticipants
it’s pluralist
butnounipolar
15.
Contemporary system of international relationsGeneral characteristics
1. Globalization;
2. Few rules to play – vanishing of international law, doubting the role of UN
6. The East rises. Top-10
by GDP
purchasing power parity
Security
Council;
Small
observation:
(PPP)
in
2020:
China,
the
USA,
India,
Japan, Germany,
Russia,
3. Non-state actors compete with states.
Terrorists
(September
11), social
Did you
noticeBrazil,
that the
each
system
of
international
Indonesia,
France,
UK.
5
of
10
are
former
media (boycott of D. Trump after elections
ofcolonies,
2020);
relations
changed
as a and
result
great
catastrophe
ex-developing
states,
areof
part
of the
Global East –of(the
4. Crisis of global leadership. Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) do not
Global South;
world) war? The Westphalian
resulted from the Thirty
lead in IRs. The USA looses and tries to give back its influence. Neither China
7. FakeWar;
newsthe
compete
with normal news. It– changes
foreign
Years’
Versailles-Washington
from
the
WWI;
nor Russia, nor the EU can
compete
with
the USA for global leadership;
political
tactics
of
states.
the poles?
Yalta-Potsdam
– discourse
from the –WWII.
Contemporary
5. How many
American
the
US-led
world
=> unipolar.
8. system
Post-reality
(post-truth,
post-irony),
changes
in
values
is the participant
only whichshould
emerged
as
a result
of developed =>
Russian discourse
–
every
get
chance
to
be
(sexual minorities compete with majority for
breaking down
of one of Or
its non-polar?
participants (not war).
multipolar.
acknowledgement).
16.
ConclusionHome
assignment
Be prepared for SWOT-analysis of the foreign political position of the
RK at the beginning of its independence (1991-1995), and then in
1996-2001, 2001-2008, 2009-2014, 2014-2022.
Can you sum
SWOT-analysis
matrix
up all this?
Strength. What was
done well?
Weaknesses. What was
needed to be improved?
Opportunities. What are Threats. What obstacles
does KZ face?
the goals?













 policy
policy history
history








