Similar presentations:
Ketoacidotic. Hypoglycemic State
1.
KetoacidoticHypoglycemic State
z
Кумар
Кишор
406и
2.
zWhat is Diabetic Ketoacidosis ?
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious
complication of diabetes that occurs
when your body produces high levels of
blood acids called ketones.The condition
develops when your body can't produce
enough insulin.
It is a life-threatening problem that
affects people with diabetes. It occurs
when the body starts breaking
down fat at a rate that is much
too fast.The liver processes the fat into
a fuel called ketones, which causes the
blood to become acidic.
3.
zKetoacidotic
Hypoglycemic state
Hypoglycemia is a condition where the blood glucose levels
are too low. The most common cause for hypoglycemia is
diabetes medication. This is because too much insulin or
medication to reduce blood sugar may drop levels too far,
causing hypoglycemia.
Below normal glucose levels (< 45 mg/dL, but symptoms
start at 60 mg/dL)
-Counter regulation starts at 67 mg/dL
-Normal blood level 80-90 mg/dL
4.
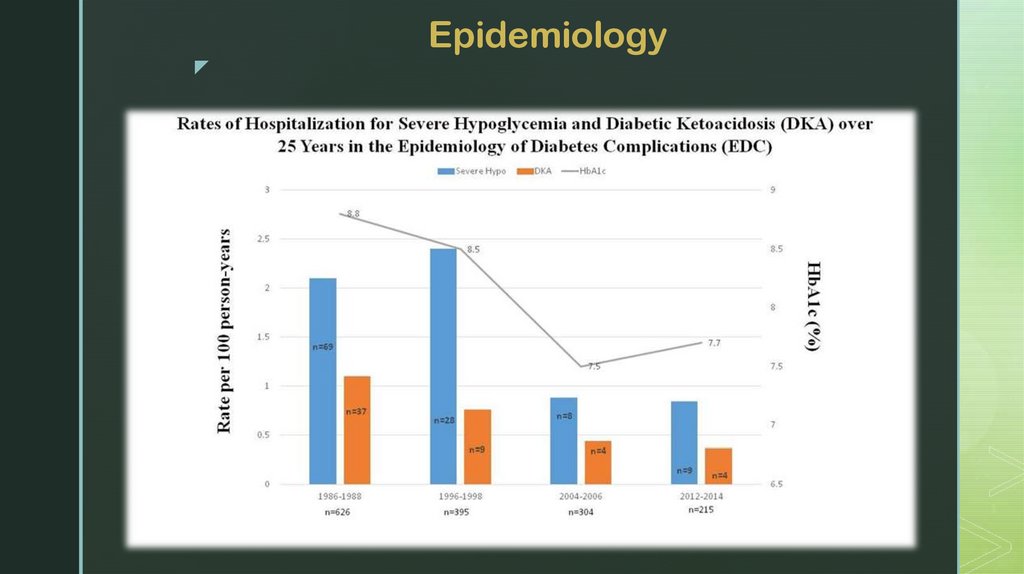
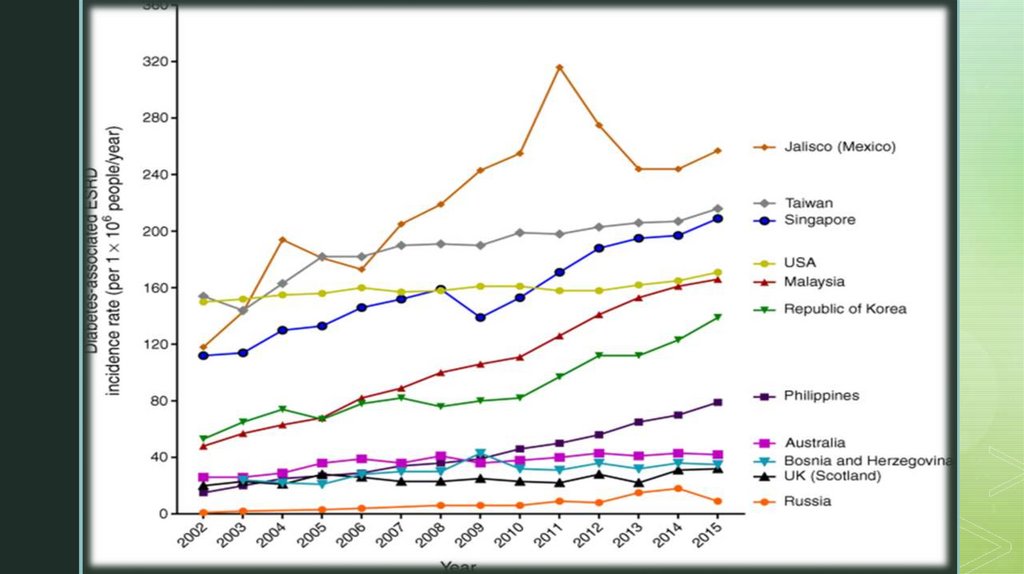
Epidemiologyz
5.
z6.
zActual Pathophysiology Of Diabetic
Ketoacidosis
7.
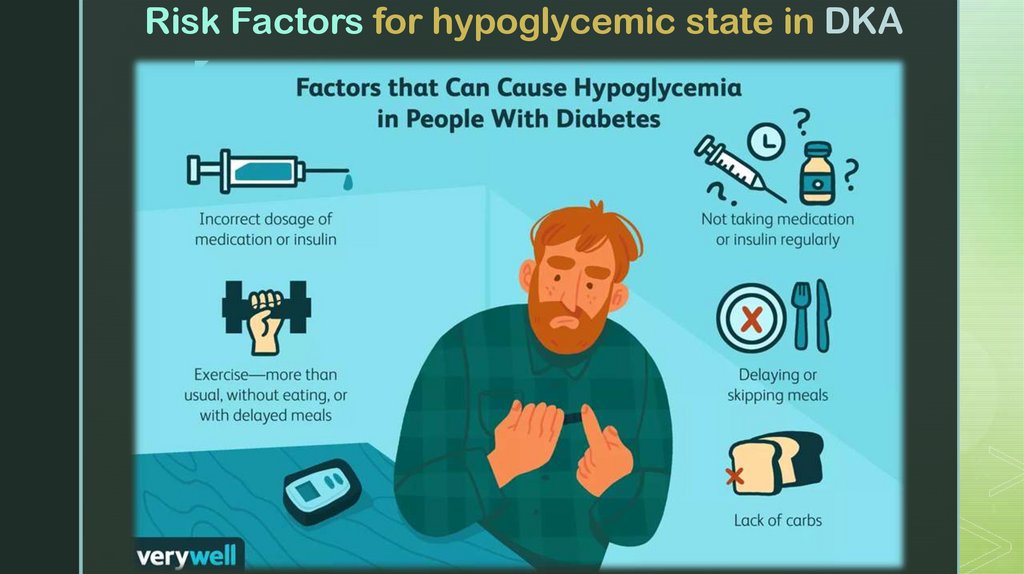
Risk Factors for hypoglycemic state in DKAz
8.
zWhat happens if you take insulin incorrectly?
Incorrect administration of insulin (e.g., too
little, too much, or at the wrong times) can
result in both transient and serious hypoand hyperglycemia, wide glycemic
excursions, severe hypoglycemia, and
DKA.
9.
zSymptoms
Signs and Symptoms Of severe
Hypoglycemia in DKA
If blood sugar levels become too low, signs and symptoms can include:
An irregular or fast heartbeat
Fatigue
Pale skin
Shakiness
Anxiety
Sweating
Hunger
Irritability
Tingling or numbness of the lips, tongue or cheek
As hypoglycemia worsens, signs and symptoms can include:
Confusion, abnormal behavior or both, such as the inability to complete routine tasks
Visual disturbances, such as blurred vision
Seizures
Loss of consciousness
10.
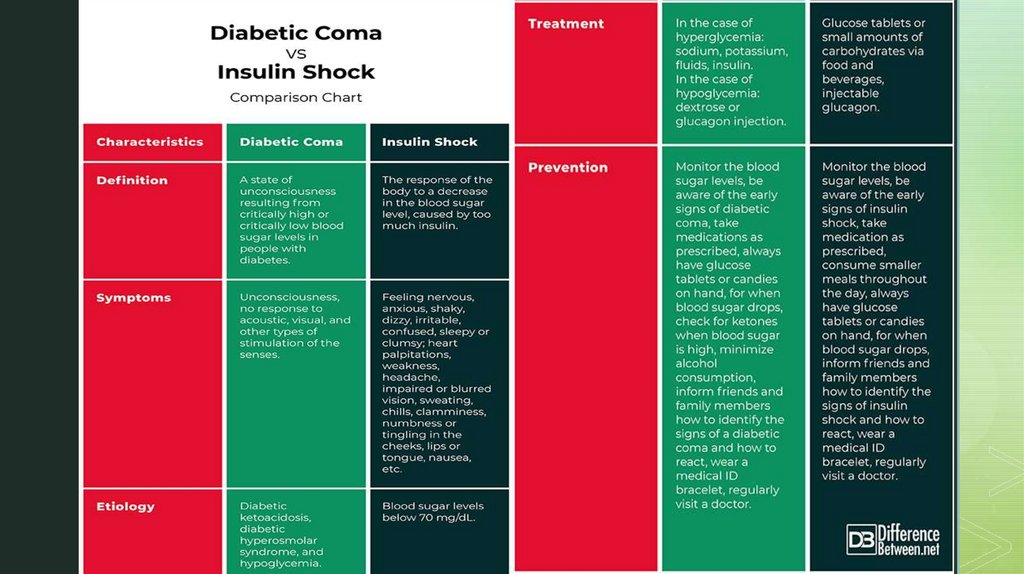
Diabetic Comaz
Diabetic coma is a life-threatening
emergency that can affect you if you
have diabetes. In a diabetic coma,
you are unconscious and unable to
respond to your environment. You are
either suffering from high blood
glucose (hyperglycemia) or low blood
glucose (hypoglycemia). You need
immediate medical attention if you go
into a diabetic coma.
During Severe Hypoglycemic state
in diabetic ketoacidosis, which is
more common in people with Type 1
diabetes, it includes life threatening
condition when:
- blood sugar as low as 250
mg/dL or even lower in some cases.
-body uses fatty acids instead of
glucose for fuel.
-Ketones develop in your urine and
bloodstream.
11.
zDiabetic coma Death
Hypoglycemic Coma
Hypoglycemia occurs predominantly in
patients taking insulin but also in patients
taking sulfonylureas, particularly longacting preparations such as
chlorpropamide and glibenclamide. The
factors which commonly predispose to
hypoglycemia, either alone or in
combination, are:
too much insulin or sulfonylurea
too little food or delayed meal
too much physical exercise.
Hypoglycemic coma was defined as a state in which
the patient was not arousable (or responded only to
pain), with a blood glucose concentration of 2.72
mmol/L (49 mg/dL) or less, and responded
symptomatically (a return of consciousness) to the
administration of intravenous glucose.
12.
Emergencytreatment of Diabetic
z
coma (due to Hypoglycemia)
If the blood sugar level is lower than 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L),
give the person an injection of glucagon. Do not try to give
fluids to drink and do not give insulin to someone with low
blood sugar.
If the blood sugar level is above 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L) wait
for medical help to arrive. Don't give sugar to someone whose
blood sugar isn't low.
13.
z14.
z15.
zTHANK YOU !!
FOR
YOUR ATTENTION











 medicine
medicine








