Similar presentations:
Political Values and Political Ideologies
1.
POLITICAL VALUES ANDPOLITICAL IDEOLOGIES
Підготували Завірюха Аліна, Погорелюк Ліза,
Зінько Лєна
2.
POLITICAL VALUESValues determine the specifics of human behavior and
policy choices. An active attitude of the individual to
politics is formed on the basis of values.
Political values are defined as the preferred recognition
by the subjects of politics (individuals, groups, classes,
nations) of the significance of certain phenomena,
processes and norms of political life, as enshrined in
their socio-political experience. They motivate, direct
and substantiate the action of the subjects of politics,
reflect the state, needs and prospects for the
development of society, its main social groups.
3.
The main political values include: humanrights, the nature, principles and forms of
the political structure and development
of society, its political institutions, ideas,
the participation of an individual in
politics, the expression and realization of
his interests, the culture of politics.
Political values can be universal,
national, but can also reflect the interests
of various classes, groups of people and
individuals.
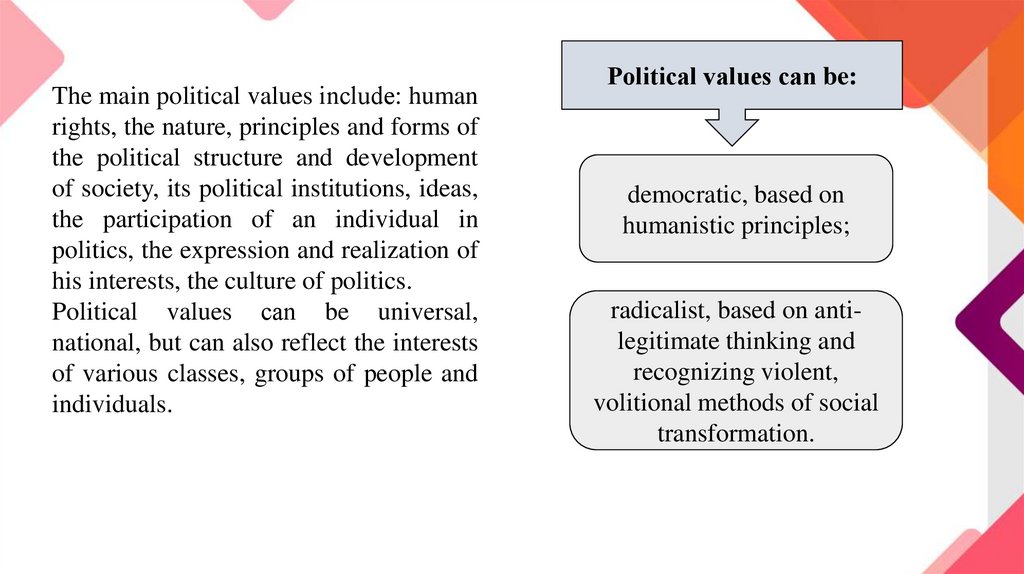
Political values can be:
democratic, based on
humanistic principles;
radicalist, based on antilegitimate thinking and
recognizing violent,
volitional methods of social
transformation.
4.
POLITICAL IDEOLOGIESPolitical ideology is a clearly
formed system of values, focused
on the expression of political
interests, the basis for formulating
the goals of political action.
The main goals of political
ideology are: first, mastery of public
consciousness;
secondly,
the
introduction into it of their value
assessments, goals and ideals of
political
development;
third,
regulation of citizens' behavior based
on these assessments, goals and
ideals
5.
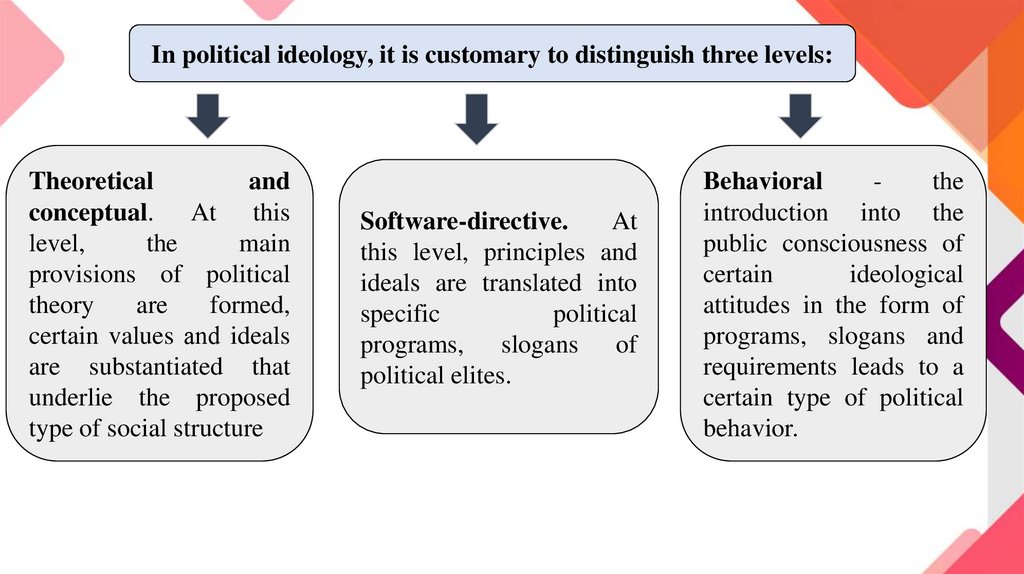
In political ideology, it is customary to distinguish three levels:Theoretical
and
conceptual. At this
level,
the
main
provisions of political
theory
are
formed,
certain values and ideals
are substantiated that
underlie the proposed
type of social structure
Software-directive.
At
this level, principles and
ideals are translated into
specific
political
programs, slogans of
political elites.
Behavioral
the
introduction into the
public consciousness of
certain
ideological
attitudes in the form of
programs, slogans and
requirements leads to a
certain type of political
behavior.
6.
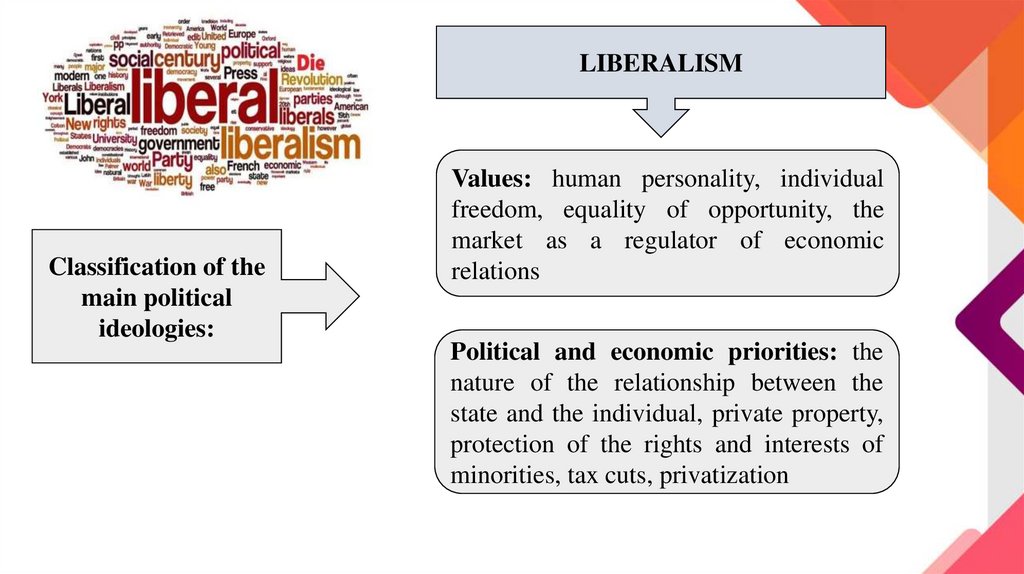
LIBERALISMClassification of the
main political
ideologies:
Values: human personality, individual
freedom, equality of opportunity, the
market as a regulator of economic
relations
Political and economic priorities: the
nature of the relationship between the
state and the individual, private property,
protection of the rights and interests of
minorities, tax cuts, privatization
7.
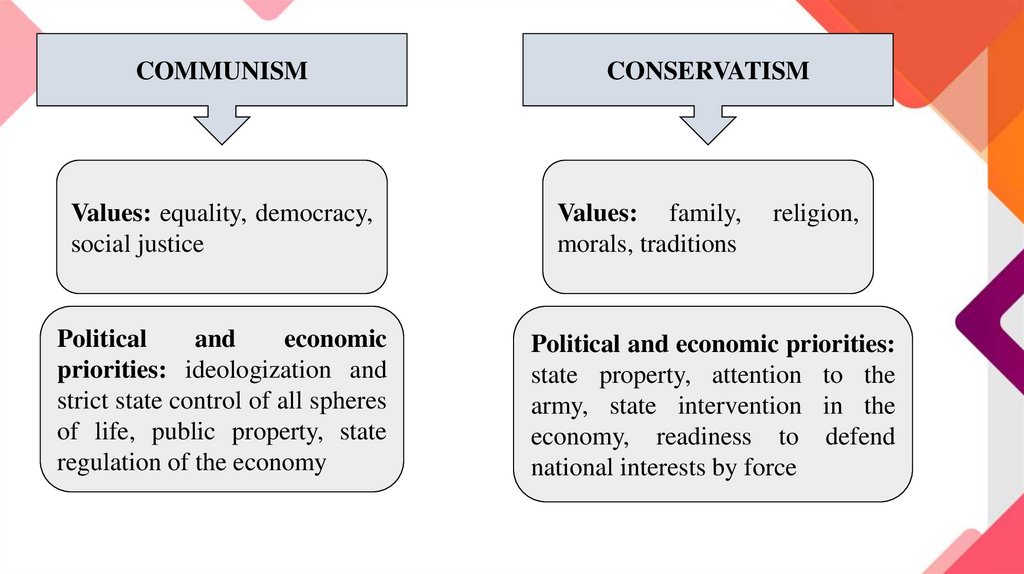
COMMUNISMValues: equality, democracy,
social justice
Political
and
economic
priorities: ideologization and
strict state control of all spheres
of life, public property, state
regulation of the economy
CONSERVATISM
Values: family,
morals, traditions
religion,
Political and economic priorities:
state property, attention to the
army, state intervention in the
economy, readiness to defend
national interests by force
8.
FASCISMValues: nation, race
Political
and
economic
priorities:
nationalism,
eviction of emigrants, priority
of
the
military-industrial
complex
9.
Types ofideologies by
methods of
political struggle:
1. Radicalism is a drastic change in existing
social and political institutions. It manifests
itself in crisis, transitional historical periods,
when there is a threat to the existence, traditions
and way of life of certain strata and groups.
2. Left-wing radicalism - (anarchism, marxism)
preference for quick and drastic ways to achieve
social equality and social justice.
3. Right-wing radicalism - (fascism, neofascism, forms of nationalism and religious
intolerance, racism) is based on the idea of the
superiority of any group (racial, national, social,
religious) over all others




 policy
policy








