Similar presentations:
Stages of development. The age of hellenism
1.
2.
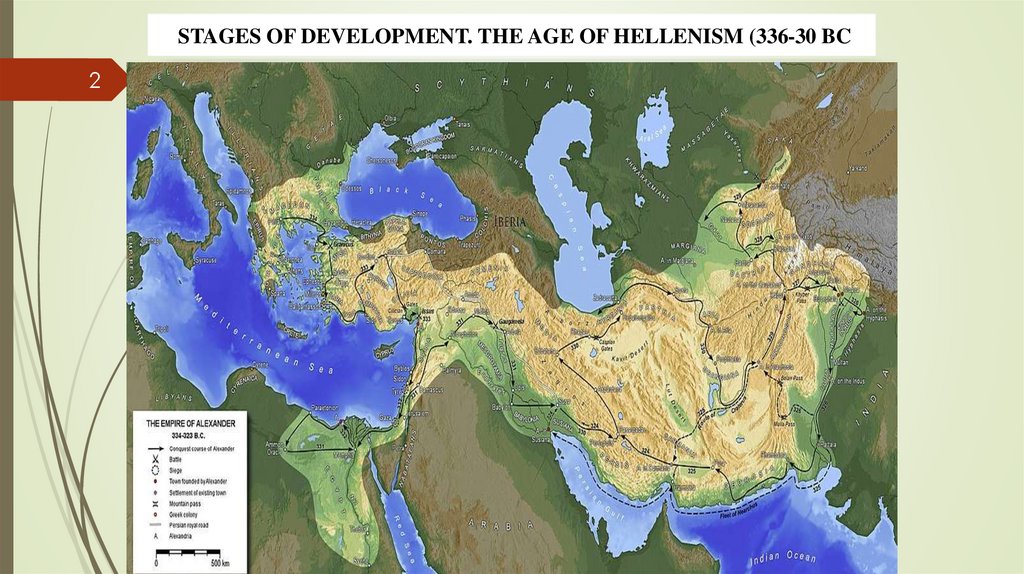
STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT. THE AGE OF HELLENISM (336-30 BC2
3.
Aristotle Gymnasium4.
ВИ––3.2.4.2.4.4.Древняя
Средиземноморье.
Ханаан.
ВИ
Греция. Этапы
развития. Эпоха эллинизма (336-30 гг
ADVANCED MINDS OF THE HELLENISTIC WORLD
до н.э.
4
Archimedes of Syracuse (287-212 BC)
Mathematician. He laid the foundations of
mechanics and became famous for his inventions,
especially in the field of military equipment .
Euclid (III century BC) Mathematician.His treatise
"Principles"(i.e., "elements") was used as a
textbook on geometry until the twentieth century.
Epicurus of Samos (341-272 BC) was
anoutstanding philosopher of his time. He created
his own system of views on the world around him
5.
Scientific achievementsThe scientific achievements of ancient Greece were associated with
philosophy.Thales discovered a number of properties of the triangle and
circle, for the first time determined that amber, rubbed with matter, attracts
light objects, discovered the attraction of iron filings by some ores. He
believed that the Moon shines not by its own, but by reflected radiation; he
pointed to the North Star and the constellations that are important for
navigation.
Pythagoras founded the school that laid the foundation for the
teaching of the Universe, subject to the laws of "harmony and number".
Aristarchus of Samos proposed a hypothesis about the rotation of the
spherical Earth around the Sun. Plato's concept of the cosmos is a classic
one in ancient science.
The system of knowledge collected and systematized by Aristotle served as
the backbone of science for almost two thousand years.Hippocrates-the" father
of medicine", summarized the practical experience of treating patients,
developed methods for diagnosing and describing many diseases, Eudoxus of
Cnidus calculated the orbits of the planets, compiled a catalog of the starry sky,
created the first astronomical observatory. Ancient Greek philosophers first gave
definitions
6.
MATERIAL CULTURE OFANCIENT GREECE
Agriculture, viticulture and horticulture, cultivated cereals, oilseeds, etc. cultures.
Olives, olive oil, wine were one of the main products of commodity exchange, and
then trade. Animal husbandry was practiced.
The cities developed handicraft andhandicraft production, including mining and
metallurgy, ceramic and textile production, construction, shipbuilding and related
crafts.
Greek builders and architects laid the
foundations for the practice of building
various structures (temples, piers,
palaestras, residential buildings,
warehouses, water supply and sewerage).
7.
Religion. MythologyGreek mythology is not only the world of religious ideas, it is the world of the
Greeks, it is a complex and vast whole, which includes historical legends, legends,
fairy tales, literary novels, free variations on mythological themes. These diverse
elements are hardly distinguishable from each other.
The mythological personifications of the elements of the earth's nature were of
great importance. The Greeks inhabited all nature with divine beings: in the groves lived
dryads, nymphs, goat-footed satyrs; in the sea-naiads and sirens (birds with the heads of
women).
8.
The ideological basis of thespiritual life of the ancient Greeks
was anthropomorphic polytheism
and mythology.
9.
Ancient Greek gods in the periodof classical Greece (5-4 centuries
BC) were sculptures of beautiful
harmonious people
10.
The Greeks did not have a fixedform of mythological tales. The
stories of myths were transmitted
in drawings of vase paintings, on
vessels, tombstones, on the walls
of temples, etc. They lived in
stage works, retellings, songs, and
ritual actions. This gave rise to a
free attitude to the content of
myths and even criticism of the
gods.
11.
Zeus is the RomanJupiter.God of the sky
and thunder, head of the
ancient Greek
Pantheon.Attributes:
One-tooth, eagle,
lightning.
12.
Poseidon is the sonof Cronus and Rhea,
and the brother of
Zeus and Hades. God
of water, seas and
oceans, as well as
earthquakes. The
Isthmian Games were
held in his
honor.Attributes:
trident, horse.
13.
Hades is sometimesfound under the
names of Pluto or
Hades, and among
the Romans under
the names of Orc or
Dit.The lord of the
underworld of the
dead.Attributes:
three-headed dog
Cerberus (Kerber),
two-pronged. The
wife is Persephone
(Proserpine).
14.
Athena is also found underthe name Pallas, among the
Romans Minerva.Goddess of
wisdom, just war, patroness
of the cities of Athens,
crafts, sciences.Attributes:
owl, snake. Dressed like a
warrior. On the chest is an
emblem in the form of the
head of a Medusa-Gorgon.
Born from the head of Zeus.
15.
Aphrodite akaCypros, in Rome —
Venus.The goddess
of love and
beauty.Attributes:
belt, apple, mirror,
dove, rose.
16.
Apollo akaPhoebusGod of the
sun, light, and
truth, patron of the
arts, sciences, and
healing, god of
divination.Attribute
s: laurel wreath,
bow and arrow.
17.
Ares the Romanshave MarsGod of
bloodthirsty, unjust
war.Attributes:
Helmet, sword,
shield.
18.
Artemis in the RomanDiana.Goddess of the
moon and hunting,
patroness of women in
labor.Attributes: quiver
with arrows, doe.
19.
Dionysus is alsoknown as Bacchus,
by the Romans as
Bacchus.God of
viticulture and
winemaking,
agriculture. Patron
of the
theater.Attributes:
a wreath of vines, a
cup of wine.
20.
Hephaestus is aRoman Volcano.God
of blacksmithing,
patron of all artisans
and fire. The wife is
Aphrodite.Attributes:
pliers, blacksmith's
furs, pylos (a
craftsman's cap).
21.
Hera in the RomansJuno.The goddess is
the patroness of
family and marriage,
the wife of
Zeus.Attributes:
single-tooth, tiara..
22.
Боги ГрецииThe main gods of the Greek pantheon are:
Zeus, Hera, Poseidon, Athena, Artemis,
Apollo, Hermes, Dionysus, Asclepius, Pan,
Aphrodite,
Ares,
Hestia.According
to
Hephaestus,
ancient
Greek
mythology, the supreme god was Zeus, the
goddess of hunting – Artemis, the god of
trade-Hermes.A characteristic
ancient
Greek
feature
religion
of
was
anthropomorphism - the deification of man,
the idea of the gods as strong, beautiful
people who are immortal and have eternal
Боги Олимпа
youth. The gods lived, according to the
Greeks, on Mount Olympus.
23.
The Delphic Oraclethe oracle at the temple of
Apollo at Delphi [located at
the foot of the southern slope
of Mount Parnassus in
Phocis.According to ancient
Greek mythology, it was
founded by Apollo himself on
the site of his victory over the
monstrous serpent Python. The
Delphic oracle, where the
priestess (Pythia) was nominally
the main person, but in fact all
the predictions were
formulated by the priests of
the temple who interpreted
her, was one of the main
diviners in the Hellenic world.Its
appearance is attributed to
the Mycenaean time, and the
final disappearance - to the IV
century AD, the heyday of the
oracle falls on the VII-V
centuries BC. e. archaic and
classical periods of the history
of Ancient Greece.
24.
The Greeks believed that it waslocated in Delphi on Mount
Parnassus, where the temple of
Apollo, where the high priestess
Pythia lived, was located. As she
sank into a state of ecstasy, she
called upon the god Apollo to
predict the future. There were
other oracles in the Greek world,
but the Delphic one was the most
important.
25.
Written languageThe ancient Greek script is
based on the Phoenician script. By
the end of Hellenism, writing was
entering the everyday life of the
ancient world. Knowledge in
Greece, unlike in Egypt, was not
sacred
(transmitted
only
to
initiates).
26.
Literature and theaterГомер
Homer is one of the founders of Greek and European literature.
The Iliad and the Odyssey are epic poems attributed to Homer, the
oldest surviving monuments of Greek literature. The basis for them
was the numerous legends of Ancient Greece about the exploits of
ancient heroes.
The work of Hesiod, who wrote the poems "Theogony" (i.e., the genealogy of the gods)
and "Works and Days", and lyrical poetry (Archilochus, Sappho, Alcaeus, Anacreon,
etc.) belongs to the VIII century BC.
Рукопись «Илиады»
V век
Одиссей в пещере
Полифема
27.
TheatreOne of the most remarkable phenomena of ancient Greek culture is the theater. It originated on
the basis of folk songs and dances during the holidays in honor of the god Dionysus.From the
ritual songs that were sung while wearing goatskins, tragedy was born (tragos-goat, ode-song);
from mischievous and cheerful songs, comedy was born.
Theatrical
performances
were
considered a school of education, and the
state paid great attention to them. The
performances were held several times a
year on major holidays and lasted for
several days in a row. 3 tragedies and 2
comedies were staged.During the heyday
of Greek culture (VI-V centuries. the most
outstanding Greek tragic poets, classics of
not only Greek, but also world literature,
lived and worked in Athens.
Театр Древней Греции
28.
Classics of comedy and tragedyAeschylus is rightly considered the father of all European tragedy
for his immortal works ("The Seven Leaders", "Prometheus",
"Oresteia", "The Persians").
Sophocles-the main creator of tragedies for the Greek theater
("Oedipus the King"," Electra", etc.)
Euripides-the ancient Greek playwright, the author of "Medea",
Эсхил
Софокл
"Hippolytus", "Iphigenia in Aulis".The classic and "father" of
Greek comedy is Aristophanes, who wrote comedies: "The
World", "Women in the People's Assembly", "Horsemen", etc
Аристофан
Еврипид
29.
Ancient Greek architectureThe leading architectural structures of classical Greece were temples, theaters, and
public buildings. But the main architectural structure is the temple. The most
famous examples that have survived to our time in the Acropolis of Athens are the
temples of the Parthenon and Erechtheion.
Styles in ancient Greek architecture
changed
successively:Doric,IonicCorinthian.A
distinctive feature of these styles is the
shape of columns - an indispensable
attribute of ancient Greek buildings.
Главный храм Древних Афин - Парфенон
30.
Ancient Greek sculptureGreek sculpture was originally inferior to
that of the ancient East. But since the V
century BC, it has reached an unprecedented
flourishing. It conveys not only the figure
and face, but also the movement and even
the feelings of the people depicted.Sculptors
of particular renown and fame were Myron,
Polycletus, Phidias, Praxiteles, Scopas, and
Lysippus.
Мирон. «Дискобол»
Скульптура ранней классики
31.
Painting of Ancient GreeceAncient Greek painting .Red-figure and black-figure vases
Painting was widespread in ancient Greece in the form of frescoes
and mosaics that adorn temples and buildings, but they have almost not
survived to our time.Examples of surviving paintings include the
famous Greek black-figure and red-figure vases.
32.
How did the Greeks imagine theThe world - "cosmos" - was world?
understood by the ancient Greeks as an
animated, beautiful spherical body inhabited by people and gods. The
basis of the worldview was mythology, which has passed a long way of
development
33.
"Man is the measure of all things!»Protagoras
At the heart of ancient Greek culture lies, first of all, the development
of a free person as a fully developed personality, involved in solving
public affairs, engaged in mental activities: philosophy, mathematics,
music, poetry, politics, receiving fame and respect in return, and
hardening physically as a result of sports. Ancient culture was
characterized by anthropocentrism – "man is the measure of all
things".Beautiful Greek statues of steelthe standard of the beauty of the
humanbody, Greek philosophy – themodel of the beauty of the human
bodythinking.
34.
Plato's Model of the Cultured ManThe first model of a cultured person in history is considered to be the ancient or
Platonic model. According to this model, a cultured person can be considered
an educated person who knows how to control himself( self-control), moral.The
type of person is an athlete, which includesphysical and spiritual perfection.You
can achieve the ideal through exercise,education, and educationso the ancient
Greeks believed.
35.
Ancient Greece – the cradle of Europeancivilization
Римская культура стала питательной почвой для культуры
романо-германских народов Европы.
36.
HellenismHellenism is a new stage in the development of material and spiritual
culture, forms of political organization and social life of the states
conquered as a result of the Eastern Campaign of Alexander the Great
(334-323 BC) before the final establishment of Roman rule in these
territories.All of its local variants had common features. On the one hand,
elements of Greek culture were necessarily present, on the other – the
Hellenistic world was formed mainly on the territory of the former Persian
power, and therefore the socio-economic and political development of the
conquered countries was similar.The rise of science: Archimedes,
Euclid.Colossus of Rhodes, Pharos lighthouse.Sculpting School:
"Laocoon", astatue of Nika of Samothrace
37.
Scientific achievements of the Hellenisticperiod
Euclid's geometry became one of the greatest achievements of the human mind.
Archimedes introduced the concept of an infinitely large number, developed the
prototype of the integral calculus, created fundamental works on statics and
hydrostatics, and was the greatest mechanical inventor in history.Aristar of Samos
proved the rotation of the Earth around the axis and its movement around the Sun.
Hipparchus of Alexandria established the length of the lunar month, the exact length
of the solar year, and calculated the distance from the Earth to the Moon and the
Sun.Eratosthenes, based on the idea of the spherical shape of the Earth, very
accurately calculated its radius, the circle, which is very close to the real one.




































 history
history








