Similar presentations:
Political science
1. POLITICAL SCIENCE
Introduction byDr. Doulatbek Khidirbekughli
2. Policy / Politics
Policy: origins from polis that means city/townPOLITIKA – in Greek means a rule on city
Politics: a general term concerning human or
group of people
Policy: the definite direction in politics, i.e. on
large scale level
3. Politics: a field of activity connected with relations between social strata, peoples, nations, states
4. Bases of Politics: Problem of achievement, keeping and use of state/governmental power.
5. Problem of Politics: a subject of permanent search.
Problem of Political Science:research of ways which are
accepted in decisions for society.
6. Policy is rule and regulation on society
Apolicy
is
a deliberate system of principles to guide
decisions and achieve rational outcomes.
A policy is a statement of intent, and is
implemented as a procedure or protocol.
Policies are generally adopted by
a
governance
body
within
an
organization. Policies can assist in
both subjective and objective decision
making
7.
Political Institute: category ofregulation of joint life and ideas
causing a moving for development of
society.
8. Political Science: complex of ideas, institutions and people.
Subsystems in PoliticalScience: economic, social,
spiritual and political branch.
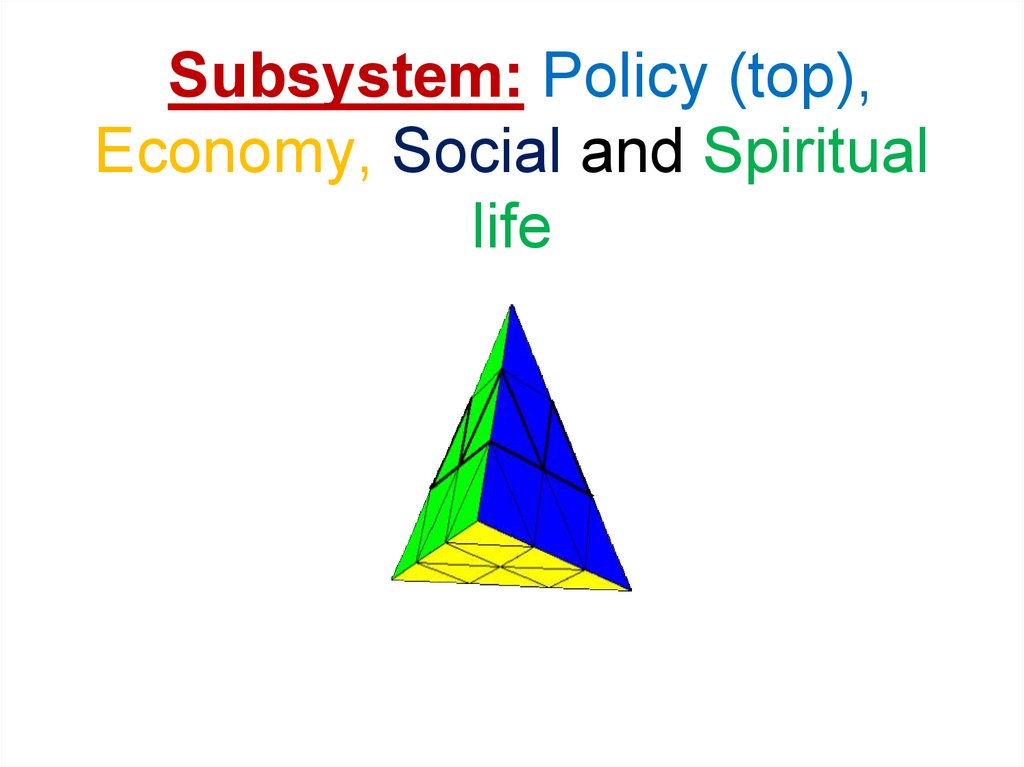
9. Subsystem: Policy (top), Economy, Social and Spiritual life
10. Subsystem: Political Science (top), Economics, Social and Spiritual Sciences
11. Auguste Comte (1798-1857): Social Sciences (top),Technical Sciences, Physics-Mathematics and Natural Sciences
Auguste Comte (1798-1857): SocialSciences (top),Technical Sciences, PhysicsMathematics and Natural Sciences
12. Political Research: historical, empirical and theoretical.
Objects of Research: state,power and power relations.
13.
Political science includes elements of othersciences:
History
Economics and Statistics
Philosophy
Sociology
14. Culturology / Cultural Studies Religious Studies
EthicsArt and Esthetics
Law
Education
15. Military Studies Psychology
LinguisticsGeography
16. Political Science partly uses in secondary roles: Mathematics Techniques and Informatics Natural Sciences
17. Political Science: Integrating role between sciences and discipline,
Presence of separate disciplines,Concerning political aspects in
other sciences.
18. Political Science + any subject = Interdisciplinary subject
Political Sociology
Political Philosophy
Political Psychology
Political Anthropology
Political Geography
Political Economy
Political History
19. History is a politics in the past, Politics is a History for today
by E. Freeman, BritishHistorian.
20. Classification of tasks in Political Science by UNESCO in 1948: 1.Political Theory: Political Theory History of ideas
2. Political Institutes:Constitution
Central Administration
Regional and Local Administration
Public Administration
Economic and Social Functions Administration
Comparative Analysis of Political Institutes
21. 3.Parties, Groups and Public opinion: Political Parties Groups and Associations Public opinion and citizens participation in
administration4. International Relations:
International Politics
Policy and International Organizations
International Law
22. Directions of policy:
• National policy / Governmental policy• Internal policy / Social policy
• Foreign policy / International policy / Global
Policy
• Economic policy / Industrial Policy / Agricultural
Policy
• Custom policy / Tax policy / Financial policy
• Military policy
• Education policy
• Technical policy





















 policy
policy








