Similar presentations:
Islamic legal system : . History
1.
TOPIC 3STUDENT: HAIDAR SAFA
GROUP:19LS4A
2.
PROJECT PLAN1. Islamic legal system : . History
. Sources
. Structure
2. Indian Law : . History
. Sources
. Structure
3. Lebanese Segal System
3.
HISTORY OF ISLAMIC LEGAL SYSTEM1. Islamic law grew along with the expanding Muslim Empire. The Umayyad dynasty caliphs, who
took control of the empire in 661, extended Islam into India, Northwest Africa, and Spain. The
Umayyads appointed Islamic judges, kadis, to decide cases involving Muslims. (Non-Muslims kept
their own legal system.)
2. Sharia law is Islam's legal system. It is derived from both the Koran, Islam's central text, and
fatwas - the rulings of Islamic scholars. ... Sharia law acts as a code for living that all Muslims
should adhere to, including prayers, fasting and donations to the poor.
4.
5.
SOURCES OF ISLAMIC LEGAL SYSTEM• The primary sources of Islamic law are :
1 . the Holy Book (The Quran)
2.The Sunnah (the traditions or known practices of the Prophet Muhammad )
3. Ijma' (Consensus)
4. Qiyas (Analogy).
6.
7.
STRUCTURE OF ISLAMIC LEGAL SYSTEM• The Qur'an is the principal source of Islamic law, the Sharia. It contains the rules by which the
Muslim world is governed (or should govern itself) and forms the basis for relations between man
and God, between individuals, whether Muslim or non-Muslim, as well as between man and things
which are part of creation.
8.
INDIAN LAW HISTORY• India has a recorded legal history starting from the Vedic ages and some sort of civil law system
may have been in place during the Bronze Age and the Indus Valley civilization. ... The
common law system – a system of law based on recorded judicial precedents- came to India with the
British East India Company.
• Coding of law also began in earnest with the forming of the first Law Commission. Under the
stewardship of its chairman, Thomas Babington Macaulay, the Indian Penal Code was drafted,
enacted and brought into force by 1862. The Code of Criminal Procedure was also drafted by
the same commission.
9.
10.
SOURCES OF INDIAN LAW• Primary Sources of Law are in the Indian constitution, enactments passed by Parliament of India,
statute, case laws, treaties and customary law. Constitution/ Charters are the fundamental
principles of law by which a government is created and a country is administered.
• Main sources of law
• The Constitution of India. This is the supreme source of law.
• Statutes. Statutes are enacted by the Parliament or the state legislatures. ...
• Customary law. ...
• Judicial decisions.
11.
STRUCTURE OF INDIAN LAW• The Indian judicial system is a single integrated system. The Constitution of India divides
the Indian judiciary into superior judiciary (the Supreme Court and the High Courts) and the
subordinate judiciary (the lower courts under the control of the High Courts). ... There are twentyfour High Courts in the country.
12.
LEBANESE LEGAL SYSTEM• The Lebanese legal system is based on and inspired by the French legal system. Just like France,
which occupied Lebanon until 1943, Lebanon is considered to be a civil law country and possesses its
own set of codes.
• Lebanon is a parliamentary democratic republic within the overall framework of confessionalism, a
form of consociationalism in which the highest offices are proportionately reserved for
representatives from certain religious communities.
13.
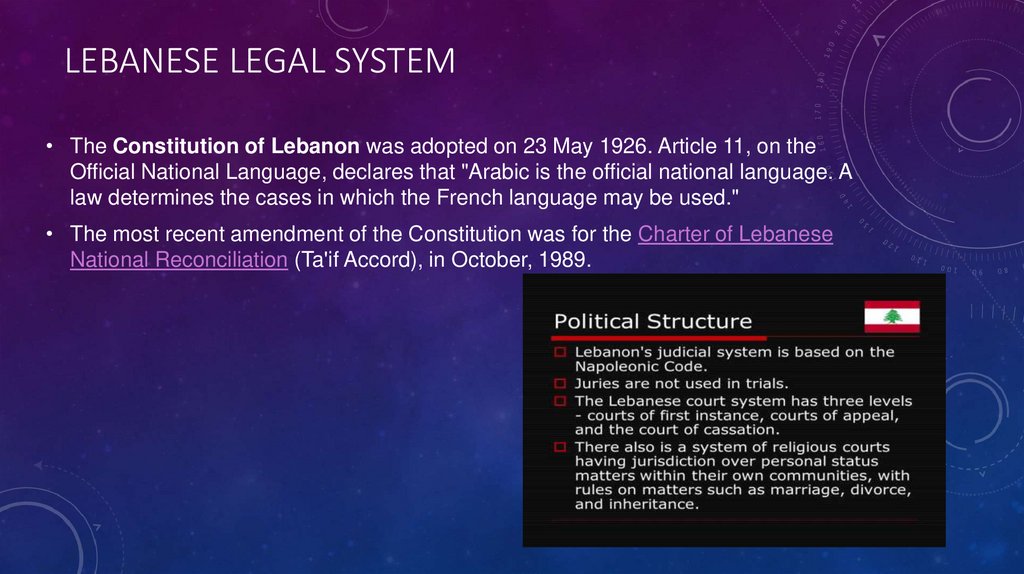
LEBANESE LEGAL SYSTEM• The Constitution of Lebanon was adopted on 23 May 1926. Article 11, on the
Official National Language, declares that "Arabic is the official national language. A
law determines the cases in which the French language may be used."
• The most recent amendment of the Constitution was for the Charter of Lebanese
National Reconciliation (Ta'if Accord), in October, 1989.












 law
law








