Similar presentations:
Medical education in Australia
1.
PSMU named after academician E.A. WagnerMinistry of Health of the Russian Federation
Medical
education in
Australia
Group 102 student report
Faculty of Medicine
Tukmacheva E.S.
Supervisor:foreign language teacher
Maslova S.M.
2.
Why Australia?Australian schools are famous for their quality of training
and research.
Five Australian universities are ranked in the world’s top
50 for medicine. It’s the University of Sydney, the
University of Melbourne and the University of Queensland.
The University of Sydney
The University of Melbourne
3.
WHICH COURSESARE AVAILABLE?
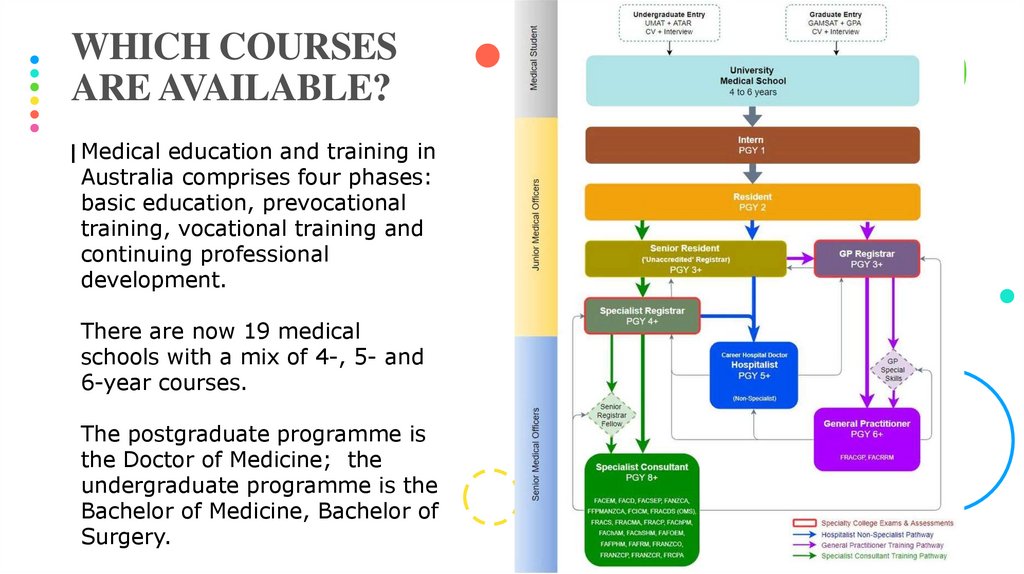
I Medical education and training in
Australia comprises four phases:
basic education, prevocational
training, vocational training and
continuing professional
development.
There are now 19 medical
schools with a mix of 4-, 5- and
6-year courses.
The postgraduate programme is
the Doctor of Medicine; the
undergraduate programme is the
Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of
Surgery.
4.
BASIC MEDICALEDUCATION
Basic medical education in
Australia is provided by 19
medical schools, enrolling
about 16 000 medical
students.
Undergraduate programs
typically last 5–6 years, and
admit secondary
school matriculants.
Applicants are usually
assessed by a high school
leaving certificate, UMAT
score and an interview.
5.
PREVOCATIONALTRAINING
Prevocational training currently
comprises a intern year for
graduates and several years of
informal training of junior
doctors, who have not yet
entered vocational training
programs.
In general, most doctors spend
two to three years practicing as
a Resident Medical Officer (RMO)
or Hospital Medical Officer (HMO)
in a hospital before commencing
specialist training.
6.
VOCATIONALTRAINING
Postgraduate vocational training
is currently provided by 15
medical colleges for about
13 000 trainees.
Initially, vocational training
focused on the expert knowledge
and skills necessary for the
specialist clinical care of
patients. There was also the
wider professional
responsibilities of doctors in
complex health care systems.
7.
CONTINUINGPROFESSIONAL
DEVELOPMENT
About 90 000 registered medical
practitioners are currently
required to undertake CPD, the
fourth and final phase of medical
education and training.
Until the advent of the National
Registration and Accreditation
Scheme for health professionals in
2010, CPD was a voluntary
activity. The Health Practitioner
National Law Act 2009 made CPD
a condition of ongoing registration
for all health professionals.
8.
STUDY MEDICINE IN AUSTRALIAAUSTRALIA HOUSES SOME OF THE
WORLD'S LEADING UNIVERSITIES
THAT OFFER HIGH -QUALITY
EDUCATION. DESPITE THE RISING
AUSTRALIAN DOLLAR, STUDENTS
ACROSS THE WORLD WANT TO
COMPLETE THEIR HIGHER
EDUCATION FROM AUSTRALIA, WHAT
WITH THE PROMISE OF LUCRATIVE
JOBS, GOOD QUALITY OF LIVING
AND FAVORABLE WEATHER WITH
BEAUTIFUL BEACHES.
9.
Cost of studyingmedicine in Australia
AUST RAL IA H AS A H IGH C OST OF
L IVIN G, WH ICH M AK E S E D UC AT ION IN
AUST RAL IA A P R ICEY OP T ION .
H OWE VER, T H E QUAL IT Y OF M E D ICAL
E D UC AT ION OF F E R ED BY AUST R ALIAN
UNIVE RSIT IES FIND S M ANY ST UD ENTS
ST IL L OP T IN G TO ST UDY H E RE.
T H E AVE RAGE C OST OF E D UCATION IN
AUST RAL IA IS ABOUT AUD 4 0 0 , 0 0 0 TO
AU D 4 5 0 , 000. BE SID ES, T H E
AUST RAL IAN GOVE R N MEN T D OE S N OT
OF F E R A C OM P L ETE M E D ICAL
SC H OLARSHIP TO IN T E R NAT ION AL
ST UD ENTS.
10.
Top 2 Australian Universities forMedicine
U NIVERS ITY O F ME LBO U RNE
RAN K ED IN T H E 20 BE ST
UN IVE RSIT IES F OR M E D IC IN E, T H E
UN IVE RSITY OF M E L BOURN E WAS
T H E F IRST M E D ICAL SC H OOL IN
AUST R AL IA.
THE AUSTRALIAN NATIONAL
UNIVERSITY MEDICAL SCHOOL
IT OFFERS AN MChD – A FOUR
YEAR GRADUATE ENTRY DEGREE









 medicine
medicine english
english education
education








