Similar presentations:
Term paper on cyber security
1.
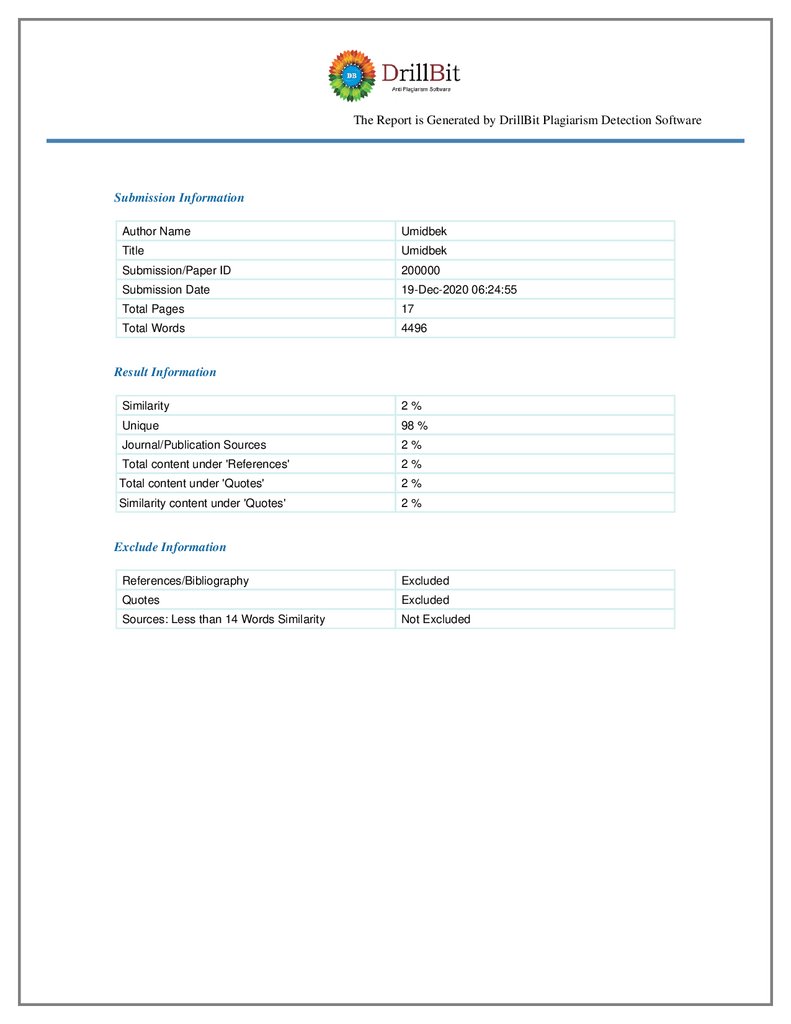
The Report is Generated by DrillBit Plagiarism Detection SoftwareSubmission Information
Author Name
Umidbek
Title
Umidbek
Submission/Paper ID
200000
Submission Date
19-Dec-2020 06:24:55
Total Pages
17
Total Words
4496
Result Information
Similarity
2%
Unique
98 %
Journal/Publication Sources
2%
Total content under 'References'
2%
Total content under 'Quotes'
2%
Similarity content under 'Quotes'
2%
Exclude Information
References/Bibliography
Excluded
Quotes
Excluded
Sources: Less than 14 Words Similarity
Not Excluded
2.
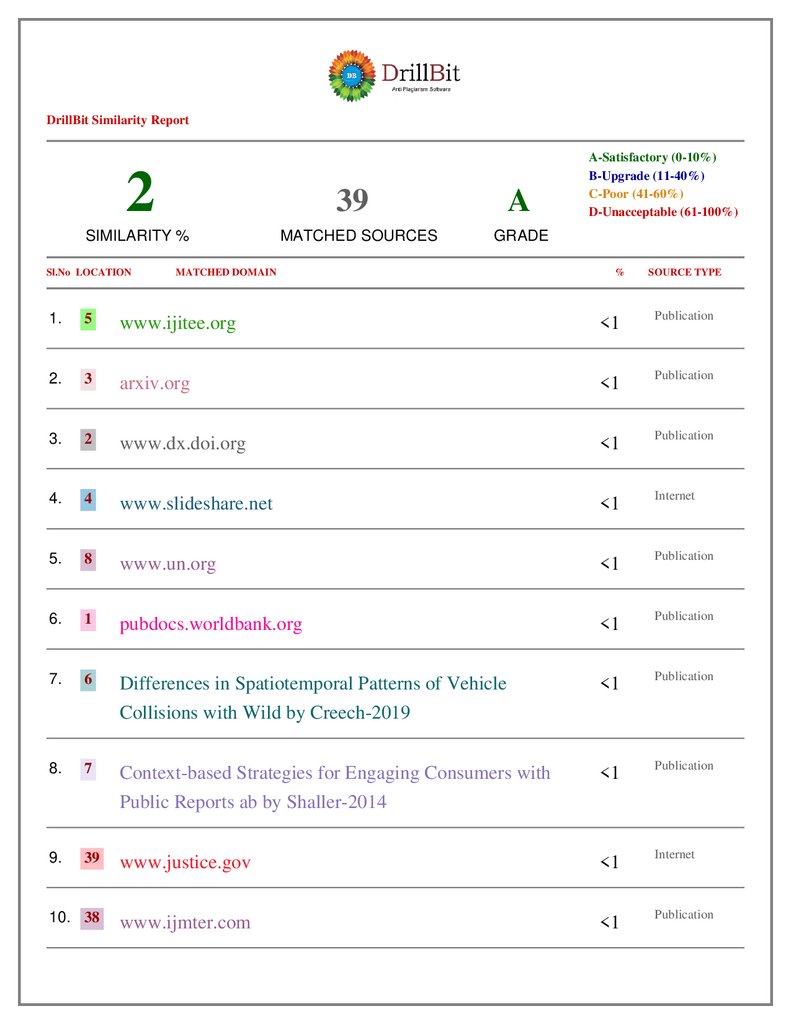
DrillBit Similarity Report2
39
SIMILARITY %
Sl.No LOCATION
MATCHED SOURCES
A
A-Satisfactory (0-10%)
B-Upgrade (11-40%)
C-Poor (41-60%)
D-Unacceptable (61-100%)
GRADE
MATCHED DOMAIN
%
SOURCE TYPE
1.
5
www.ijitee.org
<1
Publication
2.
3
arxiv.org
<1
Publication
3.
2
www.dx.doi.org
<1
Publication
4.
4
www.slideshare.net
<1
Internet
5.
8
www.un.org
<1
Publication
6.
1
pubdocs.worldbank.org
<1
Publication
7.
6
Differences in Spatiotemporal Patterns of Vehicle
Collisions with Wild by Creech-2019
<1
Publication
8.
7
Context-based Strategies for Engaging Consumers with
Public Reports ab by Shaller-2014
<1
Publication
9.
39
www.justice.gov
<1
Internet
10. 38
www.ijmter.com
<1
Publication
3.
11. 37People Care Recommendations from Native Youth to
Address Concer by Gritton-2016
<1
Publication
12. 36
IEEE 2013 International Conference on Communication
Systems and Netw by
<1
Publication
13. 35
IEEE TENCON 2015 - 2015 IEEE Region 10 Conference
- Macao (2015.11.1 by
<1
Publication
14. 34
www.comparitech.com
<1
Internet
15. 33
A Systematic Review of Fidelity of Implementation in
Parent-Mediated E by Lieberman-Betz-2015
<1
Publication
16. 32
bmcpregnancychildbirth.biomedcentral.com
<1
Publication
17. 31
Development of catalytically reactive porous membranes
for the select, by Detlev Fritsch Gis- 2006
<1
Publication
18. 30
www.arxiv.org
<1
Publication
19. 29
Restructuring charges and takeover likelihood Evidence
from the pre-a by Adut-2016
<1
Publication
20. 28
jb.asm.org
<1
Publication
21. 27
AbSRiM An AgentBased Security Risk Management
Approach for Airport , by Janssen, Stef Shar- 2019
<1
Publication
4.
22. 26A proposed model for data warehouse user behaviour
using intrusion de, by Singh, Indu Kumar,- 2012
<1
Publication
23. 25
quizlet.com
<1
Internet
24. 24
rbidocs.rbi.org.in
<1
Publication
25. 23
www.acm.org
<1
Internet
26. 22
IEEE 2011 5th International Conference on Next
Generation Mobile App
<1
Publication
27. 21
www.russianlawjournal.org
<1
Publication
28. 20
www.dx.doi.org
<1
Publication
29. 19
MARKET PRINCIPLE OFREGULATORY
COMPLIANCE PRCAND
ROLEOFREGULATORYAFFIRSONHEAL -Submited to
JNTUH,TELANGANA By '15Y61S1013'
<1
Student Paper
30. 18
www.dx.doi.org
<1
Publication
31. 17
Thesis submitted to shodhganga shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in
<1
Publication
32. 16
A Process Model of Capability Development Lessons from
the Electronic by Montealegre-2002
<1
Publication
5.
33. 15Evaluation of Atmospheric Correction Methods for the
ASTER Temperatur, by Li, Hua Wang, Hesh- 2018
<1
Publication
34. 14
IEEE 2016 IEEE Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting
(ETCM) - Guayaquil
<1
Publication
35. 13
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Article
<1
Publication
36. 12
Geo-knowledge Management and Geoconservation via
Geoparks and Geotouri by Farsani-2014
<1
Publication
37. 11
IEEE 2013 International Conference on Advanced
Computer Science and by
<1
Publication
38. 10
Development of tantalum oxynitride thin films produced
by PVD Study o by Cristea-2013
<1
Publication
39. 9
financedocbox.com
<1
Internet
6.
TERM PAPEROn
Cyber Security
Submitted to:
Amity University Tashkent
Guided by:
Submitted by:
Miss Pooja Khanna
Umidbek Kholikov
№A85204919102
Amity University Tashkent
7.
Abstract1
First of all, it is an indisputable fact that the Internet and Information Technology have
revolutionized the way of our living. Therefore, cyber security plays central role in our life.
In this term paper, I have tried to do my best to wrote this e-book a review and analysis on
2
the proposed universal rules for cyber security, risk analysis of cyber resources, threat and
preparedness levels and cyber threat tools are presented. This also involved the detailed about cyber
risks and elements and etc.
8.
Table of Contents1. Introduction __________________________________________________________2
2. UNIVERSAL ELEMENTS AND RULES IN CYBER SECURITY ______________________3
3. RISK ANALYSIS ______________________________________________________6
4. CYBER THREAT AND PREPARATION LEVELS _________________________9
5. CYBER THREAT TOOLS _____________________________________________10
6. RESULT ____________________________________________________________12
7. References.___________________________________________________________13
1
9.
Declaration:I hereby declare that the work, which is being presented in the term paper, entitle “Cyber
Security” (mitigation and attacks) in partial fulfillment for the award degree of (Bachelor Science of
Information Technology) submitted to the Amity University Tashkent is a record of my own
investigations carried under the Guidance of NTCC Name of receiver faculty of Amity institute of
Computer Science and Technology. I have not submitted the matter the matter presented in this
report anywhere for the award of any other Degree.
Date:
Name of student: Umidbek Kholikov
No: A85204919102
B.Sc. (IT): section 2. (2019-2022)
(Counter Signed by)
Name of faculty Guide: Miss Pooja Khanna
Certificate:
This is to certify that Student Umidbek Kholikov B.Sc. IT 2019-2022 Semester 3 has presented
4
an "Cyber security (mitigation and attacks)" in partial fulfilment for the award of the degree of
Bachelor Science of Information Technology, under Amity University Tashkent. Date: 18th
5
December
Faculty Guide: Miss Pooja Khanna
Amity University Tashkent
2
10.
Key Terms - Cyber security, risk analysis, threats, investigationI. Introduction
When the first computer named "Intelligent Engine" was designed by Professor Charles Babbage in
2
1837 at Cambridge University, it was not thought that it would create such a revolution, and perhaps
6
the threshold of today's wars. This technology, which has developed rapidly over time, has become
the most important environment where information is not only stored but also processed, used and
developed.
5
The transfer of this digital information world, which is used effectively by corporate users as well as
personal users, to the internet environment has made the information more attractive and targetable,
while facilitating accessibility. About the world today. It is estimated that there are 2.28 billion internet
users, 19.2 billion web pages, 1.6 billion pictures and 50 million audio-video files. This cyber world,
which is used very effectively by both individuals and institutions, has become an increasingly
dangerous place. The words cyber security, cyber-attack, and cyber warfare have settled in the words
7
of both individuals and states, and have started to contain meanings that are more serious and to make
arguments day by day (Musman and Turner 2018).
8
Cyber security can be described as "the set of tools, policies, security concepts, security assurances,
and
guidelines,
risk
management
approaches,
activities,
trainings,
best
practices and
5
technologies used to protect the assets of institutions, organizations and users in the cyber
environment."
Cyber war is "making the same attacks against countries or countries”. In cyber warfare, the critical
infrastructures of target countries such as security, health, energy, communication, water and sewage,
banking and public services are chosen as the attack area.
Countries set strategies andpolicies to ensure their cyber security. British Prime Minister Gordon
Brown stated that the understanding of the security of the country changed, “While in the 19th
century we had to ensure our maritime and air security to protect our national security, in the 21st
century we have to ensure the security of our public institutions and businesses in the virtual
world expressed in words (Dissanayake 2020).
3
11.
UNIVERSAL ELEMENTS AND RULES IN CYBER SECURITYIt is clear that cyber threats that can target a country's institutions or national security can come from
any source, given their accessibility and connections around the world. This situation necessitates
international cooperation and the application of universal rules.
A.
Cyber Security Elements
There are some issues to be taken into consideration in all kinds of measures and applications to be
developed to ensure cyber security. These are the points:
Protection of fundamental rights and freedoms
Compliance with the requirements of democratic social order
The principle of proportionality complied
Ensuring the participation of all stakeholders in decision-making processes
Addressing legal, technical, administrative, economic, political and social dimensions with
a holistic approach
Balancing security and usability
Considering the legislation of other countries and ensuring compliance as much as possible
Ensuring international cooperation
It is a fact that these issues have general priorities everywhere. In addition, the elements suggested
to be taken into consideration in determining cyber security approaches are stated below.
1) Development of National Policy and Strategy: It is necessary to develop national policies and
strategies in order for the measures to be taken against cyber-attacks to be successful.
2) Establishing the Legal Framework: It is necessary to make legal arrangements with high
deterrence against cyber-attacks.
3) Development of Technical Measures: In order to increase the security of software, hardware and
business processes, and technical measures should be developed by considering security
standards.
4) Determination of Institutional Structure: The legal framework of the duties and responsibilities
of individuals, non-governmental organizations, private sector and public institutions and
organizations should be determined.
4
12.
5) Ensuring National Cooperation and Coordination: It should not be forgotten that all systems,networks and infrastructures are interconnected, and full security cannot be mentioned without
ensuring the security of each. For this reason, it is important to ensure that all elements work in full
coordination within the framework of the determined national strategy and policy.
6) Capacity Building: The continuous development of technology causes the cyber threat tools to
change. For this reason, application developer technical personnel, management units, lawyers and
lawmakers should follow technology closely and improve their knowledge on this subject.
7) Raising Awareness: Personal users, the weakest link , should be informed about cyber threat tools
and ways of protection .
8) International Cooperation and Ensuring Harmony: The fact that all countries of the world can
be easily reached via the Internet enables crime centers to be located in different places. Considering
that the cyber threat is a danger to the whole world, legal legislation should be harmonized and
information sharing should be given importance (Fram 2015).
B. Universal Rules
The cyber attack on Estonia in 2007 made the world take into account the cyber threat myths. The
Aurora codenamed attacks on Google and other sites in China in 2010, the Conficker named worm
targeting Microsoft products in 2008, the Stuxnet worm targeting the Iran nuclear program, and
many other new attack methods actually showed that it was not right to approach the problem as
a sense of entertainment by a few hackers. After the Estonian Cyber Attacks in 2007, countries
saw the need to take more effective technical and legal measures to protect their assets and the
information security of their citizens. Security policies of NATO, United Nations, European
Union, OSIT and many other international organizations have started to be revised in this way. In
this process of change, the following universal rules have been formed:
1) Territorial Rule: The information technology infrastructure within the territory of a state is the
national sovereignty element of the state. According to the international law understanding; Every state
has the authority to improve the IT infrastructure in order to take precautions against and deal with all
kinds of threats and attacks against the information technology infrastructure of their country.
2) Rule of Liability: When the assumption is that the cyber attacks on the information system resource
in the territory of a state are originating from another country, the responsible country is expected to
investigate, assist in the arrest of criminals and support the trial process.
3) Cooperation Rule: If the cyber attack is carried out by targeting another country through the
information systems in the territory of a state, the state whose sources of attack are in its territory has
5
13.
the duty to cooperate with the victim state. According to the International Cyber Crime Convention,the parties have the right to demand the application of international tools and legal rules and the
collection of electronic evidence in criminal matters. In addition, in accordance with the North Atlantic
Treaty, the cooperation of other parties and allied countries is obligatory in case of a situation that
threatens the territorial integrity, political independence and security of any country.
4) Self-Defense Rule: According to the international penal laws, people cannot be held responsible for
unfair actions to protect themselves when they think that the laws are used illegally against their
personal freedom. At the international level, if a country thinks that an attack carried out individually
or collectively threatens its security, it has the right to respond to attacks by a method it determines,
including armed force. In fact, in accordance with Article 5 of the NATO agreement, all member states
have the right to respond to an attack on a NATO member country.
5) Data Protection Rule: Whether any data of an individual on the network falls within the scope of
data confidentiality is still a matter of investigation and debate among legal experts. The information
of real persons defined or not defined according to the EU's Data Protection Directive is considered as
personal data. In this respect, if a person's IP address on the network is obtained illegally, it cannot be
accepted as legal evidence. Again, according to the same directive, when a person transfers his personal
data to a third country, the relevant country has an obligation to protect this data. Despite the possibility
of abuse of this situation, an international regulation is needed regarding the legal legislation.
6) Maintenance Rule: According to the EU's Data Protection Directive, individuals are responsible for
taking all technical and organizational measures to prevent accidental or deliberate destruction,
modification, disclosure of data to unauthorized persons against access via network or illegal means.
Likewise, the clause of the Council of Europe Convention (1981) that individuals must take necessary
measures to prevent any data loss, access by unauthorized persons and the change of data to third
parties is clearly stated in Article 7. In this context, as the political dimensions of cyber-attacks increase,
standards for the maintenance and protection of data in terms of social, military and information
services will need to be developed.
6) Early Warning Rule: Service providers are obliged to take all kinds of technical and organizational
measures to protect the security of their services in accordance with the e-Privacy Directive EC /
2002/58. It has an obligation to coordinate similar actions with the public network provider when
necessary. In addition, according to the e-Commerce Directive, service providers are obliged to
immediately report illegal activities to the authorities of the member states.
6
14.
7) Information Rule: People have the right to know about threats to their life, safety and welfare. Ajudgment that states should be transparent about the threats to the public life and welfare of the societies
and the decisions taken against these threats in Europe makes its existence stronger day by day. The
fact that threats and the decisions taken in the face of such situations are open to access, can inform the
public and raise awareness in terms of cyber security, and may also cause unwanted information
disclosure. Nevertheless, the disclosure of the attacks carried out and the measures taken are necessary
in the legal framework in terms of strategic communication and raising public awareness.
8) Criminal Rule: Every nation has the responsibility to include the most common cybercrime in
its criminal law. Under the international criminal law, it is not possible to impose a sanction on
the person who committed a cyber attack unless the result of a situation is considered a crime
under national or international law. Unfair access to all or any part of a computer system should
be evaluated within the framework of legal obligations according to the European Union Cyber
Crimes Convention, which can be taken as a basis for the settlement of disputes in these situations
and to create a harmony.
9) Mandate Rule: Mandate management includes the support and coordination of international
efforts on cyber security. It aims to reveal international coordination and gaps in terms of legal
and political tools regarding cyber security. Today, this adaptation effort is still included in the
work plans of at least 6 international organizations. NATO has not been able to reach a clear
decision on the circumstances in which an armed attack can be carried out against cyber attacks
on member countries. In this context, it is obvious that countries should work together and in
coordination and develop strategies.
In the investigations made, it has been determined that cyber attacks are increasing every year.
For this reason, it has become of vital importance to analyze security risks and create necessary
risk models (Analysis 2016).
I. RISK ANALYSIS
The main benefits of risk analysis are listed below:
• Developing secure information management
• Ensure that the organization's critical assets are monitored and protected effectively
• To ensure the support of effective information security policies in decision making
7
15.
• To ensure the determination of practical security policies for organizationsProvide
valuable
analysis
data
for
future
predictions
Assets generally consist of information / data, documents, hardware, software, human resources
and terms. Threats can be classified as human / non-human factors, network / physical, technical /
environmental, internal / external and intentional / accidental threats. Deficits can be classified
as administrative documents, personnel, regulations, physical conditions and facilities, technical
hardware, software, communication / network- related deficits.
Mathematically, risk is calculated by multiplying the probability of a threat to the vulnerability
associated with the decrease in value of assets because of exposure to any deficit (Shevchenko et
al. 2019).
Risk = Loss * Probability
The radio analysis process generally consists of four steps. In the first step, a definition and
evaluation process should be done on assets, threats and vulnerabilities. In the second step, a total
risk assessment of the system should be made, taking into account assets, threats and existing
vulnerabilities.
In the third step, the method required to reduce the risk of existing threats is determined and
effectiveness evaluation is made. Risks should be determined by the organization and
a method should be chosen to minimize these risks as much as possible (Vepachedu 2017).
We tried to summarize which applications can be used in some risk reduction methods:
1) Access Control: systems based on password identification, physical access equipment (smart
card), authentication system can be used.
2) Password Check: Public key infrastructure (AAA), etc. encryption algorithms can be used.
3) Internet
Security
Control:
Intrusion
detection
system
(Ids),
firewall,
etc.
measures can be taken.
4) Application Security Audit: Covers applications such as database security, system file
security.
5) Physical / Environmental Security Control: It covers applications such as facility security,
institution security, entrance / exit control.
8
16.
The final risk amount is obtained by adding benefits and costs to the risk amount calculated in thesecond and third steps in the fourth step. The damage assessment is made over this risk amount and
a result document is prepared in order to prepare the ground for future studies and to see the situation
more clearly (Bulturbayevich et al. 2020).
Total Cost = Cost + Operation Cost + Work Opportunity cost
Cost is the cost of purchasing or loading an asset. Operational cost is the cost incurred to recover the
damaged asset. Business opportunity cost, on the other hand, is a waste of business for monetary gain.
Considering this calculation, the organizational risk management policy can be decided.
A. Vulnerability Risk Analysis
When one examines more closely the security vulnerabilities, which are the first risk factors, it
can be noticed that it has a life cycle. Every system has a vulnerability and this vulnerability
is likely to be attacked . If you are lucky, the vulnerabilities are discovered by the white
pirates and you have an opportunity to be closed. The date when the deficits were first noticed,
the date of discovery, the date when detailed information was given about the deficit, the date
when it was announced to the public , the date when the exploit code was published through the
websites , the date of exploitation, and the date of publication of the relevant patch to close the
deficit is called the patch date . Each patch published could be the beginning of a new
exploration, a new cycle (Bashir 2019).
B. Security Risk Assessment Methods
Some methods are used while making security risk assessment. The main ones are; Information Security
Assessment Methodology (IAM), Vulnerability Assessment Framework (VAF) and Operational Critical
Threat, Asset and Vulnerability Assessment (OCTAVE).
1) Information Security Assessment Methodology (IAM) is a method used by the NSA and the US
Department of Defense that analyzes security risks by analyzing structural vulnerabilities.
2) Vulnerability Assessment Framework (VAF) is a method developed by the US Critical Infrastructure
Assuranc e Offic e Commissio n and KPM G Marwick LLP in 1998, analyzing the vulnerabilities of the relevant
9
17.
organization's minimum basic infrastructure and selected assets and calculating the security rating as a resultof the evaluation.
3) Operational Critical Threat, Asset and Vulnerability Assessment (OCTAVE), developed by the Software
Engineering Institute of Carnegie Mellon University in the USA, consists of three stages: creating asset-based
threat scenarios, defining vulnerabilities about important facilities and evaluating risk and developing security
strategies. It is a security assessment method (Tarazan 2017).
II. CYBER THREAT AND PREPARATION LEVELS
The cyber defense preparation process can be summarized in four successive stages. In the first
stage, the mission of the institution against cyber threats should be categorized, in the second stage,
the level of preparedness should be determined to ensure the success of the mission, a strategy
plan for cyber security should be developed by determining the preparation objectives in the third
stage, and the necessary security investments should be planned and decisions should be made in
the fourth stage. Under this heading, the threats that constitute the first and second stages of cyber
defense and the steps at the preparedness levels are mentioned (Sonntag 2016).
A. Threat Levels
The basic step of cyber defense is to determine threat levels. The process of determining threat
levels is a five-step process. Table 1 in Appendix A lists the threat levels, types of attackers at
these levels, targets, strategies and methods.
B. Preparation Levels
The second step of cyber defense is determining preparedness levels. The process of determining
the preparation levels is a five-step process. Table 2 in Annex B lists the levels of preparation,
objectives, measures to be taken and suggested solutions.
III. CYBER THREAT TOOLS
It is possible to separate the effects of cyber threats into short and long term. Short-term threats are
threats that affect the daily activities of the organization, government, business and end users it targets.
10
18.
Examples of daily activities such as fraudulent activities, customer data breaches, and irregular cashwithdrawal from ATM. Long-term threats, on the other hand, are threats with long-lasting effects that
aim to change the balance of the country and society, such as industrial and military espionage,
creating social discontent and unrest, and violating national security (Woo and Kim 2014).
A. Malicious Software
They are used for purposes such as Trojan horse, virus, keyboard sniffing, spyware, malware such as
junk e-mail, obtaining data using vulnerabilities, altering or destroying them. Malware is considered
to be one of the most dangerous cyber attack tools for government, business and end users, which are
frequently preferred for their ease of use and rapid results. Malicious applications can be hardware as
well as software. Hardware keyboard listening devices are an example. Sometimes, with a small
device inserted into the device, all kinds of information entered from the keyboard (your passwords,
file names, file contents, etc.) can be recorded.
Attacks do not necessarily have to be carried out over the network. Data theft can be done by installing
malicious software on devices that are not connected to the network. Thanks to spyware installed on
ATM and POS devices, the user's data can be illegally captured or financial losses may be caused
(Henshel et al. 2015).
A. Unsafe Environments
Network security depends on the security of the network elements that form the backbone. It is
possible to attack systems and access information by exploiting the security vulnerabilities of the
product. An example of this is carried out by the virus called Stuxnet. This virus, which was
developed by taking advantage of the vulnerabilities in the PLC rootkit index of a certain product
brand, brought the industrial system to a complete halt (Hossain and Das 2017).
B. Identity Theft
In such attacks, the attacker manages to infiltrate the system by impersonating a user with permission
to access. Network attacks, message repetitions, software and exploitation attacks are examples
of identity attacks.
C. DOS Attacks
11
19.
DOS (Denial of Service) and DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks are attacks that directlytarget the system. These attacks cause serious damage by halting or disrupting systems (Kure, Islam,
and Razzaque 2018). DDOS attacks are attacks that target the information accessibility rule and aim
to bring the system to a halt by sending more requests than the operating system, server or application
can respond to.
D. Double Capture Attacks
Social engineering attacks, dictionary attacks and password guessing practices are the main methods
used in these attacks, which are considered within the scope of privacy violation. Rather, social
engineering attacks and social skills try to get people's knowledge and penetrate the system.
E. Side Channel Attacks
Side channel attacks are attacks against systems power analysis, electromagnetic applications, and
scheduled tasks. The main purpose of these attacks is to infiltrate a spy application that will gain the
encryption key. Many Smart Systems have unfortunately lost customer information, usage
information and passwords as a result of these attacks (Dissanayake 2020).
F. HTML Injection
This vulnerability takes advantage of incorrect coding that programmers do when coding. In my web
software, the fact that the data entering the database or the data extracted from the database are not
passed through a control mechanism causes an issue. By taking advantage of the vulnerability known
as XSS, session and cookie stealing is done.
Applications use the logic of returning a response to a request sent to the page. Request sent to the
page it is evaluated on the server and a response is returned. But if the page you're logged into is
redirected to a malicious url or tools like a Trojan horse have been inserted, your response will be
different than expected. In this type of attack, the aim is not to damage the web application, but rather
to reach users who visit the application.
B. SQL Injection
SQL injection is a form of attack that targets querying from a database. In this form of attack,
the attack is carried out using the query language structure.
Username and password pair of a web application database
“SELECT * FROM TABLE_PERSONEL WHERE
12
20.
username = '" + User + "' AND password = '" + Password+ "'"
If the data in the ("") signs is not filtered when sent as, the user will write here (
OR '' 1 =)
“SELECT * FROM TABLE_PERSONEL WHERE
username = '' OR '' 1 = 1 '' AND Password = '' OR '' 1 = 1 '' ''
makes it. In this case , all existing records from the query will be returned.
C. Command Injection
Generally, command (shell) injection attacks are an attack type that directly targets
servers, unlike SQL injection and XSS attacks. It aims to access information on the operating
system, database management system and server with remote access using the command line
of the web application (Sonntag 2016).
IV. RESULT
It is of great importance to assimilate the elements of cyber security in order to protect the
integrity and accuracy of our information assets in the cyber world. As this review study shows, in
order to ensure cyber security, a risk analysis should be carried out on information assets, the current
and potential threats should be identified by taking into account the analysis and the development of
cyber processes, the preparedness levels and solutions to be applied in the face of threats should be
determined and measures should be taken for popular cyber threat tools. .
13
21.
ReferencesAnalysis, Netherlands Bureau for Economic Policy. 2016. “Cyber Security Risk Assessment for the
Economy.” CPB Communication, no. July: 1–64.
Bashir, Hanad. 2019. “Cyber Security in Somalia,” no. October.
Bulturbayevich, Mullabayev B, Shakirova G Sharipdjanovna, Alabayev S Ibragimovich, and
Mirzaabdullayeva Gulnora. 2020. “International Engineering Journal For Research &
Development International Engineering Journal For Research & Development.” International
Engineering Journal for Research & Development 5 (4): 5. http://www.iejrd.com/index.php/
/article/view/768.
Dissanayake, Viraj. 2020. “A Review of Cyber Security Risks in an Augmented Reality World,” no.
October 2018: 0–7.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339941469_A_review_of_Cyber_security_risks_in_a
n_Augmented_reality_world.
Fram, Eugene H. 2015. “N Onprofit Management Dr . Eugene H . Fram Shares His Insights on
Nonprofit Managment Do Nonprofit Directors Face Cyber Security Risk ?,” no. May: 13–16.
Henshel, D., M. G. Cains, B. Hoffman, and T. Kelley. 2015. “Trust as a Human Factor in Holistic
Cyber Security Risk Assessment.” Procedia Manufacturing 3 (December): 1117–24.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2015.07.186.
Hossain, Nazmul, and Taposh Das. 2017. “Measuring the Cyber Security Risk Assessment Methods
for Scada System.” Global Journal of Engineering Science and Research Managemen, no.
July. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.824955.
Kure, Halima Ibrahim, Shareeful Islam, and Mohammad Abdur Razzaque. 2018. “An Integrated
Cyber Security Risk Management Approach for a Cyber-Physical System.” Applied Sciences
(Switzerland) 8 (6). https://doi.org/10.3390/app8060898.
Musman, Scott, and Andrew Turner. 2018. “A Game Theoretic Approach to Cyber Security Risk
Management.” Journal of Defense Modeling and Simulation 15 (2): 127–46.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1548512917699724.
Shevchenko, Svitlana, Yulia Zhdanovа, Svitlana Spasiteleva, Olena Negodenko, Nataliia Mazur,
14
22.
and Kateryna Kravchuk. 2019. “Mathematical Methods in Cyber Security: Fractals and TheirApplications in Information and Cyber Security.” Cybersecurity: Education, Science,
Technique, no. 5: 31–39. https://doi.org/10.28925/2663-4023.2019.5.3139.
Sonntag, Michael. 2016. “Cyber Security.” IDIMT 2016 - Information Technology, Society and
Economy Strategic Cross-Influences - 24th Interdisciplinary Information Management Talks 10
(2): 313–23. https://doi.org/10.2478/hjbpa-2019-0020.
Tarazan, Safak. 2017. “Regulating Cyber Security : Cyber Security and Law Faculty of Information
Technology Department of Cyber Security Ilhan Çelebi - 156937IVCM Mari Jääger 153111IVCM Andres Elliku - 144009IVCM Kaan Sadık Karadag - 156328IVCM Taimur
Tufail - 156329IVCM Regulating Cyber Security Essay Subject : Cyber Security and Law
Supervisor : Agnes Monika Kasper Tallinn 2015,” no. February.
Vepachedu, Sreenivasarao. 2017. “Cyber Security WORLD MALARIA DAY : END MALARIA
FOR GOOD,” no. May.
Woo, Pil Sung, and Balho H. Kim. 2014. “A Study on Quantitative Methodology to Assess Cyber
Security Risk of SCADA Systems.” Advanced Materials Research 960–961 (1): 1602–11.
https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.960-961.1602.
15




















 informatics
informatics








