Similar presentations:
Propositional logic
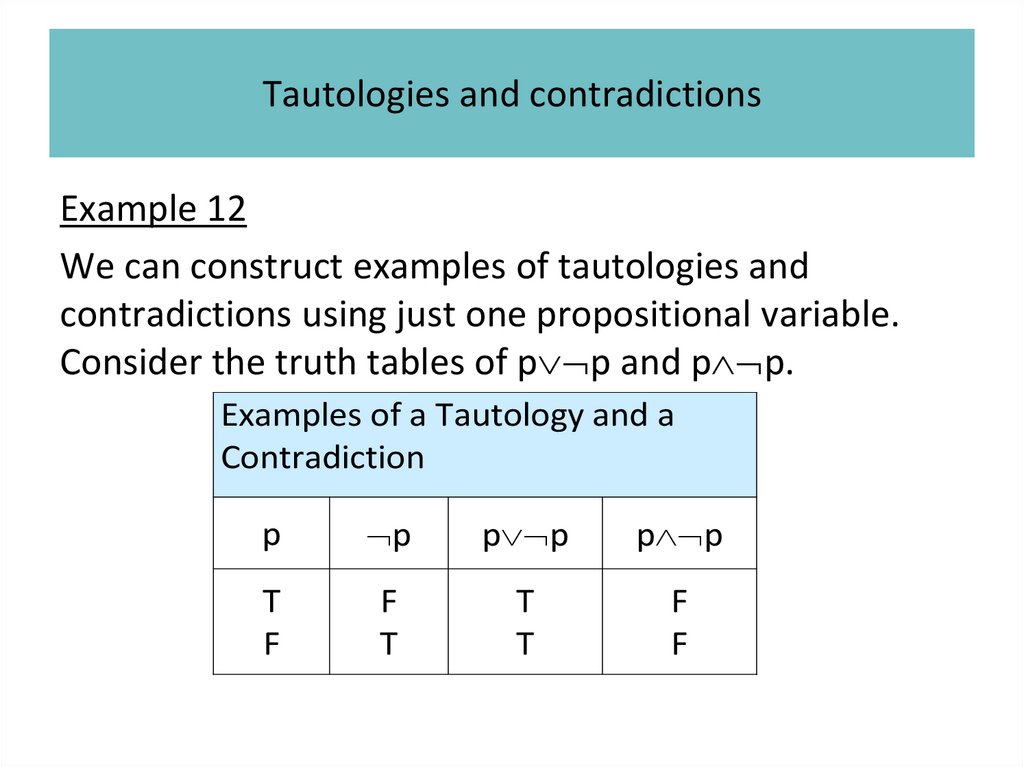
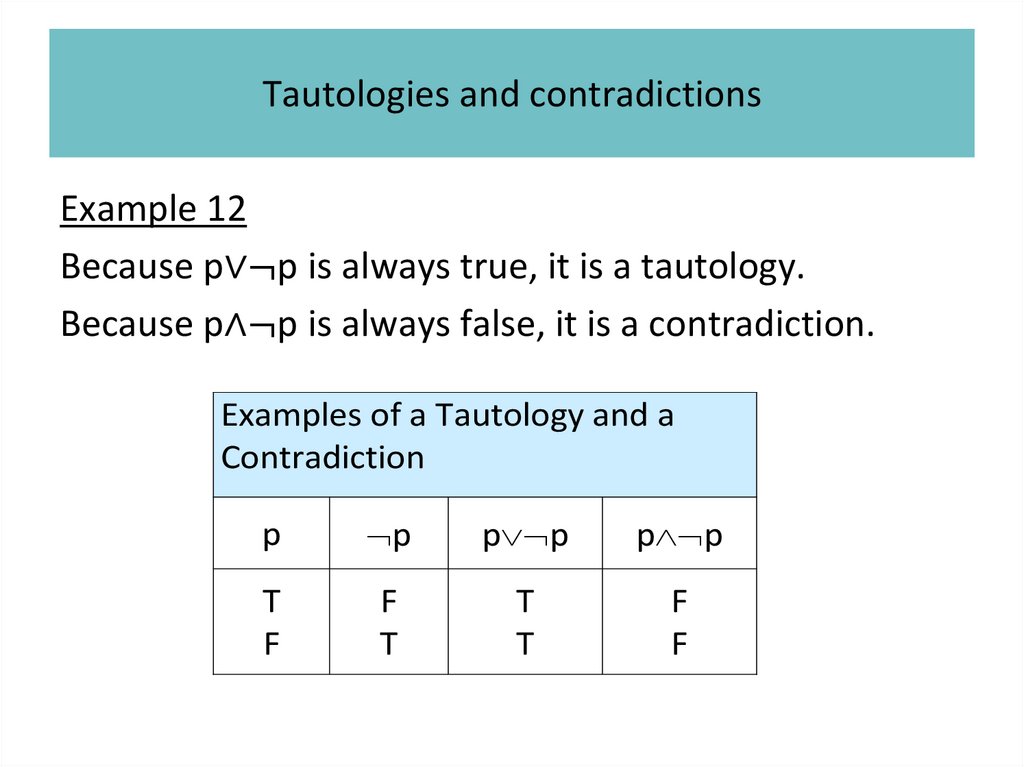
1.
Propositional logicIrina Prosvirnina
• Propositions
• Compound propositions
• Conditional statements
• Truth tables of compound propositions
• Tautologies and contradictions
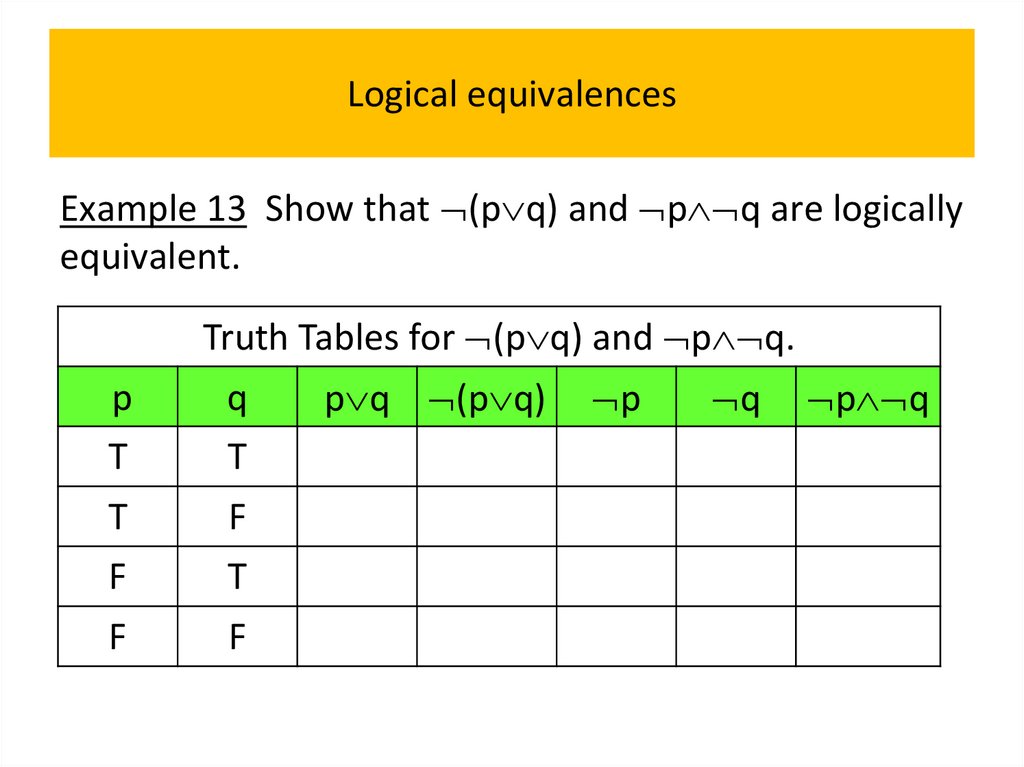
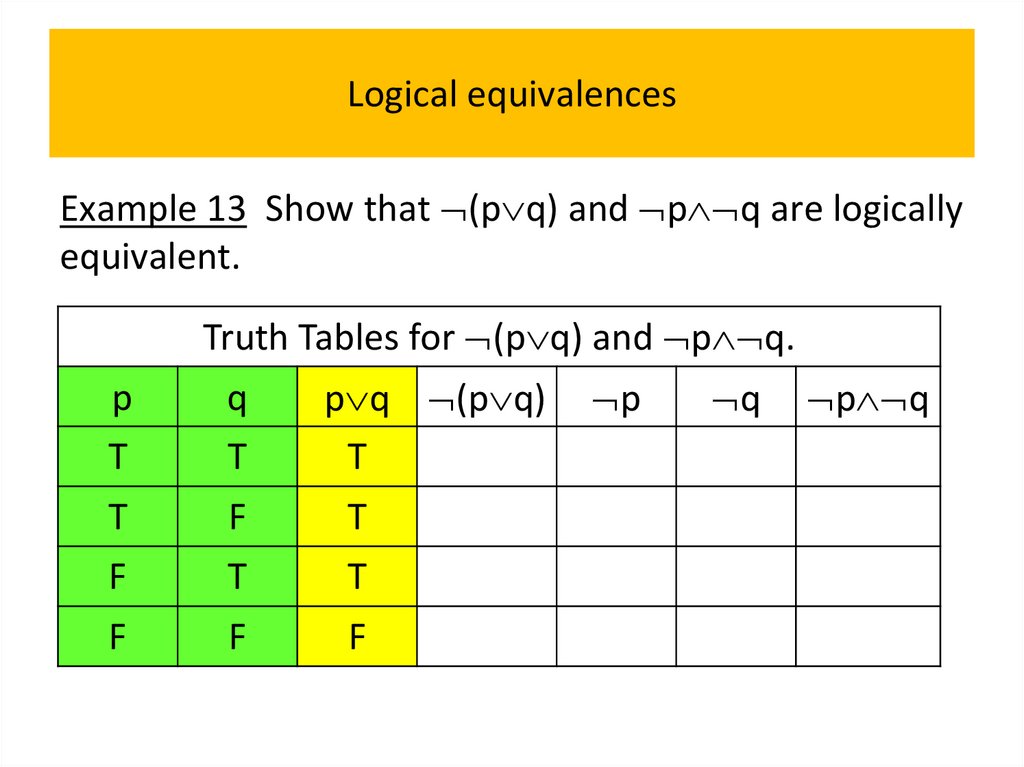
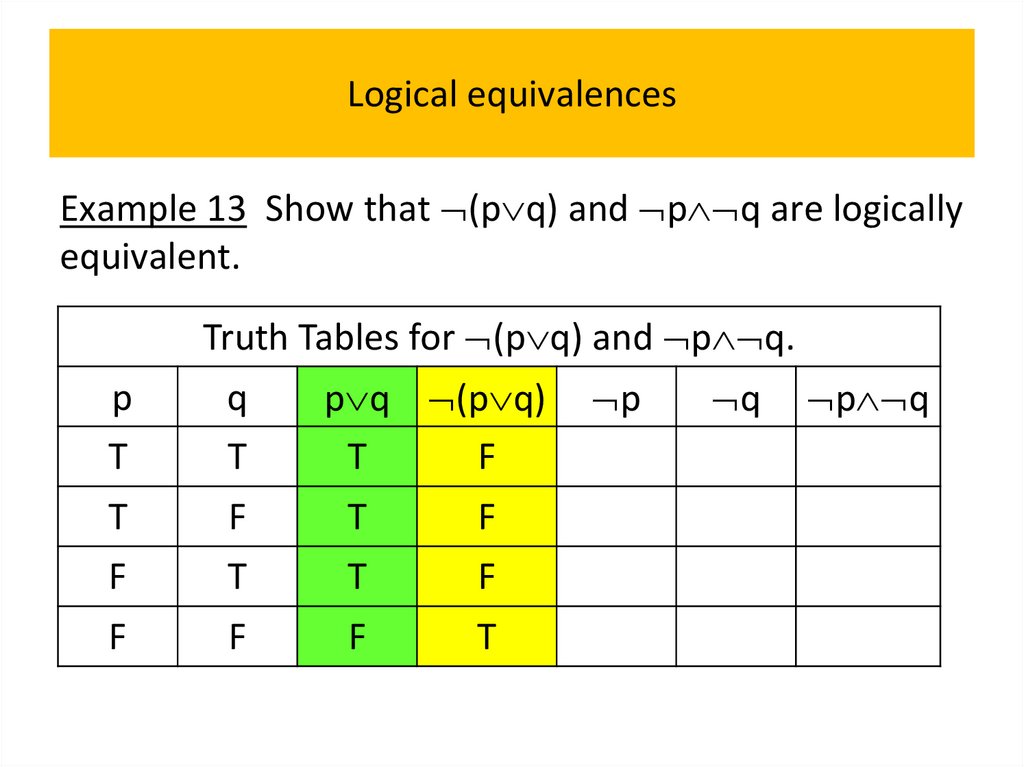
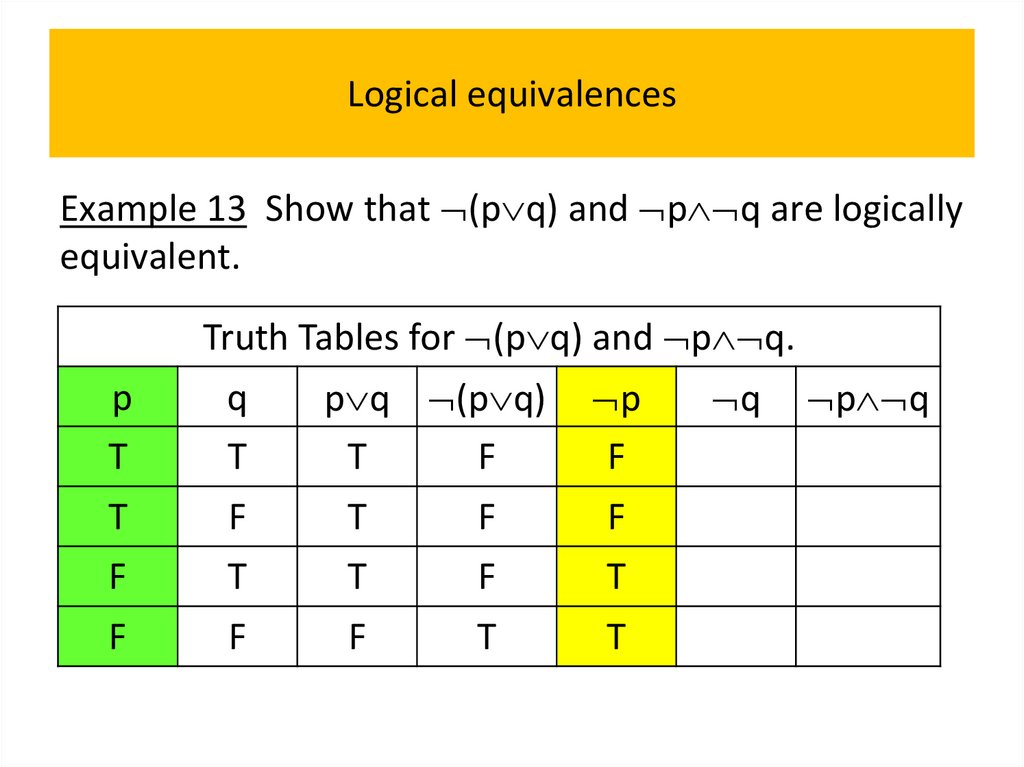
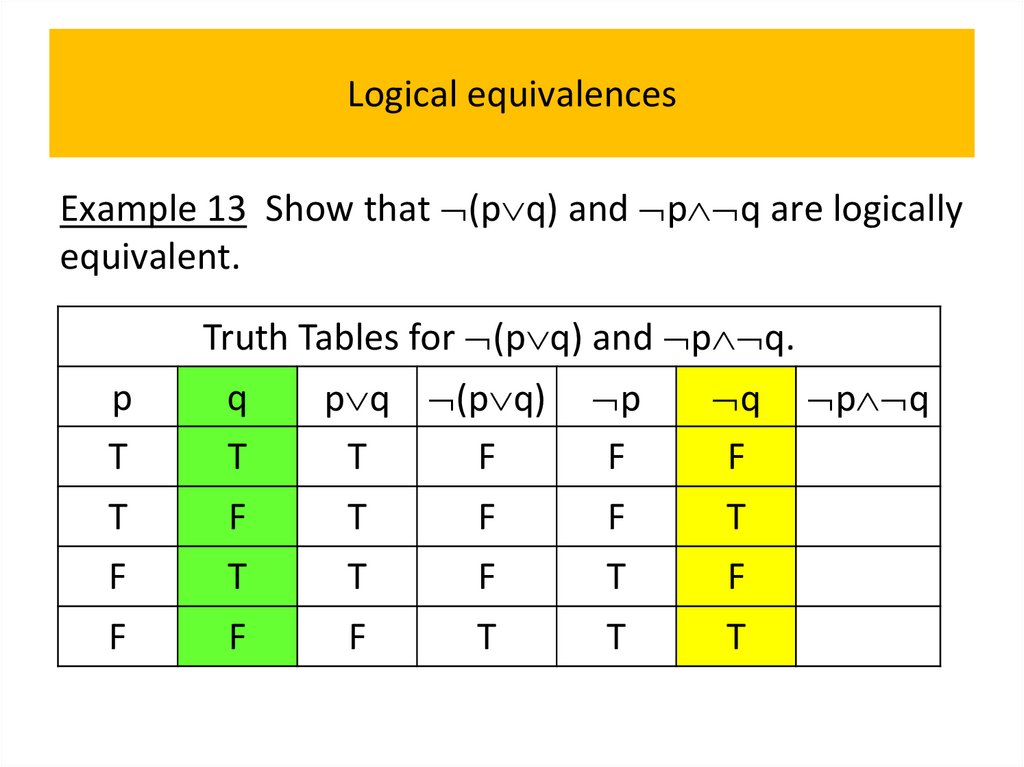
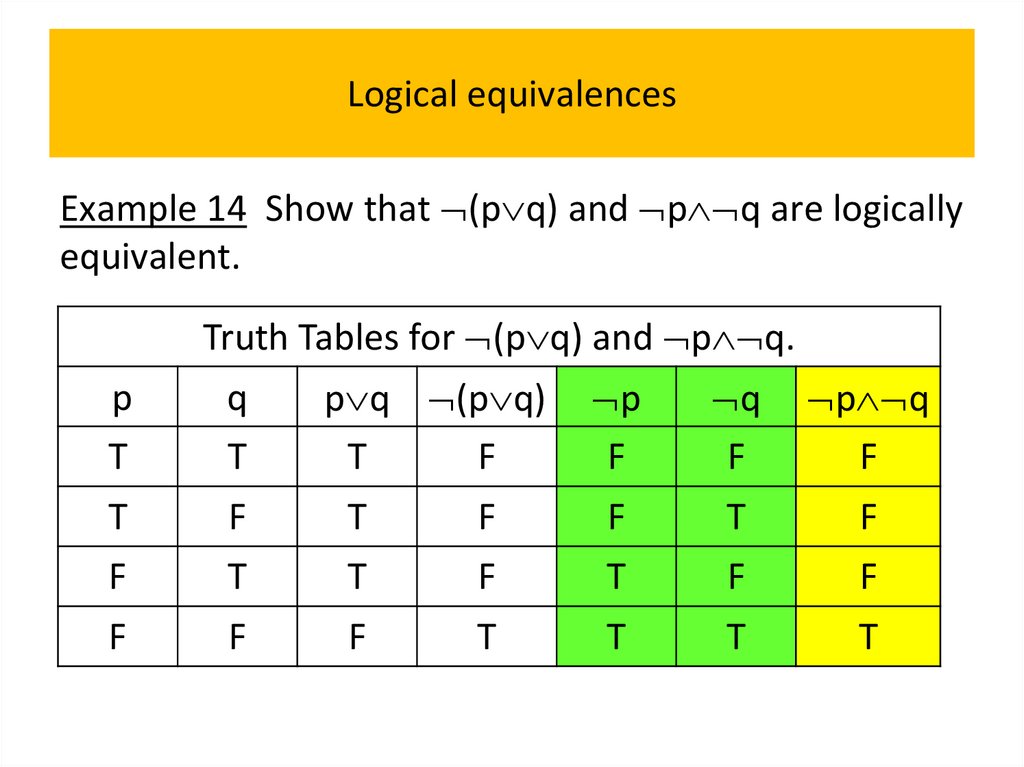
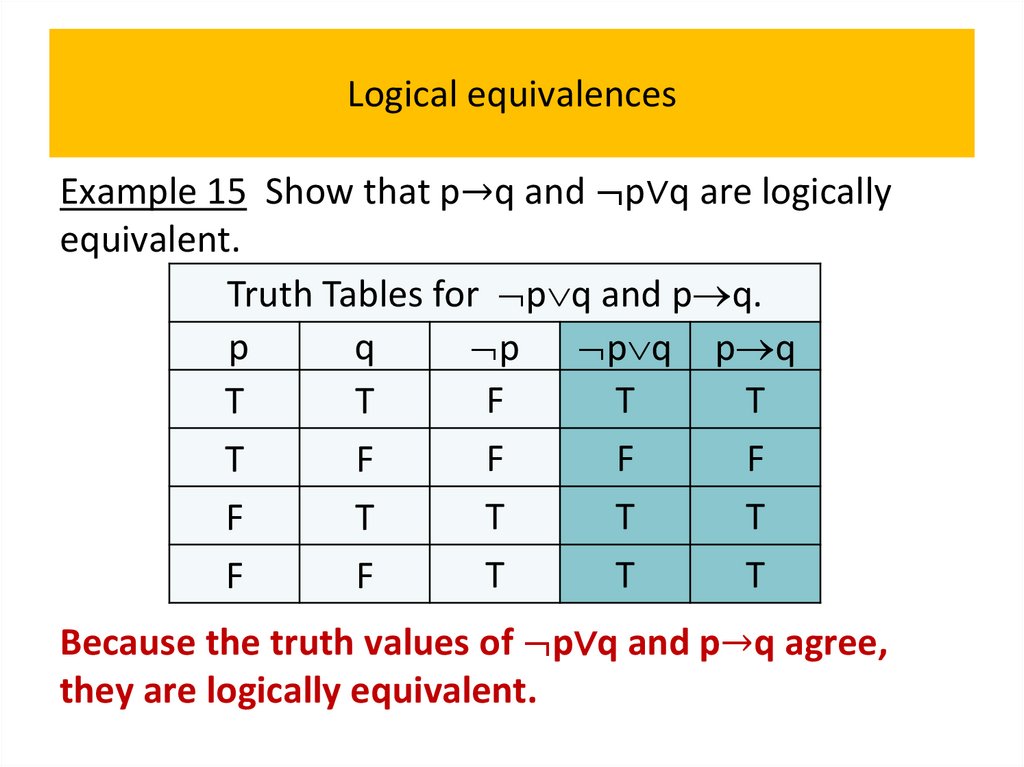
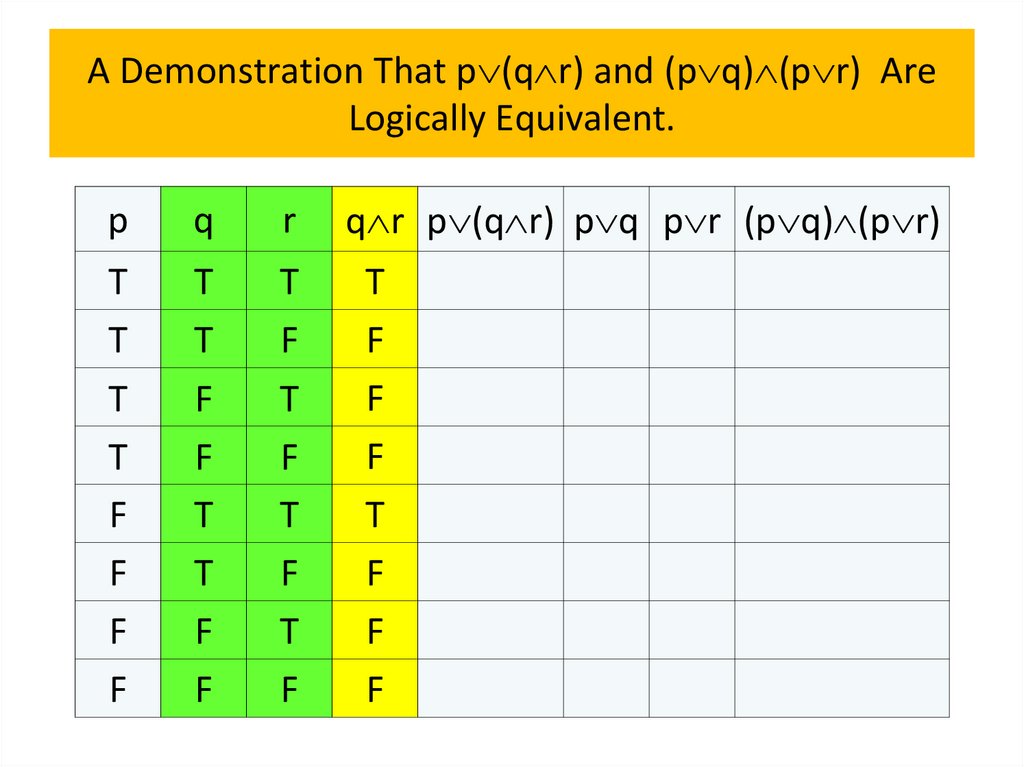
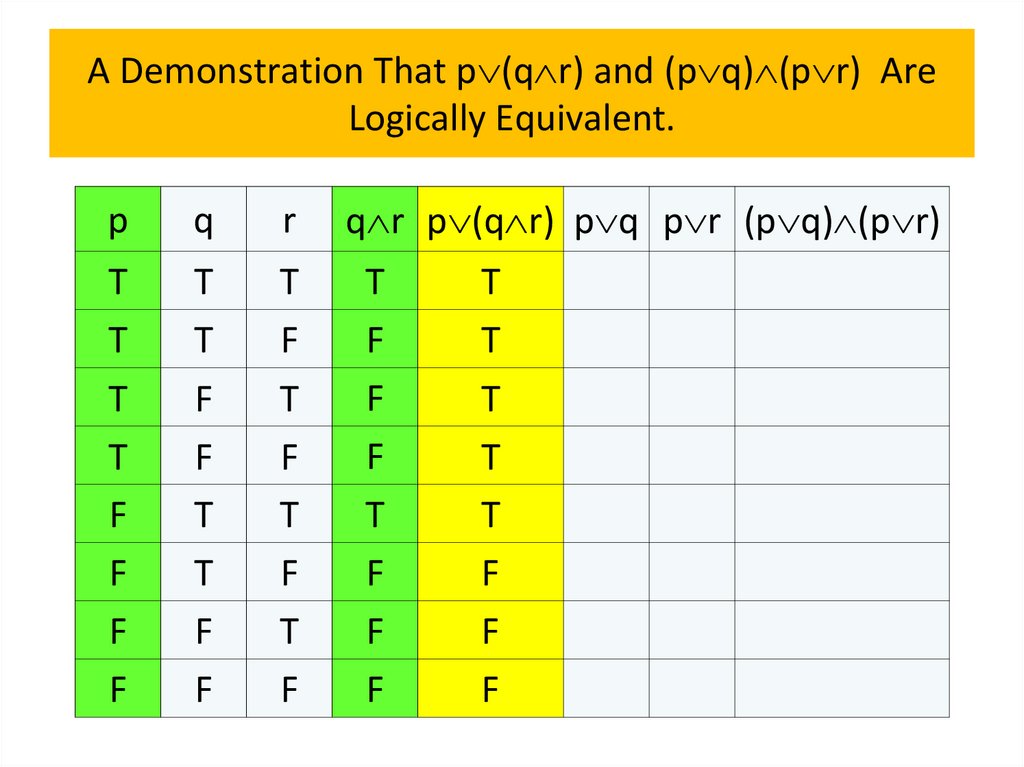
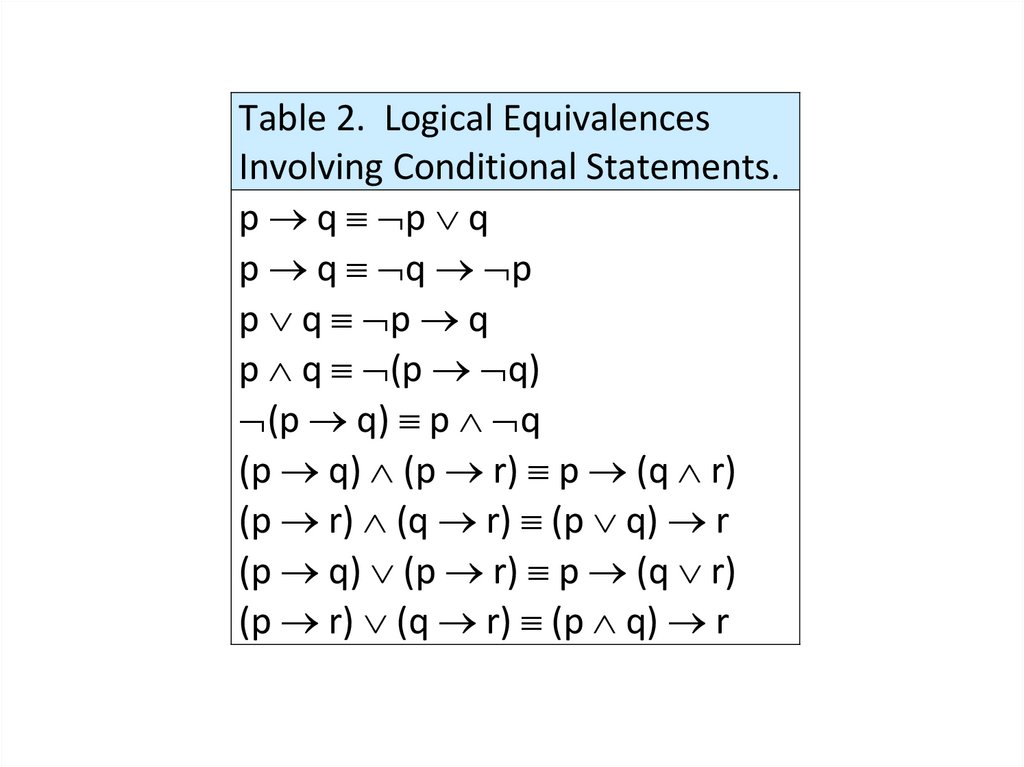
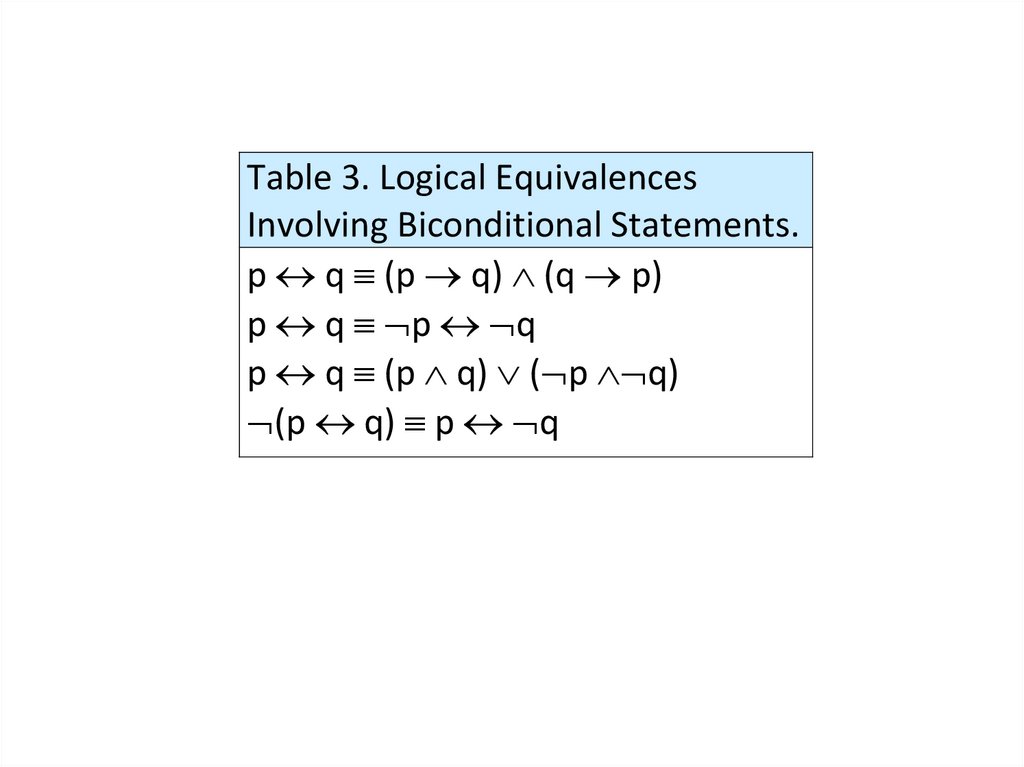
• Logical equivalences
• Propositional satisfiability
• Satisfiability problem
2.
IntroductionLogic is the study of the
principles and techniques of
reasoning.
It originated with the ancient
Greeks, led by the
philosopher Aristotle, who is
often called the father of
logic.
Aristotle
3.
IntroductionHowever, it was not until the
17th century that symbols
were used in the
development of logic.
German philosopher and
mathematician Gottfried
Leibniz introduced
symbolism into logic.
Gottfried Leibniz
4.
IntroductionNevertheless, no significant
contributions in symbolic
logic were made until those
of George Boole, an
English mathematician.
At the age of 39, Boole
published his outstanding
work in symbolic logic, An
Investigation of the Laws
of Thought.
George Boole
5.
IntroductionLogic plays a central role in the development of every area
of learning, especially in mathematics and computer
science.
Computer scientists, for example, employ logic to develop
programming languages and to establish the correctness of
programs.
Electronics engineers apply logic in the design of computer
chips.
6.
IntroductionThis chapter presents the fundamentals of logic, its
symbols, and rules to help you to think systematically, to
express yourself in precise and concise terms, and to make
valid arguments.
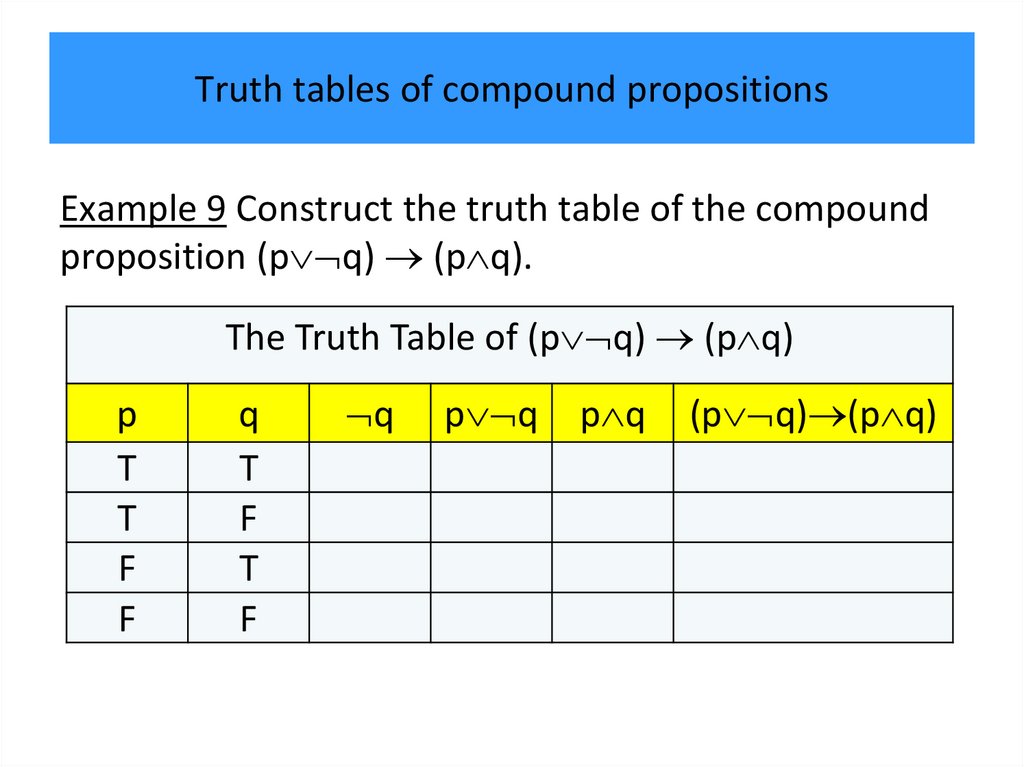
7.
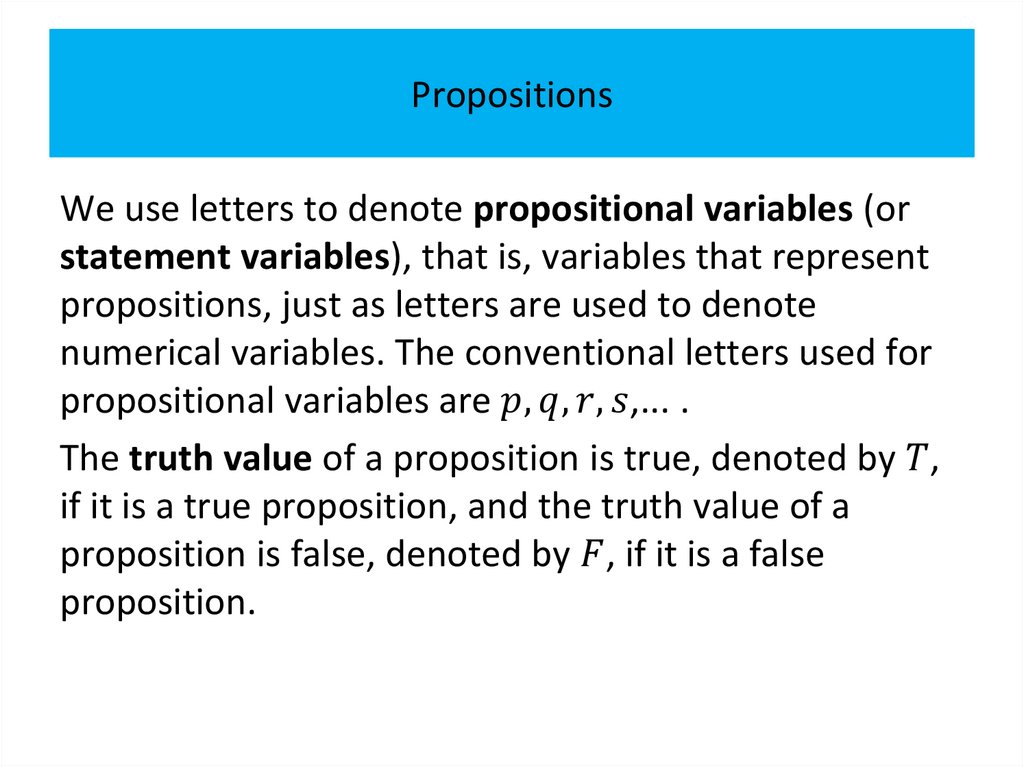
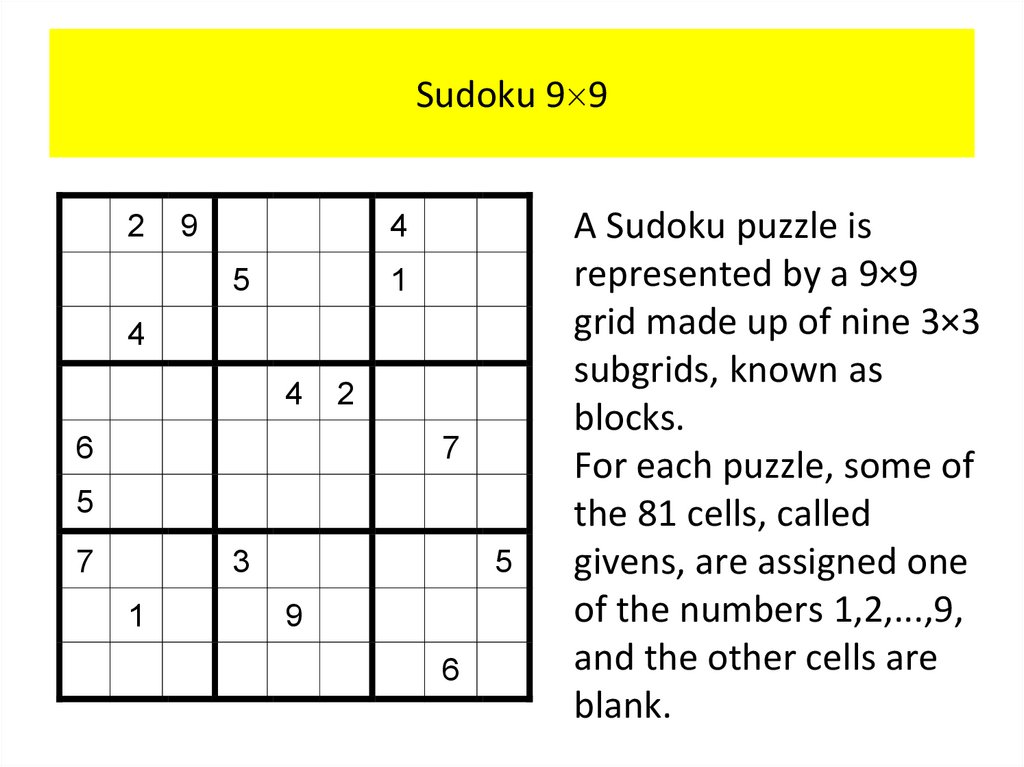
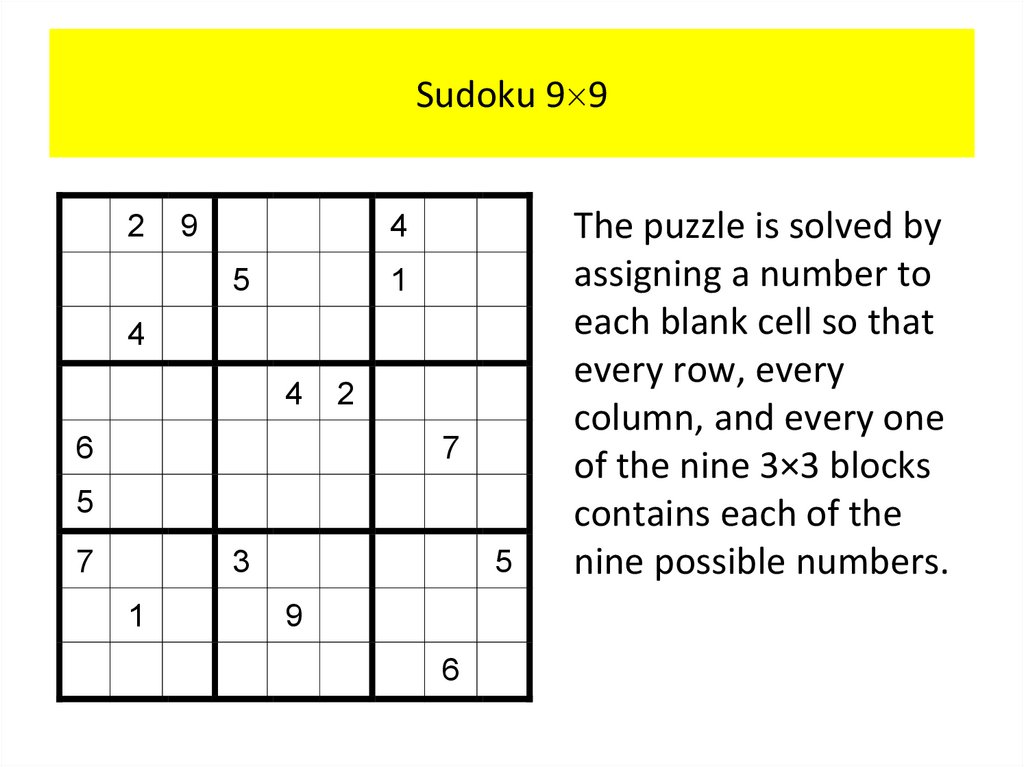
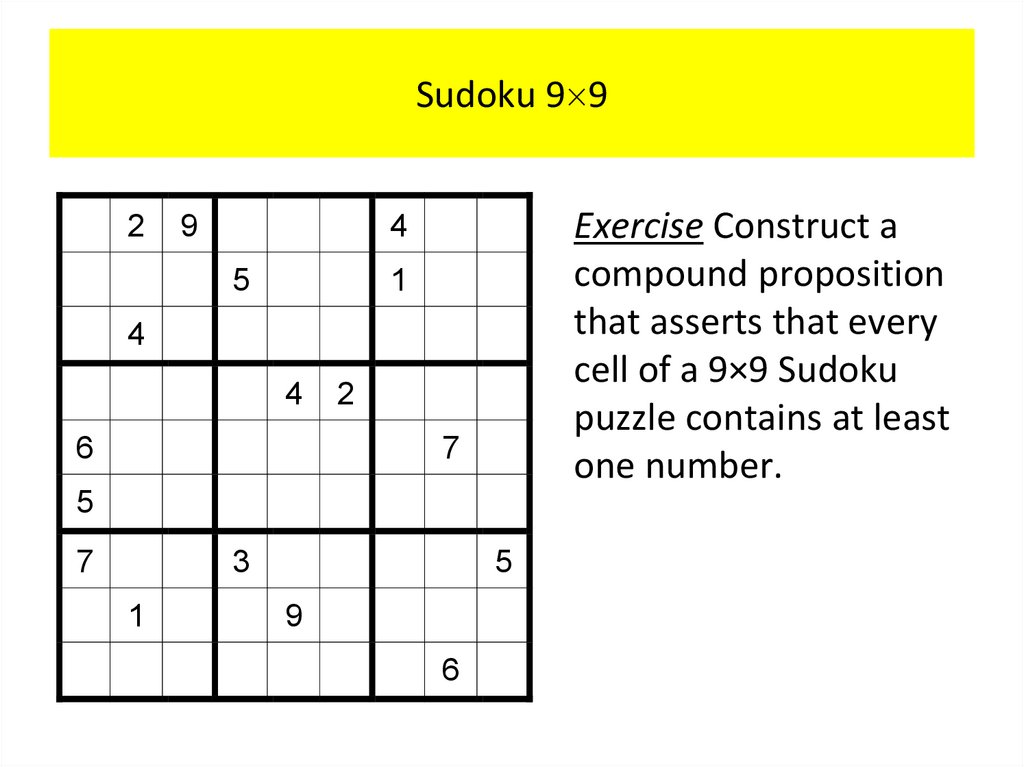
PropositionsOur discussion begins with an introduction to the basic
building blocks of logic – propositions.
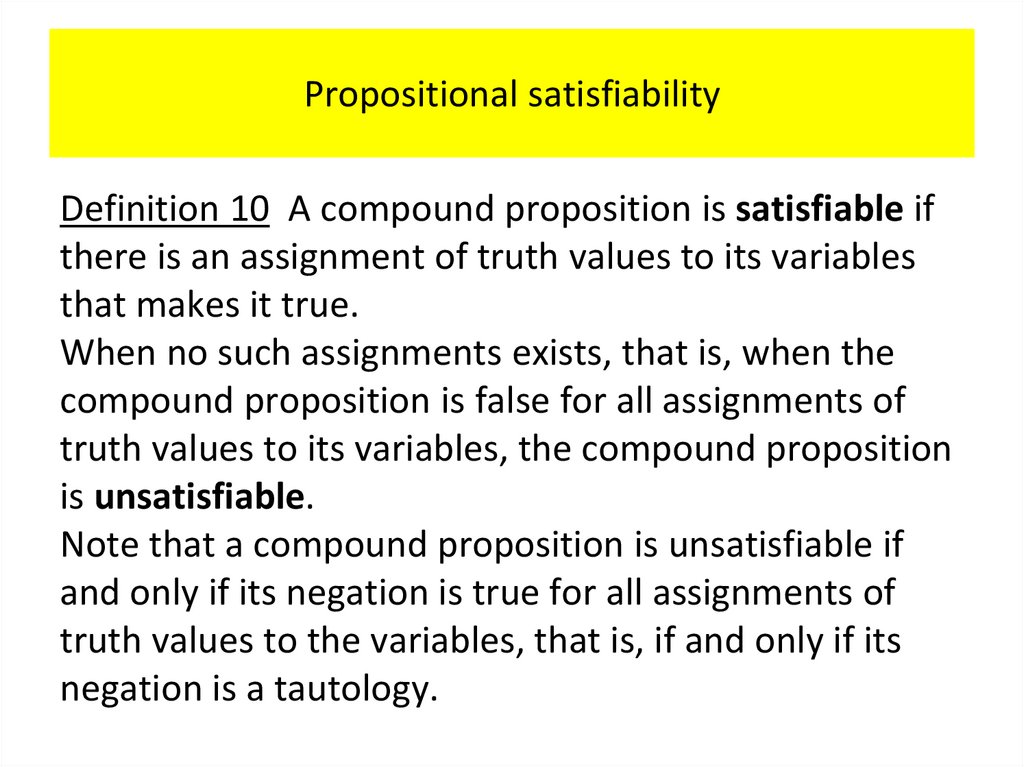
Definition 1
A proposition is a declarative sentence (that is, a
sentence that declares a fact) that is either true or
false, but not both.
8.
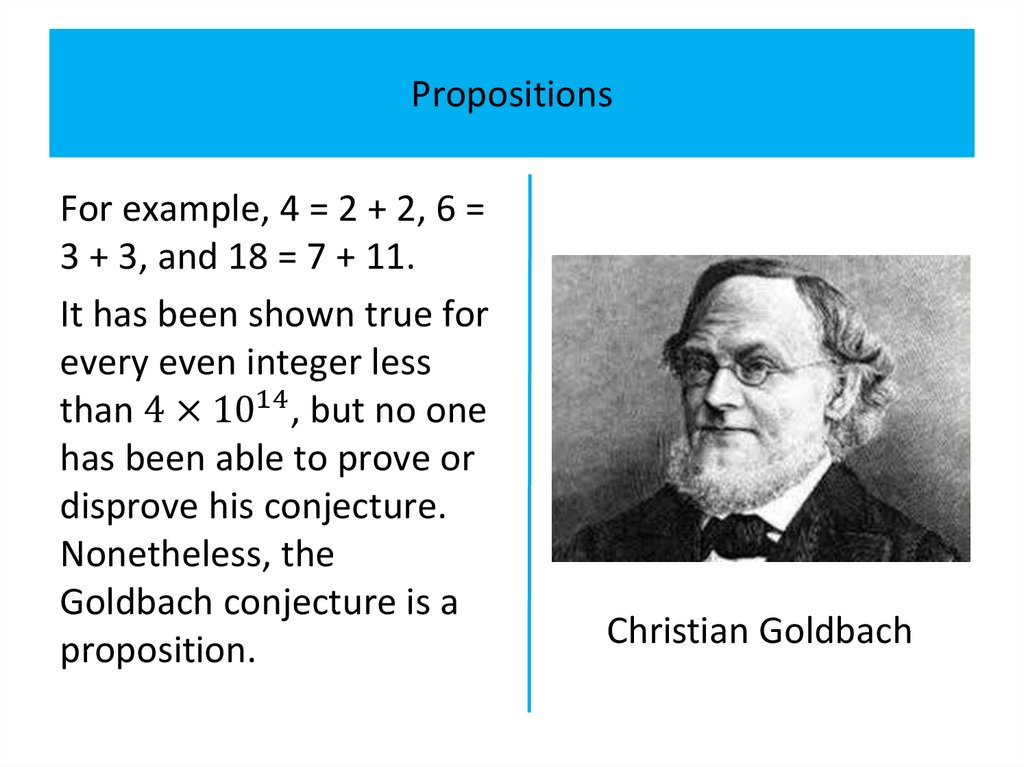
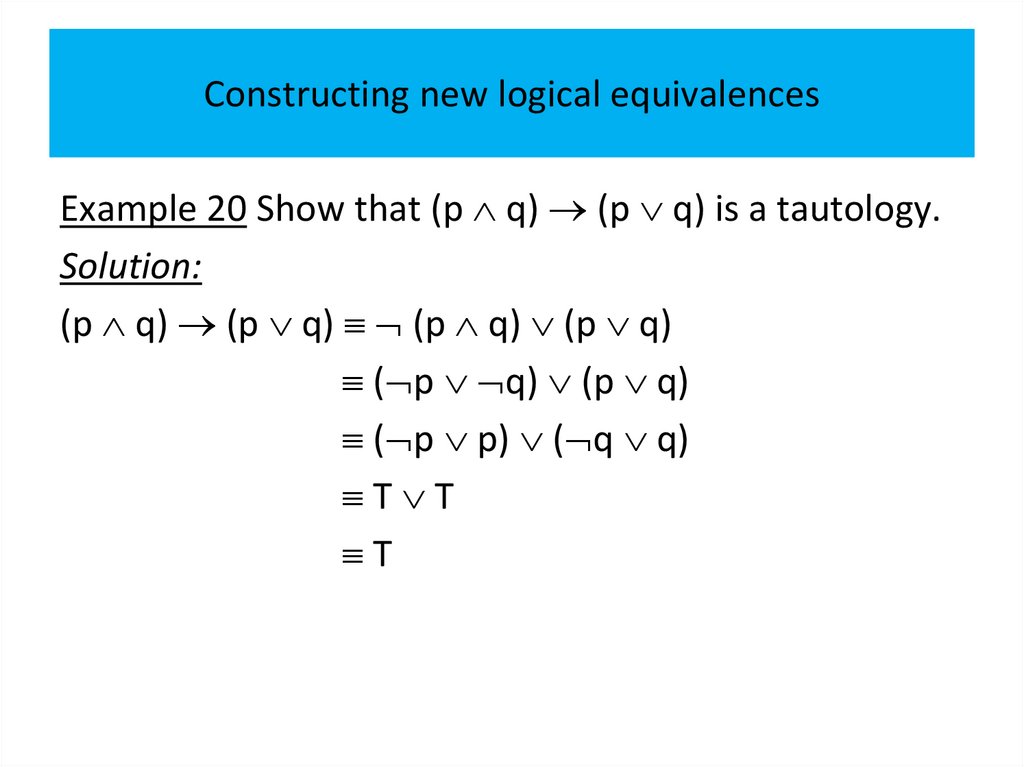
PropositionsExample 1
All the following declarative sentences are propositions.
1. Minsk is the capital of Belarus.
2. Toronto is the capital of Canada.
3. 1+1=2.
4. 2+2=3.
Propositions 1 and 3 are true, whereas 2 and 4 are false.
9.
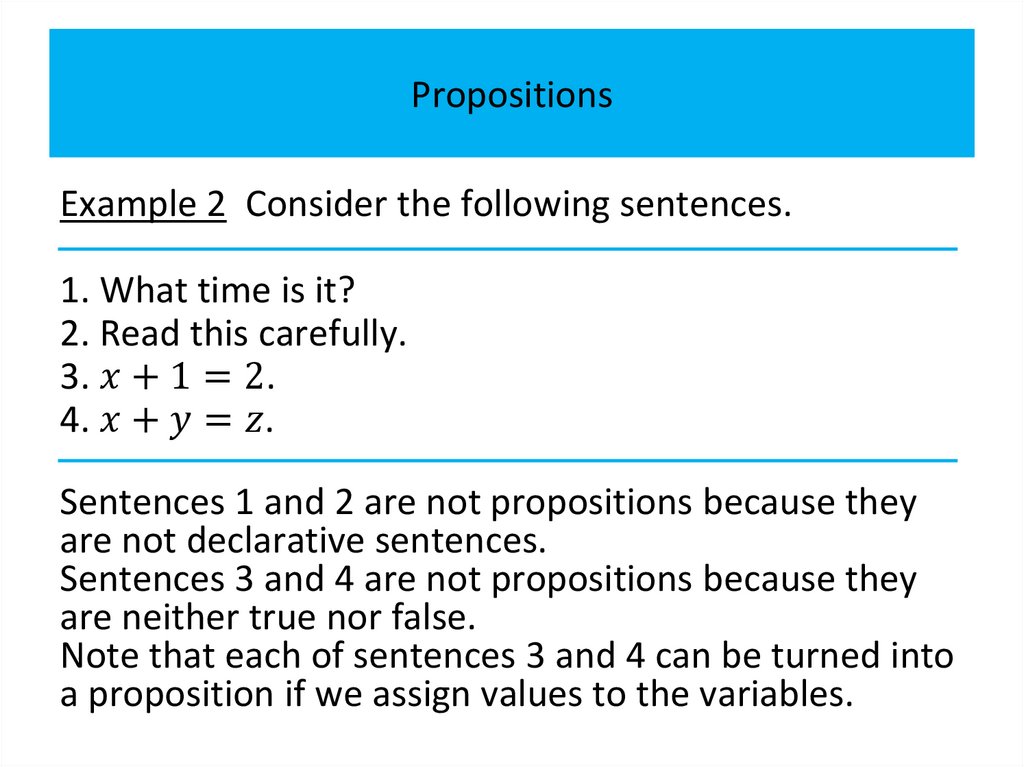
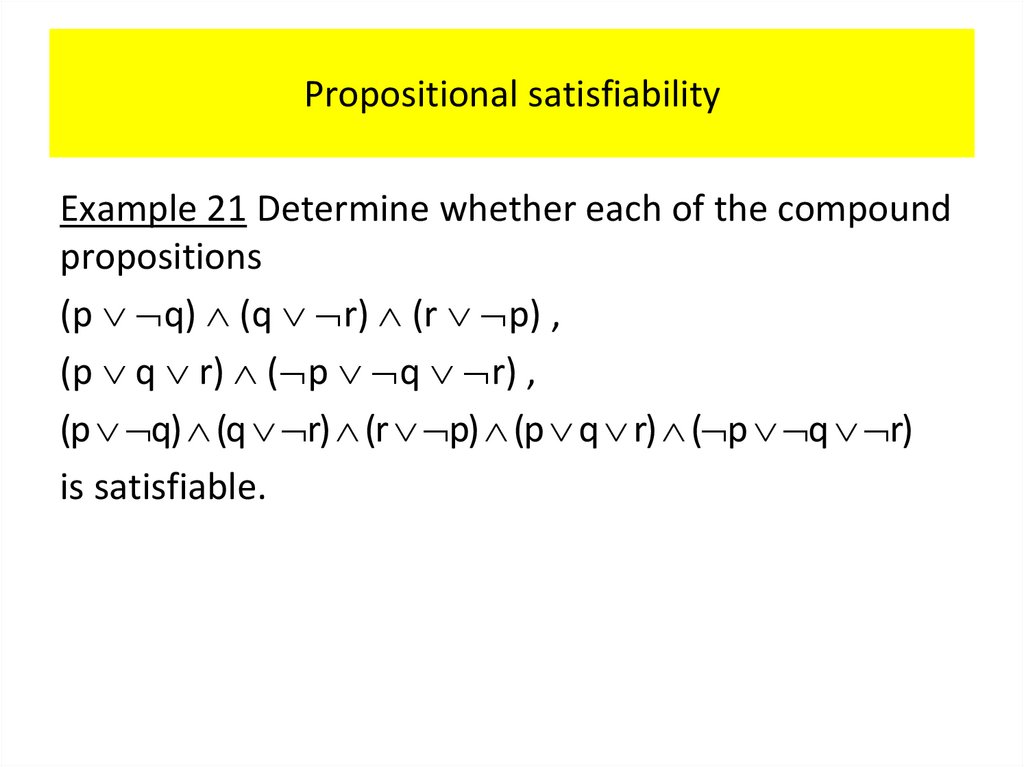
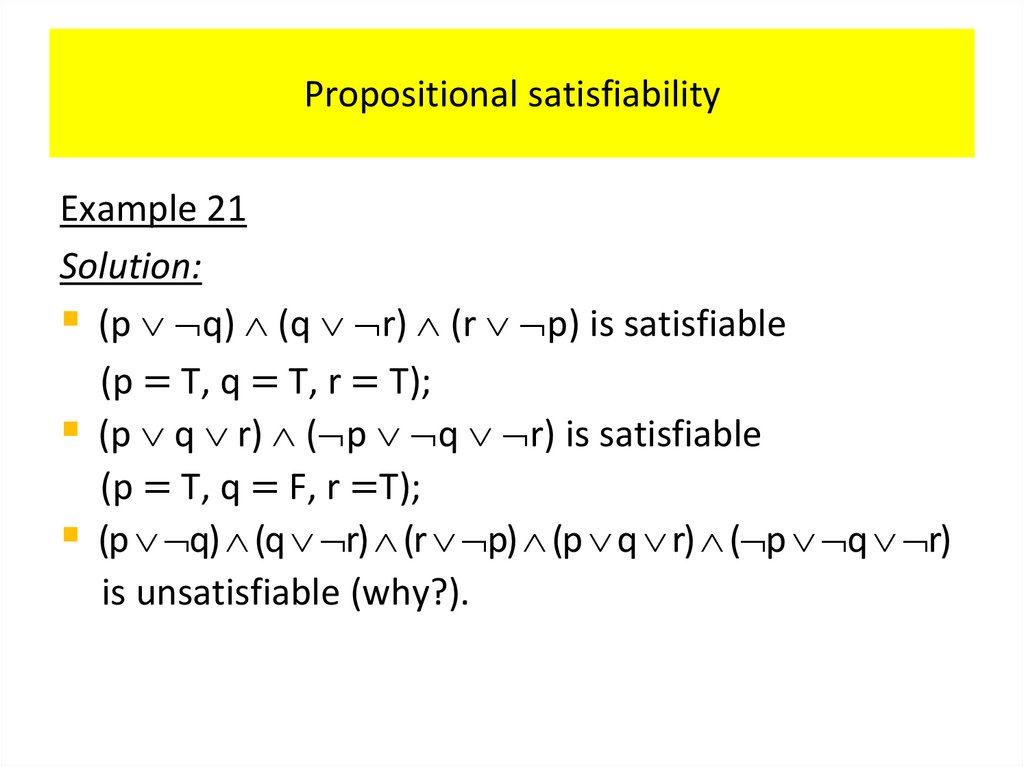
PropositionsExample 2 Consider the following sentences.
1. What time is it?
2. Read this carefully.
3.
























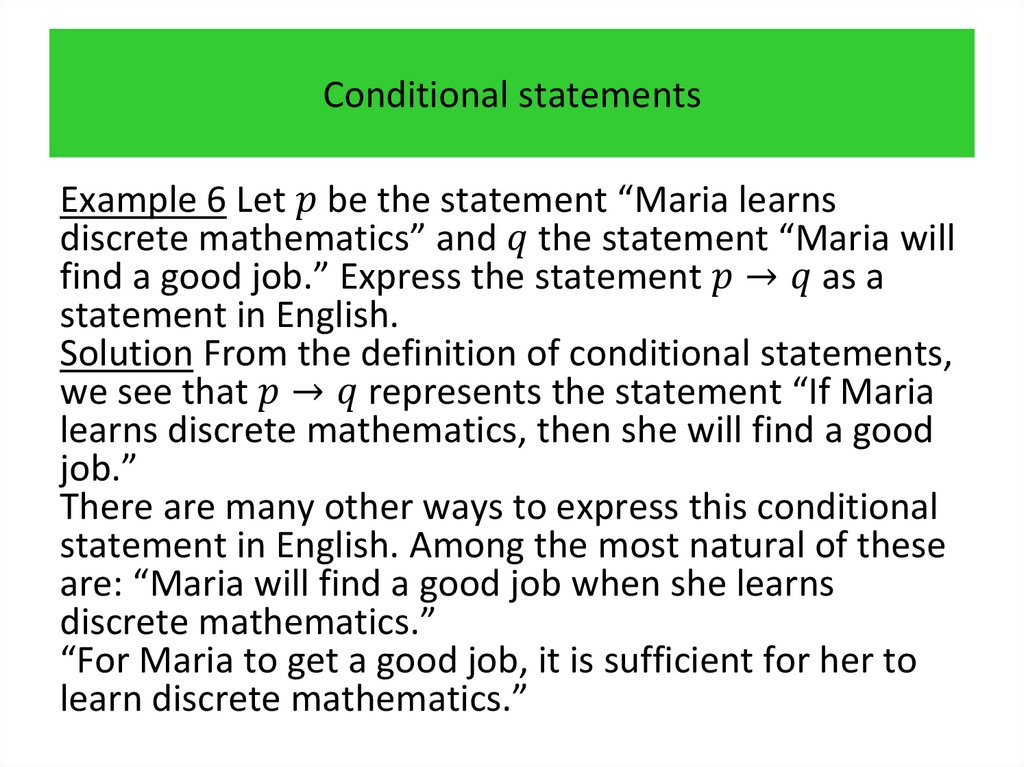


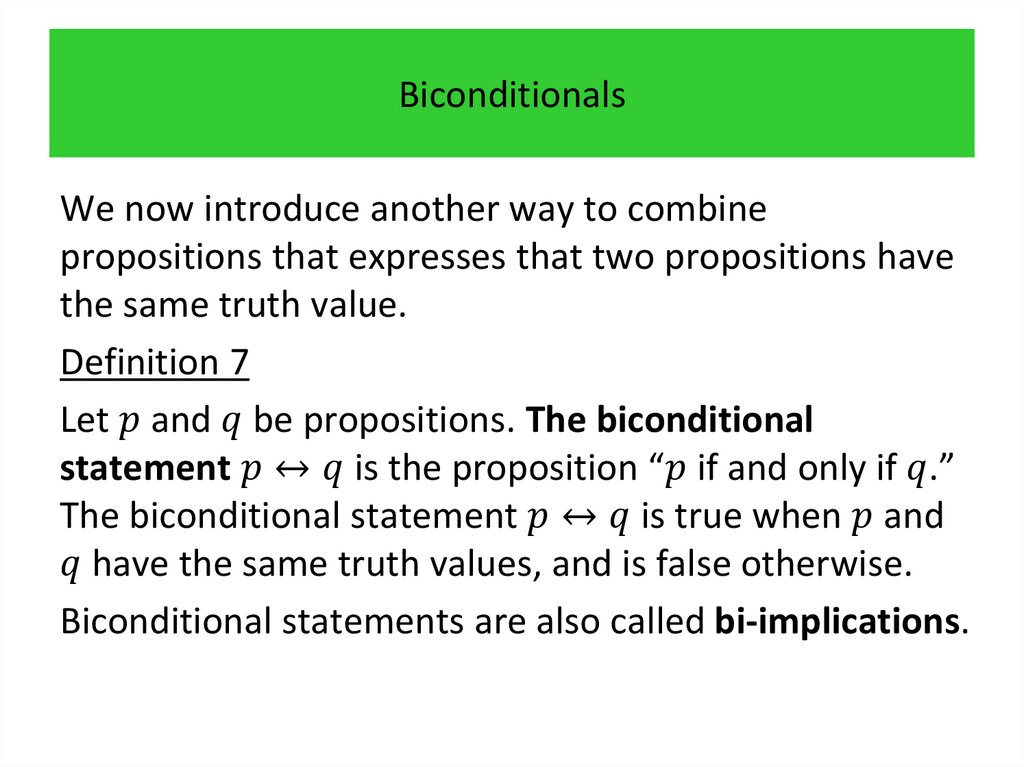
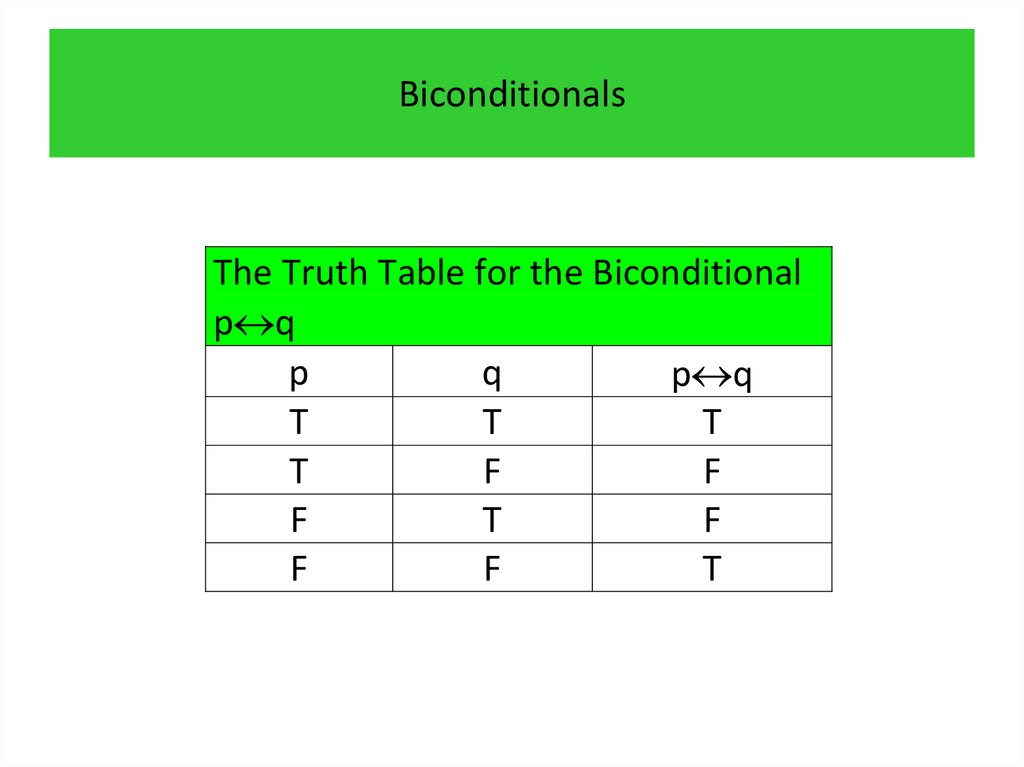
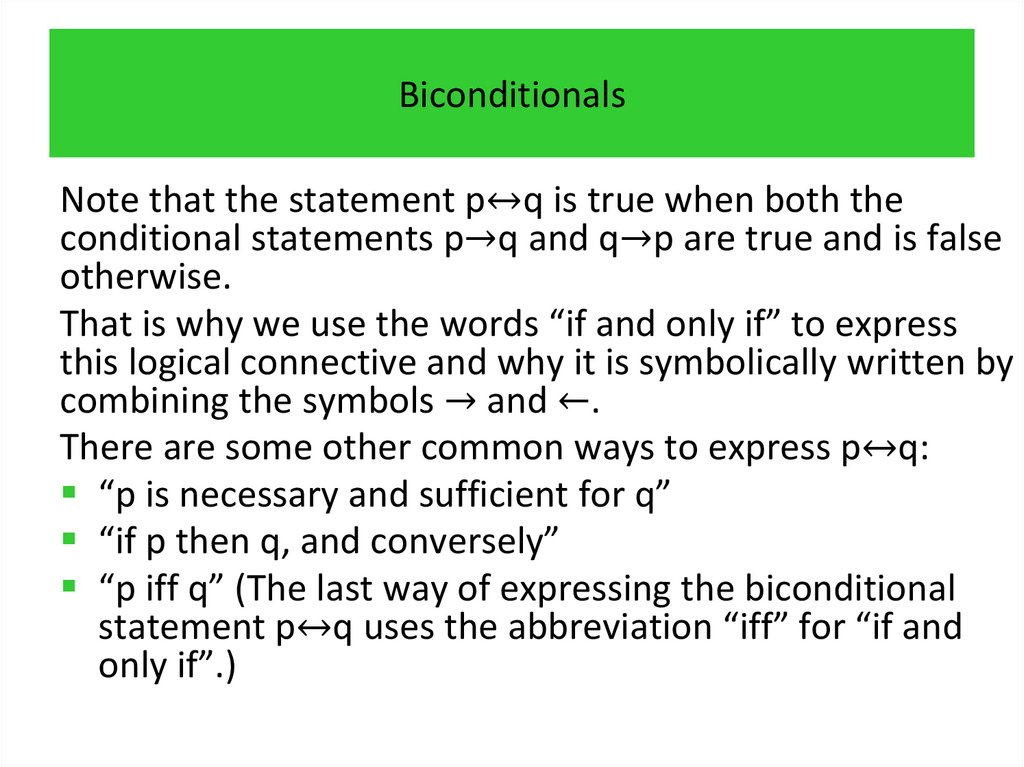


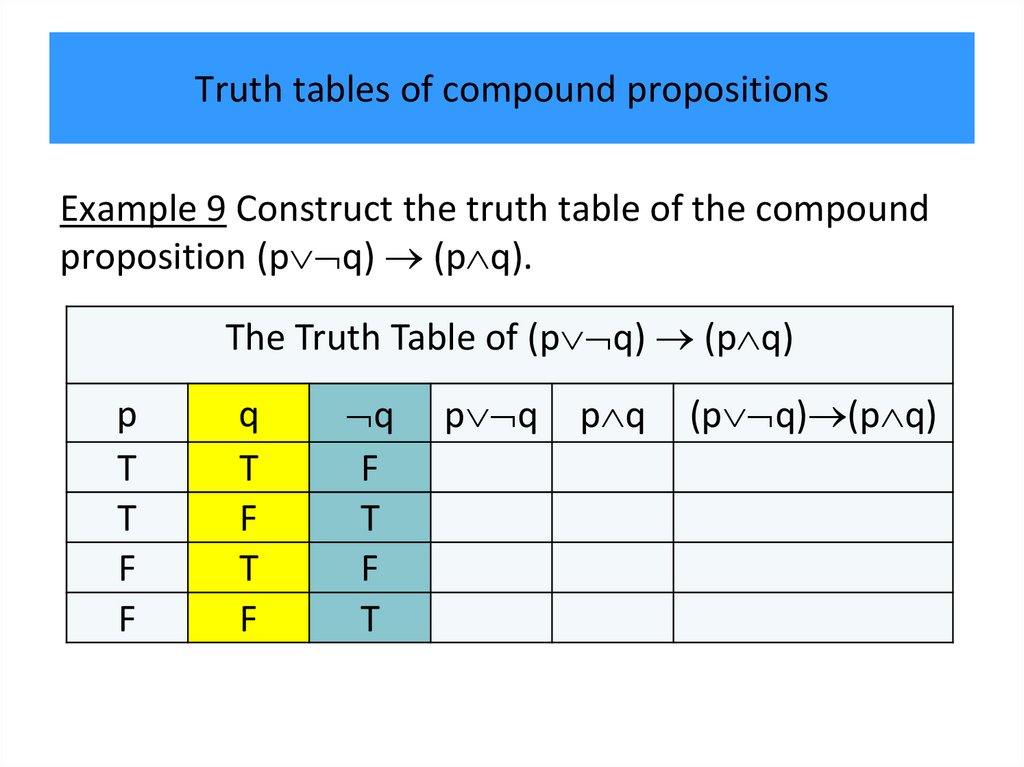
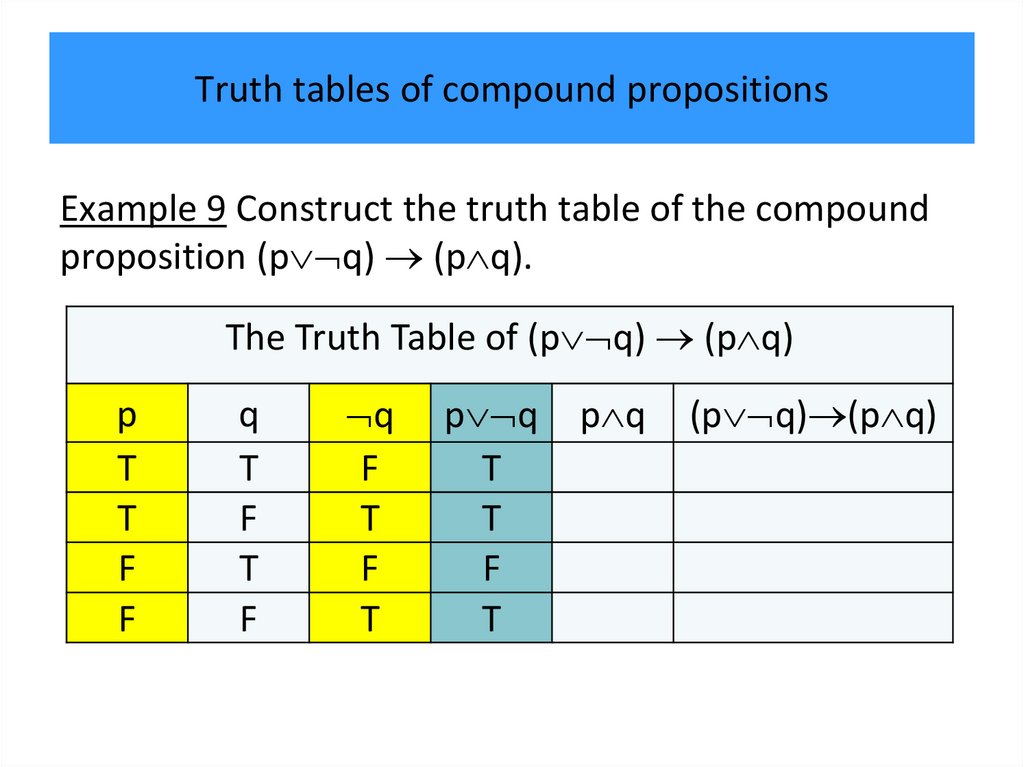
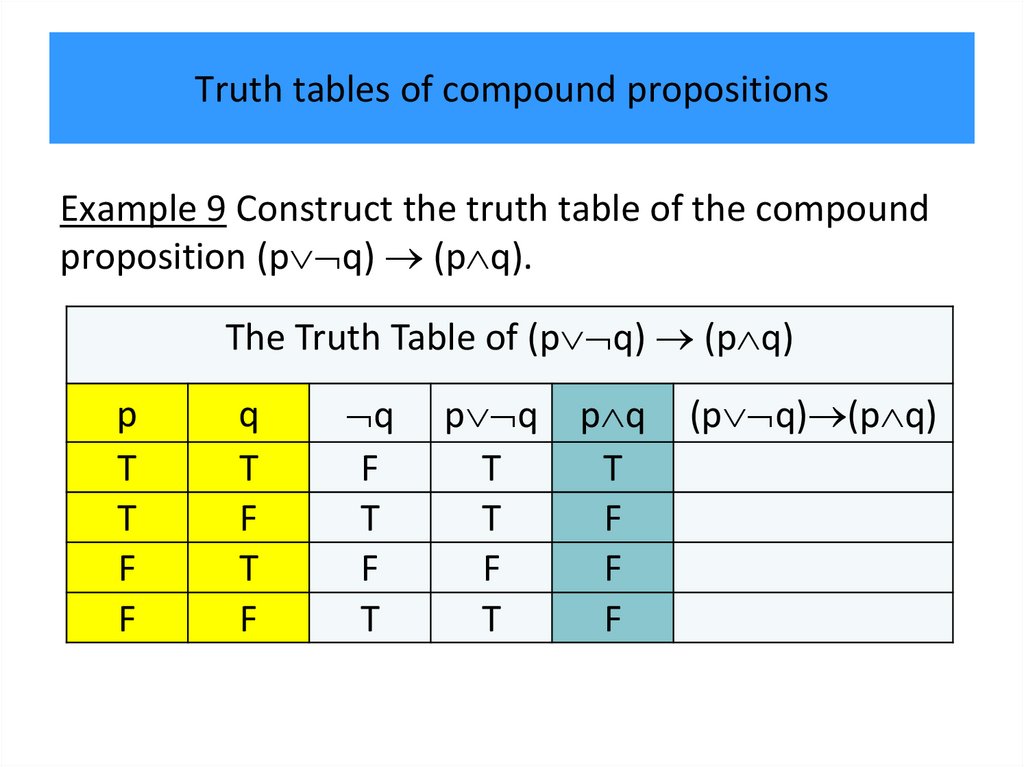
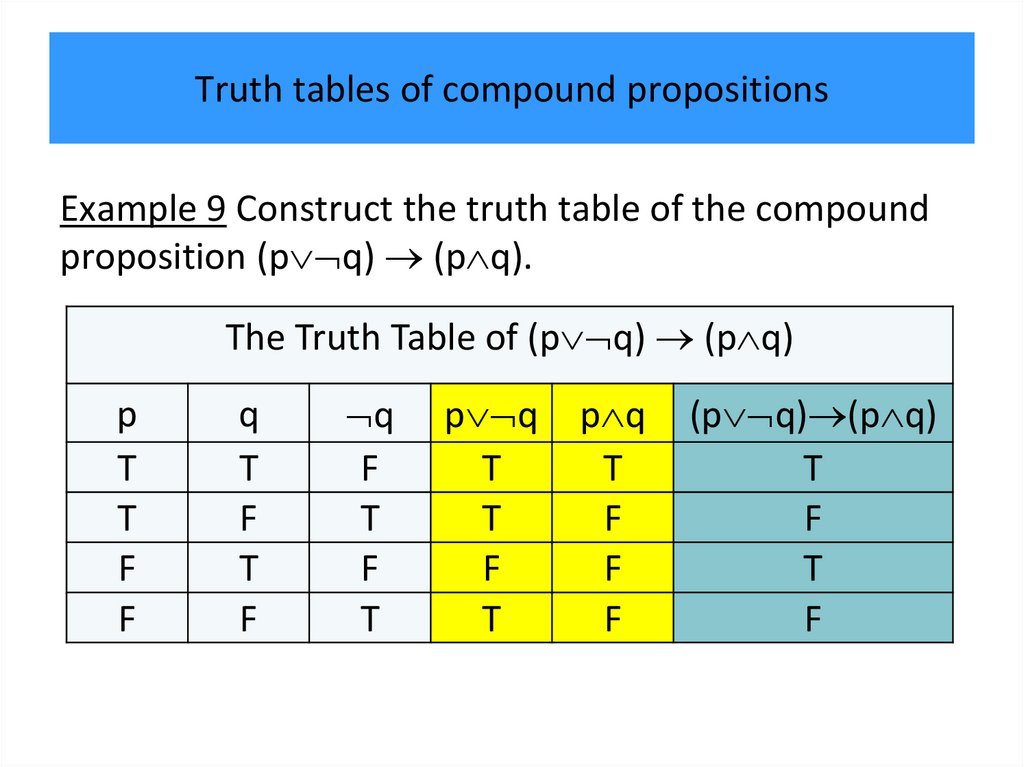















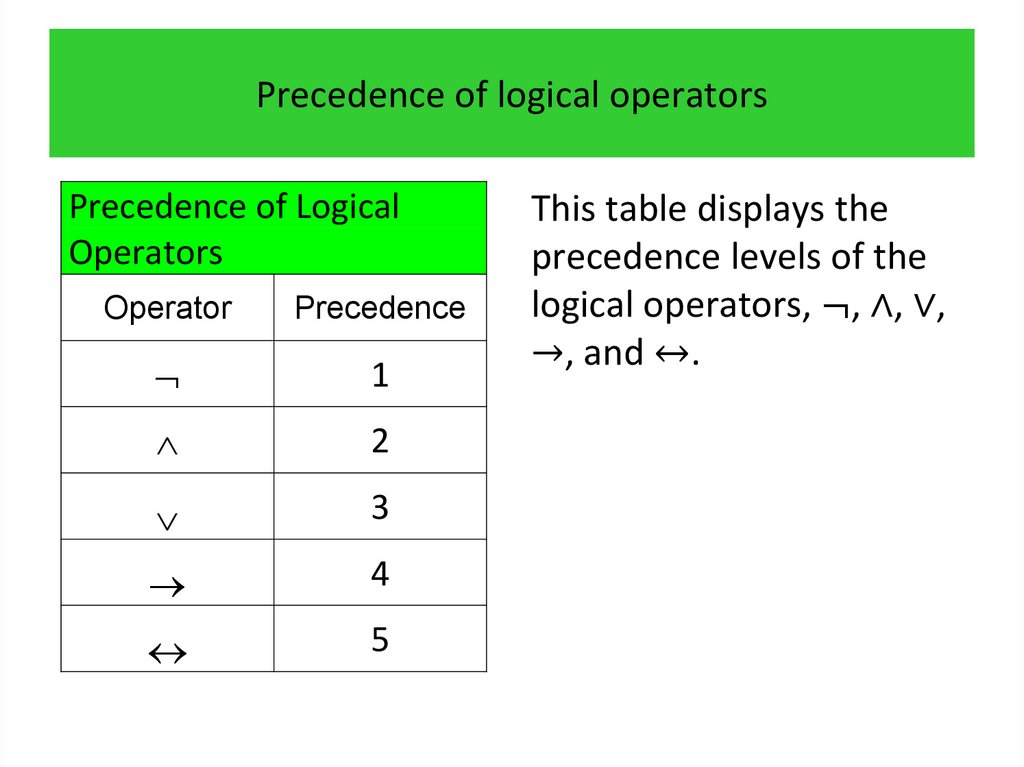
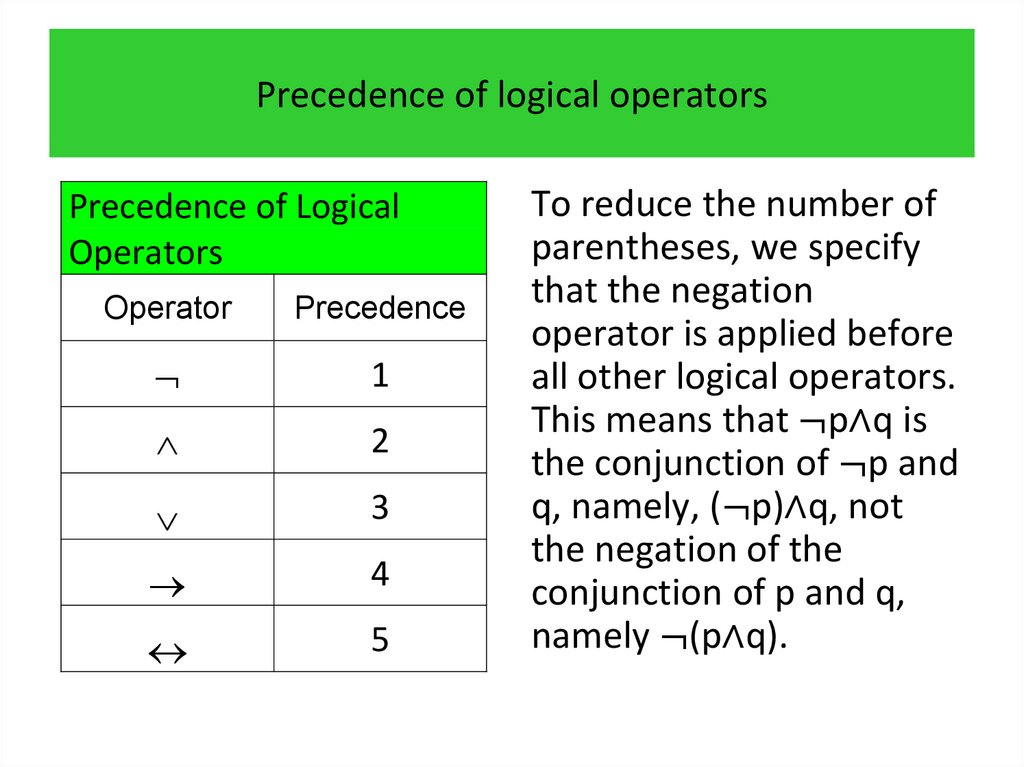
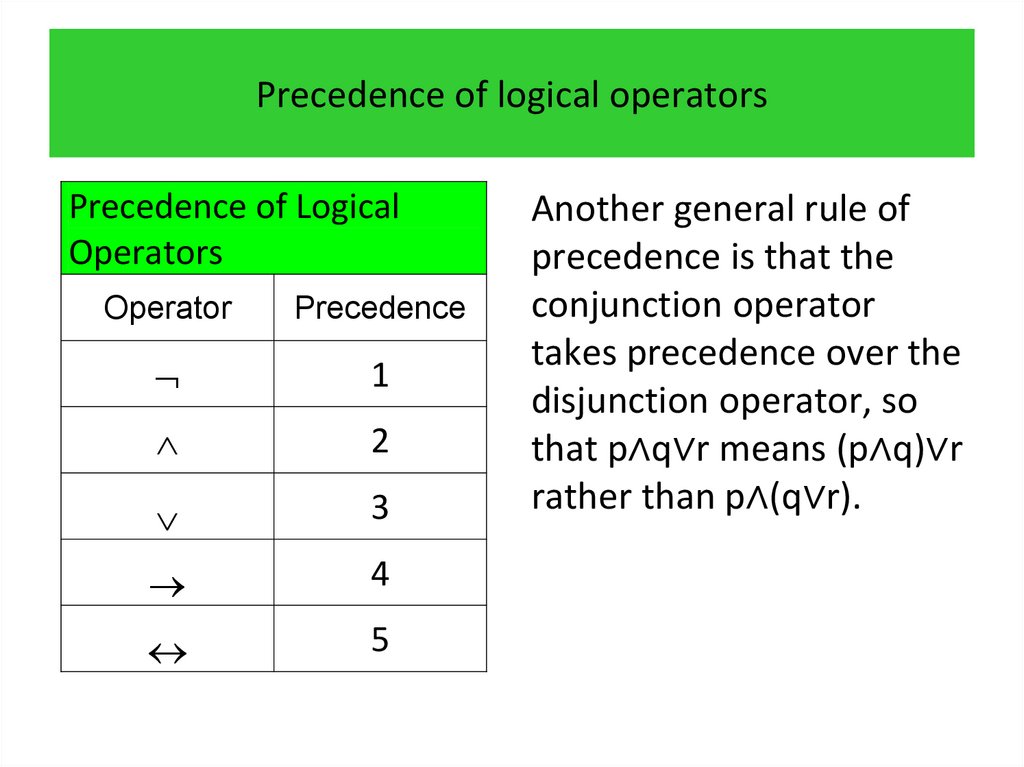
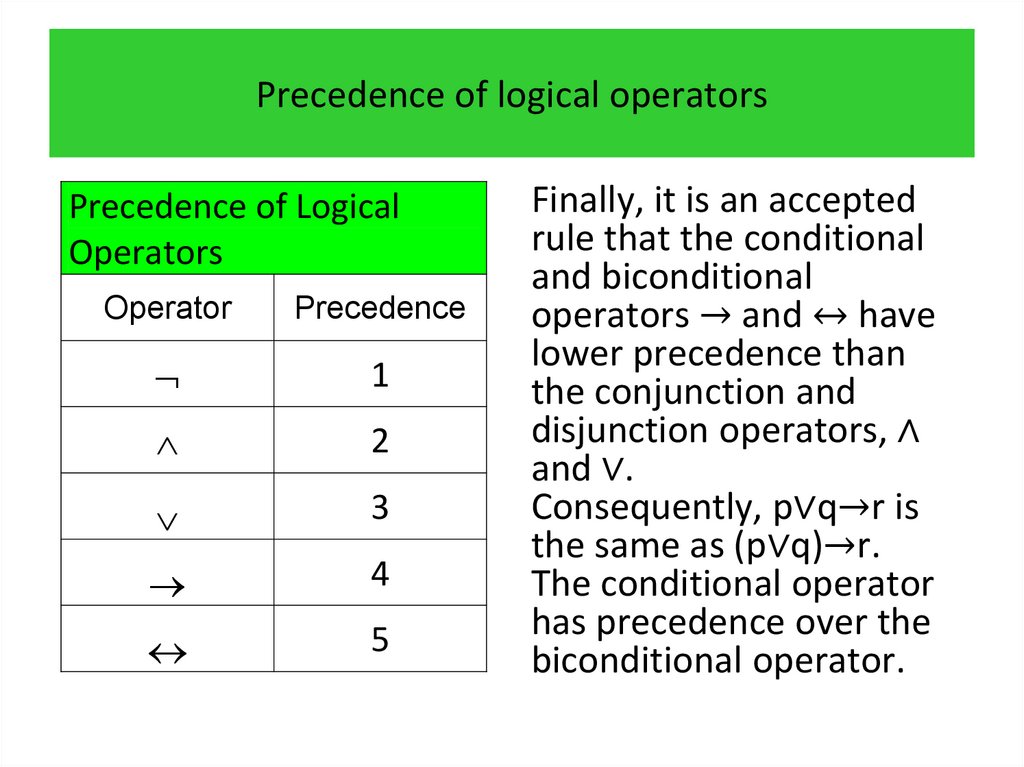



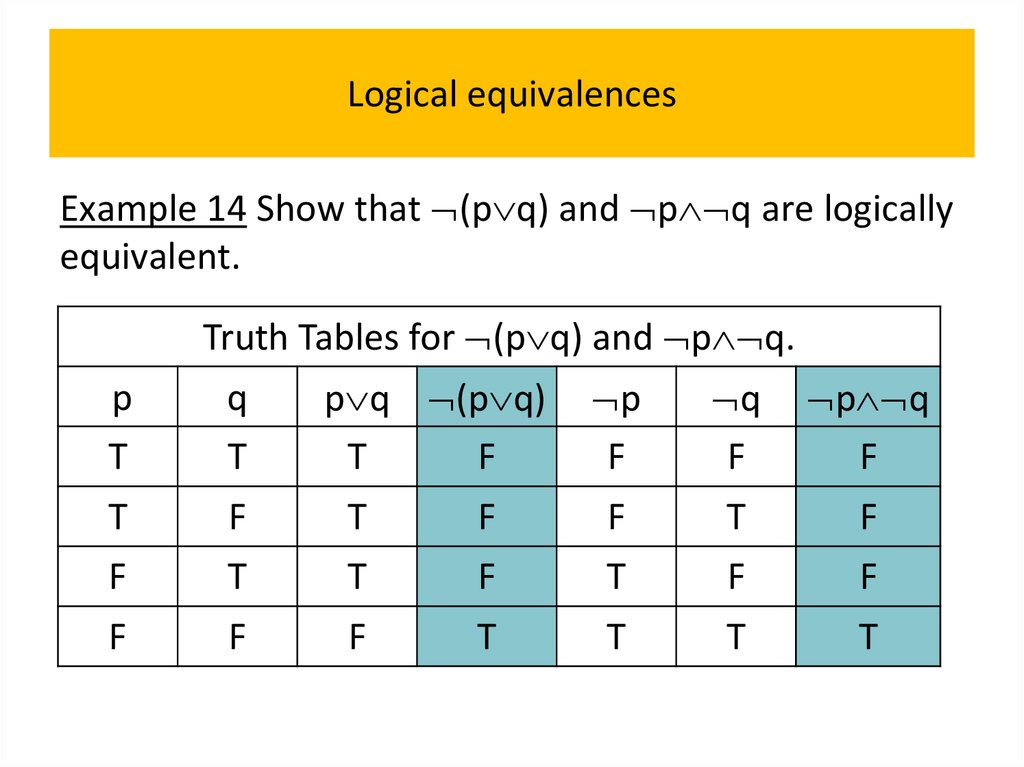
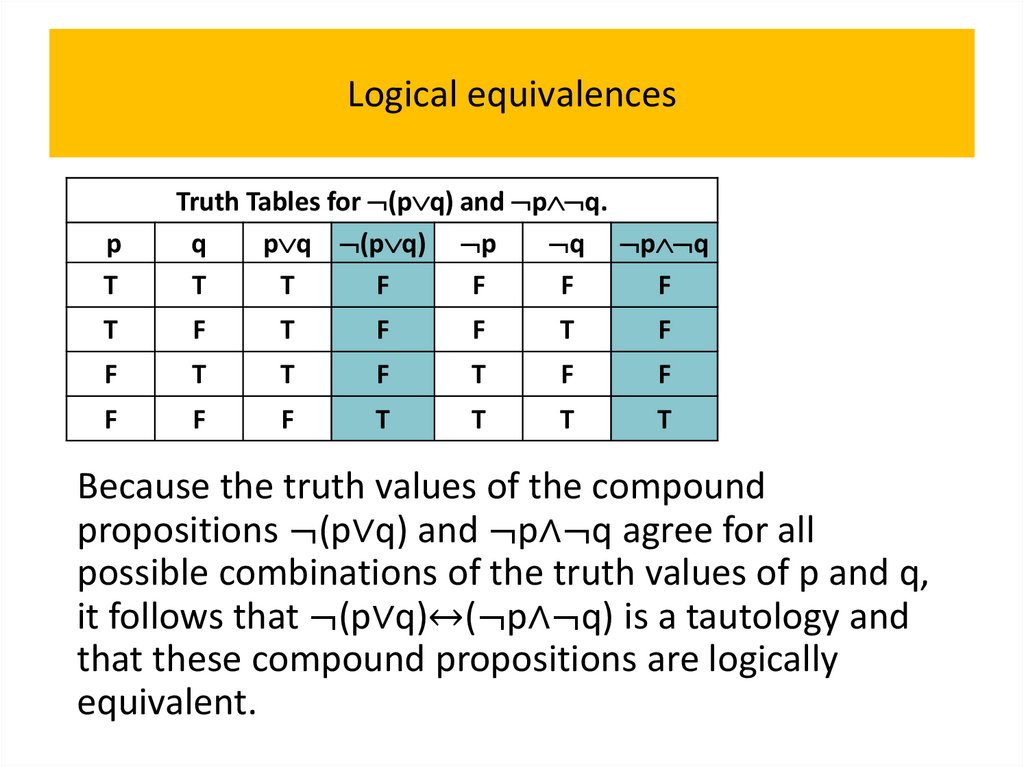
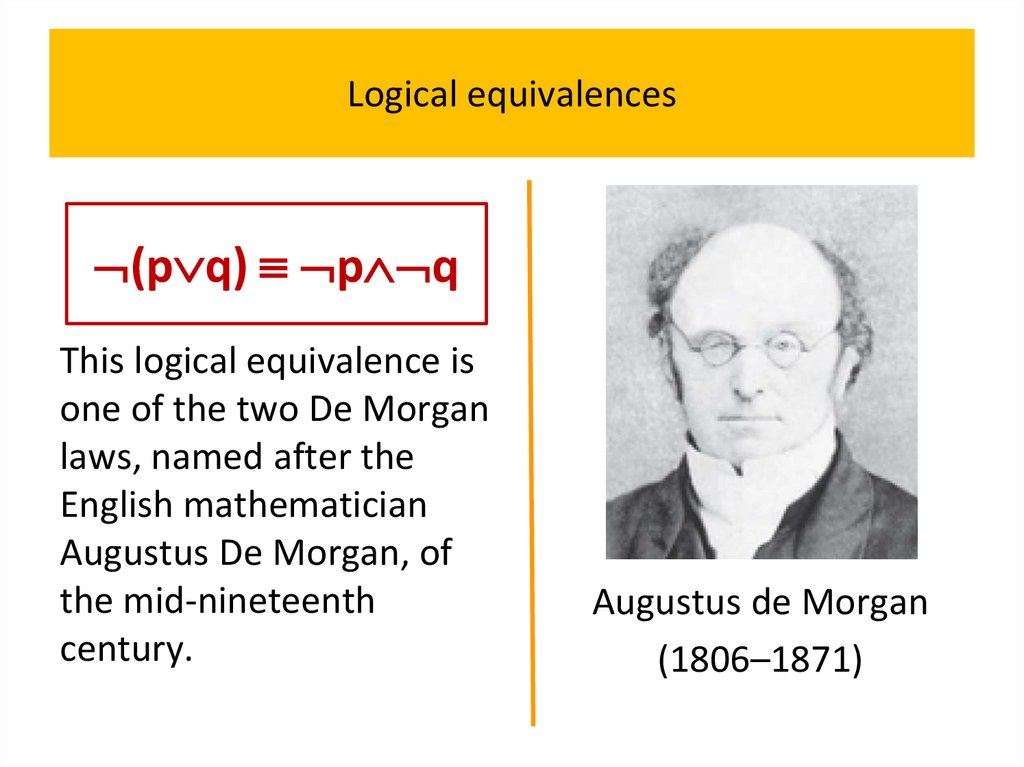

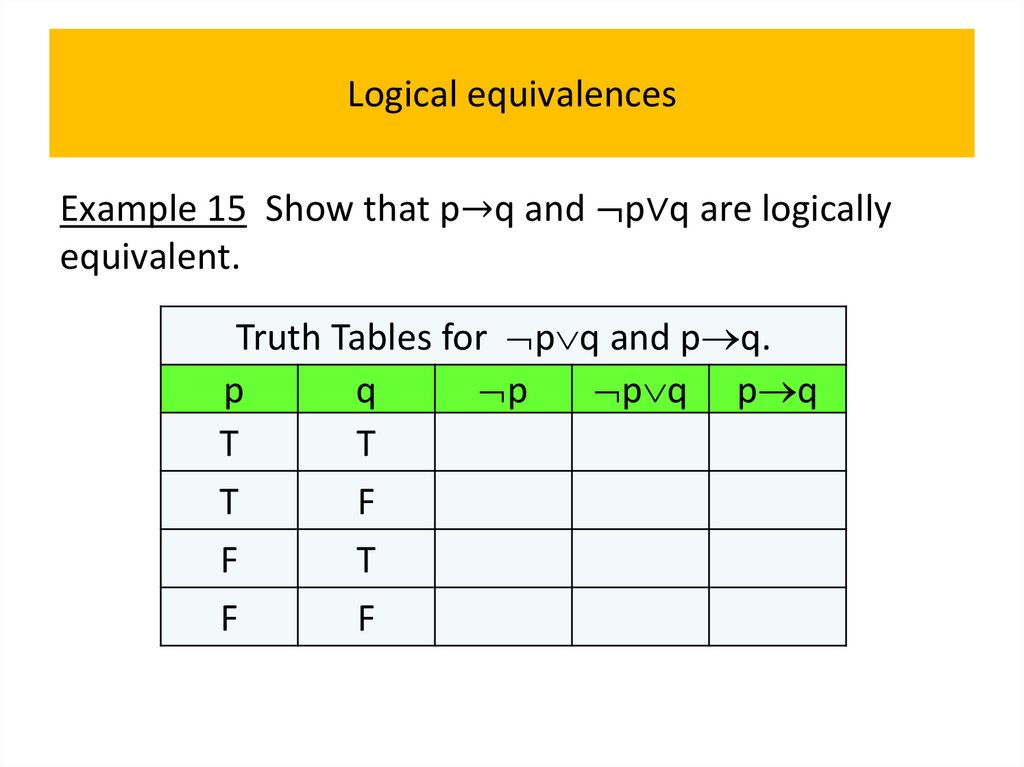
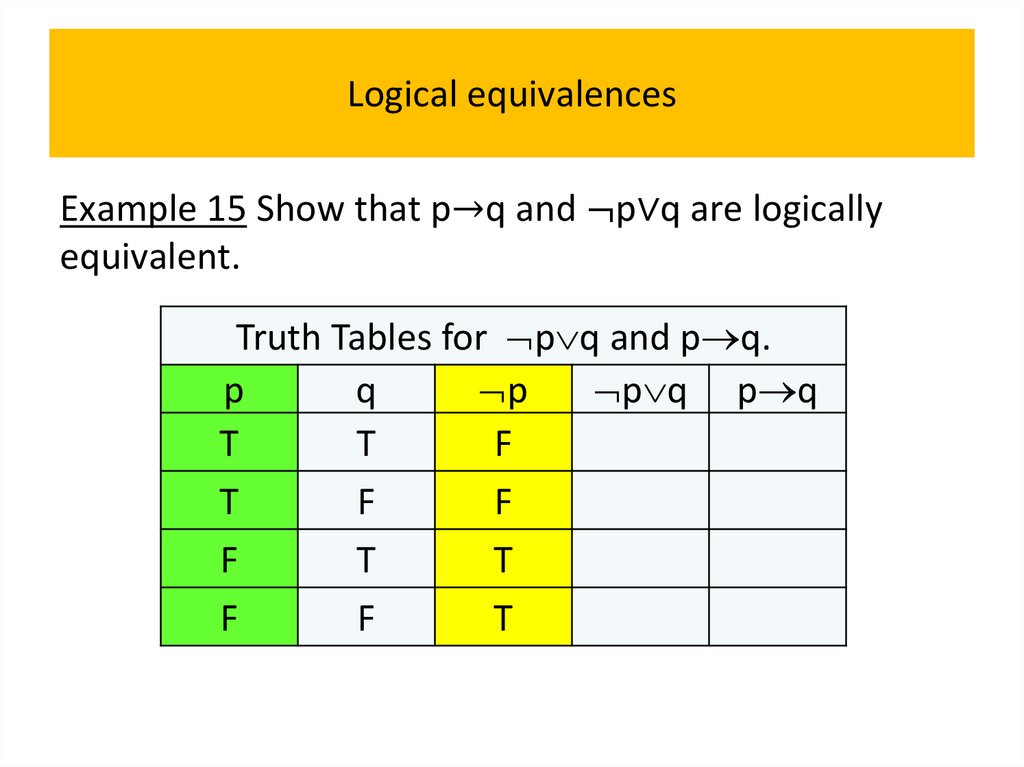
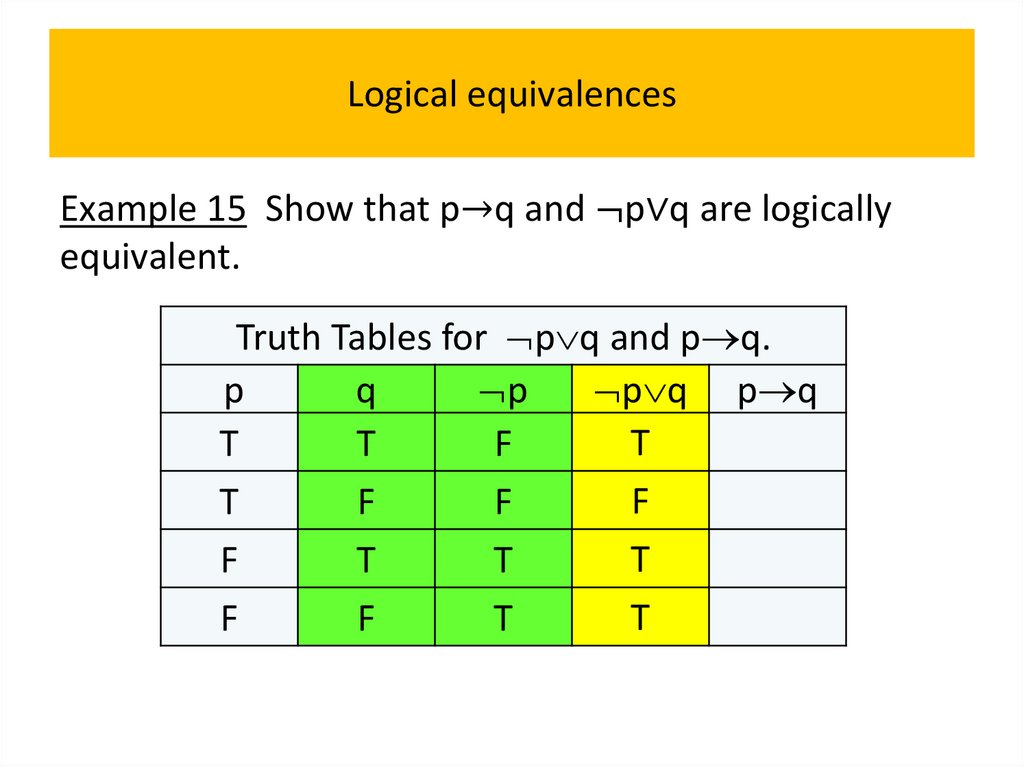
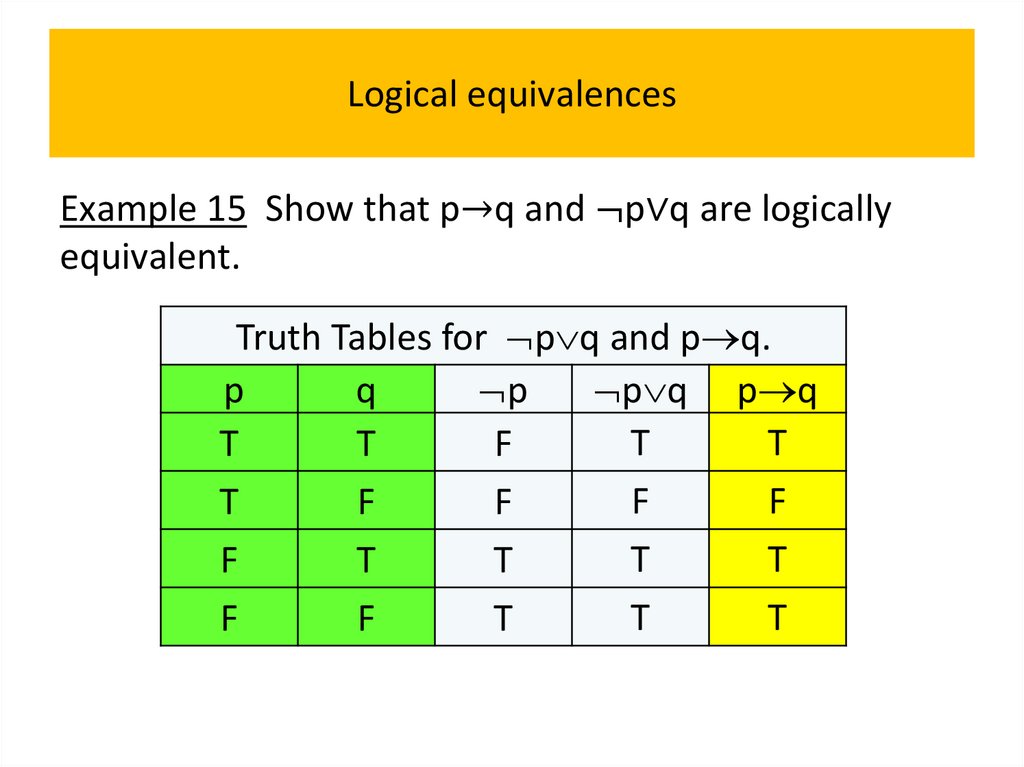
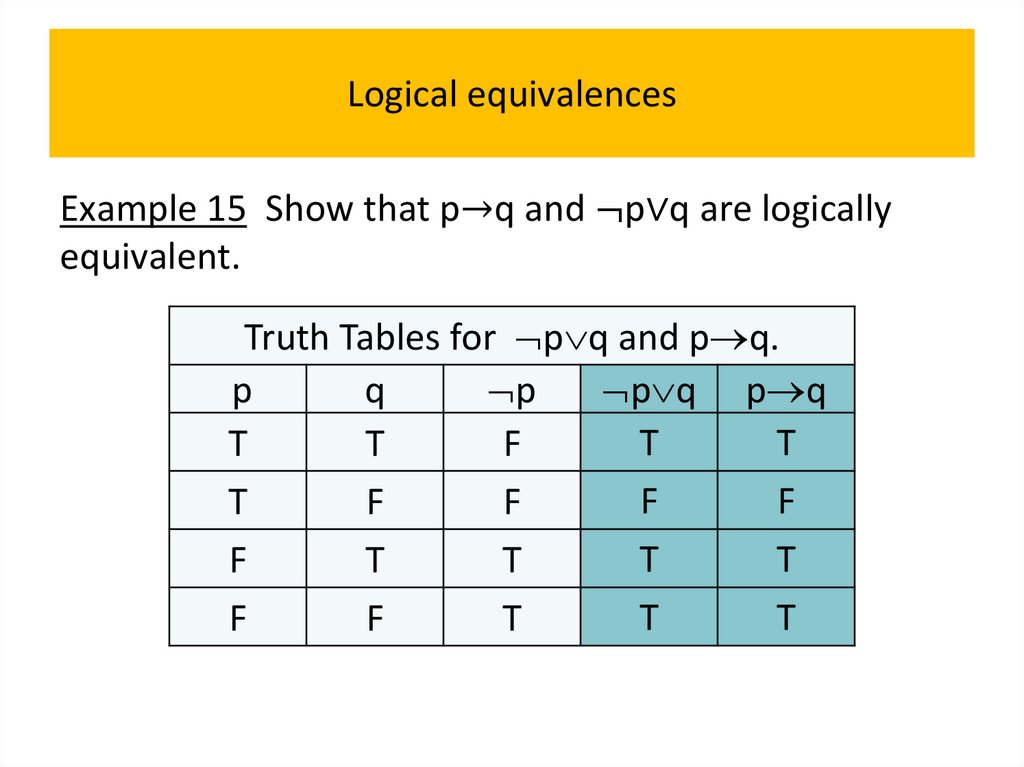


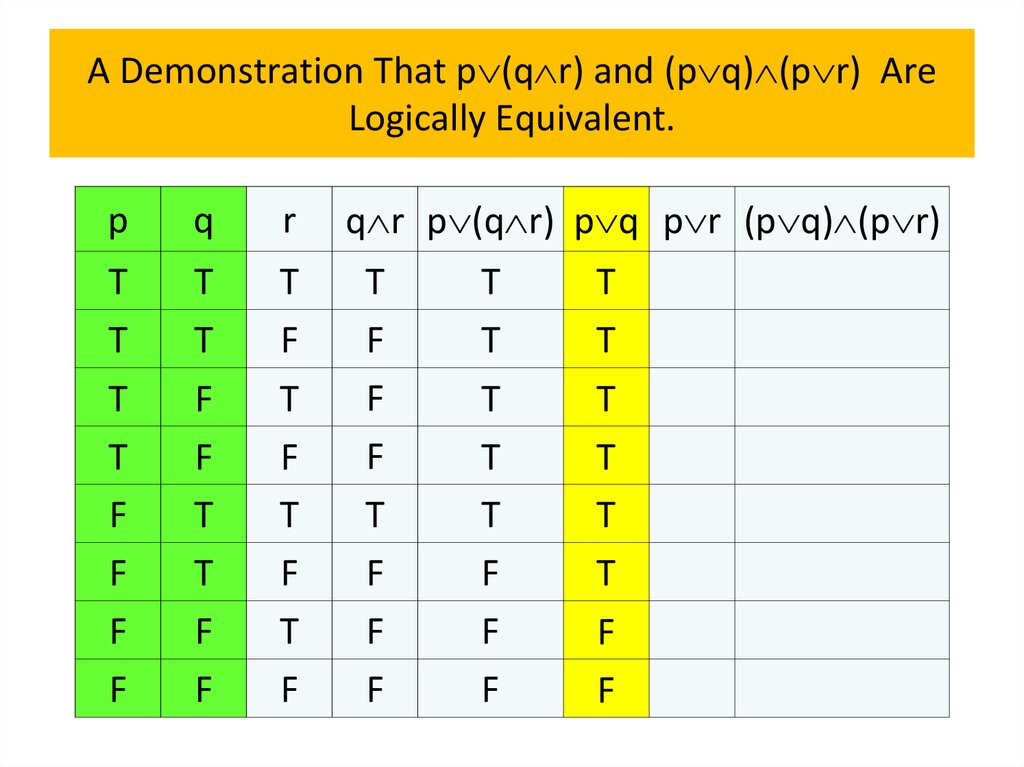
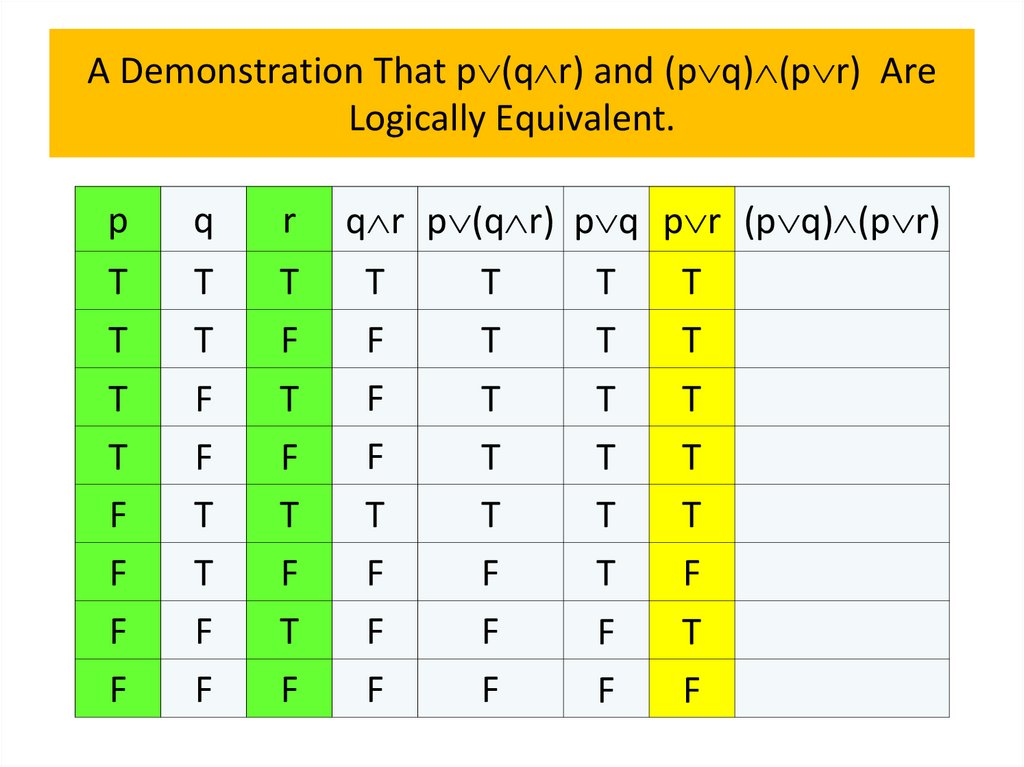
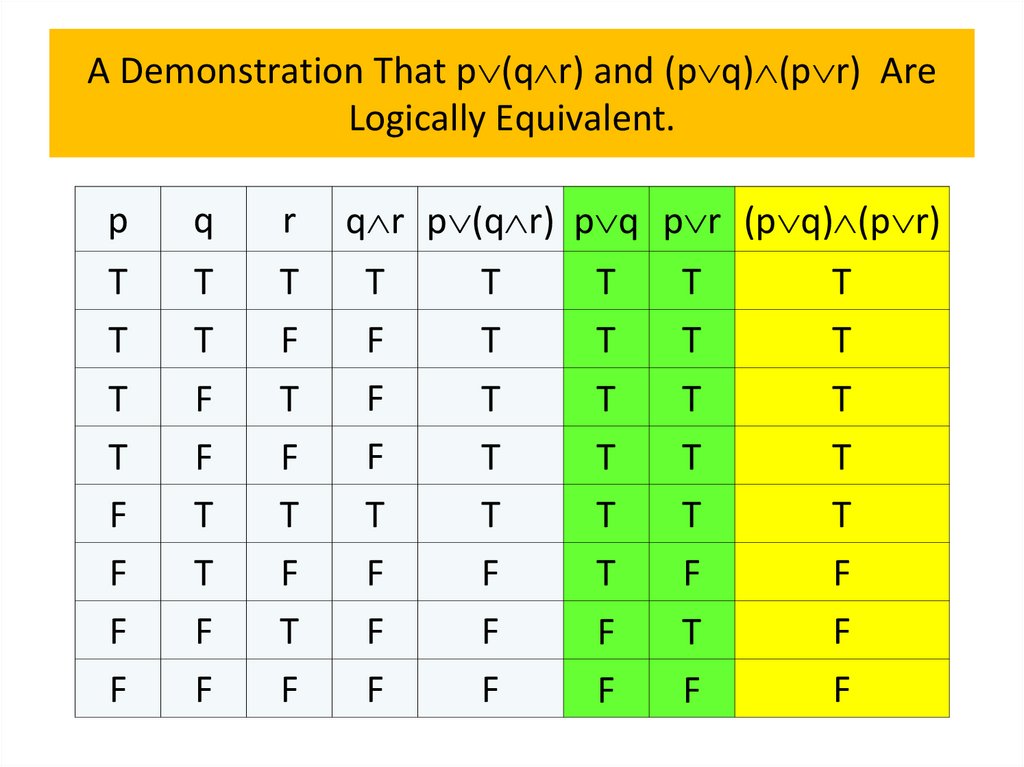
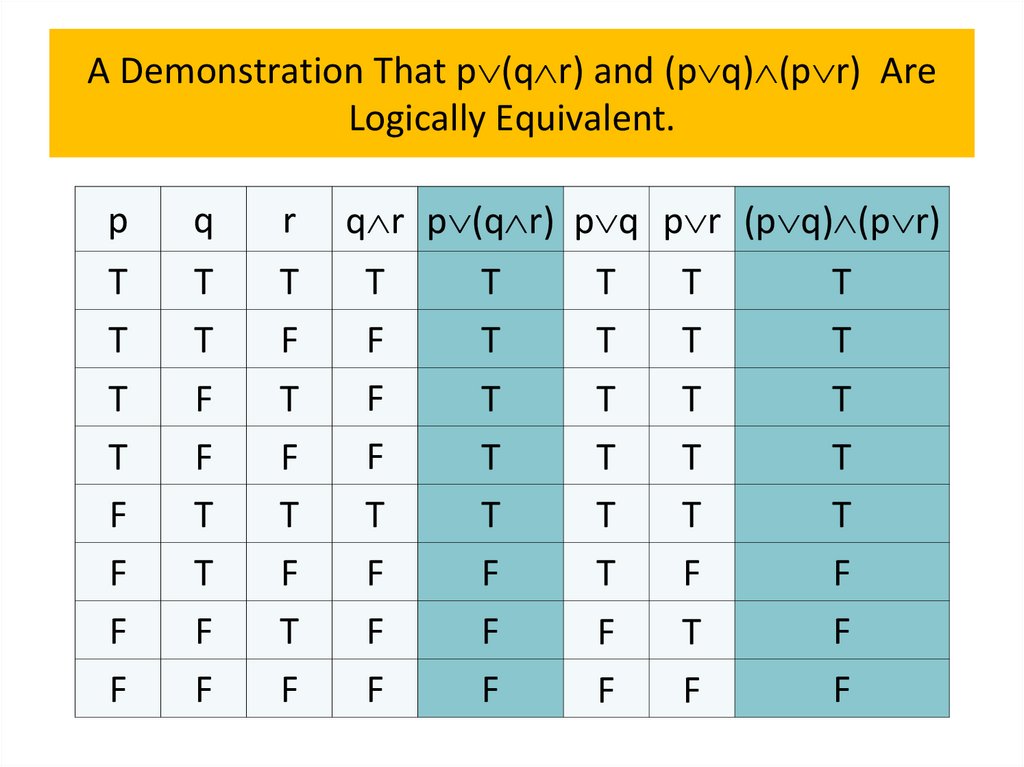






 programming
programming








