Similar presentations:
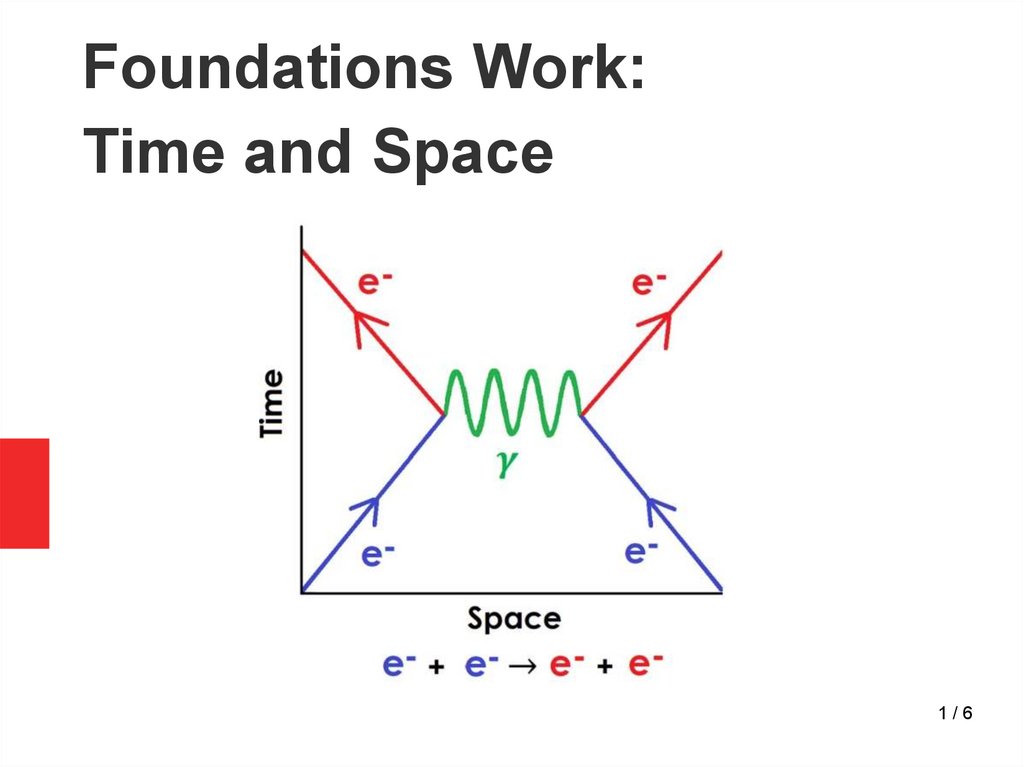
Foundations Work: Time and Space
1.
Foundations Work:Time and Space
1/6
2.
The CopenhagenInterpretation
2/6
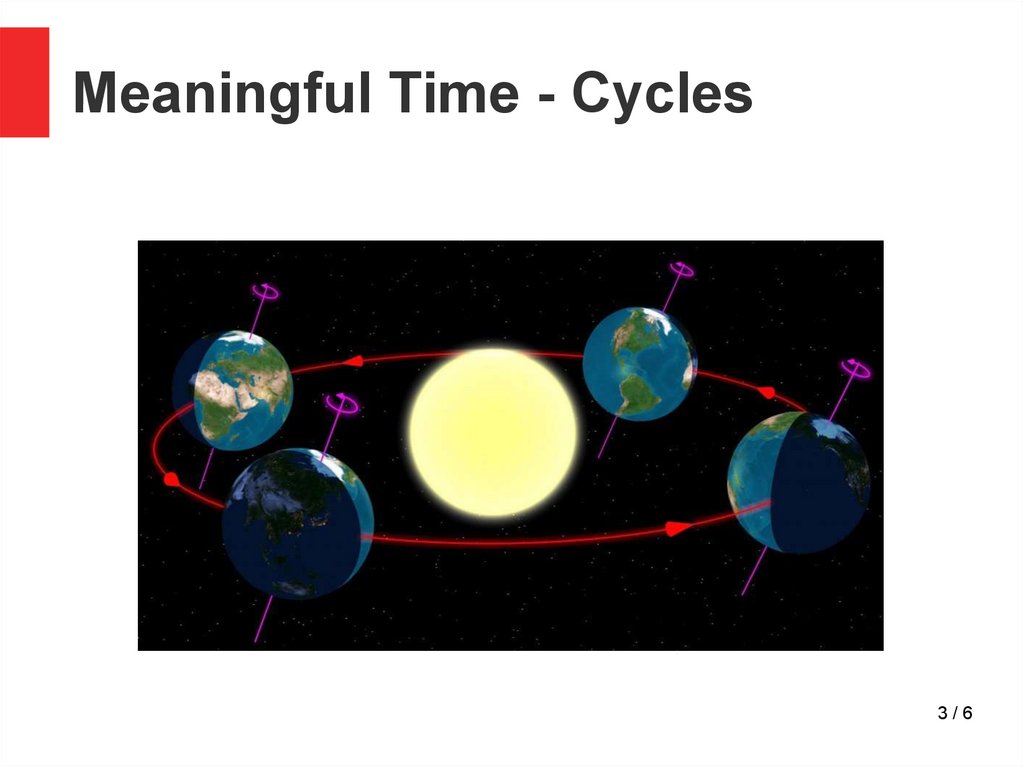
3.
Meaningful Time - Cycles3/6
4.
Circular DefinitionJanna Levin from Barnard College/Columbia University in a
short excerpt from The Illusion of Time:
“We would like to corner time as a thing, but it defies that
completely by being momentary. By only having definitions
that harken back to the notion of time itself.”
4/6
5.
The Age of the Universe5/6
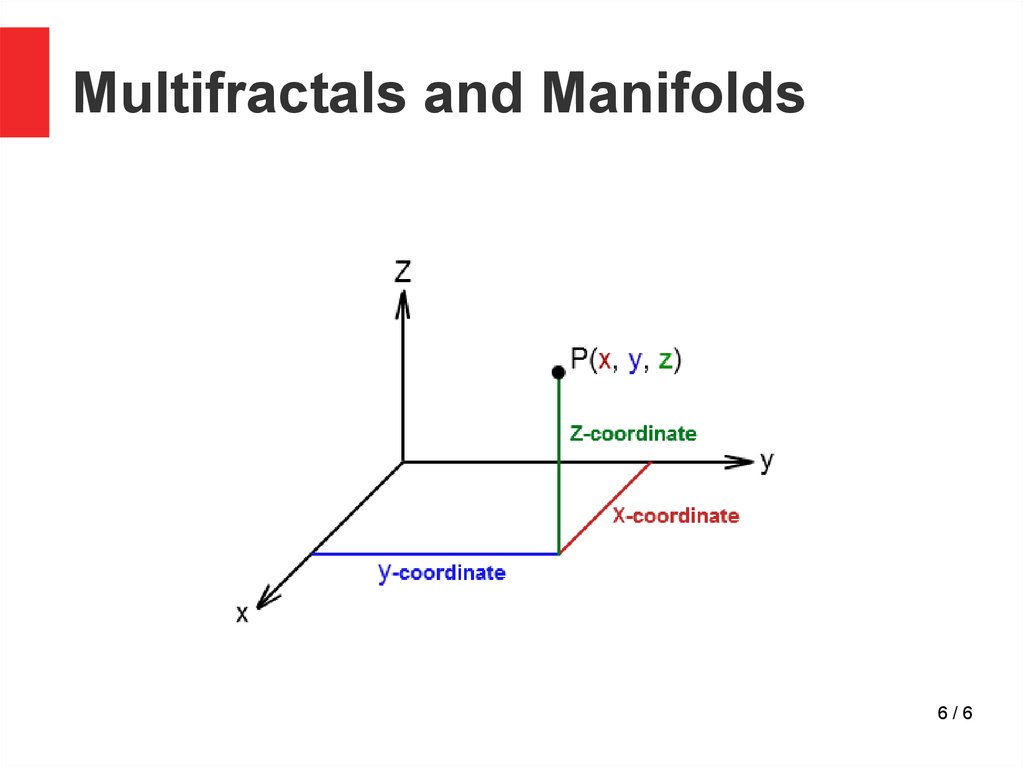
6.
Multifractals and Manifolds6/6
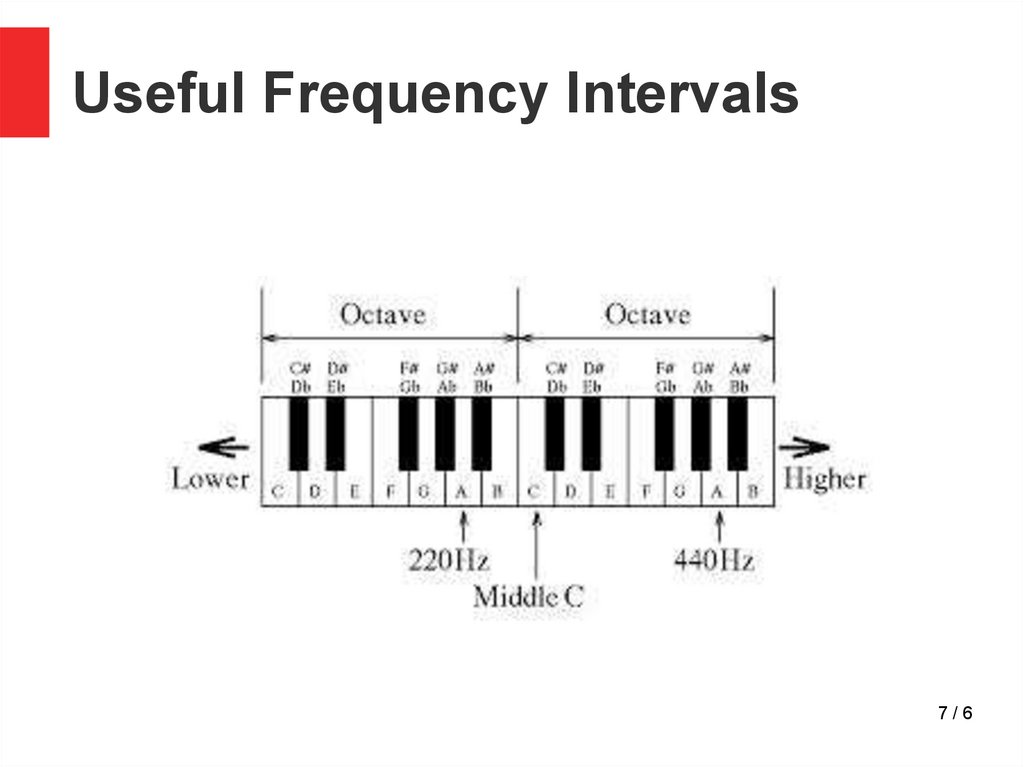
7.
Useful Frequency Intervals7/6
8.
Black Hole Scalar DistributionNasa.gov:
“Black holes can be big or small. Scientists think the
smallest black holes are as small as just one atom.”
“The largest black holes have masses that are more
than 1 million suns together.”
“Scientists think the smallest black holes formed when
the universe began.”
8/6
9.
Scalar Turbulence9/6
10.
Quantum Turbulence10 / 6
11.
The Age of the Universe11 / 6
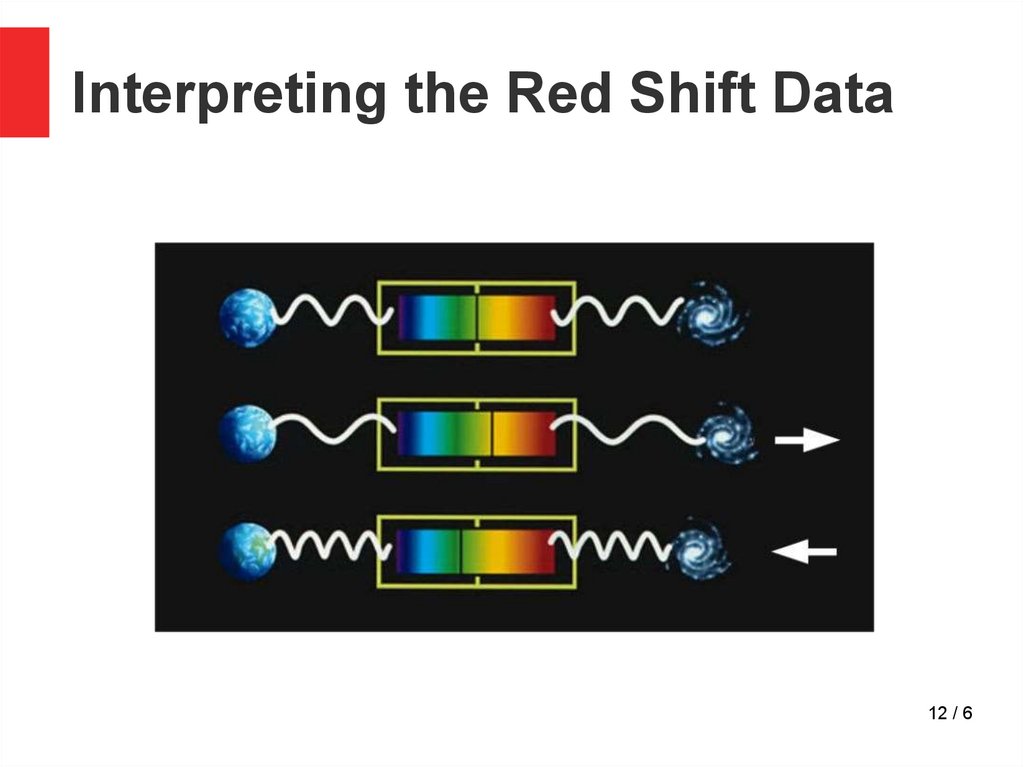
12.
Interpreting the Red Shift Data12 / 6
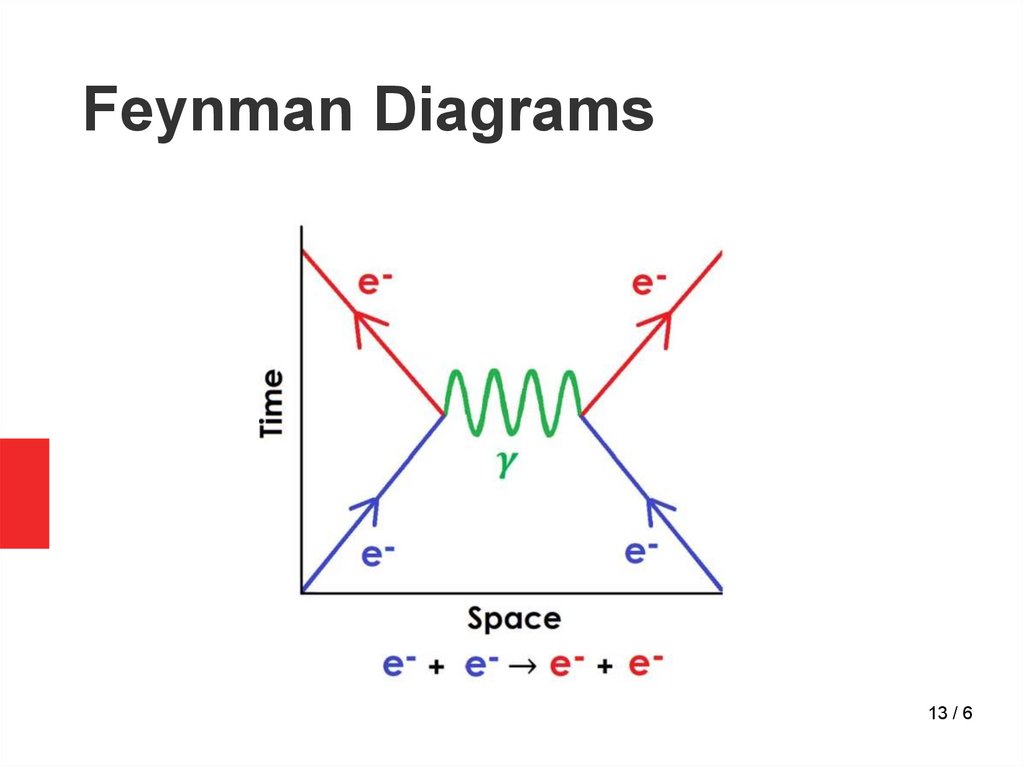
13.
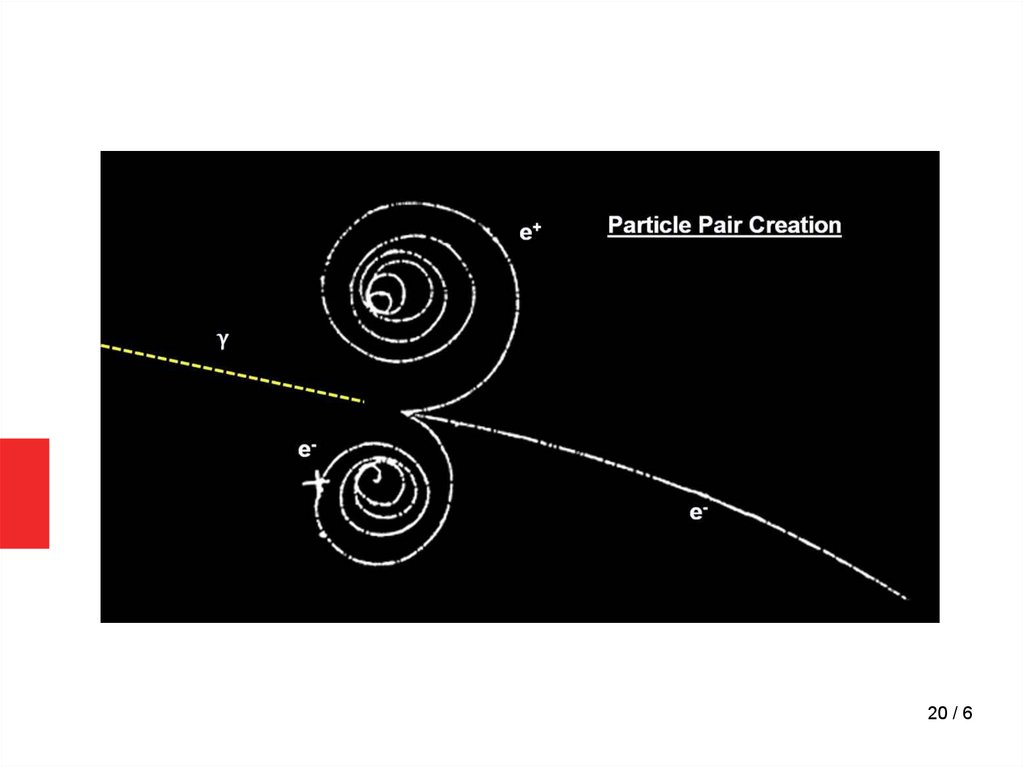
Feynman Diagrams13 / 6
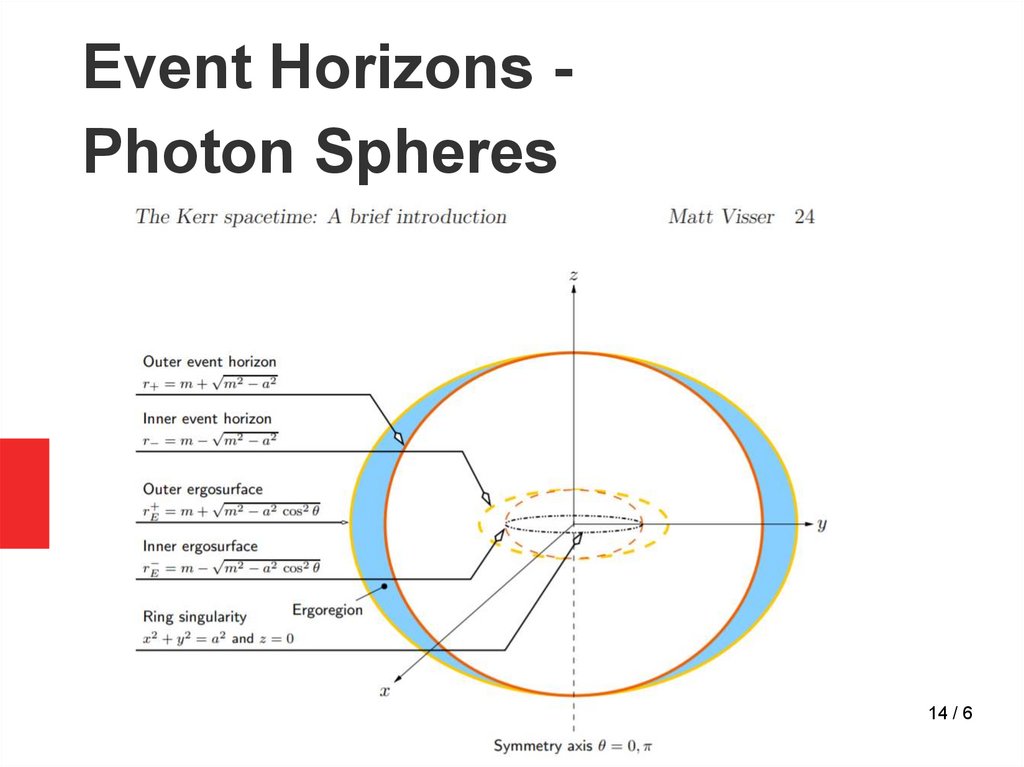
14.
Event Horizons Photon Spheres14 / 6
15.
Mirror Force Reversal15 / 6
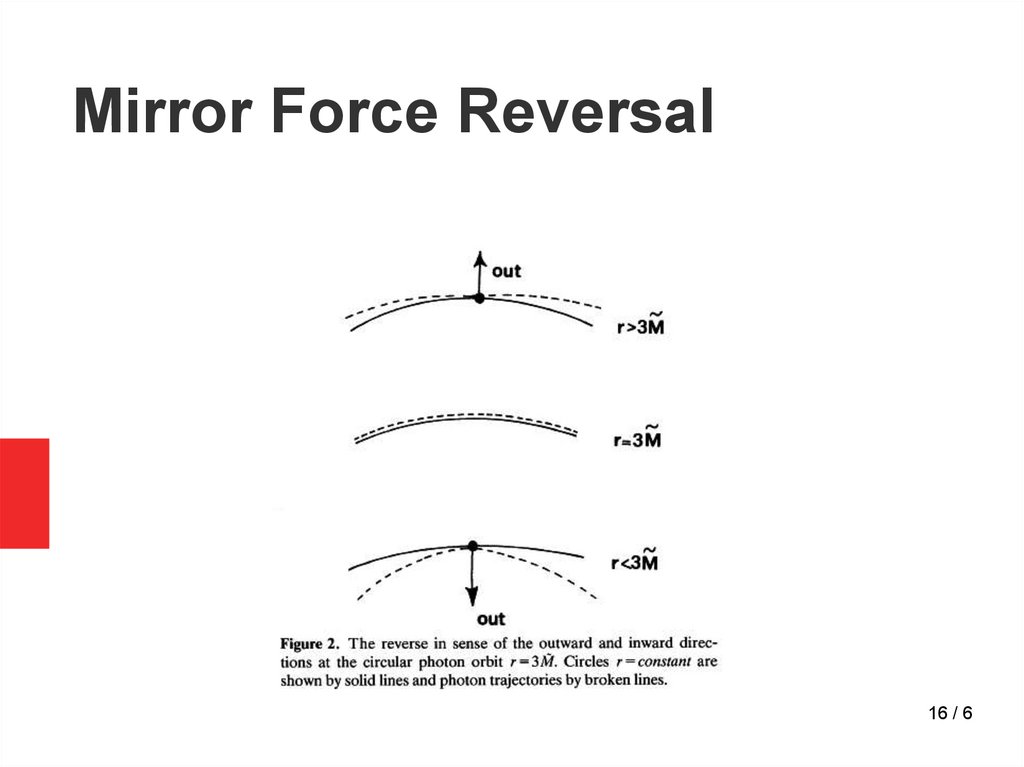
16.
Mirror Force Reversal16 / 6
17.
Eddy Black Holes17 / 6
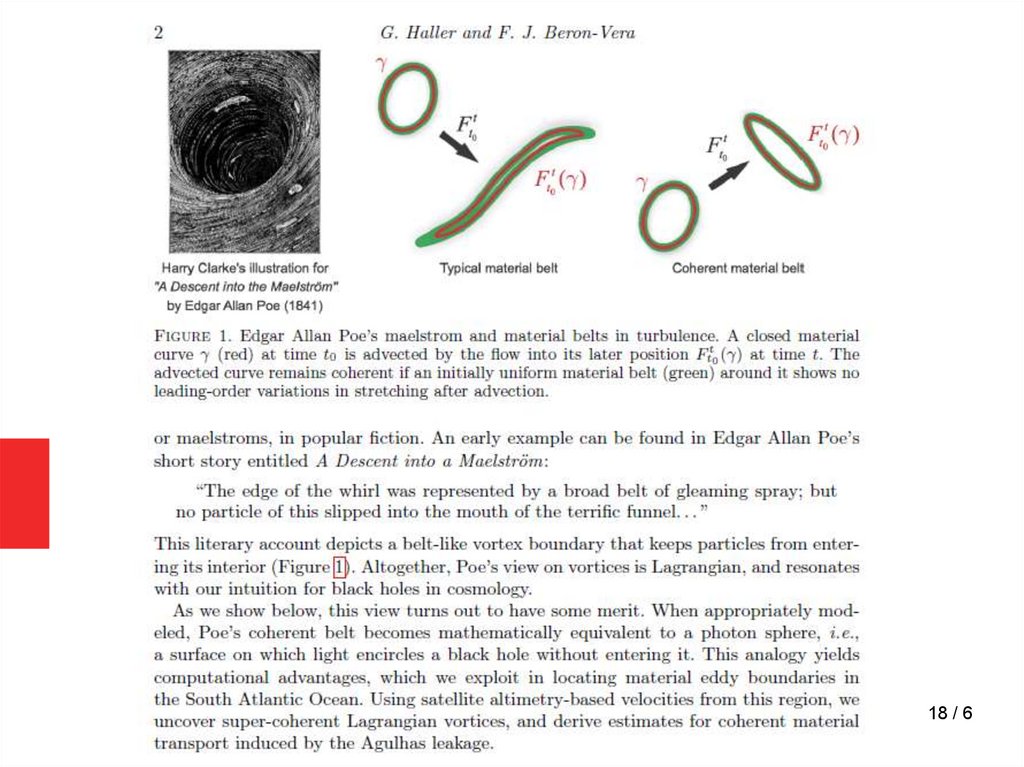
18.
18 / 619.
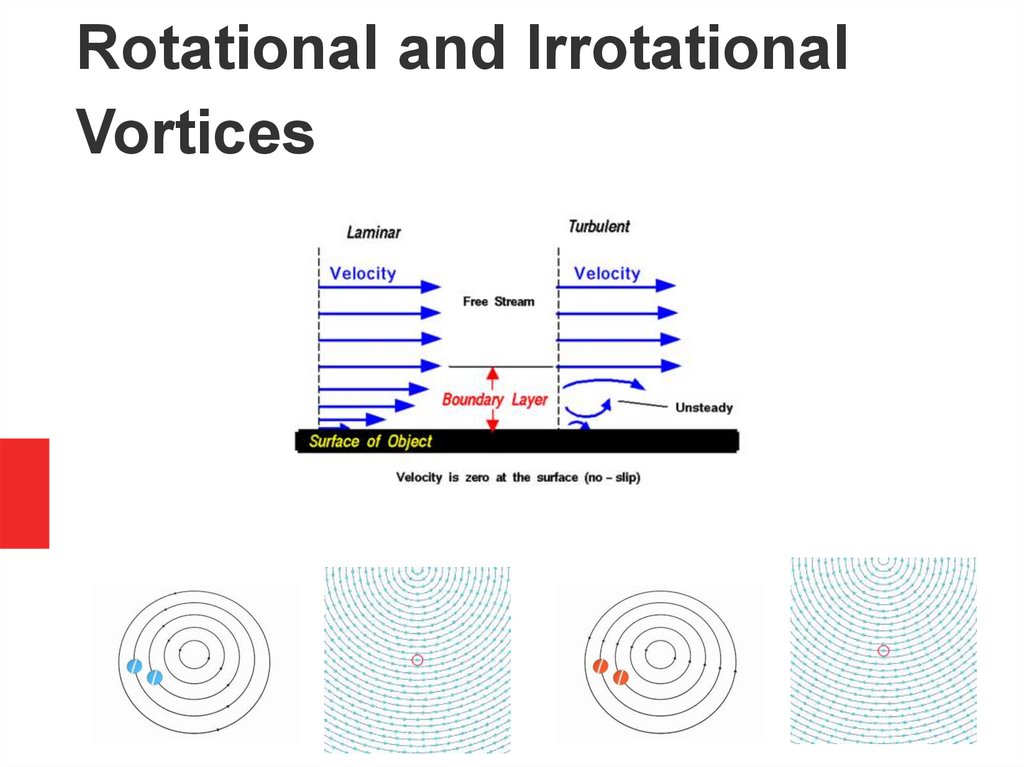
Rotational and IrrotationalVortices
19 / 6
20.
20 / 621.
Space to Time TransitionAcross an Event Horizon
“One thing that happens to an observer crossing the event
horizon is that once it is crossed the singularity lies in the
future. To the outside observer, the black hole (and inside
it, the singularity) forms a world-tube a world tube traces out a three-dimensional volume for
every moment in time.
- but to the inside observer, the singularity is now a
hypersurface (in your future).”
21 / 6
22.
Foundations Work:Time and Space
22 / 6










 astronomy
astronomy








