Similar presentations:
HIV- infection
1.
HIV- INFECTIONIdentification. HIV-infection is slowly progressing
viral disease of man (It is lethal disease at
present!!) with the parenteral mode of
transmission described by a specific damage of
the immune system of the patient with
development immunodeficiency which clinical
appears by opportunistic infections, malignant
neoplasms and various autoimmune effects.
hiv_life_cycle.asf
2.
Historical reference• 1981- СDC-center for Disease (USA) registered among homosexuals
increase morbidity of pneumocytosis and Kaposi’s sarcoma on a
background of oppression at them cellular immunity
• 1982 - D.Frensis isolated AIDS into a separate clinical syndrome
• 1983 - L.Montenje isolated both a virus of the HIV type1 and in 1986 the HIV – type 2
hiv_life_cycle.asf
• 1983 - R. Gallo isolated the HIV – type 1 (repeatedly)
• 1984- the similar virus is found out in monkeys in Asia (SIV - simian
immunodeficience virus)
Presence of the HIV - 1 is revealed in samples of blood, since the
50th years. Disease probably has arisen in Africa, and then was
distributed all over the world.
3. HIV- infection in world ( 2007)
Quantity of people living with HIVCommon —
Adults —
Women —
Children to 15 years old-
33.2 million (30.6 – 36.1 million)
30.8 million ( 28.2 – 33.6 million)
15.4 million (13.9 – 16.6 million)
2.1 million (1.9 – 2.4 million)
Quantity of people infected VIH in 2007.
Common—
2.5 million (1.8 – 4.1 million)
Adults—
2.1 million(1.4 – 3.6 million)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
Children to 15 years old— 420,000
(350,000 — 540,000)
Quantity deaths from HIV- infection in 2007.
Common —
2.1 million (1.9 – 2.4 million)
Adults—
1.7 million (1.6 – 2.1 million)
Children to 15 years old — 290,000 (270,000 – 320,000)
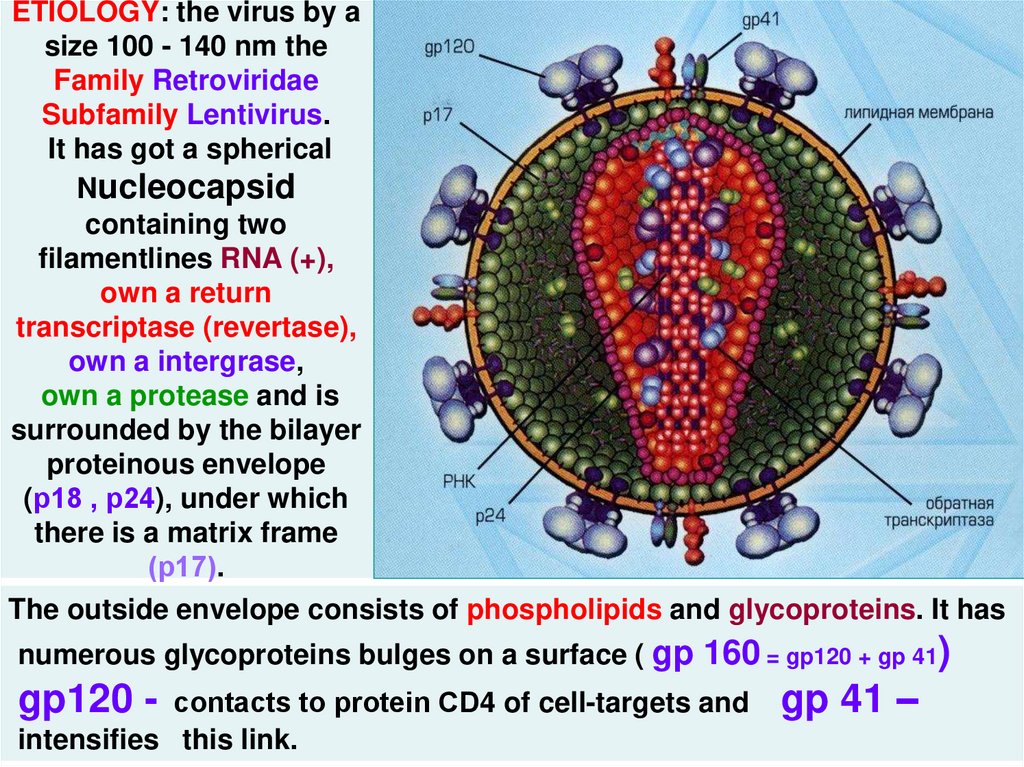
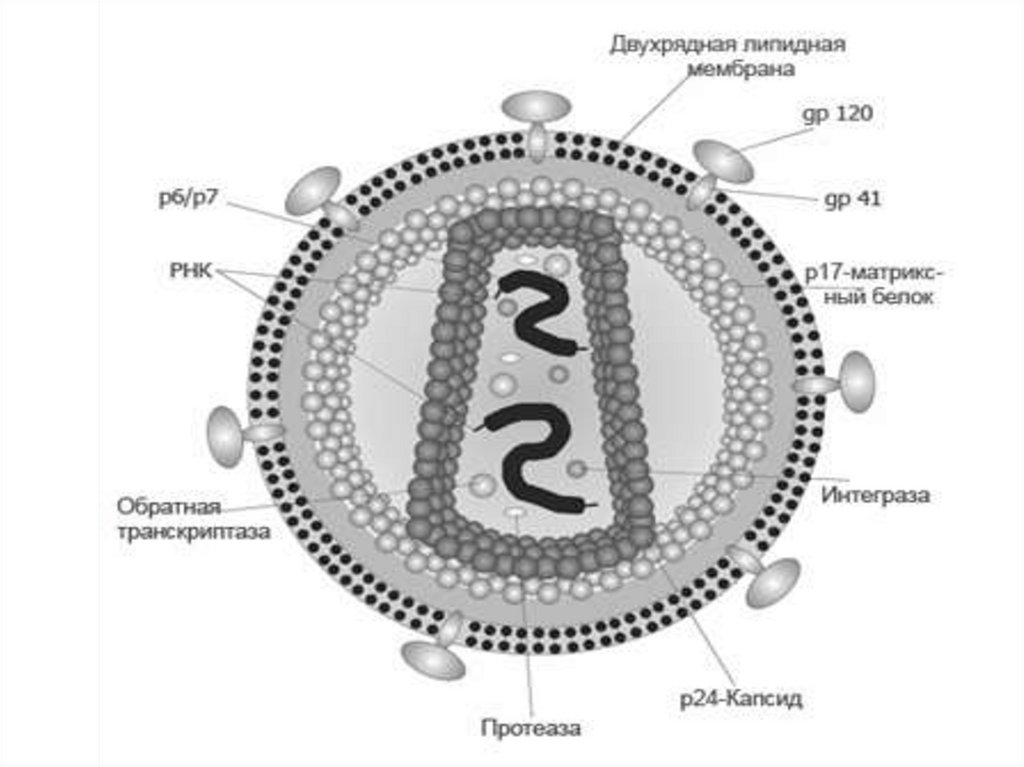
4. ETIOLOGY: the virus by a size 100 - 140 nm the Family Retroviridae Subfamily Lentivirus. It has got a spherical Nucleocapsid
containing twofilamentlines RNA (+),
own a return
transcriptase (revertase),
own a intergrase,
own a protease and is
surrounded by the bilayer
hiv_life_cycle.asf
proteinous envelope
(р18 , р24), under which
there is a matrix frame
(р17).
The outside envelope consists of phospholipids and glycoproteins. It has
numerous glycoproteins bulges on a surface ( gp 160 = gp120 + gp 41)
gp120 -
contacts to protein СD4 of cell-targets and
intensifies this link.
gp 41 –
5.
hiv_life_cycle.asf6.
Therefore virus is capable to penetrate only intothose cells, on which surface there are the proteins:
CD-4, CCR-4, XCR-5, galactozylceramid
The variability of a virus is very large because of presence
revertase ( The VIH in the life cycle is declined to
mutations in 5 times more, than a virus of a influenza)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
7.
Stability of the virus in the external environment islow:
- at desiccation is perished through 3 - 7 days ( at 25dg.С )
- in the moist environment is survived about 15 days ( at 25
dg.C )
- in a blood is survived by years!!!
- in the frozen plasma is survived till 10 years!!!
hiv_life_cycle.asf
- at warming up to 56 dg.C is inactivated through 30 min.
- at boiling is inactivated in 5 minutes
- it is sensitive to all disinfectants and fat-solvents , but is
steady to radiation!!!
8.
EPIDEMIOLOGYPandemic of a HIV- infection annually carries of millions
human lives and for its not exists: of international
boundaries, groups of hazard, social, material, religious
differences!!!
Today 45 million was infected and 41 million died.
The source - is infectious man in any period of illness,
but particularly during primary clinical manifestations
and in a stage AIDS ( acquired immunodeficiency s-me)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
It is found out in : BLOOD, LYMPH, SEMEN, less –
milk, a vaginal secretion, the least- saliva, tears, sweat
of the patient.
9.
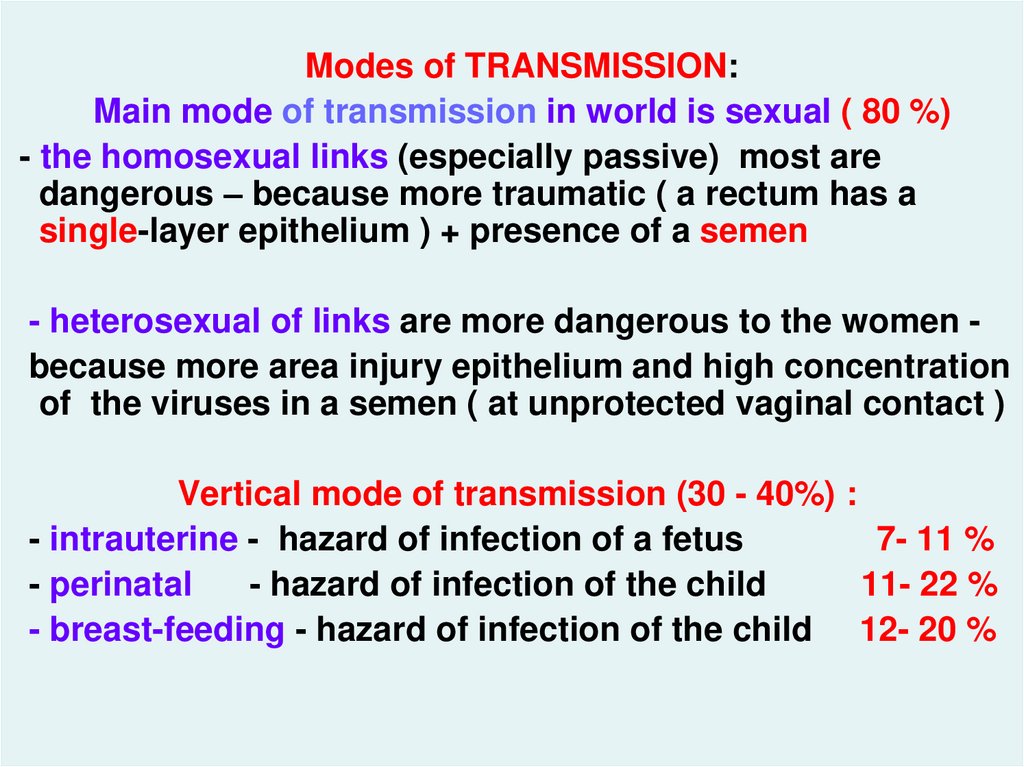
Modes of TRANSMISSION:Main mode of transmission in world is sexual ( 80 %)
- the homosexual links (especially passive) most are
dangerous – because more traumatic ( a rectum has a
single-layer epithelium ) + presence of a semen
- heterosexual of links are more dangerous to the women because more area injury epithelium and high concentration
of the viruses in a semen ( at unprotected vaginal contact )
hiv_life_cycle.asf
Vertical mode of transmission (30 - 40%) :
- intrauterine - hazard of infection of a fetus
7- 11 %
- perinatal
- hazard of infection of the child
11- 22 %
- breast-feeding - hazard of infection of the child 12- 20 %
10.
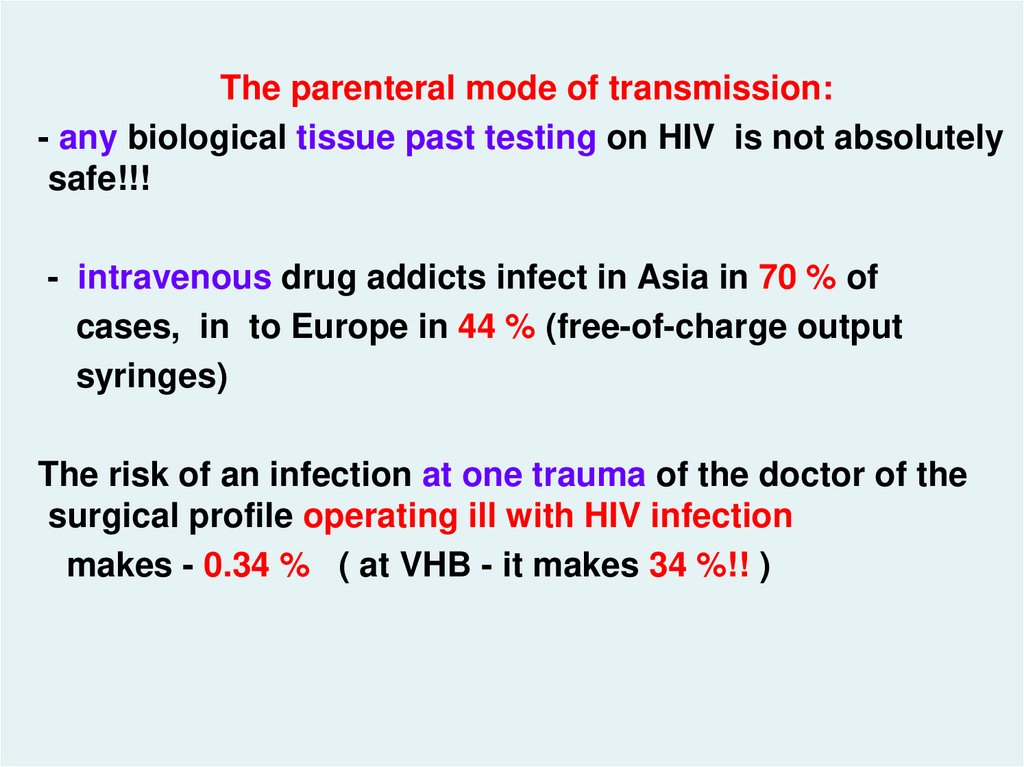
The parenteral mode of transmission:- any biological tissue past testing on HIV is not absolutely
safe!!!
- intravenous drug addicts infect in Asia in 70 % of
cases, in to Europe in 44 % (free-of-charge output
syringes)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
The risk of an infection at one trauma of the doctor of the
surgical profile operating ill with HIV infection
makes - 0.34 % ( at VHB - it makes 34 %!! )
11.
The risk оf an infection atone contact
with the
source of a VIH infection:
- blood and its components
90%
- intravenous drug addicts
30%
hiv_life_cycle.asf
- vertical mode of transmission
- unprotected anual contact
- unprotected vaginal contact
30%
1%
0,1%
12.
VIH - is not transmitted by :- at touches, embraces, hand shakes, kisses ( if in a saliva
there is not impurity of a blood)
- at joint residing in one apartment, through tableware,
clothes, nutrition, linen, subjects communal of use,
toies and etc.
hiv_life_cycle.asf
- through air (even at sneeze and cough)
- at bathing in water, through sports equipment (which are
not polluted by a blood)
- through stings of insects and animals.
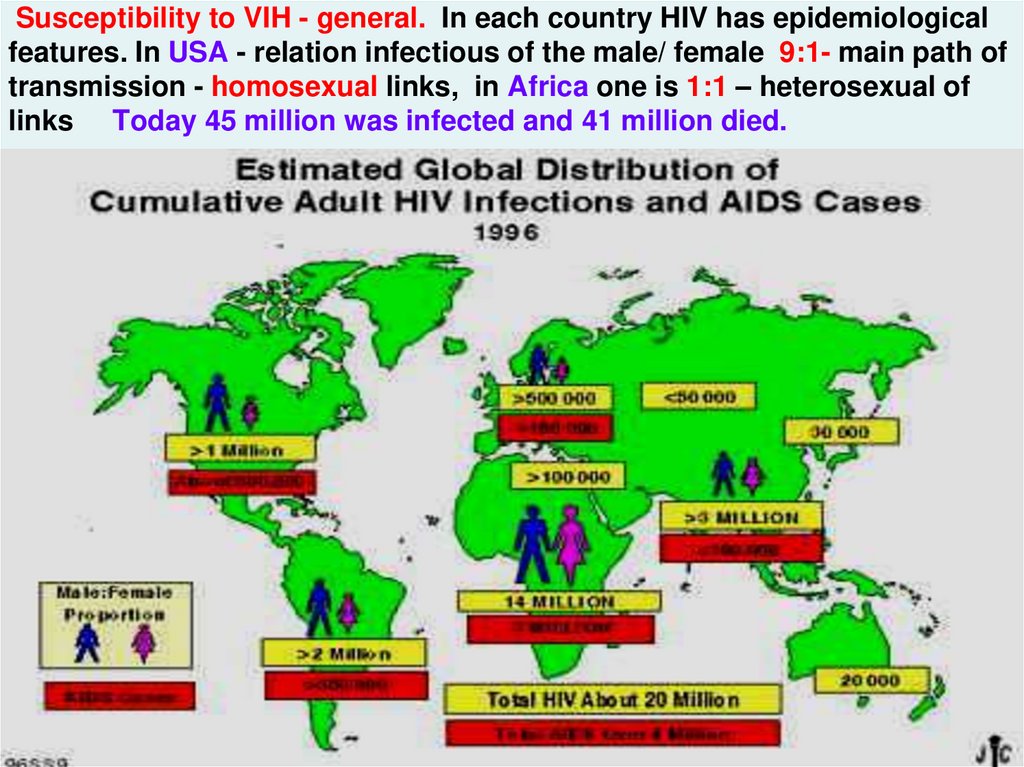
13. Susceptibility to VIH - general. In each country HIV has epidemiological features. In USA - relation infectious of the male/
female 9:1- main path oftransmission - homosexual links, in Africa one is 1:1 – heterosexual of
links Today 45 million was infected and 41 million died.
hiv_life_cycle.asf
14.
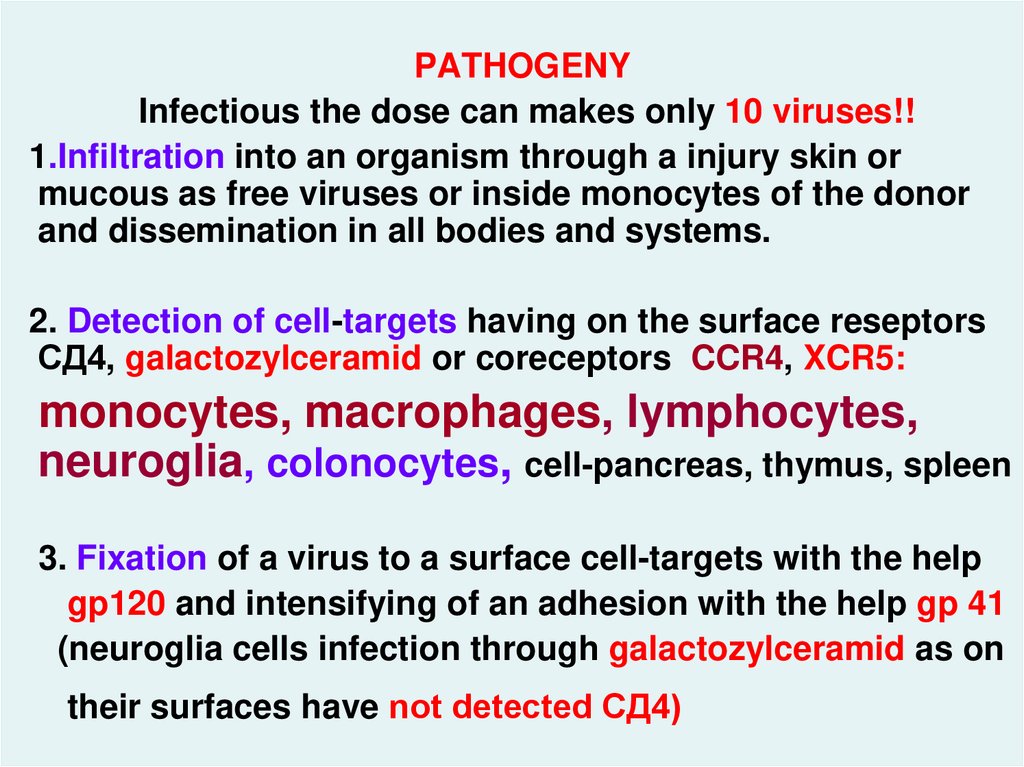
PATHOGENYInfectious the dose can makes only 10 viruses!!
1.Infiltration into an organism through a injury skin or
mucous as free viruses or inside monocytes of the donor
and dissemination in all bodies and systems.
2. Detection of cell-targets having on the surface reseptors
СД4, galactozylceramid or coreceptors CCR4, XCR5:
monocytes, macrophages, lymphocytes,
neuroglia, colonocytes, cell-pancreas, thymus, spleen
hiv_life_cycle.asf
3. Fixation of a virus to a surface cell-targets with the help
gp120 and intensifying of an adhesion with the help gp 41
(neuroglia cells infection through galactozylceramid as on
their surfaces have not detected СД4)
15.
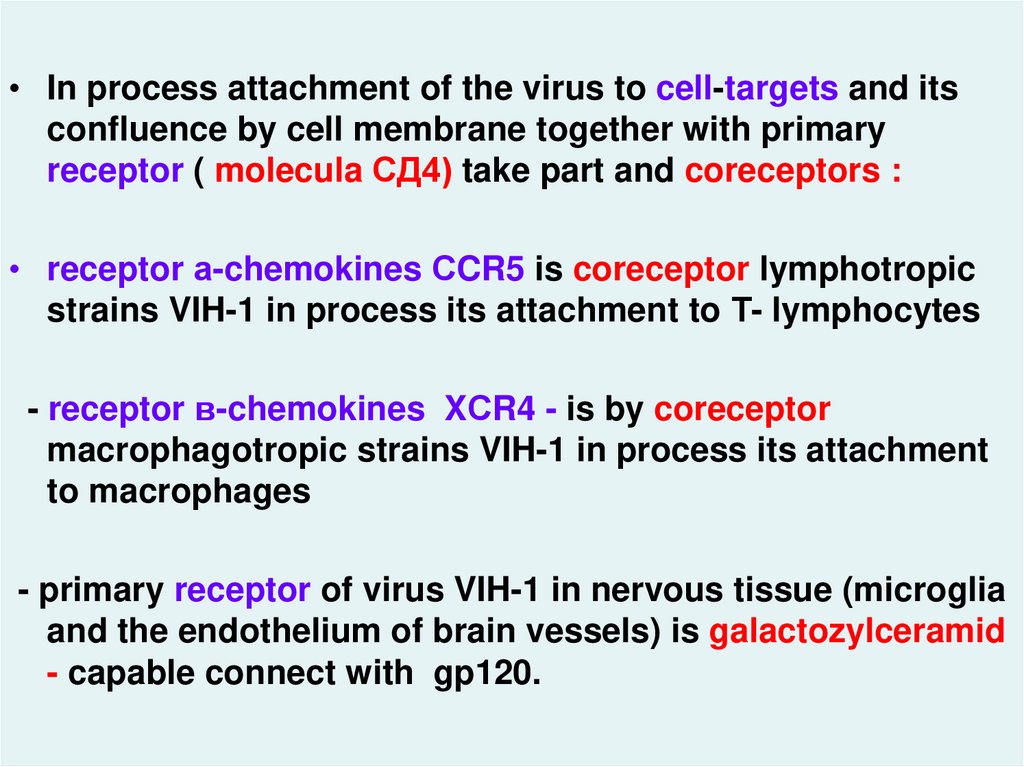
• In process attachment of the virus to cell-targets and itsconfluence by cell membrane together with primary
receptor ( molecula СД4) take part and coreceptors :
• receptor а-chemokines СCR5 is coreceptor lymphotropic
strains VIH-1 in process its attachment to Т- lymphocytes
- receptor в-chemokines XСR4 - is by coreceptor
macrophagotropic strains VIH-1 in process its attachment
to macrophages
hiv_life_cycle.asf
- primary receptor of virus VIH-1 in nervous tissue (microglia
and the endothelium of brain vessels) is galactozylceramid
- capable connect with gp120.
16.
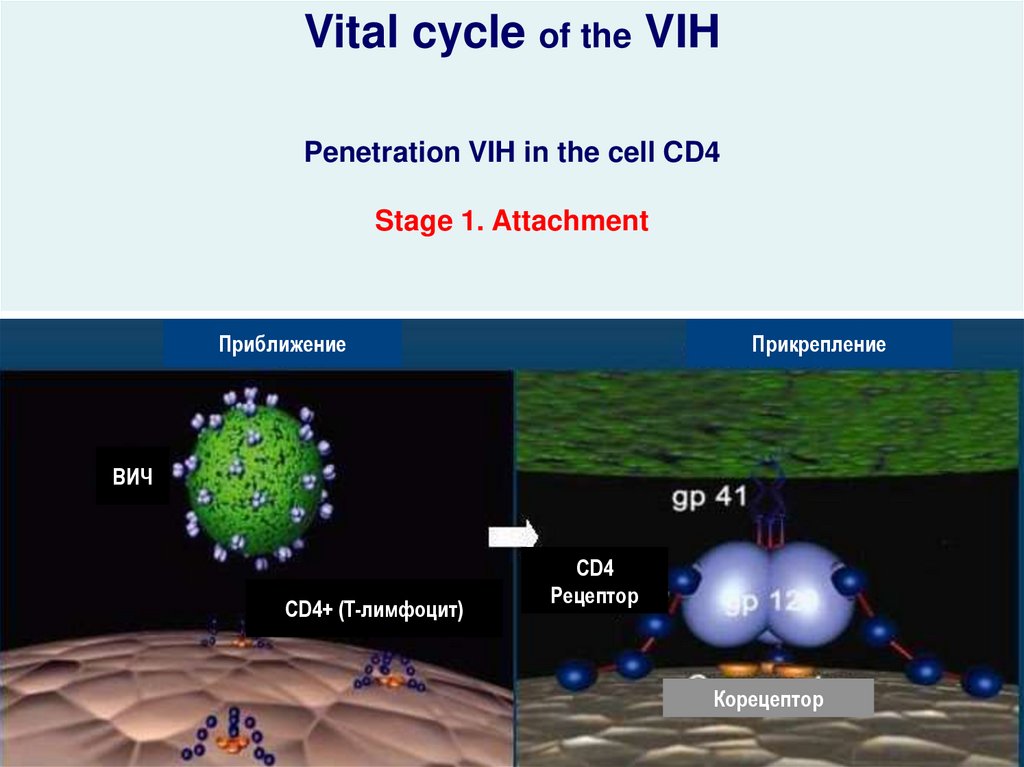
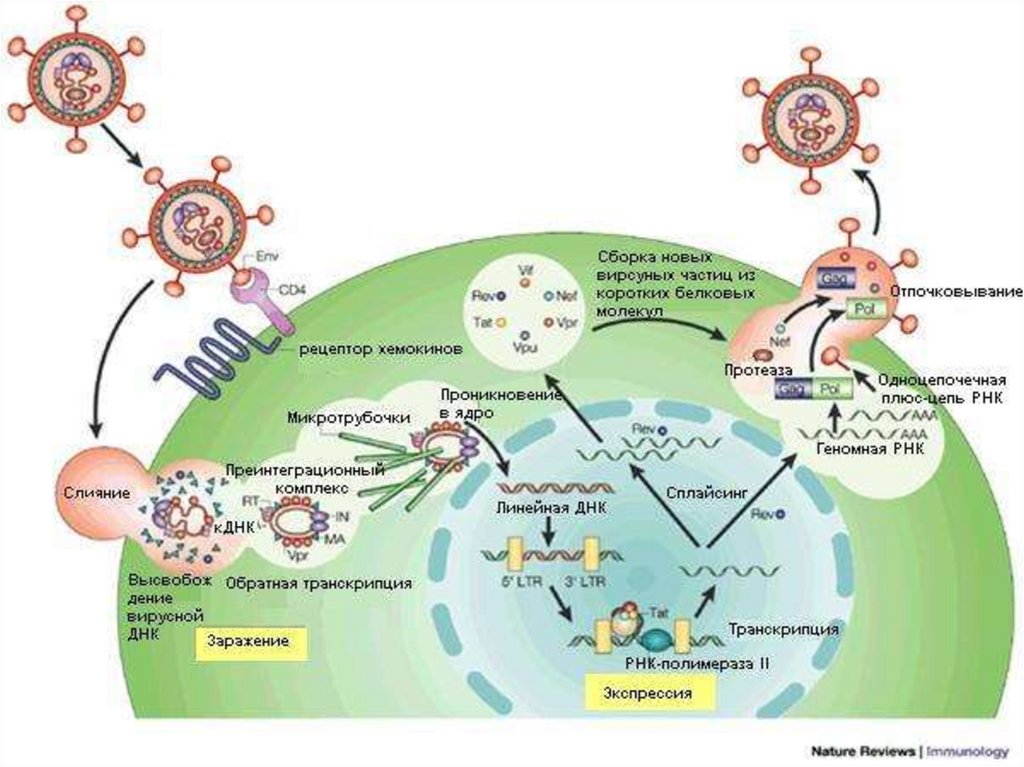
Vital cycle of the VIHPenetration VIH in the cell CD4
Stage 1. Attachment
Приближение
Прикрепление
hiv_life_cycle.asf
ВИЧ
CD4+ (T-лимфоцит)
CD4
Рецептор
Корецептор
17.
Attachmenthiv_life_cycle.asf
The HIV Life Cycle; Merck & Co 2006
18.
Stage 3. СonfluenceВнедрение и «зацепление»
hiv_life_cycle.asf
После внедрения gp41 «скручивается» и
сцепляет мембраны вируса и клетки
19.
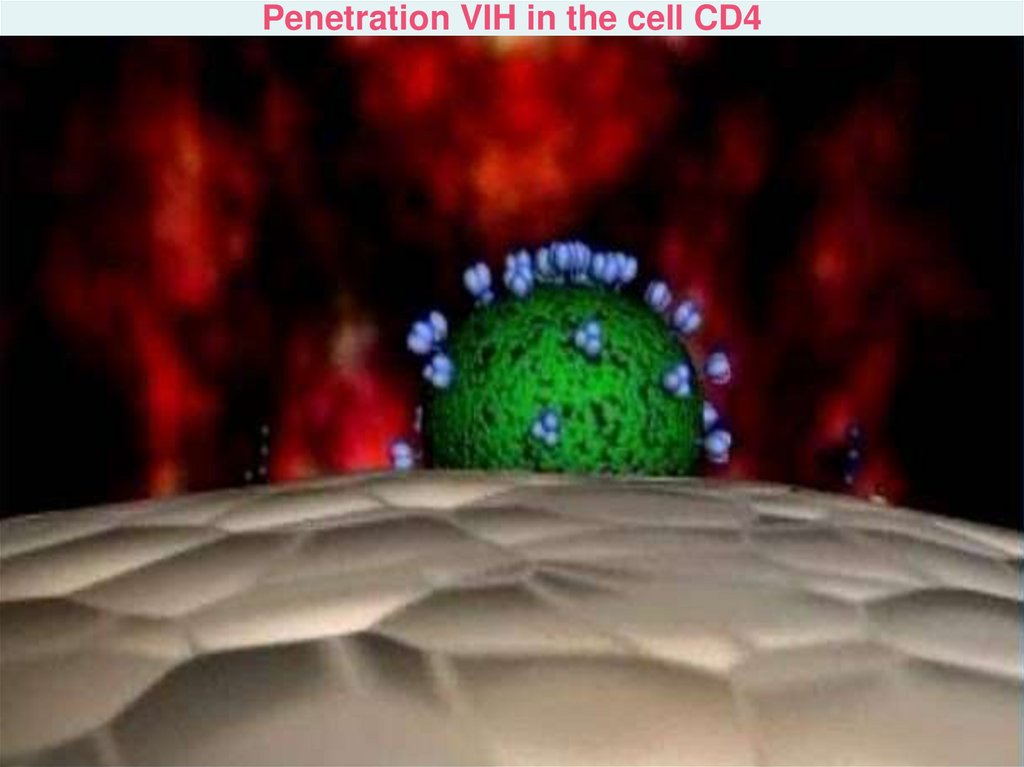
Penetration VIH in the cell CD4hiv_life_cycle.asf
20.
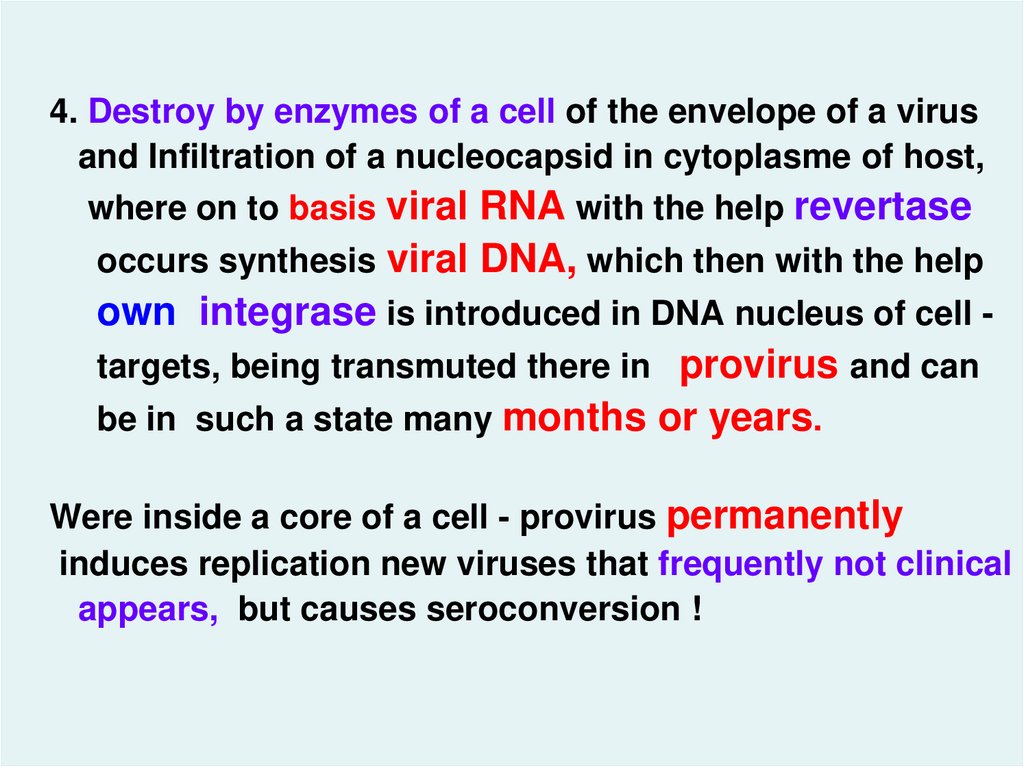
4. Destroy by enzymes of a cell of the envelope of a virusand Infiltration of a nucleocapsid in cytoplasme of host,
where on to basis viral RNA with the help revertase
occurs synthesis viral DNA, which then with the help
own integrase is introduced in DNA nucleus of cell targets, being transmuted there in provirus and can
be in such a state many months or years.
hiv_life_cycle.asf
Were inside a core of a cell - provirus permanently
induces replication new viruses that frequently not clinical
appears, but causes seroconversion !
21.
5. The maximal induction the viruses is registered in astages primary clinical manifestations and AIDS.
6. The antigenrecognition and antigenpresentation
function of macrophages and monocytes is oppressed
simultaneously with increase of formation by them of
various mediators (pyrogens, cachexins, tumornecrossis
of the factor etc.)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
7. The considerable injury of the population СД4lymphocytes fulfilling key role in immune processes,
that result is violation of cooperation immune cells, loss
by them of ability to the adequate answer on allogenic and
autoantigenic exposures, that promotes clinical
manifestation of the opportunistic infections and
neoplasms
22.
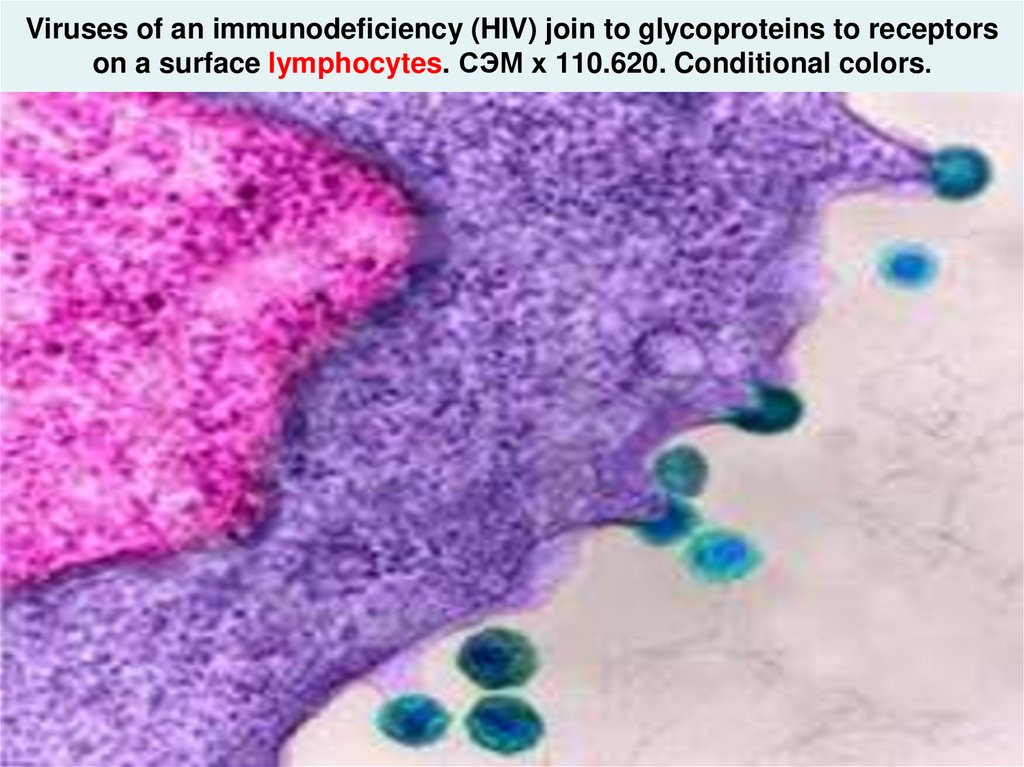
hiv_life_cycle.asf23. Viruses of an immunodeficiency (HIV) join to glycoproteins to receptors on a surface lymphocytes. СЭМ х 110.620. Conditional
colors.hiv_life_cycle.asf
24.
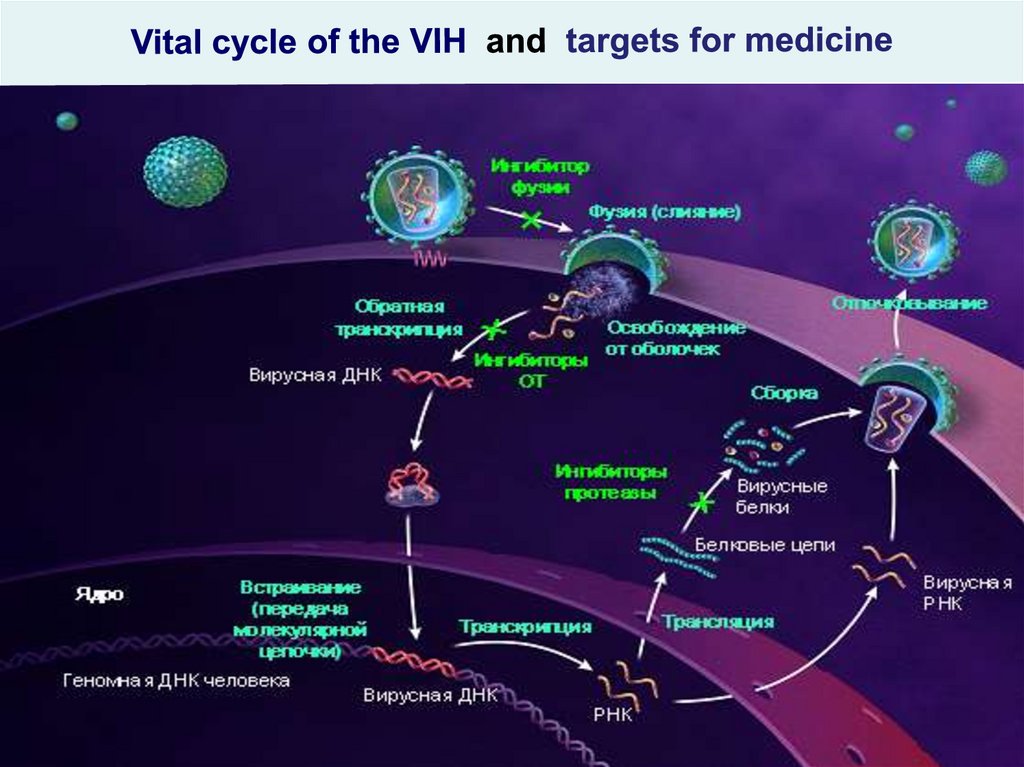
Vital cycle of the VIH and targets for medicinehiv_life_cycle.asf
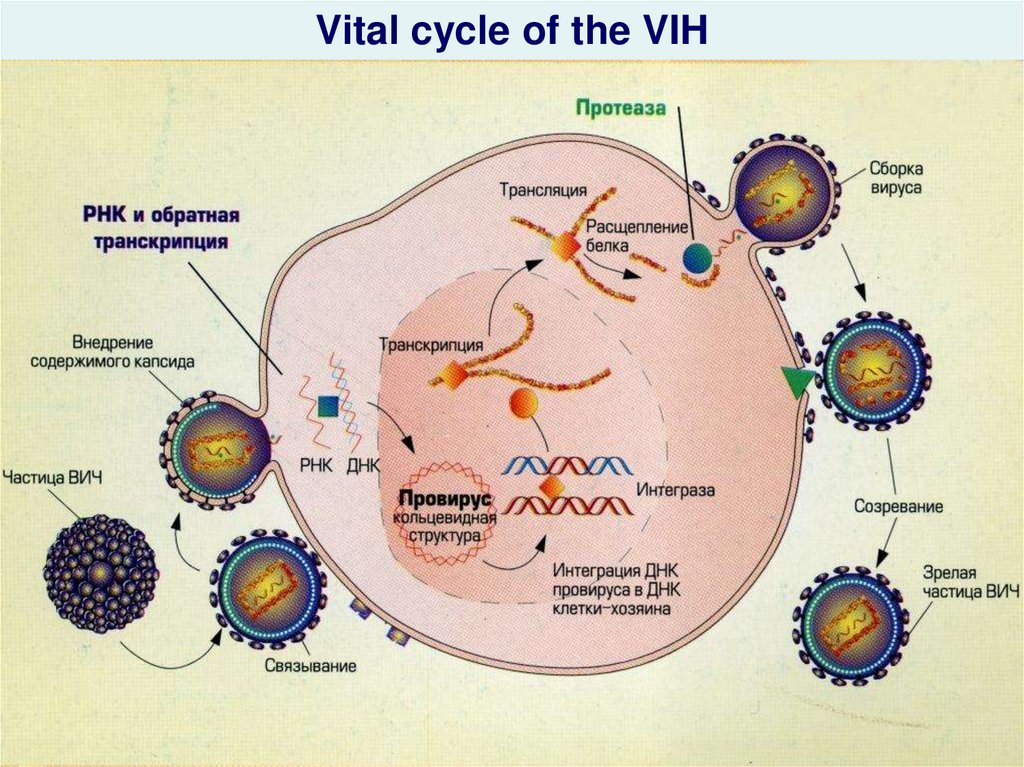
25. Vital cycle of the VIH
hiv_life_cycle.asf26.
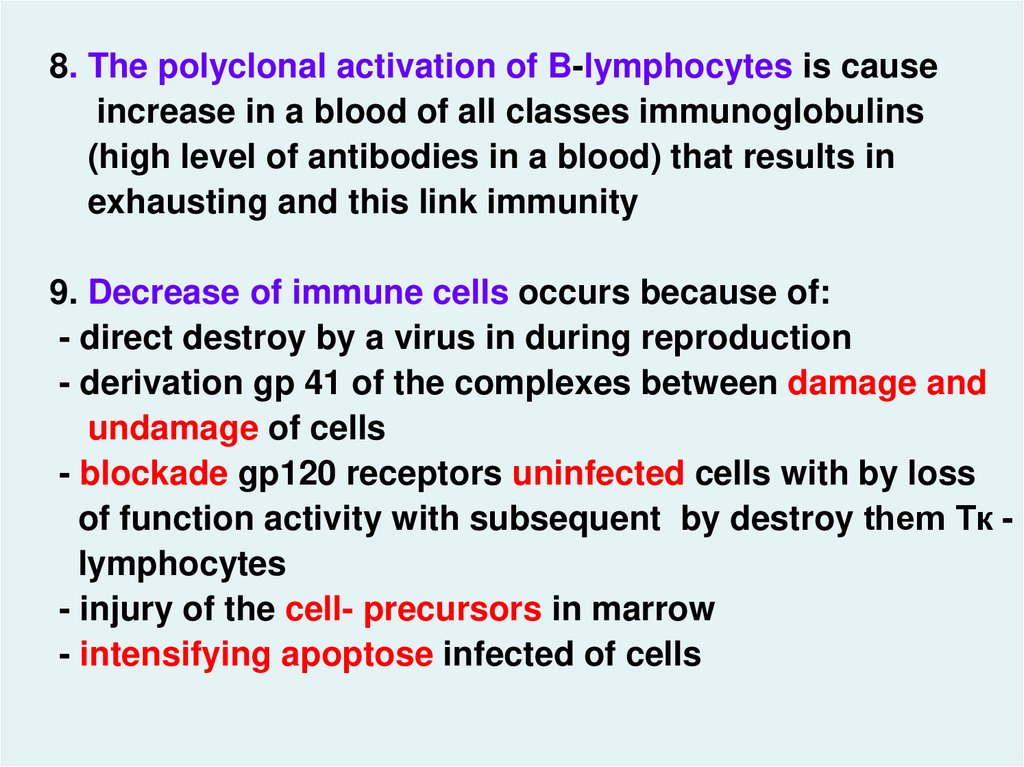
8. The polyclonal activation of B-lymphocytes is causeincrease in a blood of all classes immunoglobulins
(high level of antibodies in a blood) that results in
exhausting and this link immunity
9. Decrease of immune cells occurs because of:
- direct destroy by a virus in during reproduction
- derivation gp 41 of the complexes between damage and
undamage of cells
- blockade gp120 receptors uninfected cells with by loss
of function activity with subsequent by destroy them Тк lymphocytes
- injury of the cell- precursors in marrow
- intensifying apoptose infected of cells
hiv_life_cycle.asf
27.
10. Occurs anergy of a skin and mucous, are depressedinflammatory responses.
11. Under influence of manifold co-factors or superinfections, toxic effects (narcotics) begining the intensive
replication of viruses (in the end of secondary latent
period) with mass destruction immune cells, that results
in appearance AIDS-indicator diseases, make progress
which even on a background of specific treatment
results in death of the patients
PATHOMORFOLOGY
(the manifestations are diversiform)
- lymphadenopathy with involution of a glandular tissue
- demyelination and sponge degeneration of the nervous
tissues
hiv_life_cycle.asf
28.
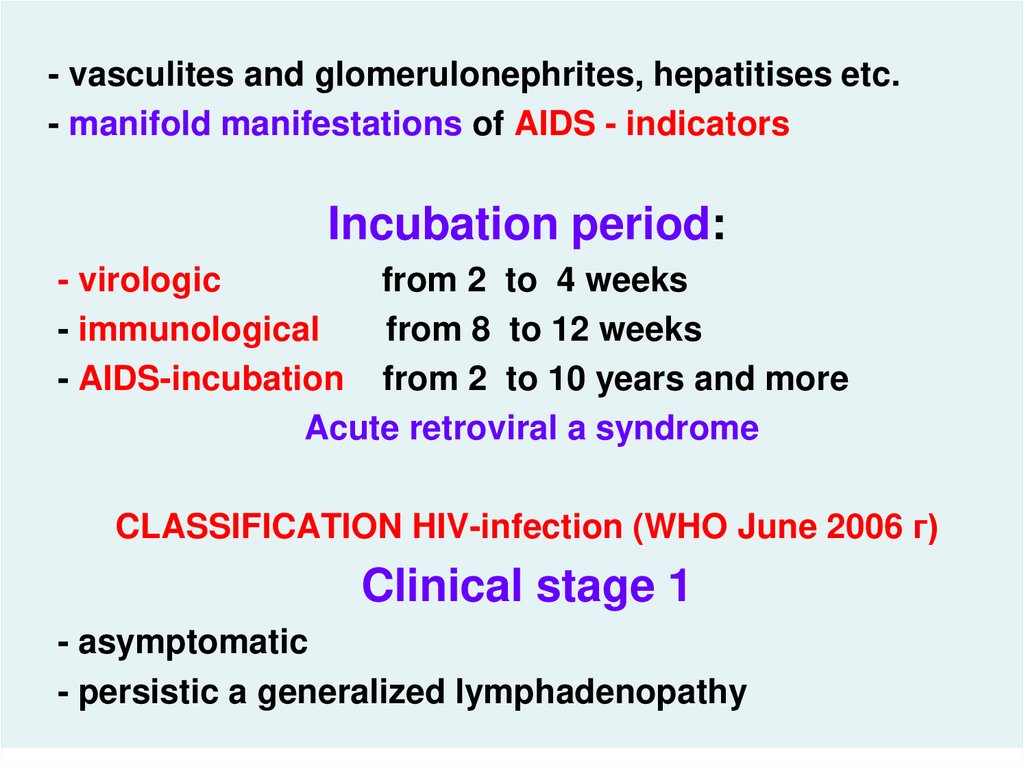
- vasculites and glomerulonephrites, hepatitises etc.- manifold manifestations of AIDS - indicators
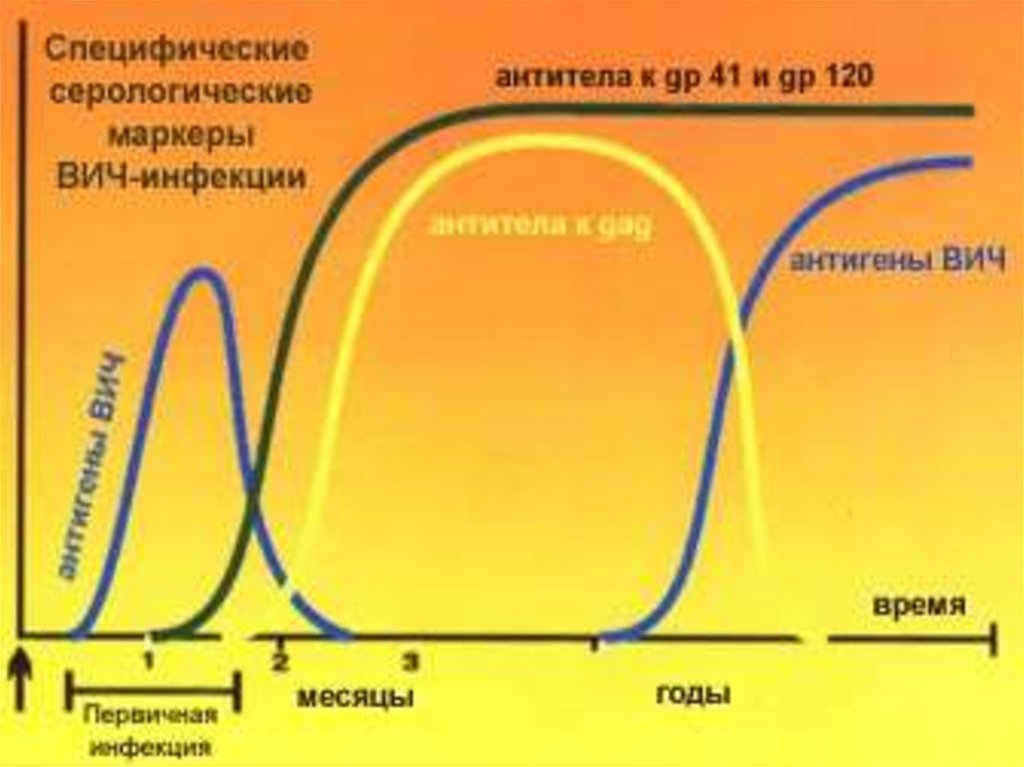
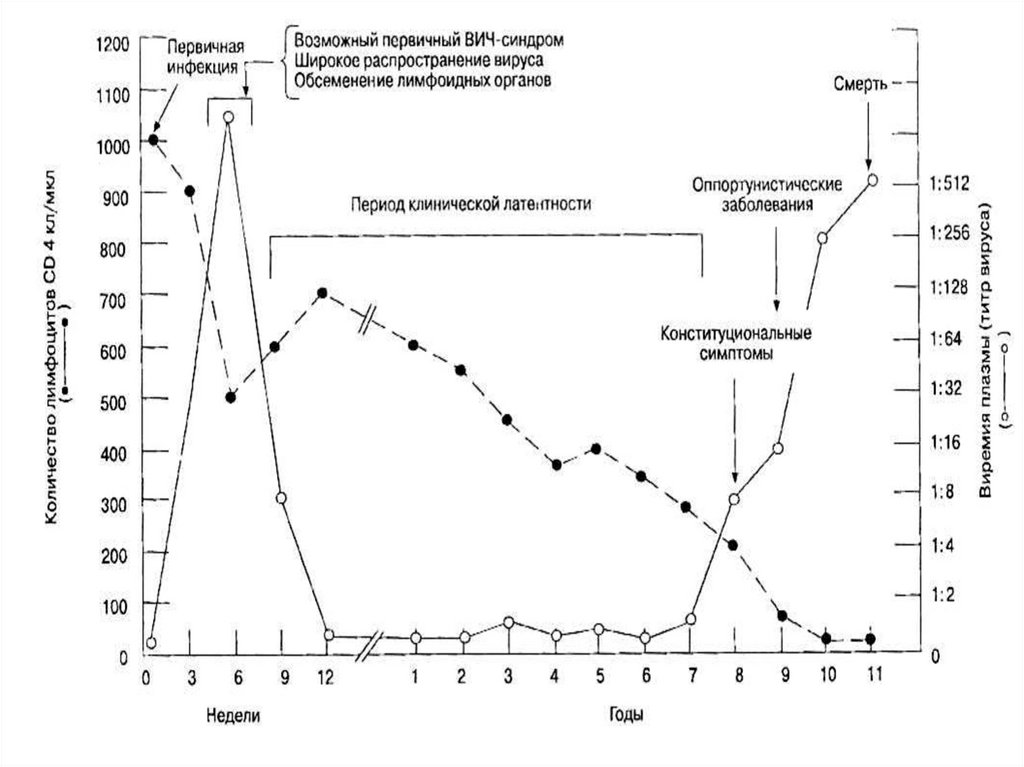
Incubation period:
- virologic
from 2 to 4 weeks
- immunological
from 8 to 12 weeks
- AIDS-incubation from 2 to 10 years and more
Acute retroviral a syndrome
hiv_life_cycle.asf
CLASSIFICATION HIV-infection (WHO June 2006 г)
Clinical stage 1
- asymptomatic
- persistic a generalized lymphadenopathy
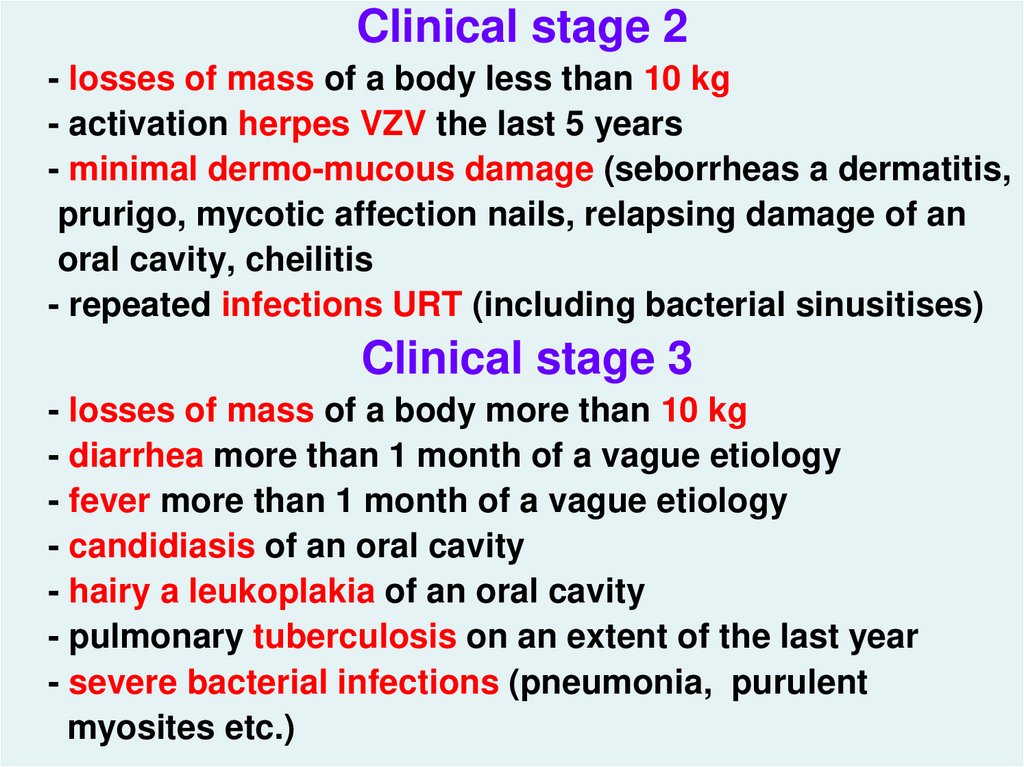
29.
Clinical stage 2- losses of mass of a body less than 10 kg
- activation herpes VZV the last 5 years
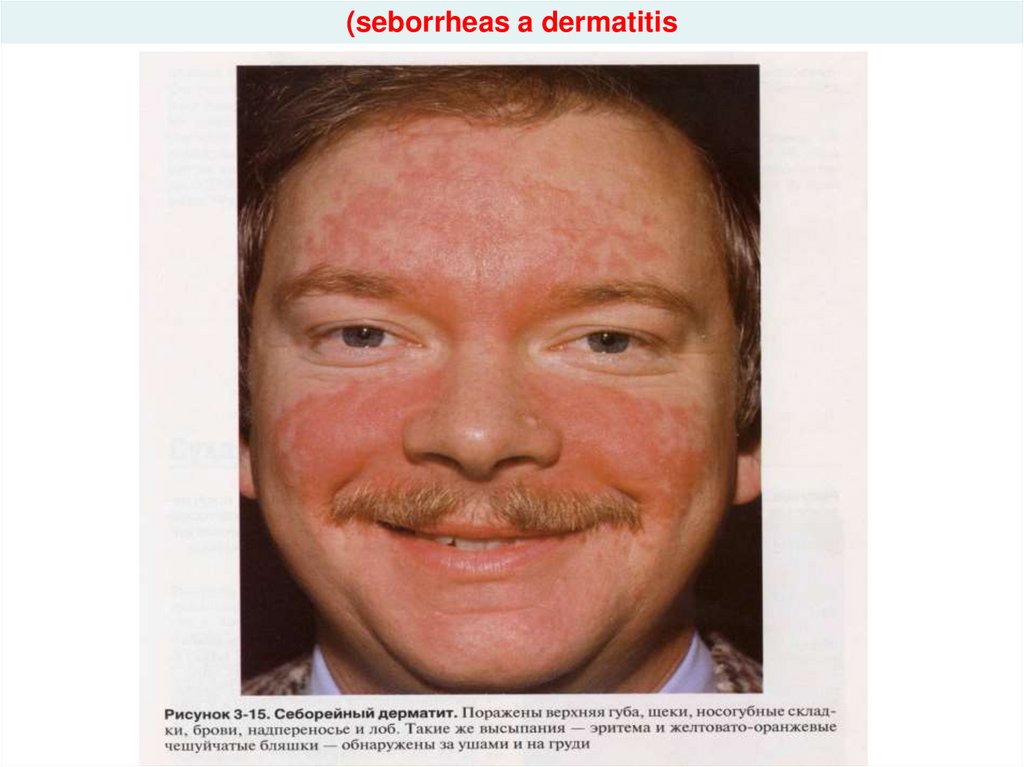
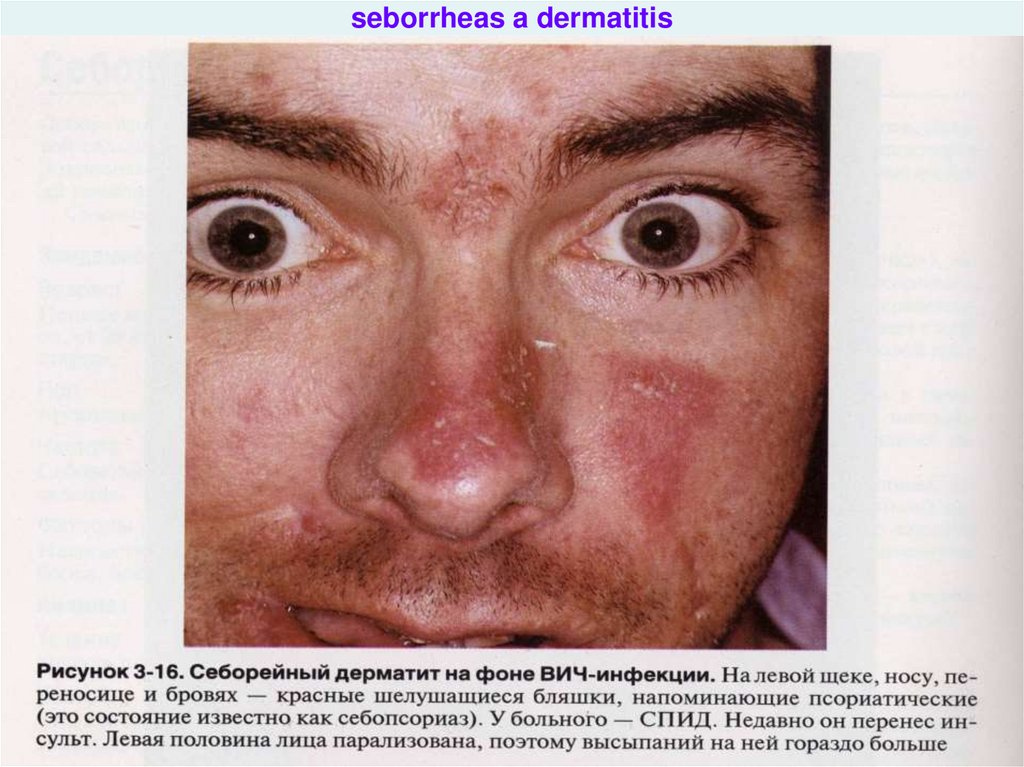
- minimal dermo-mucous damage (seborrheas a dermatitis,
prurigo, mycotic affection nails, relapsing damage of an
oral cavity, cheilitis
- repeated infections URT (including bacterial sinusitises)
Clinical stage 3
- losses of mass of a body more than 10 kg
- diarrhea more than 1 month of a vague etiology
- fever more than 1 month of a vague etiology
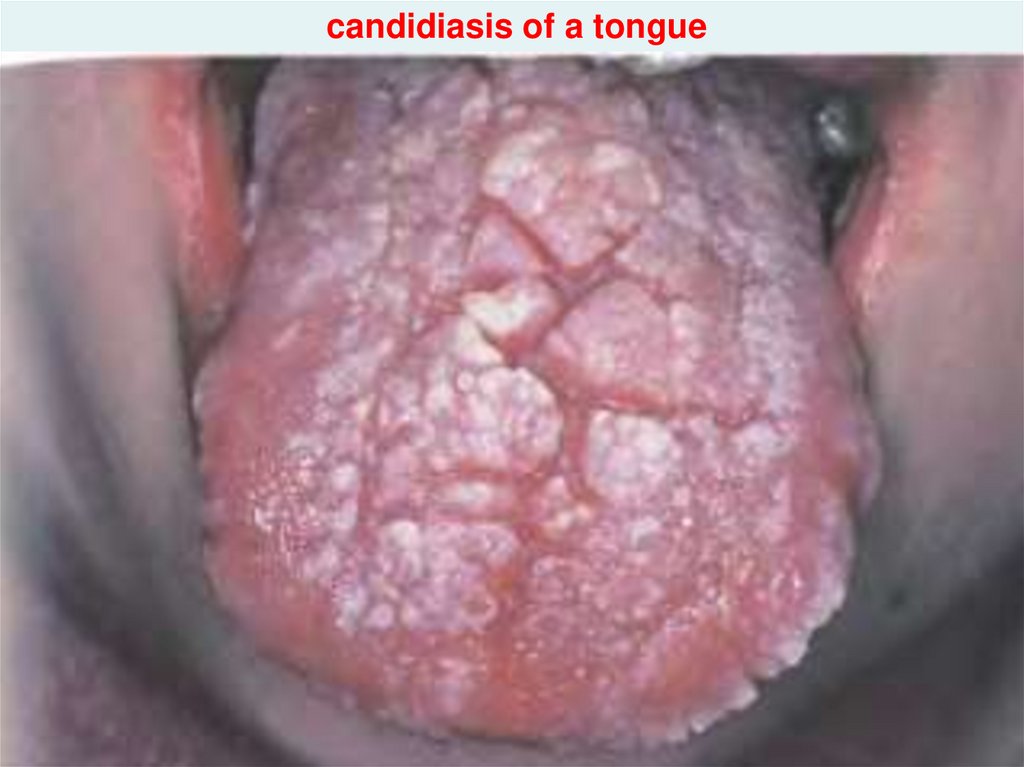
- candidiasis of an oral cavity
- hairy a leukoplakia of an oral cavity
- pulmonary tuberculosis on an extent of the last year
- severe bacterial infections (pneumonia, purulent
myosites etc.)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
30.
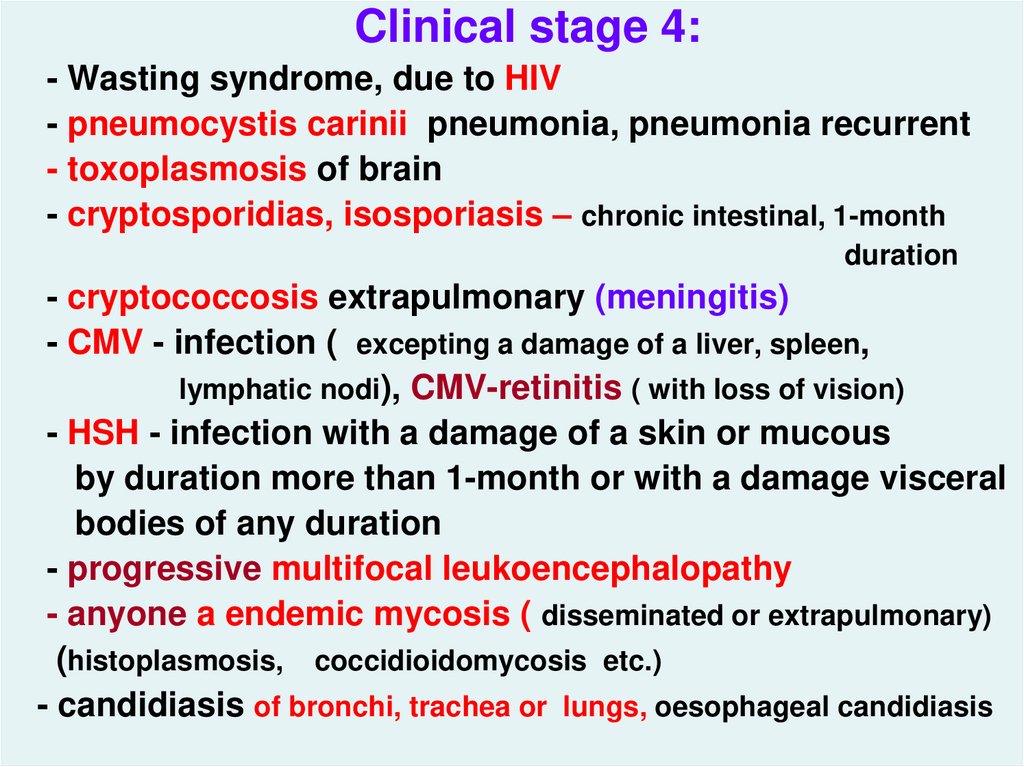
Clinical stage 4:- Wasting syndrome, due to HIV
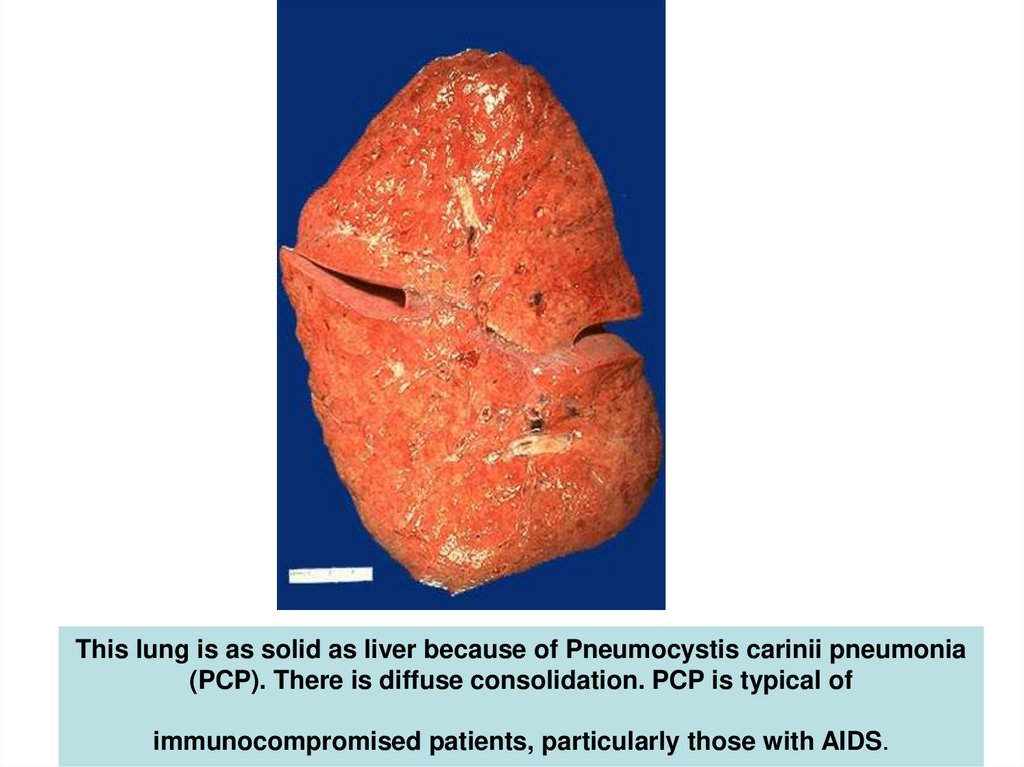
- pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, pneumonia recurrent
- toxoplasmosis of brain
- cryptosporidias, isosporiasis – chronic intestinal, 1-month
duration
- cryptococcosis extrapulmonary (meningitis)
- CMV - infection ( excepting a damage of a liver, spleen,
lymphatic nodi), CMV-retinitis ( with loss of vision)
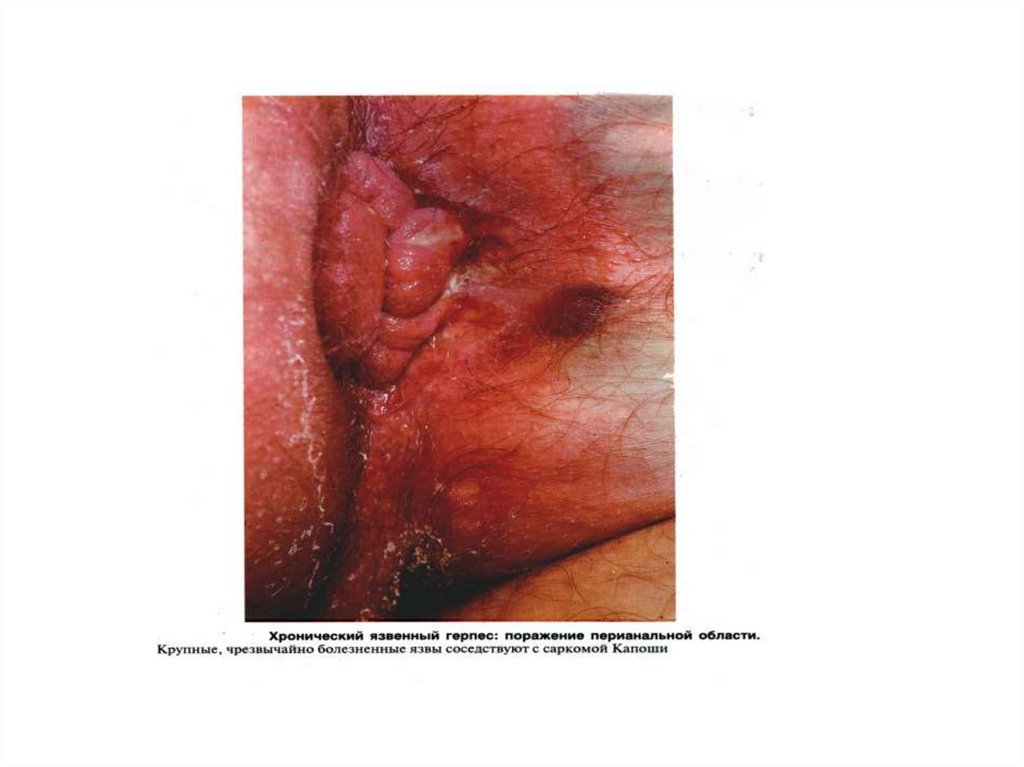
- HSH - infection with a damage of a skin or mucous
by duration more than 1-month or with a damage visceral
bodies of any duration
- progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- anyone a endemic mycosis ( disseminated or extrapulmonary)
(histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis etc.)
- candidiasis of bronchi, trachea or lungs, oesophageal candidiasis
hiv_life_cycle.asf
31.
- visceral leishmaniasis- extrapulmonary a tuberculosis
- atypical mycobacteriosis disseminated or extrapulmonary)
B - cellular malignant lymphoma – brain, Burkitt`s sarcoma
- Kaposi*s sarcoma
- encephalopathy, HIV-related
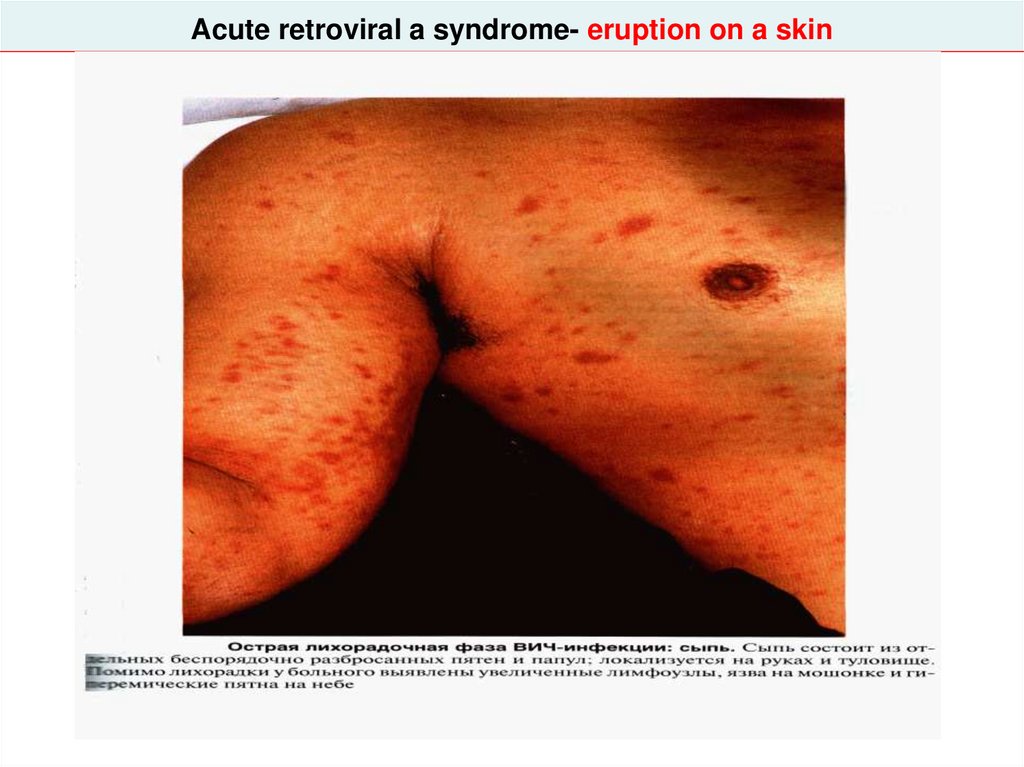
CLINIC ACUTE RETROVIRAL of a SYNDROME:
- high fever
- adenopathy
- pharyngitis
- eruption on a skin and mucous
- myalgia - diarrhea hiv_life_cycle.asf
96 %
74 %
70 %
70 %
54 %
32 %
32.
- headache - nausea and vomiting - hepatospleenmegaly - lowering mass of a body - candidiasis of an oral cavity -32 %
27 %
14 %
13 %
12 %
- neurologic manifestations 12 %
(aseptic meningitis, meningocephalitis, peripheral
neuropathy, paresis, s-m Гийена - Барре, psychosis)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
All these manifestations are stipulated only HIV and after 36 months ( even without any treatment) disappear and for
the patient is starting the secondary latent period from 2 up
to 15 and more than years.
33. Acute retroviral a syndrome- eruption on a skin
hiv_life_cycle.asf34. (seborrheas a dermatitis
hiv_life_cycle.asf35. seborrheas a dermatitis
hiv_life_cycle.asf36. candidiasis of a tongue
hiv_life_cycle.asf37.
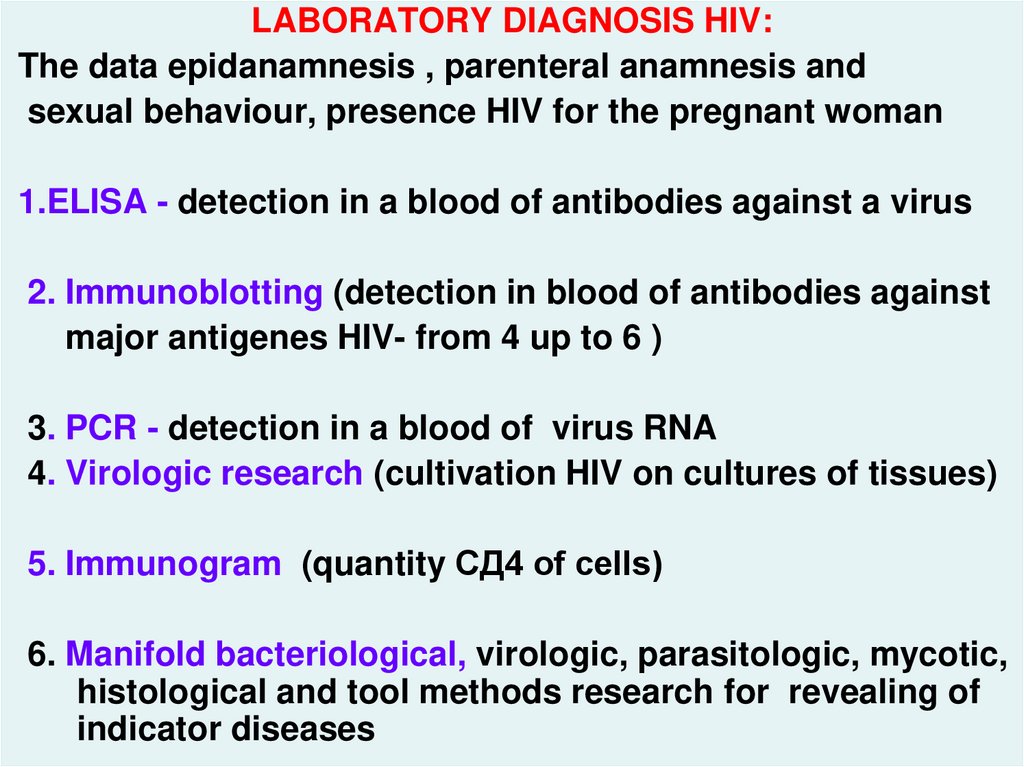
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS HIV:The data epidanamnesis , parenteral anamnesis and
sexual behaviour, presence HIV for the pregnant woman
1.ELISA - detection in a blood of antibodies against a virus
2. Immunoblotting (detection in blood of antibodies against
major antigenes HIV- from 4 up to 6 )
3. PCR - detection in a blood of virus RNA
4. Virologic research (cultivation HIV on cultures of tissues)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
5. Immunogram (quantity СД4 of cells)
6. Manifold bacteriological, virologic, parasitologic, mycotic,
histological and tool methods research for revealing of
indicator diseases
38.
hiv_life_cycle.asf39.
hiv_life_cycle.asf40.
ANTIRETROVIRAL TREATMENT ( ART)АRТ is a reception of specific drugs, which
operating on various components HIV, prevent it
to develop and to be multiplied
АRТ - does not cure of a HIV-INFECTION completely, but
improves quality of life and allows essentially
slows down development AIDS
АRТ - allows sharply to lower quantity of a virus in
organism and longer to save effective operation
the immune system
АRТ - will be carried out continuously and all life!!!
АRТ - is assigned only at lowering quantity СД4
lymphocytes from 350 and is lower in 1 mcl. of a blood (It is
hiv_life_cycle.asf
often starting from 2-nd clinical stage of the disease)
41.
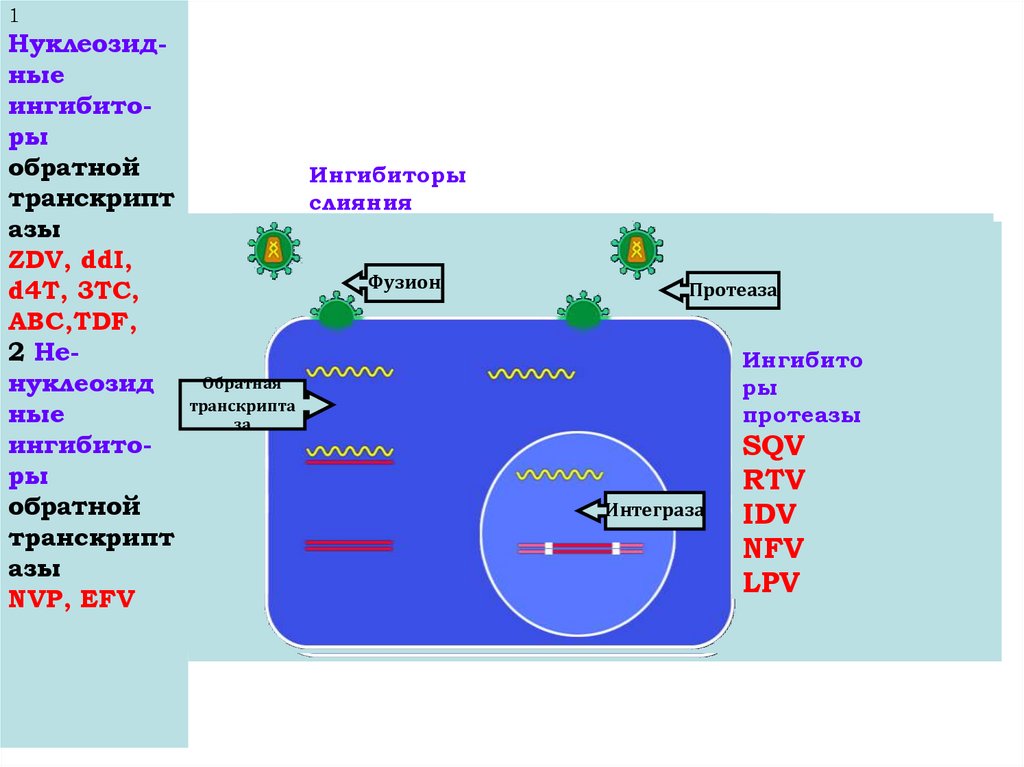
GROUPS ANTIRETROVIRAL of DRUGS:1.Nucleozid`s inhibitors return transcriptasa(d4T, AZT, ddl, 3TC …)
2. Unnucleozid`s inhibitors return transcriptasa (EFV, NVP …)
3. Inhibitors of a protease: (NFV, Ipv/rtv, IDV, RTV, SQV …)
Triple therapy (on one drug from each of the listed above
groups with replacement on the following triple
combination will be used only at appearance of stability
to the first group!!!
The mechanism of operation of drugs from each of groups
represented on the following slide
hiv_life_cycle.asf
42.
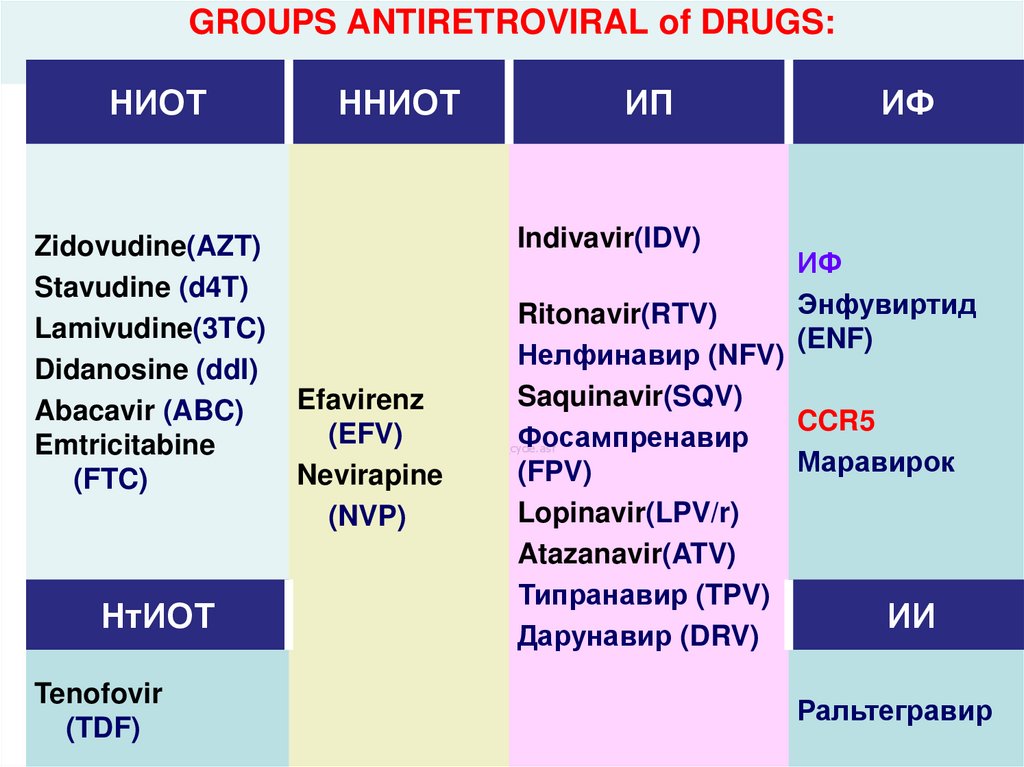
hiv_life_cycle.asf43. GROUPS ANTIRETROVIRAL of DRUGS:
НИОТZidovudine(AZT)
Stavudine (d4T)
Lamivudine(3TC)
Didanosine (ddI)
Abacavir (ABC)
Emtricitabine
(FTC)
НтИОТ
Tenofovir
(TDF)
ННИОТ
ИП
Indivavir(IDV)
ИФ
ИФ
Энфувиртид
(ENF)
Ritonavir(RTV)
Нелфинавир (NFV)
Saquinavir(SQV)
Efavirenz
CCR5
(EFV)
Фосампренавир
hiv_life_cycle.asf
Маравирок
(FPV)
Nevirapine
Lopinavir(LPV/r)
(NVP)
Atazanavir(ATV)
Типранавир (TPV)
ИИ
Дарунавир (DRV)
Ральтегравир
44.
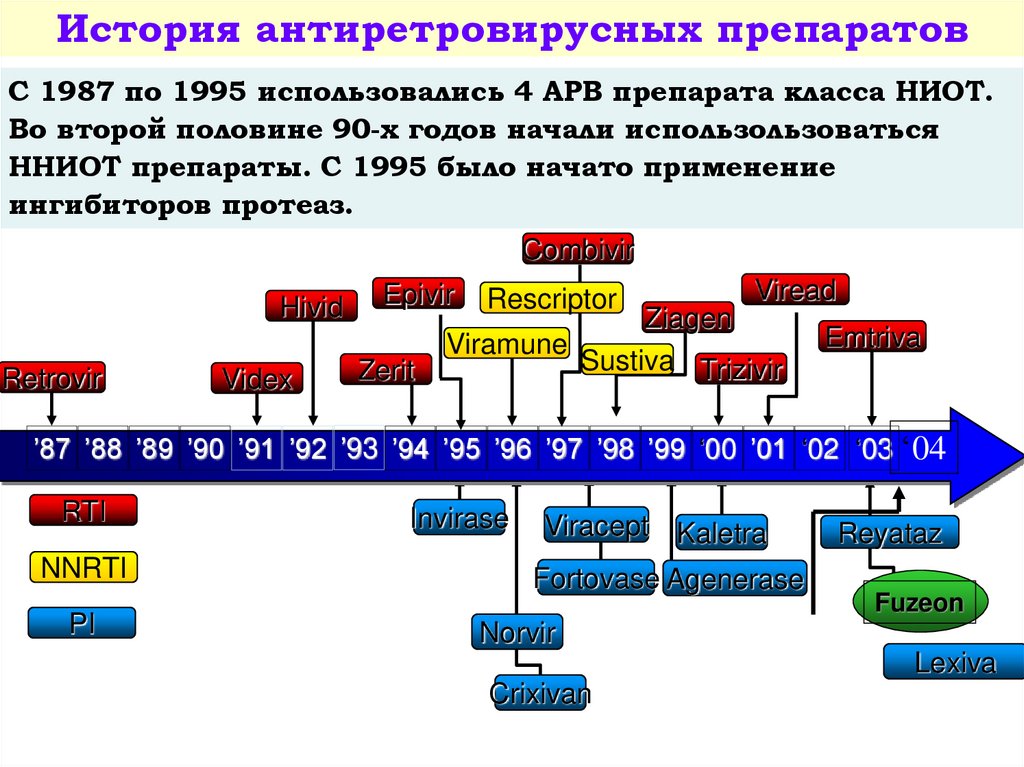
История антиретровирусных препаратовС 1987 по 1995 использовались 4 АРВ препарата класса НИОТ.
Во второй половине 90-х годов начали использользоваться
ННИОТ препараты. С 1995 было начато применение
ингибиторов протеаз.
Combivir
Hivid
Retrovir
Videx
Epivir
Zerit
Rescriptor
Viread
Ziagen
Viramune
Sustiva Trizivir
Emtriva
’87 ’88 ’89 ’90 ’91 ’92 ’93 ’94 ’95hiv_life_cycle.asf
’96 ’97 ’98 ’99 ‘00 ’01 ‘02 ‘03 ‘04
RTI
NNRTI
PI
Invirase
Viracept Kaletra
Fortovase Agenerase
Reyataz
Fuzeon
Norvir
Lexiva
Crixivan
45.
1) Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase InhibitorsVidex EC
Emtriva
Epivir
Eg : Emtricitabine
200 mg once a day
Eg : Lamivudine or 3TC
300-mg tablet once a day
150 mg tablet twice a day
Eg : Didanosine or ddI
400 mg enteric coated
capsules
hiv_life_cycle.asf
Retrovir
Viread
Eg : Zidovudine or AZT
Eg : Tenofovir
100 mg and 300 mg capsules
300 mg tablets
10 mg/mL IV solution
once a day
10 mg/mL oral solution
Zerit
Eg : Stavudine or d4T
15, 20, 30 and 40 mg
capsules
1 mg/mL oral solution
46.
2) Non-Nucleoside Reverse TranscriptaseInhibitors
Sustiva
Eg : Efavirenz
50, 100 and 200 mg capsules
Viramune
Eg : Nevirapine
200 mg tablets
50 mg/5 mL oral suspension.
hiv_life_cycle.asf
3) Fusion Inhibitor
Fuzeon
Eg : Enfuvirtide
90 mg
47.
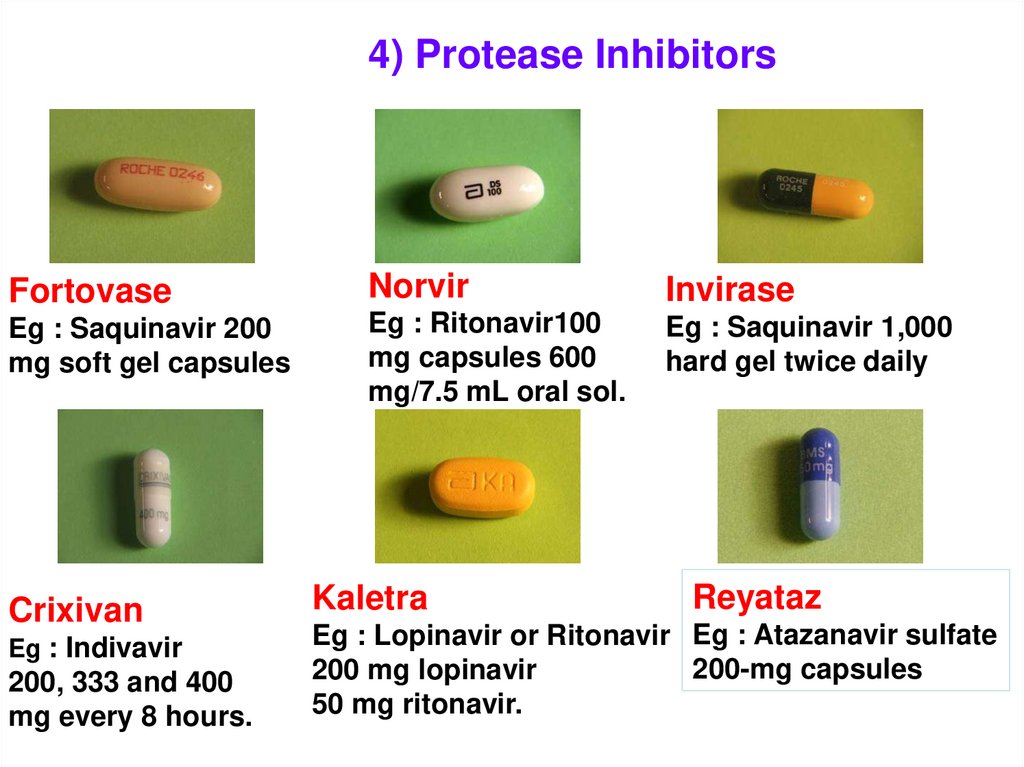
4) Protease InhibitorsFortovase
Norvir
Invirase
Eg : Saquinavir 200
mg soft gel capsules
Eg : Ritonavir100
mg capsules 600
mg/7.5 mL oral sol.
Eg : Saquinavir 1,000
hard gel twice daily
hiv_life_cycle.asf
Crixivan
Eg : Indivavir
200, 333 and 400
mg every 8 hours.
Kaletra
Reyataz
Eg : Lopinavir or Ritonavir Eg : Atazanavir sulfate
200-mg capsules
200 mg lopinavir
50 mg ritonavir.
48.
1)TruvadaEmtricitabine / Emtriva 200 mg
Tenofovir / Viread
300 mg
2)Combivir
Lamivudine / Epivir 150 mg
Zidovudine / Retrovir 300 mg
3)Epzicom
Lamivudine 300 mg
Abacavir 600 mg
hiv_life_cycle.asf
4)Trizivir
Zidovudine / Retrovir 300 mg
Lamivudine / Epivir 150 mg
Abacavir / Ziagen
300 mg
49.
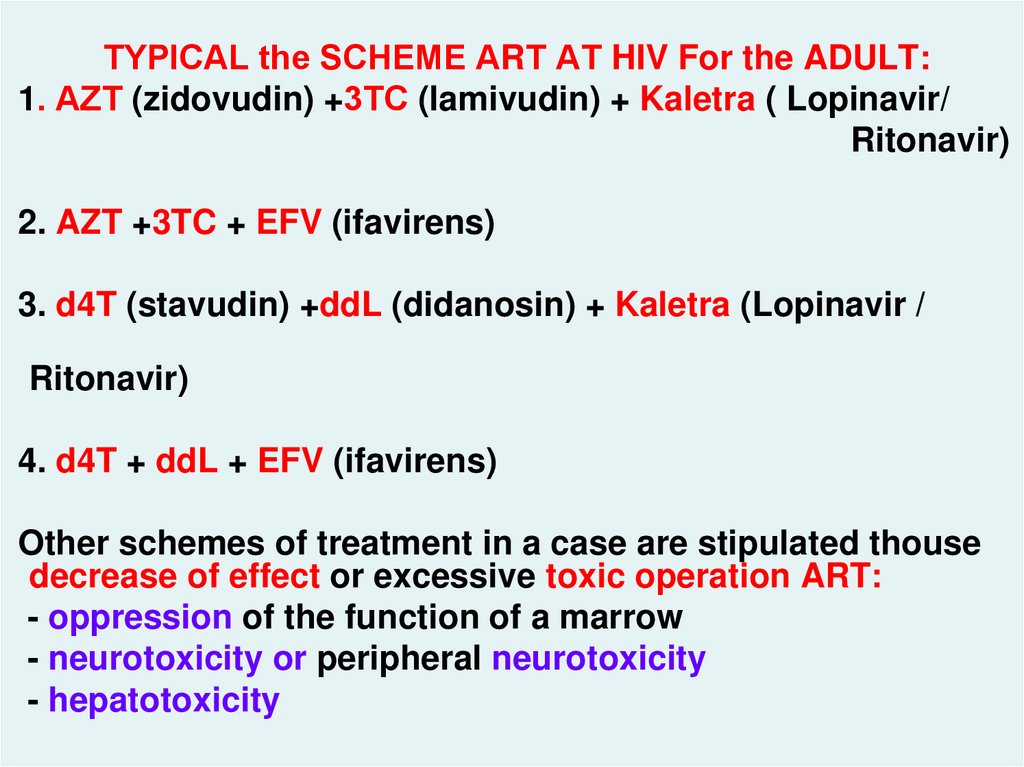
TYPICAL the SCHEME АRТ AT HIV For the ADULT:1. АZT (zidovudin) +3ТС (lamivudin) + Kaletra ( Lopinavir/
Ritonavir)
2. AZT +3TC + EFV (ifavirens)
3. d4T (stavudin) +ddL (didanosin) + Kaletra (Lopinavir /
Ritonavir)
hiv_life_cycle.asf
4. d4T + ddL + EFV (ifavirens)
Other schemes of treatment in a case are stipulated thouse
decrease of effect or excessive toxic operation ART:
- oppression of the function of a marrow
- neurotoxicity or peripheral neurotoxicity
- hepatotoxicity
50.
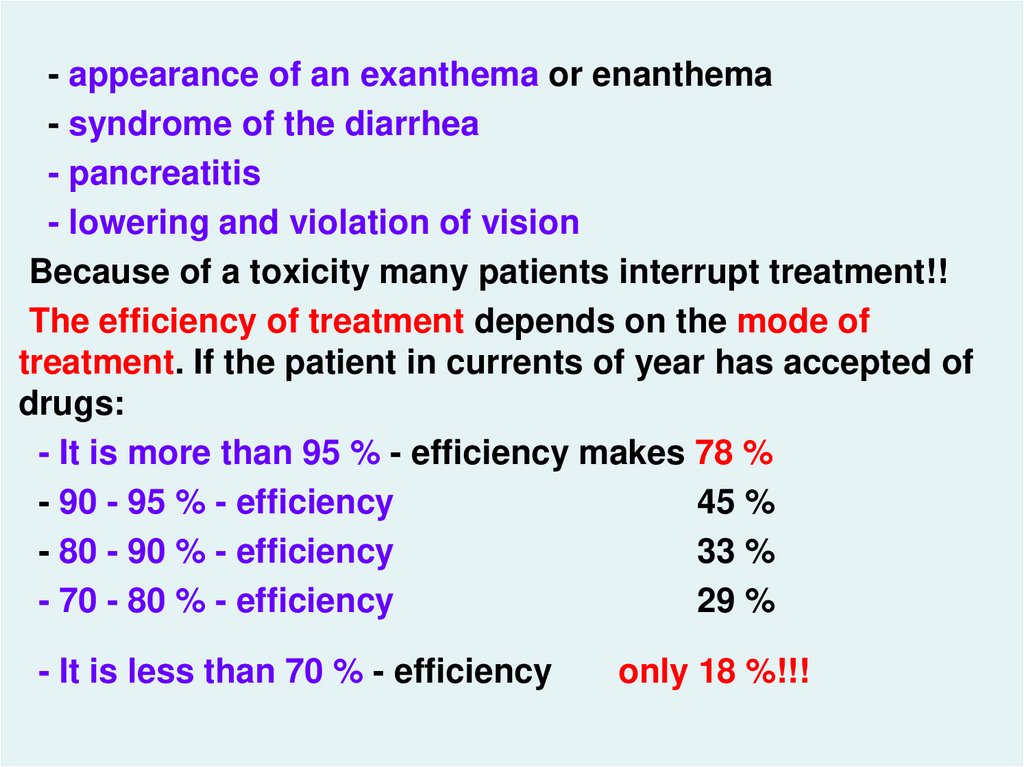
- appearance of an exanthema or enanthema- syndrome of the diarrhea
- pancreatitis
- lowering and violation of vision
Because of a toxicity many patients interrupt treatment!!
The efficiency of treatment depends on the mode of
treatment. If the patient in currents of year has accepted of
drugs:
- It is more than 95 % - efficiency makes 78 %
- 90 - 95 % - efficiency
45 %
- 80 - 90 % - efficiency
33 %
- 70 - 80 % - efficiency
29 %
hiv_life_cycle.asf
- It is less than 70 % - efficiency
only 18 %!!!
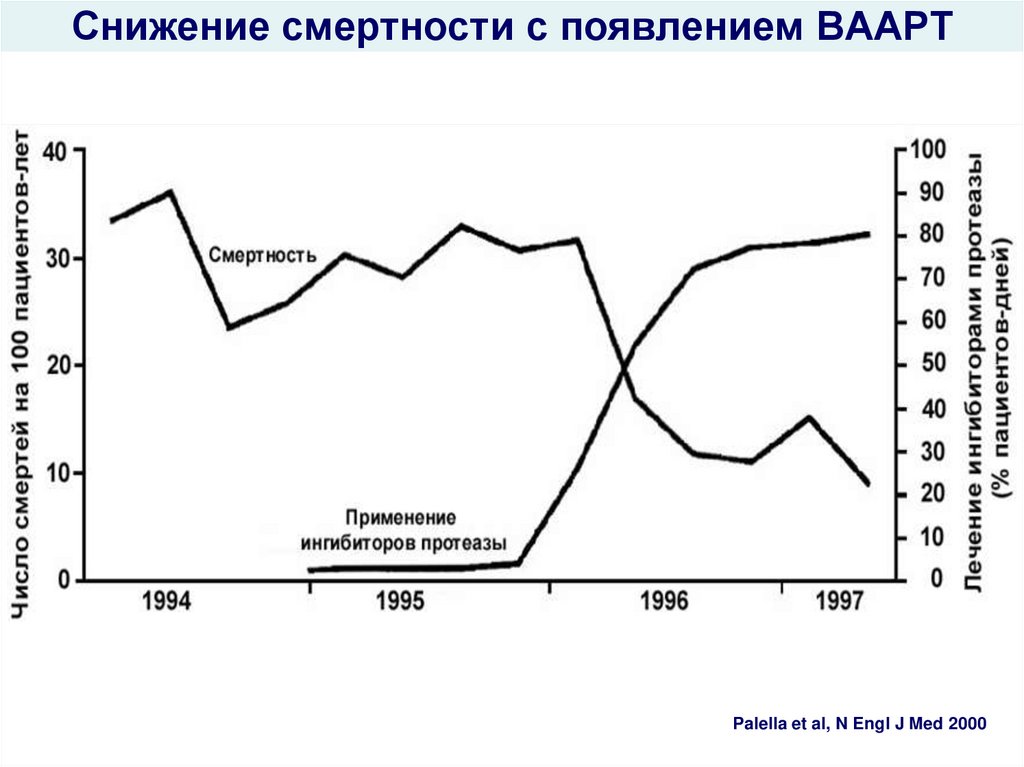
51. Снижение смертности с появлением ВААРТ
hiv_life_cycle.asfPalella et al, N Engl J Med 2000
52.
PROPHYLAXIS (there is no specific prophylaxis!!!)- revealing groups of hazard and their testing ( with
permissions of the patient!!!)
- careful research of all biological tissues obtained from the
man on HIV (donors)
- usage of medical gloves
- usage of masks,shields, glasses, aprons- for protection of
a skin and mucous
- usage of a «scoop» technique dressing disperser hood on
a needle of a utilised squirt
- at transmission during operation of the tool from hands in
hands to utillize « a neutral field » - little table, tray
- washing hands, disinfection of tools, ware, linen,
equipments
hiv_life_cycle.asf
53.
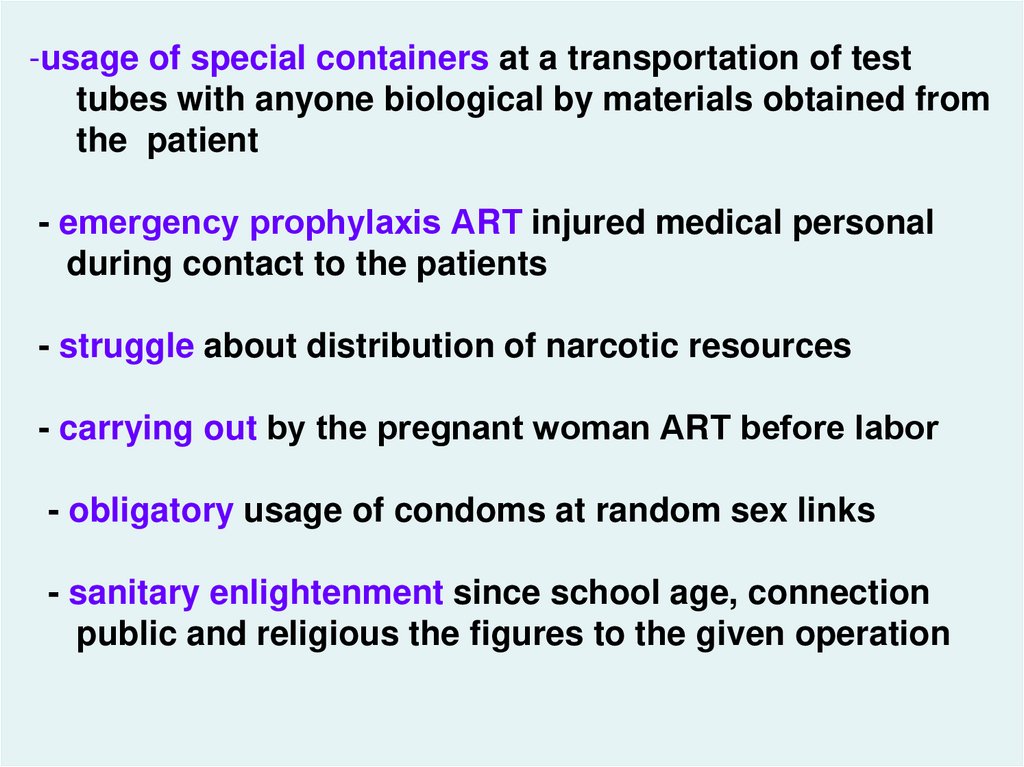
-usage of special containers at a transportation of testtubes with anyone biological by materials obtained from
the patient
- emergency prophylaxis АRТ injured medical personal
during contact to the patients
- struggle about distribution of narcotic resources
- carrying out by the pregnant woman АRТ before labor
hiv_life_cycle.asf
- obligatory usage of condoms at random sex links
- sanitary enlightenment since school age, connection
public and religious the figures to the given operation
54.
ENDING OF THE LECTUREhiv_life_cycle.asf
55.
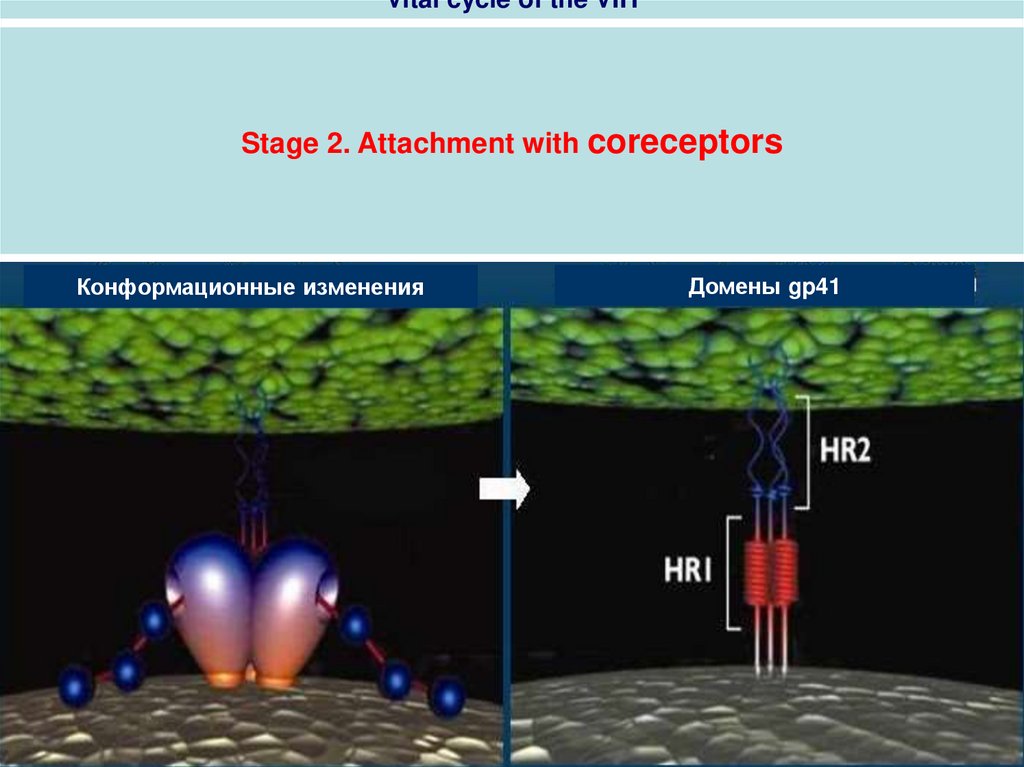
Vital cycle of the VIHStage 2. Attachment with coreceptors
Домены gp41
Конформационные изменения
hiv_life_cycle.asf
56.
hiv_life_cycle.asf57.
hiv_life_cycle.asf58. This lung is as solid as liver because of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP). There is diffuse consolidation. PCP is typical
hiv_life_cycle.asfThis lung is as solid as liver because of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
(PCP). There is diffuse consolidation. PCP is typical of
immunocompromised patients, particularly those with AIDS.
59.
1Нуклеозидные
ингибиторы
обратной
транскрипт
азы
ZDV, ddI,
d4T, 3TC,
ABC,TDF,
2 Ненуклеозид
ные
ингибиторы
обратной
транскрипт
азы
NVP, EFV
Ингибиторы
слияния
EFV (T20)
Фузион
Фузион
РНК РНК
РНК
Обратная
Обратная
от
транскрипта
транскрипта
за
за
ОТ
ОТ
РНК РНК
РНК
ДНК
ДНК
ДНК
ОТ
от
ОТ
ДНК ДНК
ДНК
ДНК ДНК
ДНК
Протеаза
Протеаза
РНК РНК
РНК
ПРОТЕИНЫ
ПРОТЕИНЫ
ПРОТЕИНЫ
hiv_life_cycle.asf
РНК
РНК
РНК
Интеграза
Интеграза
ПРОВИРУС
ПРОВИРУС
ПРОВИРУС
Ингибито
Ингибито
ры
ры
протеазы
протеазы
SQV
SQV
RTV
RTV
IDV
IDV
NFV
NFV
LPV
LPV



















 medicine
medicine








