Similar presentations:
Networks and telecommunications
1. Networks and telecommunications
NETWORKS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONSTeacher: Ibraimova Assel
2.
Purposes:to
gaining
knowledge
of
the
fundamentals of construction, operation
and use of computer networks of varying
size, possibilities of their implementation
on the basis of the underlying
technologies and standards.
3.
1.2.
3.
4.
Plan of Lecture:
Network topologies, IP-addressing.
Stack protocols: TCP / IP, OSI. LANs and WANs.
Wired and wireless networking technologies.
Internet-Based Services.
4.
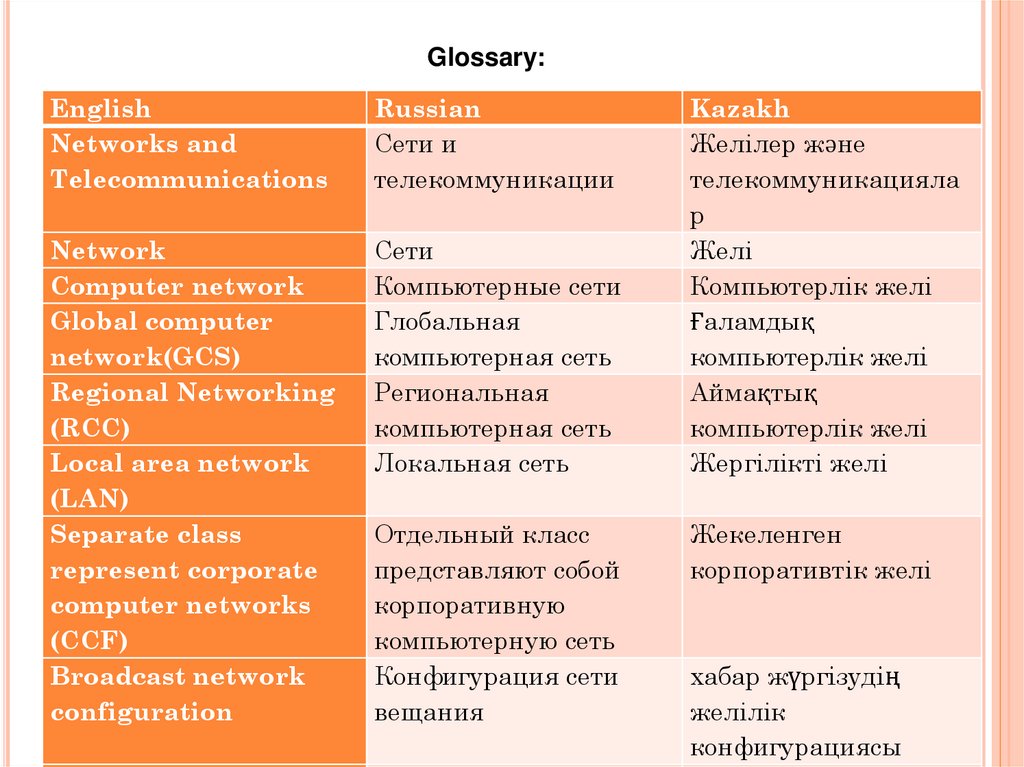
Glossary:English
Networks and
Telecommunications
Russian
Сети и
телекоммуникации
Network
Computer network
Global computer
network(GCS)
Regional Networking
(RCC)
Local area network
(LAN)
Separate class
represent corporate
computer networks
(CCF)
Broadcast network
configuration
Сети
Компьютерные сети
Глобальная
компьютерная сеть
Региональная
компьютерная сеть
Локальная сеть
Отдельный класс
представляют собой
корпоративную
компьютерную сеть
Конфигурация сети
вещания
Kazakh
Желілер және
телекоммуникацияла
р
Желі
Компьютерлік желі
Ғаламдық
компьютерлік желі
Аймақтық
компьютерлік желі
Жергілікті желі
Жекеленген
корпоративтік желі
хабар жүргізудің
желілік
конфигурациясы
5.
Brief description of terms:Computer network set of nodes (computers,
terminals, peripherals) having the possibility of
information exchange with each other using a special
communication hardware and softwarenetwork with
respect to peer access control to data paths in these
networks distributed among the nodes.
Network analyzer interception method as they
move along the lines intranet connection
Any part of the network resource or a network of
computers (such as disk, directory, printer, etc.) that
can used by the application during operation.
6. Computer network
COMPUTER NETWORKA computer network or data network is a
telecommunications
network
which
allows computers to exchange data.
In computer networks, networking devices
exchange data with each other using a data
link. The connections between nodes are
established using either cable media or wireless
media. The best-known computer network is
the Internet.
7.
Network computer devices that originate, route andterminate the data are called network nodes.
Computer networks differ in the transmission
medium used to carry their signals, communications
protocols to organize network traffic, the network's size,
topology and organizational intent.
In the late 1950s early networks of computers
included the military radar system Semi-Automatic
Ground Environment (SAGE).
In
1976
John
Murphy
of
Datapoint
Corporation created ARCNET, a token-passing network
first used to share storage devices.
In 1995 the transmission speed capacity for Ethernet
increased from 10 Mbit/s to 100 Mbit/s. By 1998, Ethernet
supported transmission speeds of a Gigabit. Subsequently,
higher speeds of up to 100 Gbit/s were added (as of 2016).
8.
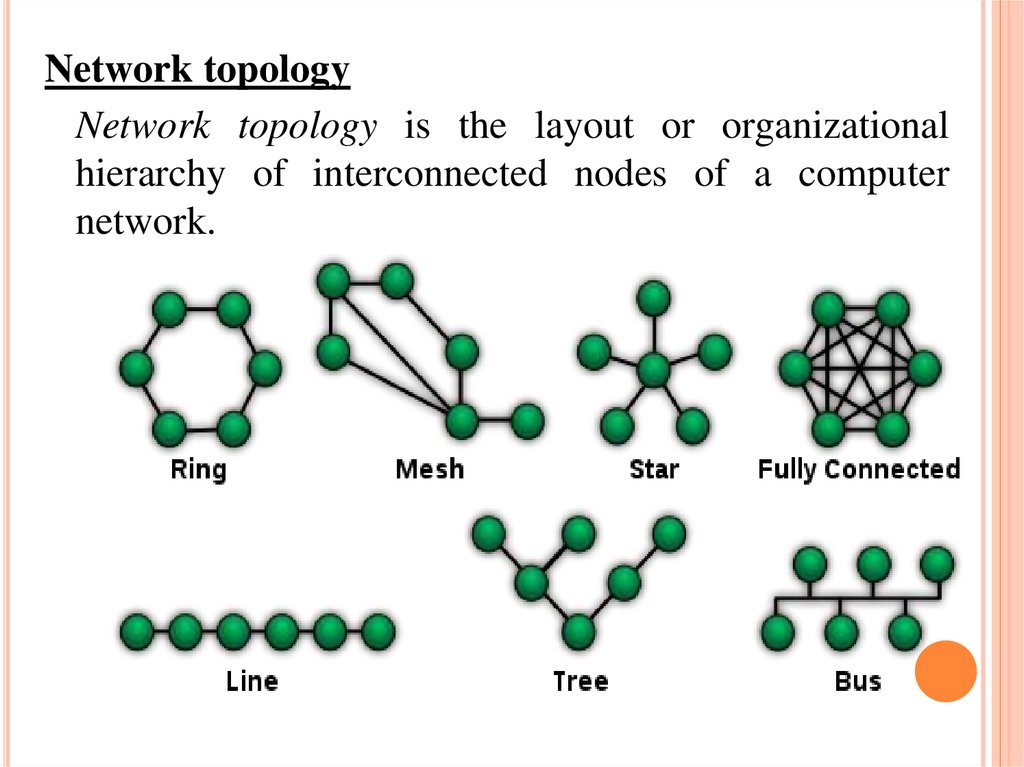
Network topologyNetwork topology is the layout or organizational
hierarchy of interconnected nodes of a computer
network.
9.
1.2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Common layouts are:
A bus network: all nodes are connected to a common medium
along this medium. This was the layout used in the
original Ethernet, called 10BASE5 and 10BASE2.
A star network: all nodes are connected to a special central node.
This is the typical layout found in a Wireless LAN, where each
wireless client connects to the central Wireless access point.
A ring network: each node is connected to its left and right
neighbour node, such that all nodes are connected and that each
node can reach each other node by traversing nodes left- or
rightwards. The Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) made use
of such a topology.
A mesh network: each node is connected to an arbitrary number of
neighbours in such a way that there is at least one traversal from
any node to any other.
A fully connected network: each node is connected to every other
node in the network.
A tree network: nodes are arranged hierarchically.
10.
IP addressAn Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a
numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer,
printer) participating in a computer network that uses
the Internet Protocol for communication.
The designers of the Internet Protocol defined an IP
address as a 32-bit number and this system, known as Internet
Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is still in use today.
IP addresses are usually written and displayed in humanreadable notations, such as 172.16.254.1 (IPv4), and
2001:db8:0:1234:0:567:8:1 (IPv6).
11.
A telecommunications network is a collection ofterminal nodes, links are connected so as to
enable telecommunication between the terminals.
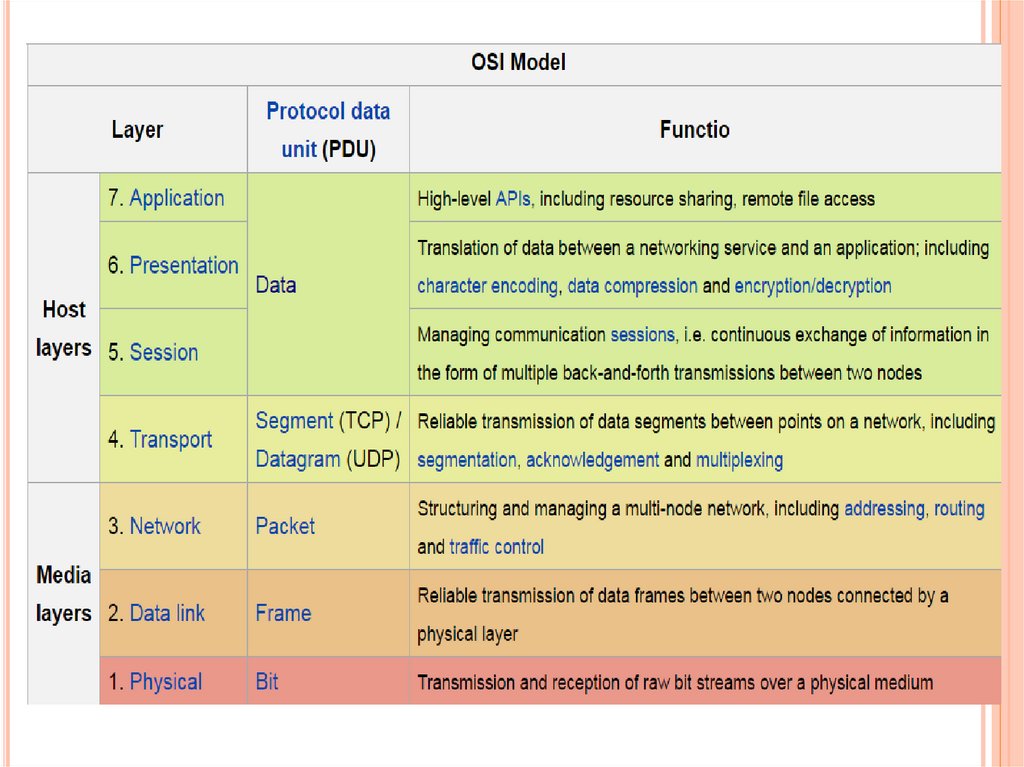
The Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model)
is a conceptual model that characterizes and standardizes the
communication functions of a telecommunication or computing
system without regard to their underlying internal structure and
technology.
The model is a product of the Open Systems
Interconnection project at the International Organization for
Standardization (ISO), maintained by the identification
ISO/IEC 7498-1.
12.
13.
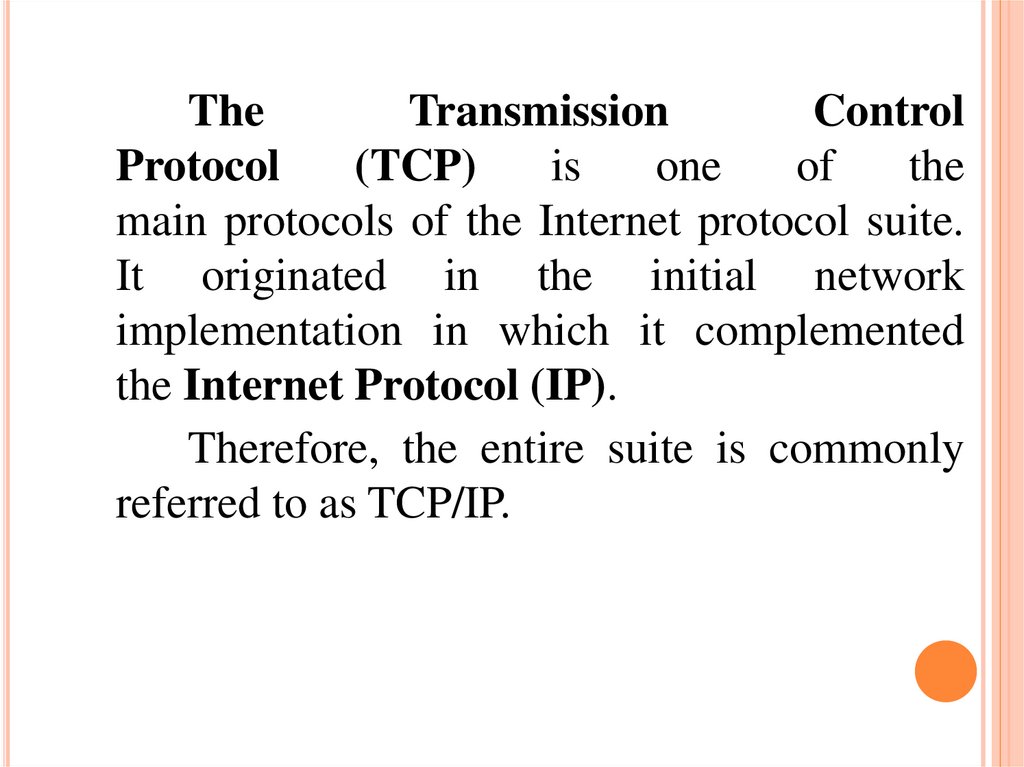
TheTransmission
Control
Protocol
(TCP)
is
one
of
the
main protocols of the Internet protocol suite.
It originated in the initial network
implementation in which it complemented
the Internet Protocol (IP).
Therefore, the entire suite is commonly
referred to as TCP/IP.
14.
There are many different network structures thatTCP/IP can be used across to efficiently route
messages, for example:
1. wide area networks (WAN)
2. metropolitan area networks (MAN)
3. local area networks (LAN)
4. Internet area networks (IAN)
5. campus area networks (CAN)
6. virtual private networks (VPN)
15.
LAN (local area network) is a group of computers andnetwork devices connected together, usually within
the same building.
MAN (metropolitan area network) is a larger network
that usually spans several buildings in the same city or
town.
WAN (wide area network), in comparison to a MAN,
is not restricted to a geographical location, although it
might be confined within the bounds of a state or
country.
16.
Wired technologiesThe orders of the following wired technologies are, roughly, from
slowest to fastest transmission speed.
1.
Coaxial cable is widely used for cable television systems,
office buildings, and other work-sites for local area networks.
2.
ITU-T G.hn technology uses existing home wiring (coaxial
cable, phone lines and power lines) to create a high-speed (up
to 1 Gigabit/s) local area network.
3.
Twisted pair wire is the most widely used medium for all
telecommunication.
4.
An optical fiber is a glass fiber. It carries pulses of light that
represent data.
17.
Wireless technologies1.
Terrestrial
microwave
–
Terrestrial
microwave
communication uses Earth-based transmitters and receivers
resembling satellite dishes.
2.
Communications satellites – Satellites communicate via
microwave radio waves.
3.
Cellular and PCS systems use several radio communications
technologies.
4.
Radio and spread spectrum technologies – Wireless local
area networks use a high-frequency radio technology similar
to digital cellular and a low-frequency radio technology.
5.
Free-space optical communication uses visible or invisible
light for communications. In most cases, line-of-sight
propagation is used, which limits the physical positioning of
communicating devices.
18.
Internet-based Self-services (ISS) are asubtype of services driven by self-service
technologies which provide technological
interfaces allowing customers to use
services independently of the involvement
of direct service employee. Self-ticket
purchasing and self-check-in for a flight
using the Internet are examples of
Internet-based self-services.
19. Questions
QUESTIONS1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
How long is an IPv6 address?
What flavor of Network Address Translation can be
used to have one IP address allow many users to
connect to the global Internet?
What are the two main types of access control lists
(ACLs)?
Which WLAN IEEE specification allows up to
54Mbps at 2.4GHz?
Which of the following is the valid host range for the
subnet on which the IP address 192.168.168.188
255.255.255.192 resides?
What protocol does PPP use to identify the Network
layer protocol?
Which protocol does DHCP use at the Transport
layer?
Where is a hub specified in the OSI model?














 internet
internet english
english








