Similar presentations:
The Foundations of Planning
1. The Foundations of Planning
2. Learning Objectives
• Define planning• Explain the potential benefits of planning
• Identify the potential drawbacks of planning
• Compare strategic and tactical plans
• Compare directional and specific plans
3. Learning Objectives
• Discuss Management by Objectives• Outline the strategic management process
• Describe the four grand strategies
• Explain SWOT analysis
• Learn how entrepreneurs and bureaucratic
managers approach strategy
4.
Set ControlStandards
Provide
Direction
Reasons
for Planning
Minimize Waste
or Redundancy
Reduce the
Impact of Change
5.
Rigid Assumptionsof Stability
Arguments
Against
Strategic
Planning
Environmental
Turbulence
Intuition
and Creativity
Focus on Today’s
Competition
Preoccupation with
Current Success
6. Does Planning Improve Performance?
• Financial results• Environmental concerns
• Quality and implementation
7.
How Do Strategic and TacticalPlans Differ?
Time Frame
Scope
Objectives
8.
The Time Frameof Planning
Short-Term
Plans
Long-Term
Plans
9.
Specific PlansLow
General
Directional Plans
High
Flexibility
Objectives
Clear
10.
Single-Useand Standing Plans
Unique
Situations
Ongoing
Operations
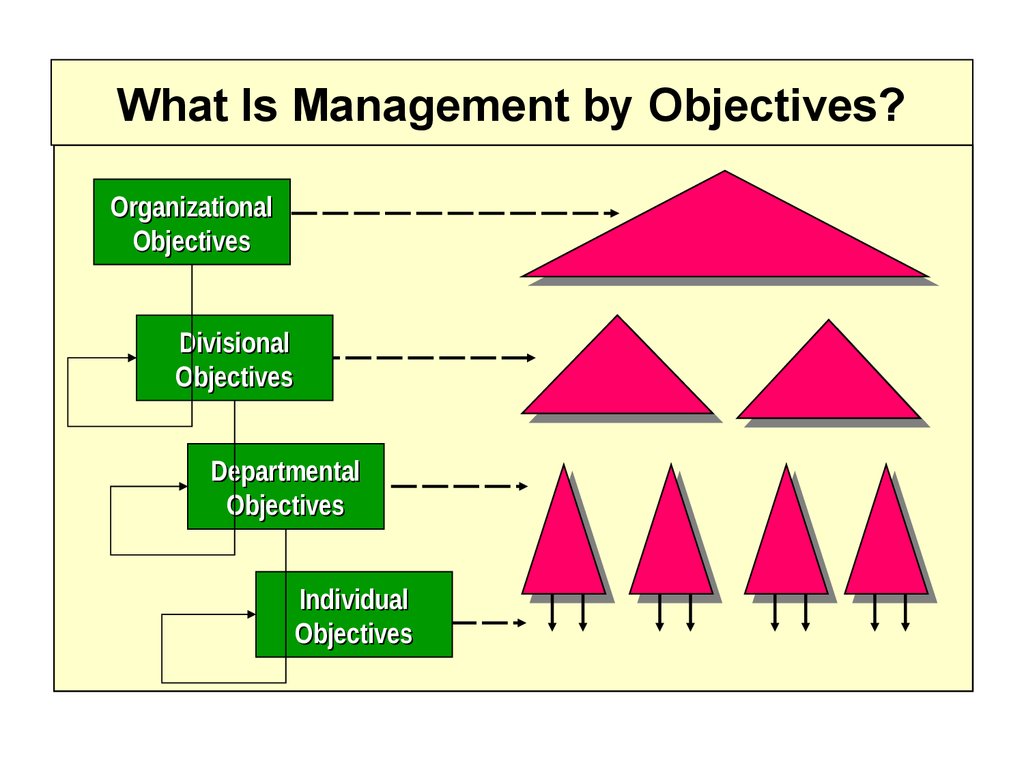
11.
What Is Management by Objectives?Organizational
Objectives
Divisional
Objectives
Departmental
Objectives
Individual
Objectives
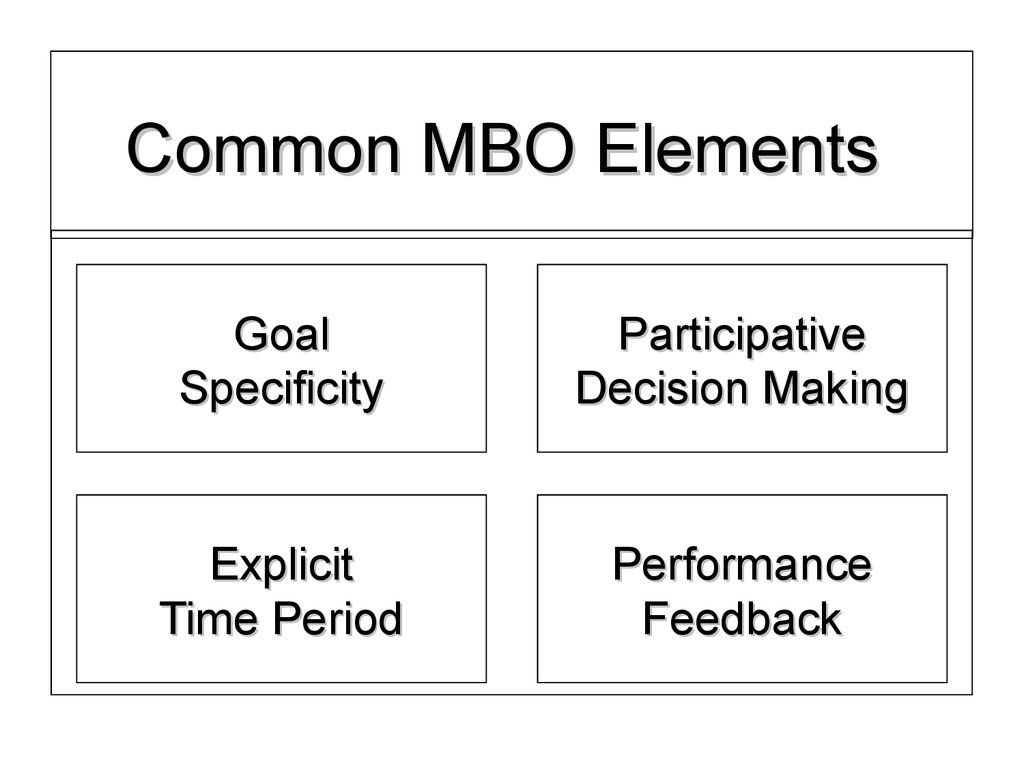
12.
Common MBO ElementsGoal
Specificity
Participative
Decision Making
Explicit
Time Period
Performance
Feedback
13.
GoalDifficulty
Goal
Specificity
Does MBO
Work?
Top
Management
Participation
14. Setting Employee Objectives
• Identify key job tasks• Set specific hard goals
• Let employees participate
• Prioritize goals
• Build in feedback
• Reward goal attainment
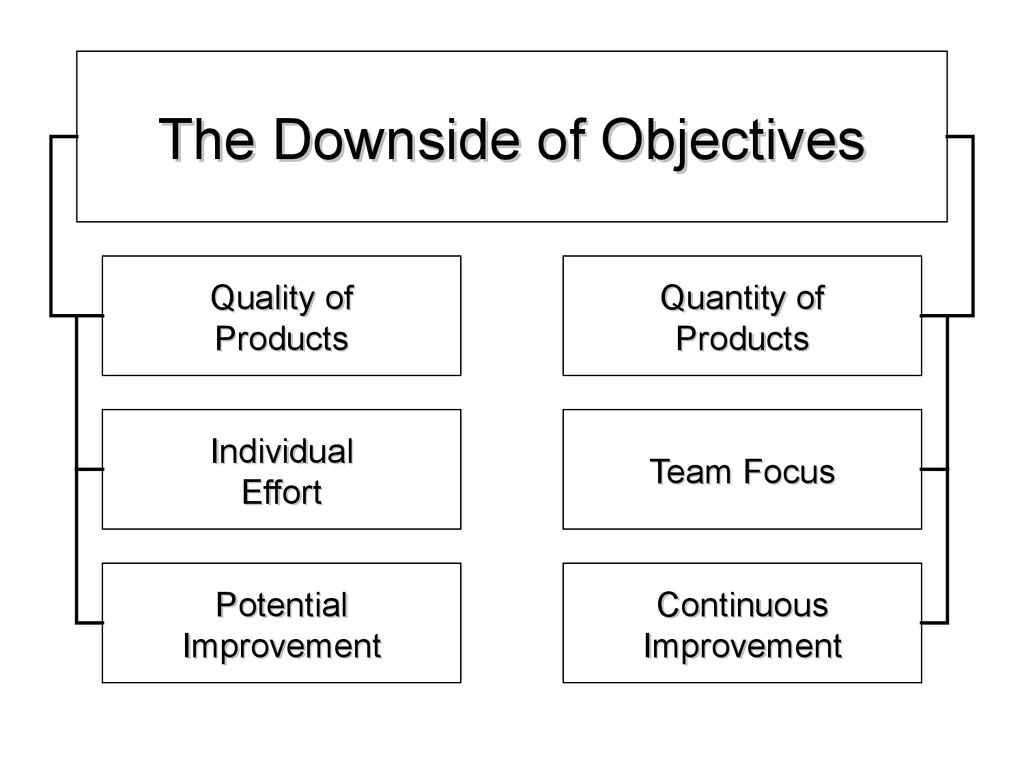
15. The Downside of Objectives
Quality ofProducts
Quantity of
Products
Individual
Effort
Team Focus
Potential
Improvement
Continuous
Improvement
16.
The Strategic Management ProcessSet Mission,
Objectives,
and Strategies
Analyze the
Environment
Identify
Opportunities
and Threats
Analyze
Resources
Identify
Strengths and
Weaknesses
Reassess
Mission and
Objectives
Formulate
Strategies
Implement
Strategies
Evaluate
Results
17.
Starting the StrategicManagement Process
18.
Analyzing theEnvironment
Environmental
Environmental
Scanning
Scanning
Competitive
Competitive
Intelligence
Intelligence
19.
StrengthsThreats
SWOT
Analysis
Opportunities
Weaknesses
20. Identifying Opportunities
Organization’sResources
Opportunities in
the Environment
Organization’s
Opportunities
21.
GrowthGrowth
Stability
Stability
The
The Grand
Grand Strategies
Strategies
Combination
Combination
Retrenchment
22.
Determining ACompetitive Strategy
Cost
Leadership
Differentiation
Focus
23.
What HappensAfter Strategies
Are Formulated?
Implementation
Implementation
Evaluation
Evaluation
24.
BenchmarkingQuality As
A Strategic
Weapon
ISO 9000
Six Sigma
25.
The EntrepreneurialPersonality
Common
Personality
Traits
Three
Critical
Factors
Other
Important
Factors
26. Comparing Entrepreneurs and Traditional Managers
CharacteristicsManagers
Entrepreneurs
• Primary Motivation
• Traditional Rewards
• Personal Rewards
• Time Orientation
• Short-Term Goals
• Long-Term Goals
• Activity
• Delegate/Supervise
• Direct Involvement
• Risk Propensity
• Low
• Moderate
• View of Failure/Errors
• Avoidance
• Acceptance





















 management
management








