Similar presentations:
Developing school children’s foreign language communicative competence
1.
Developing school children’s foreignlanguage communicative
competence
Anna Kashcheeva
2.
Introduction3.
IntroductionTrainings on Teaching Exam Classes
Trainings on Teaching Young Learners
TKT 3 Modules preparation course
TKT YL preparation course
Cambridge CELTA
akashcheeva@bkc.ru
anna_kashcheeva@inbox.ru
4.
Have you ever taken a teachertraining course in English?
When was it?
Where was it?
Was it useful?
5.
Aims of the courseto highlight and raise awareness of
• some basic principles of teaching English using
communicative approach
• young learners’ characteristics
• ways of motivating young learners
• how analyse and evaluate materials
• some practical ideas for teaching young learners
6.
Aims of the first sessionto highlight and raise awareness of
• sources of motivation and learning environment
• age groups and young learners’ characteristics
• the art of lessons planning for different age groups
• developing learner autonomy
7.
https://www.google.ru8.
9.
Harmer, J. (2001). The Practice of English Language Teaching. Essex: Pearson Education Limited10.
Harmer, J. (2001). The Practice of English Language Teaching. Essex: Pearson Education Limited11.
https://www.google.ru12.
_______________motivation is when you engage in
an activity in order to reach a
certain goal
13.
Extrinsicmotivation is when you engage in
an activity in order to reach a
certain goal
14.
Intrinsicmotivation comes from within the
individual.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
How can we influence learners’ motivation?https://www.google.ru
20.
How can we influencelearners’ motivation?
Ur, P., A Course in English Language Teaching, CUP, 2012
21.
MotivationWhat do we have to do to motivate young learners?
22.
MotivationWhat do we have to do to motivate young learners?
•Grab their attention
•Get them interested
•Make them feel challenged
•Keep them engaged
•Praise them
•Use a variety of activities
23.
How to grab kids’ attention?24.
How to grab kids’ attention?a visual aid
a piece of music, a song or a
chant
a question
a story
a word or phrase
25.
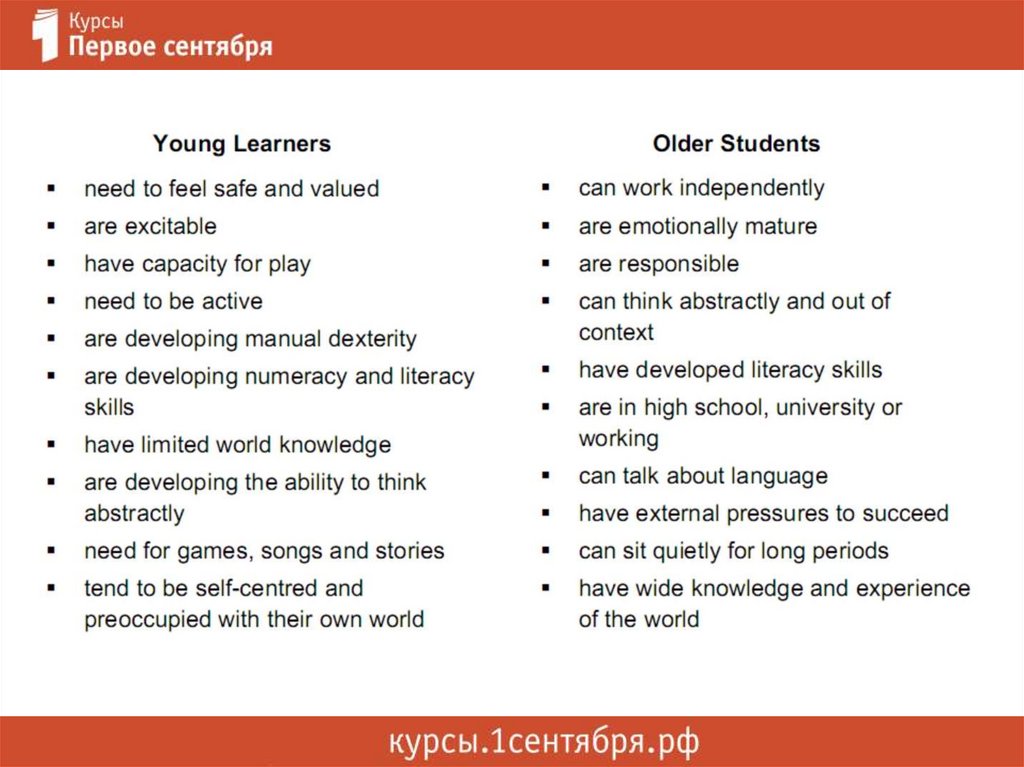
AGE GROUPS26.
Characteristics of Young Learners27.
Characteristics of Young Learnershttps://www.google.ru
28.
Characteristics of Young Learners•still developing cognitively, linguistically, socially,
emotionally and physically
•often have no obvious reason for learning English
•may not always have well-developed literacy
skills to support their learning of English
•may often learn slowly and forget quickly
TKT YL, Handbook for teachers
29.
Does it refer to kids or older students?https://www.google.ru
30.
31.
How do children learn their first language?32.
How do children learn their first language?a) by imitating adults
b) by experimenting and trying out hypotheses
about how the language works
c) both of the above
33.
How do children learn their first language?a) by imitating adults
b) by experimenting and trying out hypotheses
about how the language works
c) both of the above
34.
How important is motivation in successfullanguage learning?
a) not really important
b) the most important factor
c) an important factor but not the only one
35.
How important is motivation in successfullanguage learning?
a) not really important
b) the most important factor
c) an important factor but not the only one
36.
ASSUMPTIONS ABOUT AGE AND LANGUAGELEARNING
1. Younger children learn languages better than older
ones; children learn better than adults.
2. Foreign language learning in school should be
started at as early an age as possible.
3. Children and adults learn languages basically the
same way.
4. Adults have a longer concentration span than
children.
5. It is easier to interest and motivate children than
adults.
37.
Behaviourist view and audio-lingual approach38.
Behaviourist view and audio-lingual approachimitation, practice and habit formation;
repetition in the form of drills,
accuracy and the avoidance of errors;
positive reinforcement and praise
Skinner B.F., Verbal behaviour, 1957
39.
What can we do at the very beginning of the lessonwhen we work with primary school children?
40.
What can we do at the very beginning of the lesson?https://www.google.ru
41.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CSqVcTcQ_pc42.
How are you?I’m happy
43.
How are you?I’m sad
44.
How are you?I’m tired
45.
How are you?https://www.google.ru
46.
- How are you?- I’m ...
47.
AnalysisWhy do we teach emotions?
What other routines might we use in class?
48.
AnalysisWhy do we teach emotions?
What other routines might we use in class?
49.
Reward Chart50.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
51.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
52.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
53.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
https://www.google.ru
54.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
https://www.google.ru
55.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
https://www.google.ru
56.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
https://www.google.ru
57.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
https://www.google.ru
58.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
Music and movement
https://www.google.ru
59.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
Music and movement
https://www.google.ru
60.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
Music and movement
Focused task
https://www.google.ru
61.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
Music and movement
Focused task
https://www.google.ru
62.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
Music and movement
Focused task
Story
https://www.google.ru
63.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
Music and movement
Focused task
Story
https://www.google.ru
64.
Lesson structurefor primary school children
Hello circle
Revision
New Language
Music and movement
Focused task
Story
Homework, goodbye
https://www.google.ru
65.
Characteristics of juniors and teens66.
Characteristics of juniors and teensAccording to Brewster (2004: 27) juniors and teens:
• are still in the process of learning their L1;
• learn more slowly and forget things quickly;
• can easily be distracted;
• are self-oriented;
• are very energetic and enthusiastic;
• can be disruptive or over-active;
• are very emotional and can get bored easily;
• can be focused for a significant time if interested.
Brewster, J., Gail, E., Girard, D. (2004). The Primary English Teacher’s Guide. Essex: Pearson Education Limited
67.
Characteristics of juniors and teensAlthough Penny Ur suggests that teenage students are in fact
overall the best language learners (1996:286), there is a belief
that teenagers are often less motivated than both younger
children and adults (Puchta 1999: 4).
Puchta, H., Schratz, M. (1999). Teaching Teenagers. Model activity sequences for humanistic language learning. Essex: Pearson Education Limited
Ur, P. (1996). A Course in Language Teaching. Cambridge University Press
68.
Characteristics of juniors and teensAccording to Harmer (2001:39), young learners need
individual attention and approval from the teacher, whereas
peer approval might be essential for adolescents. Also,
children usually have a low awareness of the social skills
basic to cooperative interaction. What is more, they might
present outright discipline problems being apathetic and
unruly.
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, Pearson, 2001
69.
Teacher’s role70.
Teacher’s role• find ways how to motivate students
• cater for different learning styles
• provide varied interesting activities
• create and exploit opportunities to personalise and go at
learners' pace
• have clear rules
• encouraging learners to perform better in class
• promote learner autonomy
71.
Teaching TipsSet regular achievable goals
Set relevant homework
Record keeping
Review
Peer teaching
Self-correction
Progress reports
72.
Practical IdeasEnglish Language Teaching Global Blog at
https://oupeltglobalblog.com/category/young-learners/
73.
Practical IdeasTeaching tools, articles and free teaching
resources at
https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/teaching-kids
74.
Practical IdeasFlashcards and
visuals at
https://ru.pinterest.com
75.
Practical IdeasFree teaching resources at
https://supersimpleonline.com/free-teaching-resources/
76.
Summary• sources of motivation and learning
environment
• age groups and young learners’ characteristics
• the art of lessons planning for different age
groups
• developing learner autonomy
77.
TaskCreate a procedure of a lesson
for secondary school children.
https://www.google.ru












































































 english
english








