Similar presentations:
Human rights protection during armed conflict
1. Human Rights Protection During Armed Conflict
HUMAN RIGHTSPROTECTION DURING
ARMED CONFLICT
Elina Abdullaeva
Higher School of Economics
Faculty of Law
Moscow, 2019
2. Outline
■ Legal framework in armed conflicts■ International Humanitarian Law & International Human Rights Law:
what is the difference?
■ Mutual reinforcement of International Humanitarian Law & International
Human Rights Law
■ Cases concerning the Turkey-Cyprus issue
■ Cases concerning the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh
■ Case concerning the war in Bosnia and Herzegovina
■ Overview of the cases in which Article 2 or Article 3 applied
■ Conclusion
3. War has changed.
War has changed.■
development of nuclear
and biological weapons
■
new techniques of warfare
■
growth of cities population
■
increased lethality
4. International Humanitarian Law & International Human Rights Law: what is the difference?
International Humanitarian Law &International Human Rights Law:
what is the difference?
International Humanitarian Law
(IHL)
■ applicable only in context of armed
conflict
■ based on distinctions between
civilians and combatants
■ less important territorial link of
person
■ lex specialis
International Human Rights Law
(IHRL)
■ always applicable
■ provides protection for every
human being regardless of his or
her status
■ essentially territorial
5. Mutual reinforcement of International Humanitarian Law & International Human Rights Law
Mutual reinforcement of InternationalHumanitarian Law & International Human
Rights Law
"Lex specialis derogat generali", but
■ the protection provided by Human Rights law continued in armed conflict
■ nothing in Human Rights treaties shows that they would not be applicable in context
of armed conflict
"Human Rights Law and Humanitarian Law are complementary and mutually
reinforcing"
© Human Rights Council
6. Frequently applied articles of European Convention on Human Rights
Frequently applied articles of EuropeanConvention on Human Rights
■ Article 2 (Right to life)
■ Article 3 (Prohibition of torture)
■ Article 5 (Right to liberty and security)
■ Article 6 (Right to a fair trial)
■ Article 8 (Right to respect for private and family life)
■ Article 13 (Right to an effective remedy)
7. Cases concerning the Turkey-Cyprus issue
Cases concerning theTurkey-Cyprus issue
Varnava and Others v. Turkey
18 September 2009 (Grand Chamber)
A continuing violation of:
-Article 2 (right to life) on account of the failure of the
authorities to conduct an effective investigation into
the fate of the nine men who disappeared;
-Article 3 (prohibition of inhuman treatment) in
respect of the applicants;
-Article 5 (right to liberty and security) by virtue of the
failure of the authorities to conduct an effective
investigation into the fate of two of the missing men.
8. Cases concerning the Turkey-Cyprus issue
Cases concerningthe Turkey-Cyprus
issue
Andreou v. Turkey
27 October 2009
A violation of Article 2 (right to
life) of the Convention. The use
of potentially lethal force
against the applicant had not
been “absolutely necessary”
and had not been justified by
any of the exceptions permitted
under Article 2 of the
Convention.
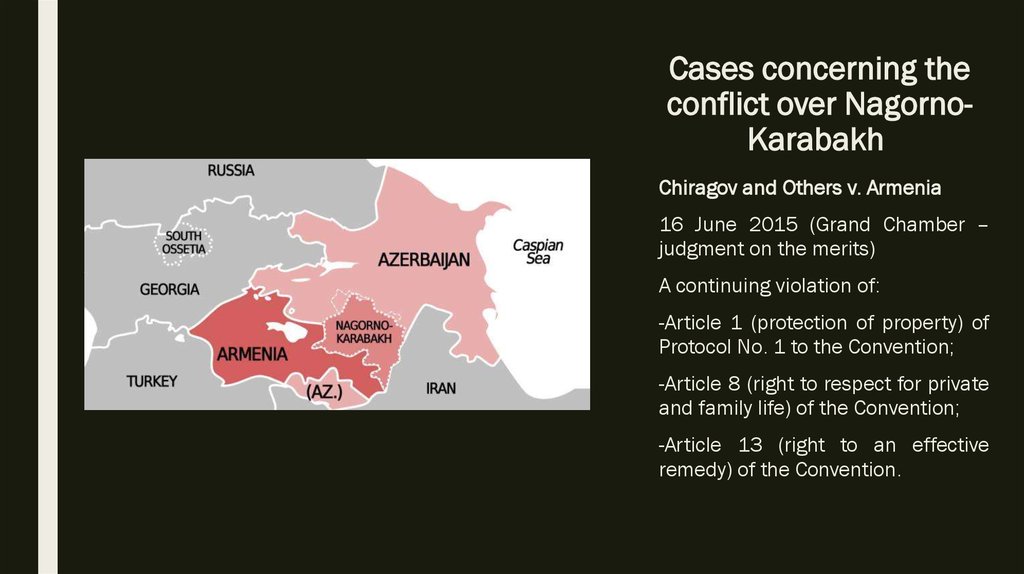
9. Cases concerning the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh
Cases concerning theconflict over NagornoKarabakh
Chiragov and Others v. Armenia
16 June 2015 (Grand Chamber –
judgment on the merits)
A continuing violation of:
-Article 1 (protection of property) of
Protocol No. 1 to the Convention;
-Article 8 (right to respect for private
and family life) of the Convention;
-Article 13 (right to an effective
remedy) of the Convention.
10. Cases concerning the conflict over Nagorno-Karabakh
Cases concerning the conflict overNagorno-Karabakh
Sargsyan v. Azerbaidjan
16 June 2015 (Grand Chamber – judgment on the merits)
A continuing violation of:
-Article 1 (protection of property) of Protocol No. 1 to the Convention;
-Article 8 (right to respect for private and family life);
-Article 13 (right to an effective remedy) of the Convention. The Court considered in particular
that while it was justified by safety considerations to refuse civilians access to the village, the
State had a duty to take alternative measures in order to secure the applicant’s rights as long
as access to the property was not possible.
11. Case concerning the war in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Case concerningthe war in Bosnia
and Herzegovina
Maktouf and Damjanović v.
Bosnia and Herzegovina 18 July
2013 (Grand Chamber)
-a violation of Article 7 (no
punishment without law) of the
Convention
The Court found that the
applicants could have received
lower sentences had the 1976
Code been applied.
12. Overview
Lack of effective investigation into thedeaths of civilians (Article 2):
Inhuman and degrading treatment
(Article 3)
■ Inderbiyeva v. Russia
■
Er and Others v. Turkey
■ Al-Skeini and Others v. the
United Kingdom
■
Pitsayeva and Others v. Russia
■ Kadirova and Others v. Russia
■ Jaloud v. the Netherlands
■ Meryem Çelik and Others v. Turkey
■ Al-Saadoon & Mufdhi v. the United
Kingdom
■ Hassan v. the United Kingdom
■ Benzer and Others v. Turkey
13. Conclusion
■ IHL & IHRL are both applicable in situation of armedconflict; these branches of law are mutually
reinforcing
■ While IHL is applicable in situation of armed conflict,
whether it is international or non-international, IHRL
is applicable regardless for such context
■ Although IHL is applied as lex specialis, the protection
provided by IHRL continued in armed conflict
■ Articles 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 of ECHR are frequently applied
in situation of armed conflict
■ IHRL provides more coherent as well as a more
realistic regulation of conduct in armed conflicts in
general and in non-international armed conflicts in
particular
Conclusion
14. References:
■Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms, 1950
■
ICRC, “How is the term “armed conflict” defined in international humanitarian law?”
■
Jean Pictet et al., eds., Geneva Convention I for the Amelioration of the Condition of the Wounded and Sick in Armed
Forces in the Field: Commentary (Geneva, ICRC, 1952), p. 32.
■
Prosecutor v. Duško Tadic ́, para. 70.
■
Prosecutor v. Ramush Haradinaj et. al., case No. IT-04-84-T, Judgement of 3 April 2008, paras. 49 and 60.
■
Varnava and Others v. Turkey
■
Andreou v. Turkey
■
Chiragov and Others v. Armenia
■
Sargsyan v. Azerbaidjan
■
Maktouf and Damjanović v. Bosnia and Herzegovina
■
Al-Skeini and Others v. the United Kingdom
15. Thank you for your attention!
Elina Abdullaevaeeabdullaeva@edu.hse.ru














 life safety
life safety








