Similar presentations:
Developing Global Managers
1.
Developing Global Managers1
2. Cultural Influences on Organizational Behavior
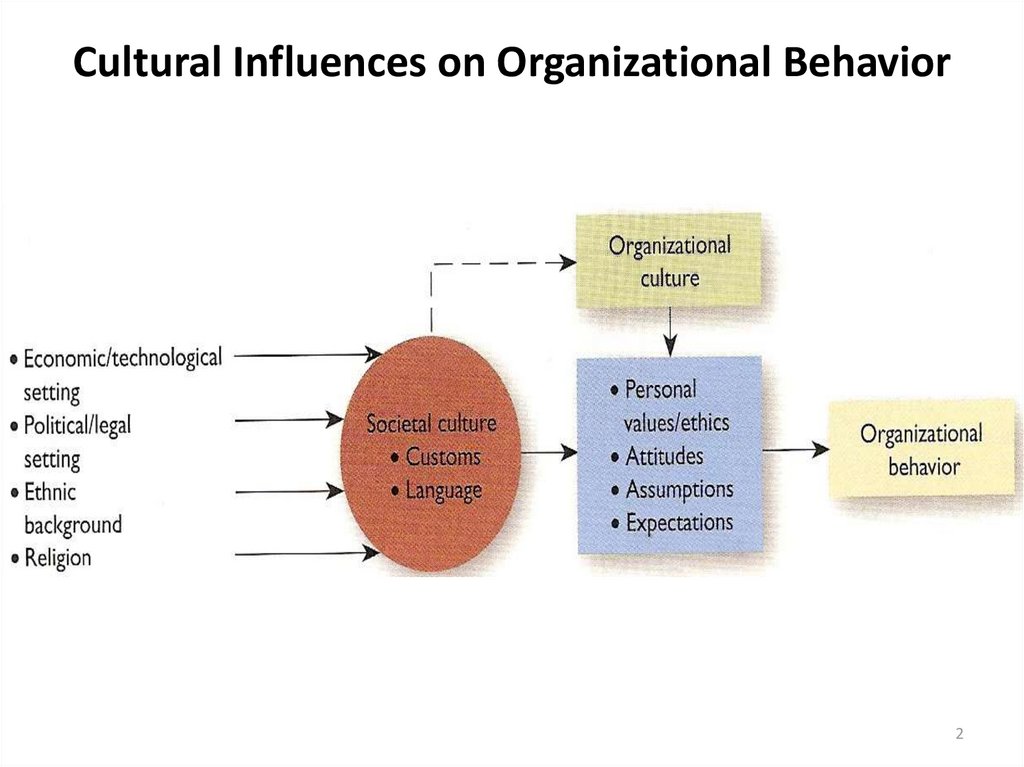
23. A Model of Societal and Organizational Cultures
• Societal culture– Beliefs and values about what is desirable and
undesirable in a community of people, and a set
of formal or informal practices to support the
values
3-3
4. Ethnocentrism
• Ethnocentrism– belief that one’s native country, culture, language,
and behavior are superior to all others.
3-4
5.
The Hofstede Study:116,000 IBM employees from 53 countries worldwide
Power distance. How much inequality does someone
expect on social situations?
Individualism – collectivism. How loosely or closely is
the person socially bonded?
Masculinity – femininity. Does the person embrace
stereotypically competitive, performance oriented
masculine traits or nurturing, relationship-oriented
feminine traits?
Uncertainty avoidance. How strongly does the person
5
desire highly structured situations?
6. Becoming Cross-Culturally Competent
Cultural Paradoxes Require Cultural Intelligence,the ability to interpret ambiguous crosscultural situations accurately.
6
7.
Emotional intelligence: ability to manageoneself and interact with others in mature and
constructive ways.
Test: Fill in the test on your emotional
behavior in the University setting.
Tick (v) the answer you think applies.
Add points which, to your mind, are missing.
7
8. Project GLOBE
• GLOBE (Global Leadership and OrganizationalBehavior Effectiveness)
– attempt to develop an empirically based theory to
describe, understand, and predict the impact of
specific cultural variables on leadership and
organizational processes and the effectiveness of
these processes
3-8
9. Basic Cultural Dimensions from the GLOBE project
1. Power distance - How equally should power be distributed?2. Uncertainty avoidance - How much should social norms and
rules reduce uncertainty and unpredictability?
3. Institutional collectivism - How much should loyalty to the
social unit override individual interests?
4. In-group collectivism - How strong should one's loyalty be to
family or organization?
5. Gender egalitarianism - How much should gender
discrimination and role inequalities be minimized?
6. Assertiveness - How confrontational and dominant should one
be in social relationships?
7. Future orientation - How much should one delay gratification
by planning and saving for the future?
8. Performance orientation - How much should individuals be
rewarded for improvement and excellence?
9. Humane orientation - How much should individuals be
rewarded for being kind, fair, friendly, and generous?
9
10. Bringing the GLOBE Cultural Dimensions to Life
• The automatic listing and announcement of prayertimes anywhere in the world
• A compass showing the direction of prayer toward
Mecca
• A complete transcription of Koran in Arabic with
accompanying English translation
10
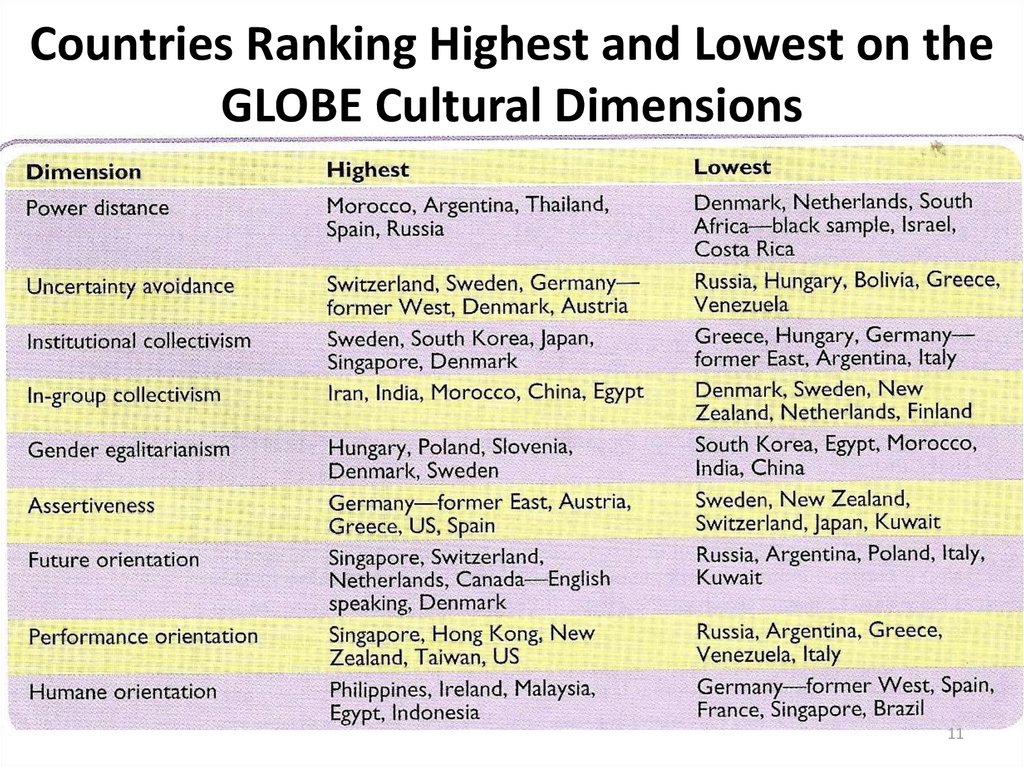
11. Countries Ranking Highest and Lowest on the GLOBE Cultural Dimensions
1112. Individualism vs Collectivism
• Individualistic culturePrimary emphasis on personal freedom and
choice.
• Collectivist culture
Personal goals less important than community
goals and interests.
12
13. High-context and Low-context cultures -nonverbal situational cues -precise and brief written and spoken words
Monochronic vs Polychronic culturestime is precise and firmly measured
time as multidimensional, fluid, and flexible
people prefer to do one thing at a time
people like to tackle multiple tasks at the
same time.
13
14. Cultural Perceptions of Time
• Monochronic time– preference for doing one thing at a time because
time is limited, precisely segmented, and schedule
driven
• Polychronic time
– preference for doing more than one thing at a
time because time is flexible and
multidimensional
3-14
15.
What is your attitude toward time?15















 management
management








