Similar presentations:
Literature. Review
1.
LiteratureReview
CSR: investigating theory and research in the Marketing context
European Journal of Marketing Vol.42 No.9/10,2008
2018315039 박혜정
2018315002 아이다나
2018310652 육문용
2018310902 김정천
2.
Table of Content :We’re going to present about
1. Introduction .................................................
3
2. Research Methodology.................................
6
3. Operational Definitions.................................
18
4. Analysis & Findings .......................................
21
5. Discussion ....................................................... 10
Group Project
2
3.
About the Review DissertationIntroduction
Purpose
-Develop an integrating overview of the theory of CSR applied in MKT
-Asks whether, to what extent and how the discipline of MKT has addressed CSR
Design
-Clarify core concepts and Operational Definitions
-54 Leading articles (1995~2005) analyzed
Findings
In terms of
-Publication Characteristic
-Research Design
-Variables, Sampling, level of Analysis
-Issues raised & Key findings
-Broadened perspective in Empirical R (expand focus beyond consumers)
-Contribute to a Multidimensional view of the future customer
Group Project
3
4.
CSR exactly addresses the potentially NEGATIVE aspects of their behavior,which is difficult to control
>
Why is it important?
Necessity of the Review
This is an important task because the way Research Literature
treats CSR impacts what students and other constituencies learn
Important to managers & managers to be, it might
influence their Thinking and Behaviors
Group Project
4
5.
About the Review DissertationBackground
>
MKT & CSR
Situation goin’ on
Idea: Firms’ activities have negative results
Fact: Firms take environmental considerations
Importance of Ethical Behavior
Related Regulations & Laws
MKT
CSR & MKT
Tricky Point
• The idea is broader and encompassing
complex & ambiguous
• Reflected by multiple and different views
and perspectives
CSR
MKT-Lens of CSR
Group Project
5
6.
Development of ConceptMarketing
Product
The Wealth of Nations
Adam Smith
AMA in MKT Terms
Dr. Philip Kotler
AMA Board of Directors
Group Project
exchange
end-result
FOCUS
Customer
The ‘MKT concept' proposes that in order to satisfy the
organizational objectives, an organization should anticipate the
needs and wants of potential consumers and satisfy them more
effectively than its competitors
The process of planning and executing the conception, pricing,
promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create
exchanges that satisfy individual and organisational goals
MKT is a social and managerial process by which individuals and
groups obtain what they want and need through creating,
offering and exchanging products of value with others
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and
processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and
exchanging offerings that have value for customers,
clients, partners, and SOCIETY at large
6
7.
Stakeholder ApproachPhilip Kotler
“The organization's marketing task is to
determine the needs, wants and interests of
target markets and to achieve the desired results
more effectively and efficiently than
competitors, in a way that
preserves or enhances the consumer's or
society's well-being."
Group Project
7
8.
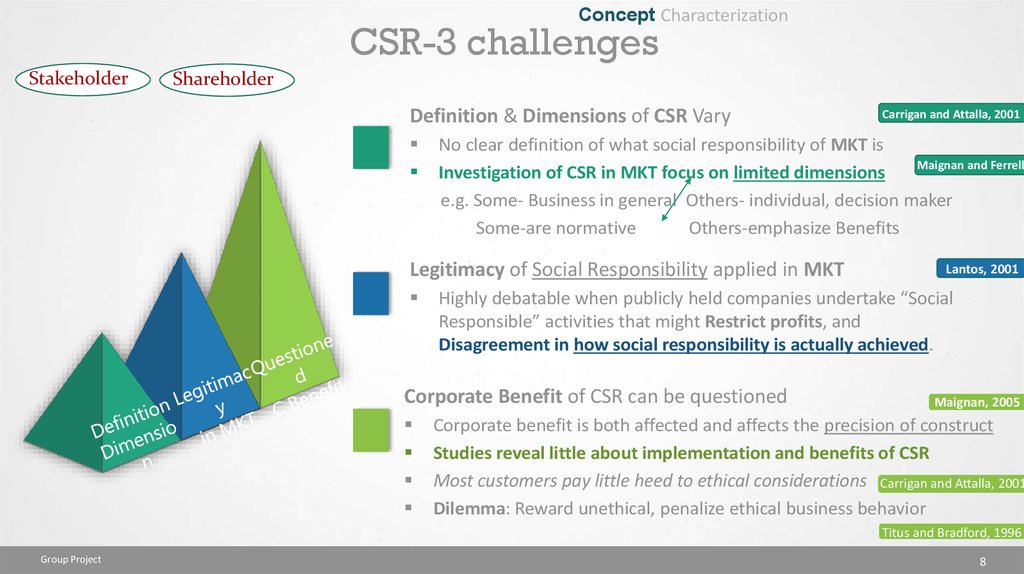
Concept CharacterizationCSR-3 challenges
Stakeholder
Shareholder
Definition & Dimensions of CSR Vary
No clear definition of what social responsibility of MKT is
Maignan and Ferrell
Investigation of CSR in MKT focus on limited dimensions
e.g. Some- Business in general Others- individual, decision maker
Some-are normative
Others-emphasize Benefits
Legitimacy of Social Responsibility applied in MKT
Lantos, 2001
Highly debatable when publicly held companies undertake “Social
Responsible” activities that might Restrict profits, and
Disagreement in how social responsibility is actually achieved.
Corporate Benefit of CSR can be questioned
Carrigan and Attalla, 2001
Maignan, 2005
Corporate benefit is both affected and affects the precision of construct
Studies reveal little about implementation and benefits of CSR
Most customers pay little heed to ethical considerations Carrigan and Attalla, 2001
Dilemma: Reward unethical, penalize ethical business behavior
Titus and Bradford, 1996
Group Project
8
9.
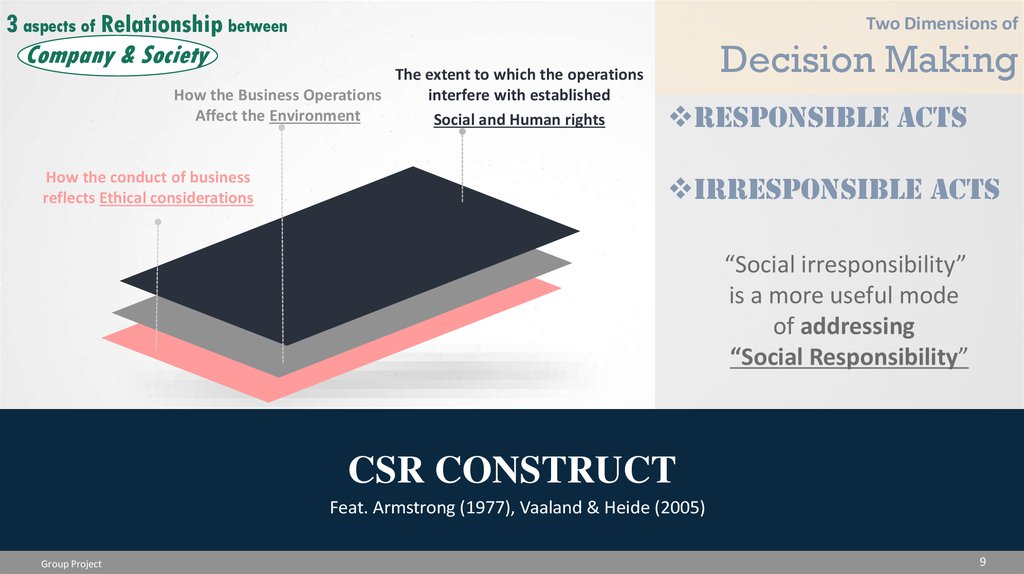
3 aspects of Relationship betweenTwo Dimensions of
Decision Making
Company & Society
The extent to which the operations
interfere with established
How the Business Operations
Affect the Environment
Social and Human rights
How the conduct of business
reflects Ethical considerations
Responsible Acts
Irresponsible Acts
“Social irresponsibility”
is a more useful mode
of addressing
“Social Responsibility”
CSR CONSTRUCT
Feat. Armstrong (1977), Vaaland & Heide (2005)
Group Project
9
10.
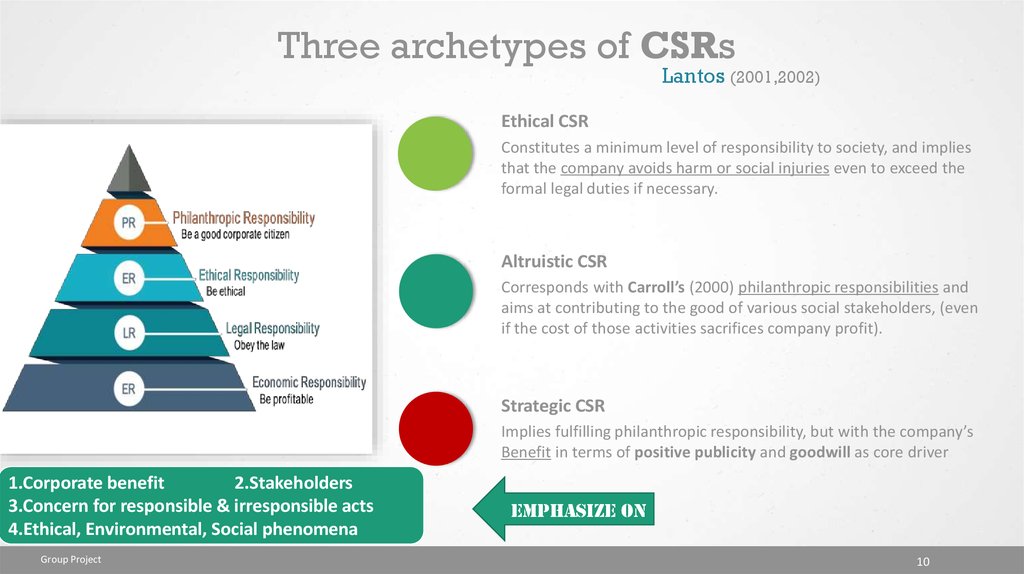
Three archetypes of CSRsLantos (2001,2002)
Ethical CSR
Constitutes a minimum level of responsibility to society, and implies
that the company avoids harm or social injuries even to exceed the
formal legal duties if necessary.
Altruis
tic
Ethic
al
Strat
egic
Altruistic CSR
Corresponds with Carroll’s (2000) philanthropic responsibilities and
aims at contributing to the good of various social stakeholders, (even
if the cost of those activities sacrifices company profit).
Strategic CSR
Implies fulfilling philanthropic responsibility, but with the company’s
Benefit in terms of positive publicity and goodwill as core driver
1.Corporate benefit
2.Stakeholders
3.Concern for responsible & irresponsible acts
4.Ethical, Environmental, Social phenomena
Group Project
Emphasize ON
10
11.
Operationally Defining CSRStakeholder Approach
AMA d e f i n i t i o n o f CSR
“Corporate social responsibility is
management of Stakeholder
Concern for responsible and
irresponsible acts related to environmental,
ethical and social phenomena in a way
that creates corporate benefit”
Group Project
11
12.
Research MethodologySelection of journals
Identification of articles
Analytical procedure
Group Project
12
13.
Selection of journalsGeneral Journal
Why MKT journals?
Because they focus solely on marketing
and because they capture most
adequately the developments in the field
PICK
Why Only US & European journals?
Until now – marketing as dealt with
in the literature has been dominated by
researchers from this part of the world.
Specialized Journal
Group Project
Most Advanced
13
14.
KeywordsOverview of the
54 theoretical and empirical
studies of
CSR in the MKT context
in the period 1995~2005
15.
Review ofKeywords
Literature
Group Project
15
16.
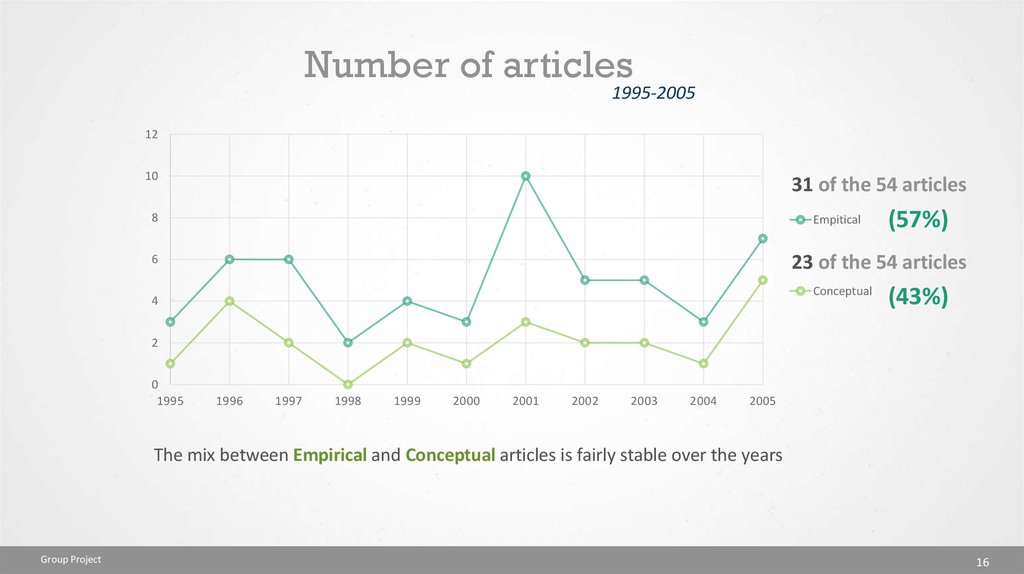
Number of articles1995-2005
12
10
31 of the 54 articles
8
Empitical
(57%)
23 of the 54 articles
6
Conceptual
4
(43%)
2
0
1995
1996
1997
1998
1999
2000
2001
2002
2003
2004
2005
The mix between Empirical and Conceptual articles is fairly stable over the years
Group Project
16
17.
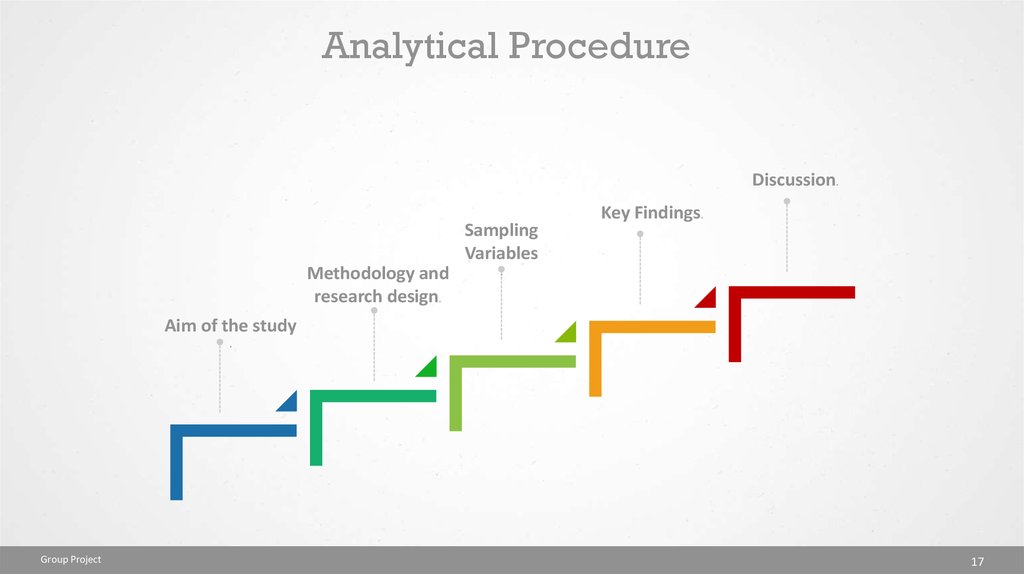
Analytical ProcedureDiscussion.
Sampling
Variables
Methodology and
research design.
Key Findings.
.
Aim of the study
.
Group Project
17
18.
Operational definitions• Types:
Theoretical/conceptual(23)
Empirical(31)
• Theme:
Ethics
Environment
Society
Major
Constructs/variables
Theoretical/conceptual
studies
• Level of analysis:
Intra-organizational
Inter-relational
Network
Group Project
18
19.
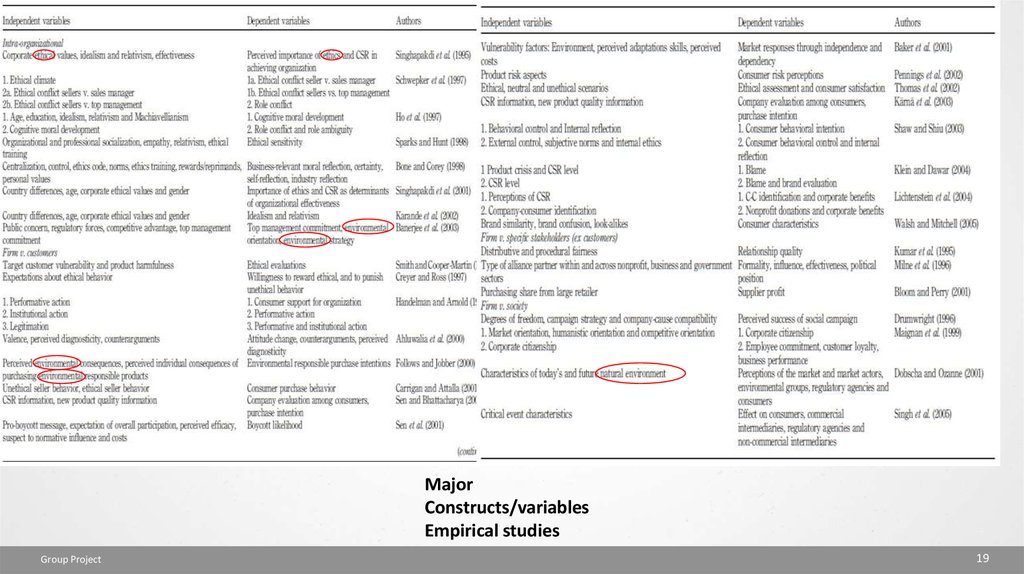
MajorConstructs/variables
Empirical studies
Group Project
19
20.
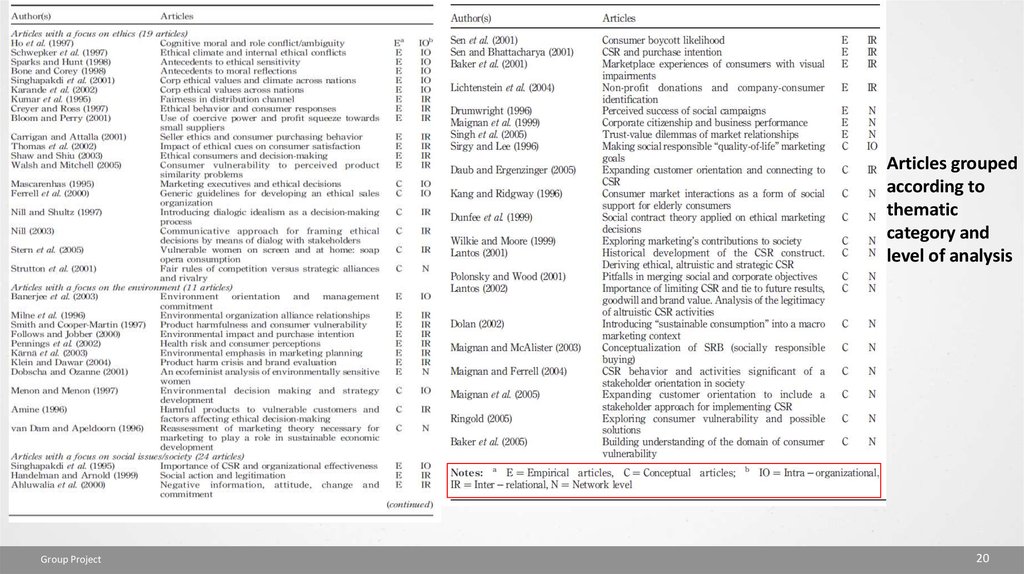
Articles groupedaccording to
thematic
category and
level of analysis
Group Project
20
21.
Analysis & Findings ——Research designs• Among the empirical studies, various types of survey design dominate with three-quarters of the studies. The
remaining are evenly split between pure experimental designs and a combination of
survey/experimental/qualitative and pure qualitative studies.
• The conceptual studies are primarily theoretical and explorative by employing a comprehensive literature review
(e.g. Wilkie and Moore,1999; Lantos, 2001, 2002). Only two out of the total of 23 conceptual studies apply case
illustrations.
• In other words, nine out of ten studies of CSR apply consumers/marketers as data sources. This is somewhat surprising
taking into consideration that CSR by nature is about the interface between business and society and the public
perceptions of the firm.
• The studies employ a large variety of dependent and independent variables. This variety represents strength by providing
different angles of attack to the phenomenon of CSR. But the variety also reduces consistency and limits validation of
prior studies.
In the following we present the major knowledge claims made in the selected article base, organized into the three thematic
categories and three levels of analysis.
Group Project
21
22.
Ethics• Intra-organizational
• Inter-relational
• Network
Group Project
22
23.
Environment• Intra-organizational
• Inter-relational
• Network
Group Project
23
24.
Society• Intra-organizational
• Inter-relational
• Network
Group Project
24
















 literature
literature








