Similar presentations:
BC621_EN_46A
1.
BC621 - SAP IDoc Interface (Development)BC621
SAP IDoc Interface
(Development)
SAP AG 1999
2.
CopyrightCopyright 2000 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
Neither this training manual nor any part thereof may
be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means,
or translated into another language, without the prior
consent of SAP AG. The information contained in this
document is subject to change and supplement without prior
notice.
All rights reserved.
SAP AG 1999
3.
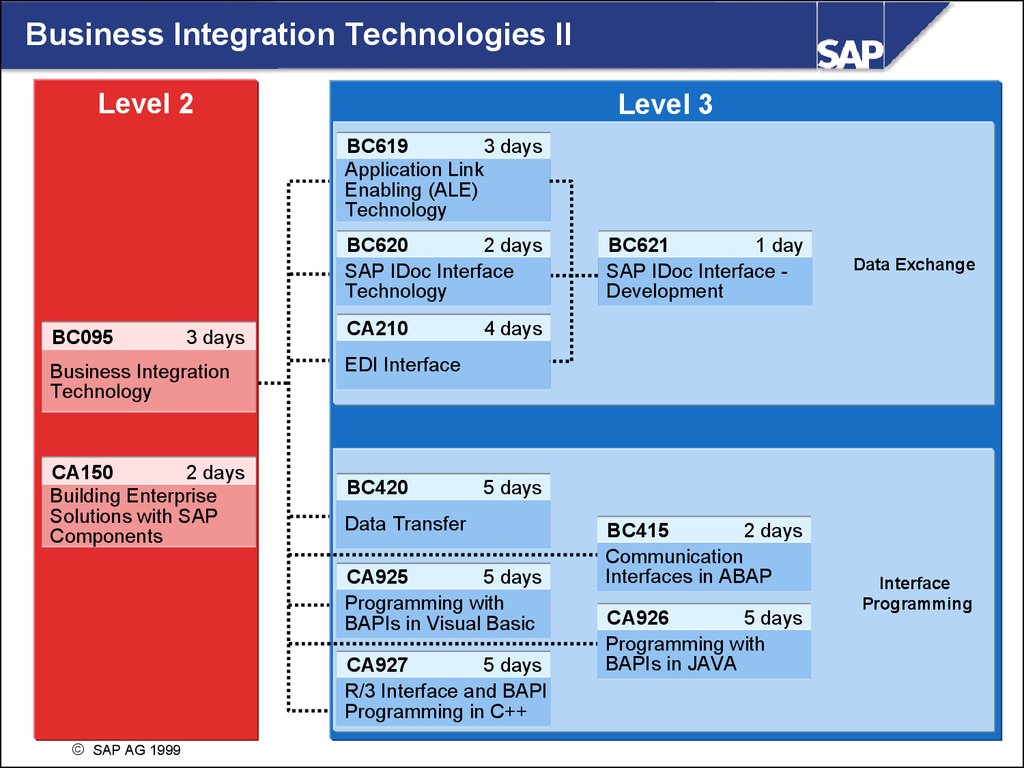
Business Integration Technologies IILevel 2
Level 3
BC619
3 days
Application Link
Enabling (ALE)
Technology
BC620
2 days
SAP IDoc Interface
Technology
BC095
3 days
Business Integration
Technology
CA150
2 days
Building Enterprise
Solutions with SAP
Components
CA210
Data Exchange
4 days
EDI Interface
BC420
5 days
Data Transfer
CA925
5 days
Programming with
BAPIs in Visual Basic
CA927
5 days
R/3 Interface and BAPI
Programming in C++
SAP AG 1999
BC621
1 day
SAP IDoc Interface Development
BC415
2 days
Communication
Interfaces in ABAP
CA926
5 days
Programming with
BAPIs in JAVA
Interface
Programming
4.
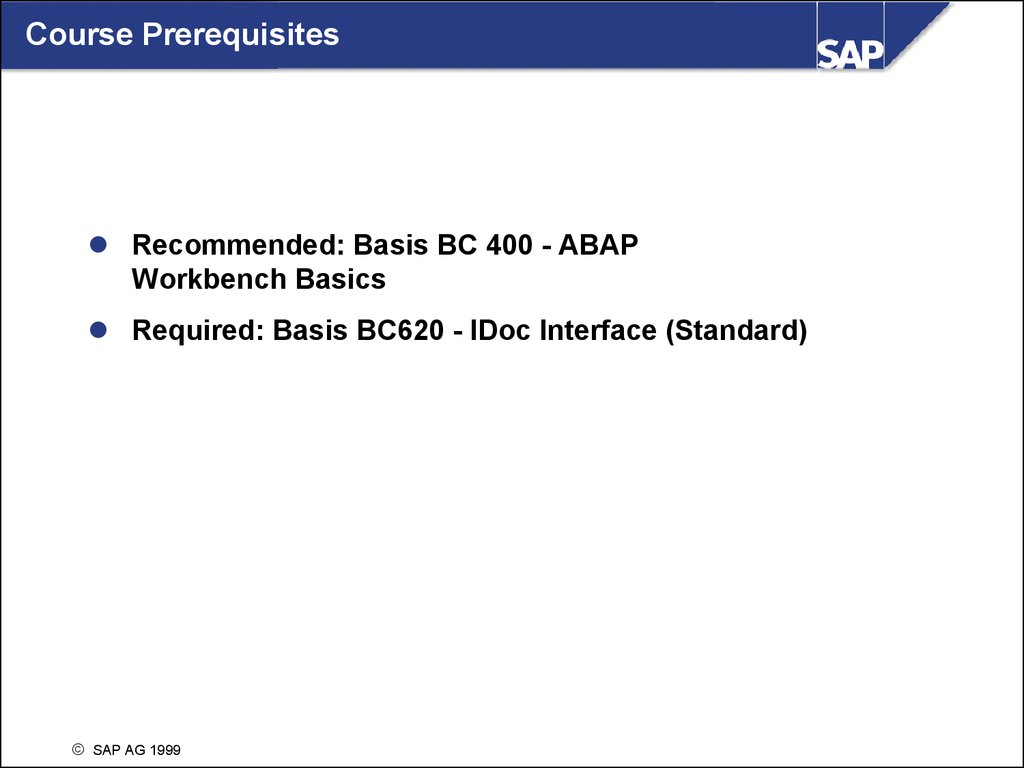
Course PrerequisitesRecommended: Basis BC 400 - ABAP
Workbench Basics
Required: Basis BC620 - IDoc Interface (Standard)
SAP AG 1999
5.
Target GroupABAP Developers
Consultants
SAP AG 1999
6.
Introduction: ContentsCourse Goals
Course Objective(s)
Course Content
Course Overview Diagram
Main Business Scenario
SAP AG 1999
7.
Course GoalsAt the conclusion of this course, you will be
able to:
Extend IDoc types
Define new IDoc types
SAP AG 1999
8.
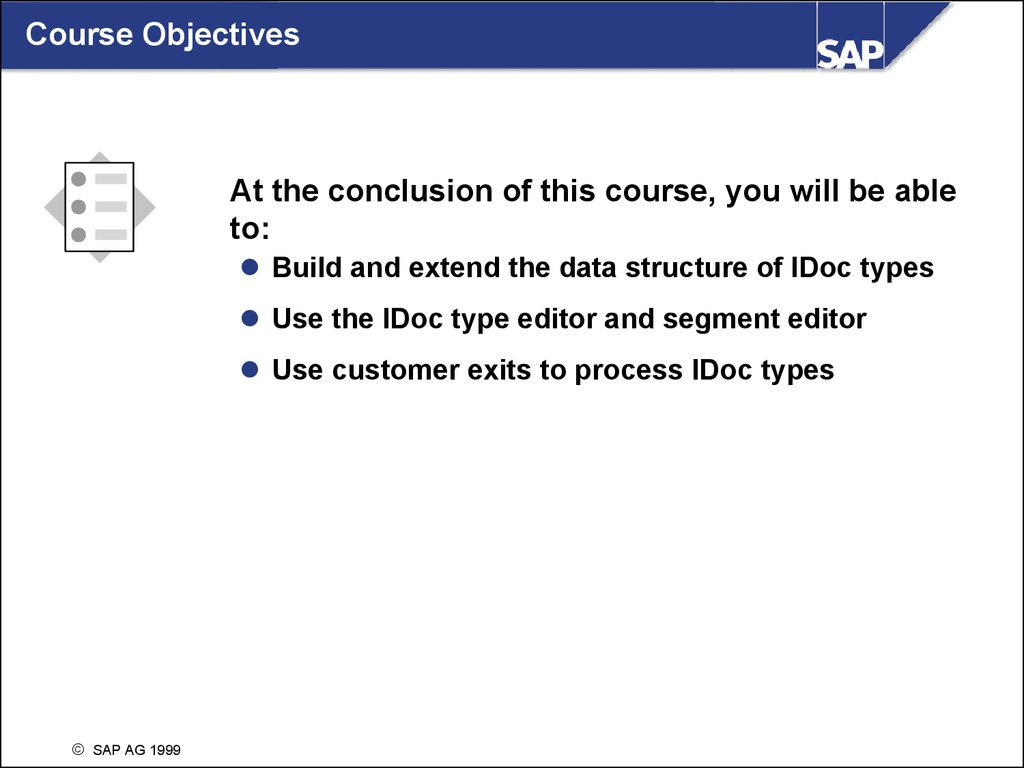
Course ObjectivesAt the conclusion of this course, you will be able
to:
Build and extend the data structure of IDoc types
Use the IDoc type editor and segment editor
Use customer exits to process IDoc types
SAP AG 1999
9.
Course ContentPreface
Unit 1
Introduction
Unit 2
Development Environment for IDoc Types
Unit 3
Extension of IDoc Types
Unit 4
Development of IDoc Types
Appendix
SAP AG 1999
10.
BC621 Course Overview DiagramDevelopment
of IDoc Types
Extension of
IDoc Types
1
Introduction
SAP AG 1999
Development
Environment for
IDoc Types
11.
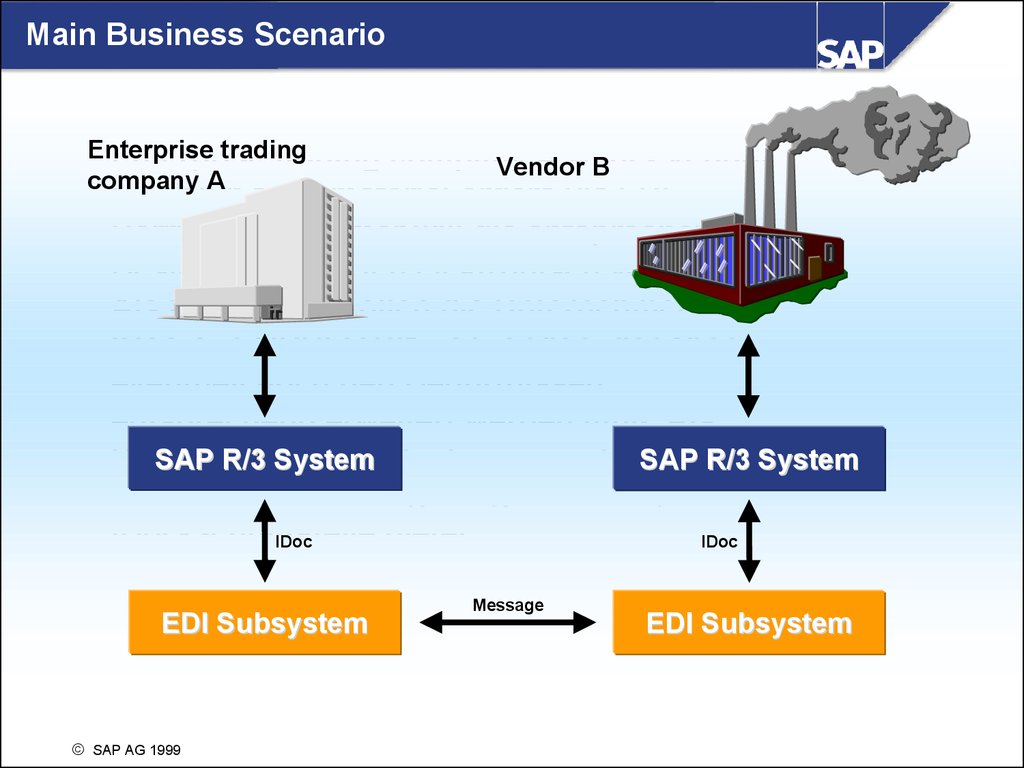
Main Business ScenarioEnterprise
trading
Enterprise
trading
company A
company
A wants
Vendor
Vendor
B
B to ship their material orders via EDI.
Herrmann & Riemer will die entsprechenden
Bestellungen gleich elektronisch verbuchen.
Als Grundlage wollen die Unternehmen den
IDoc-Typ ORDLGT01 verwenden, der aber
eventuell noch den Bedürfnissen
entsprechend erweitert werden muß. Als
Projektteammitglied
informieren SieSAP
sichR/3
also
SAP R/3 System
System
über die Entwicklungsmöglichkeiten, die die
IDoc-Schnittstelle
bietet.
IDoc
IDoc
EDI Subsystem
SAP AG 1999
Message
EDI Subsystem
12.
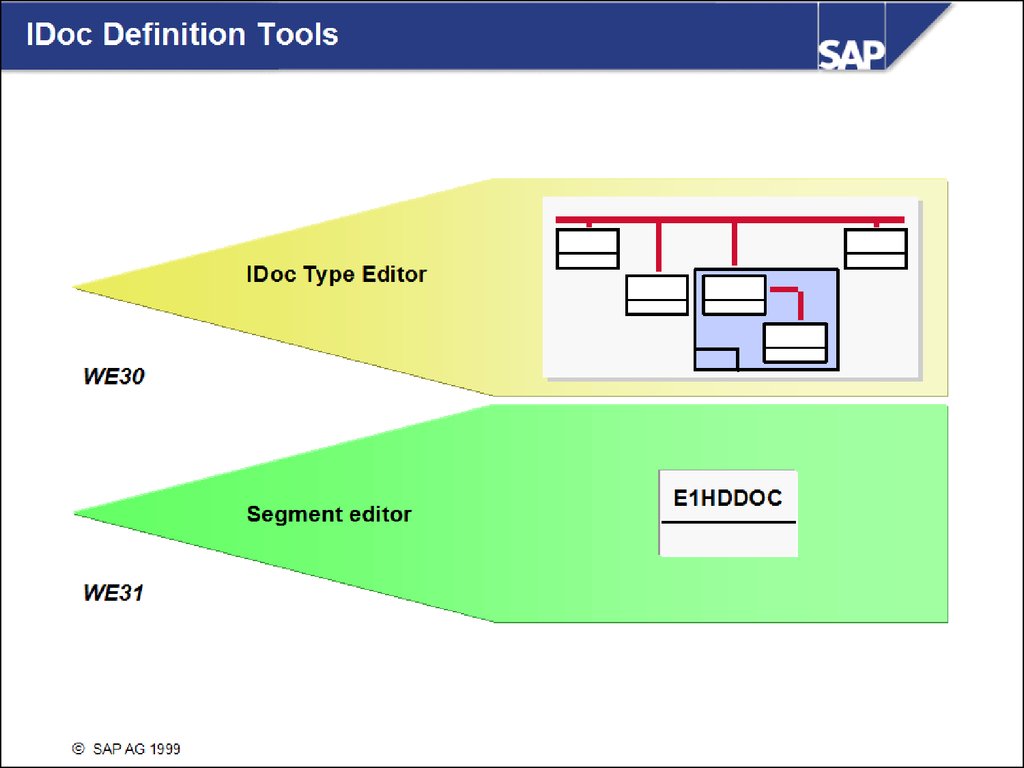
Development Environment for IDoc TypesData Structures:
IDoc Record Types
IDoc Types
IDoc Segments
Development and Extension
SAP AG 1999
13.
Course ObjectivesUnderstand the development environment for IDoc
types
Describe the functionality of the development
environment for IDoc types
Explain the difference between development and
extensions
SAP AG 1999
14.
Course Overview DiagramDevelopment
of IDoc Types
2
Extension of
IDoc Types
Development
Environment
for IDoc Types
Introduction
SAP AG 1999
15.
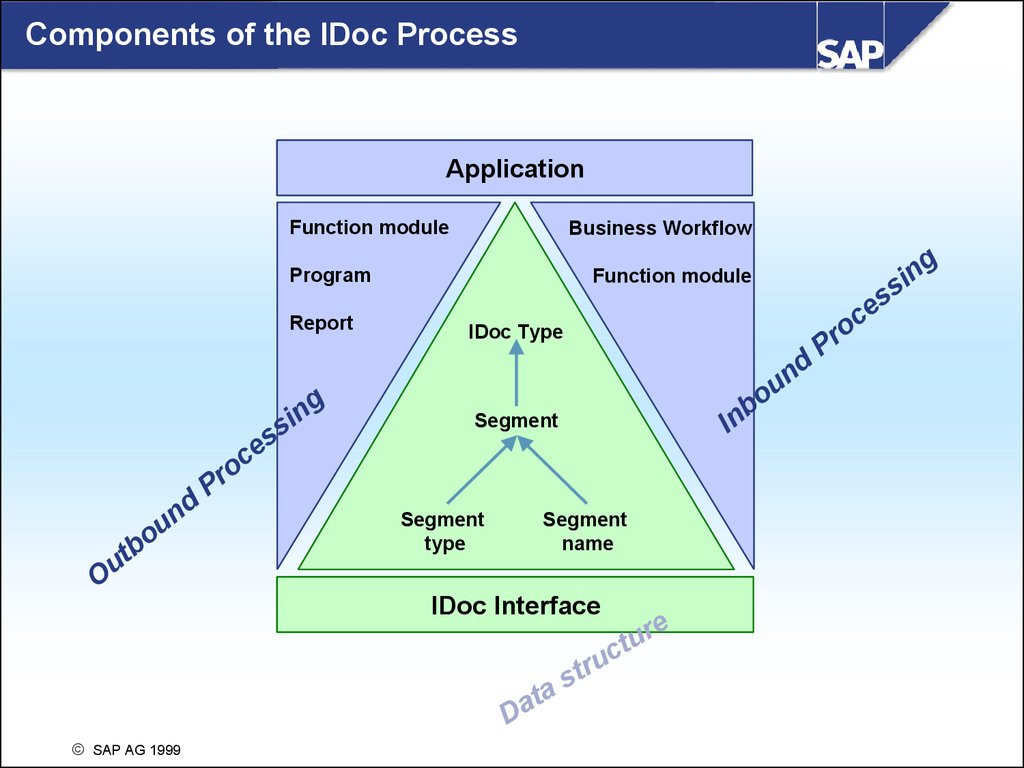
Components of the IDoc ProcessApplication
Function module
Business Workflow
Program
Report
ng
i
s
s
e
oc
tb
u
O
d
n
u
o
IDoc Type
d
n
u
o
b
In
Segment
Pr
Segment
type
Segment
name
IDoc Interface
ta
a
D
SAP AG 1999
ng
i
ss
Function module
u
r
t
s
e
r
u
t
c
e
c
o
Pr
16.
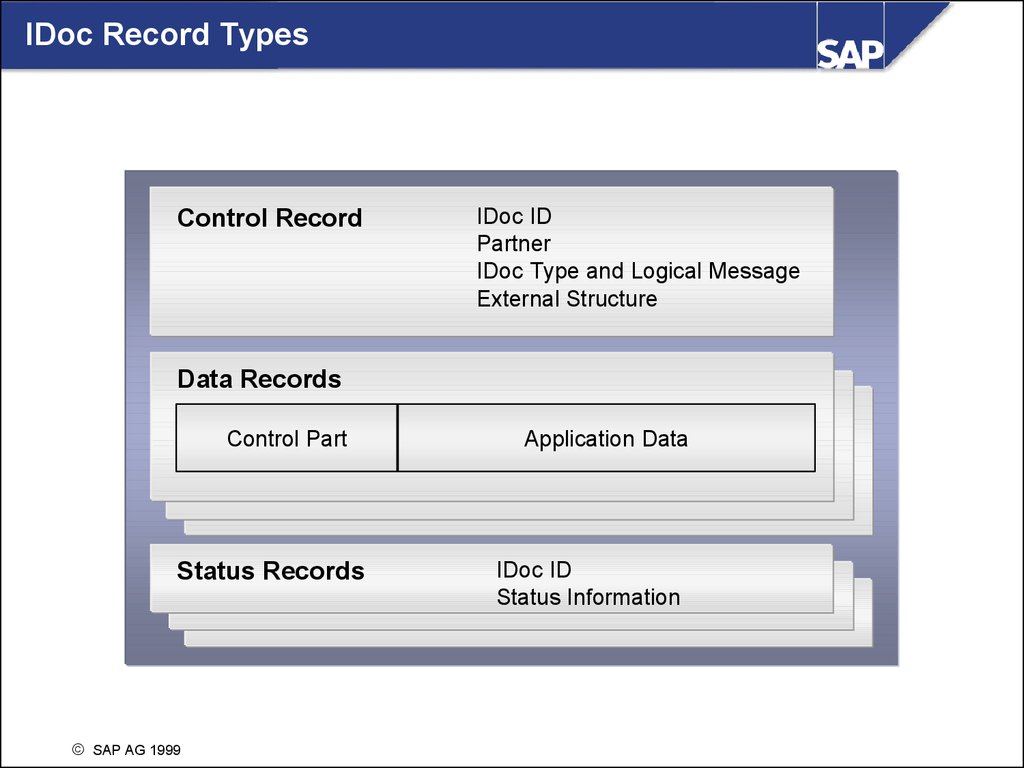
IDoc Record TypesControl Record
IDoc ID
Partner
IDoc Type and Logical Message
External Structure
Data Records
Control Part
Status Records
SAP AG 1999
Application Data
IDoc ID
Status Information
17.
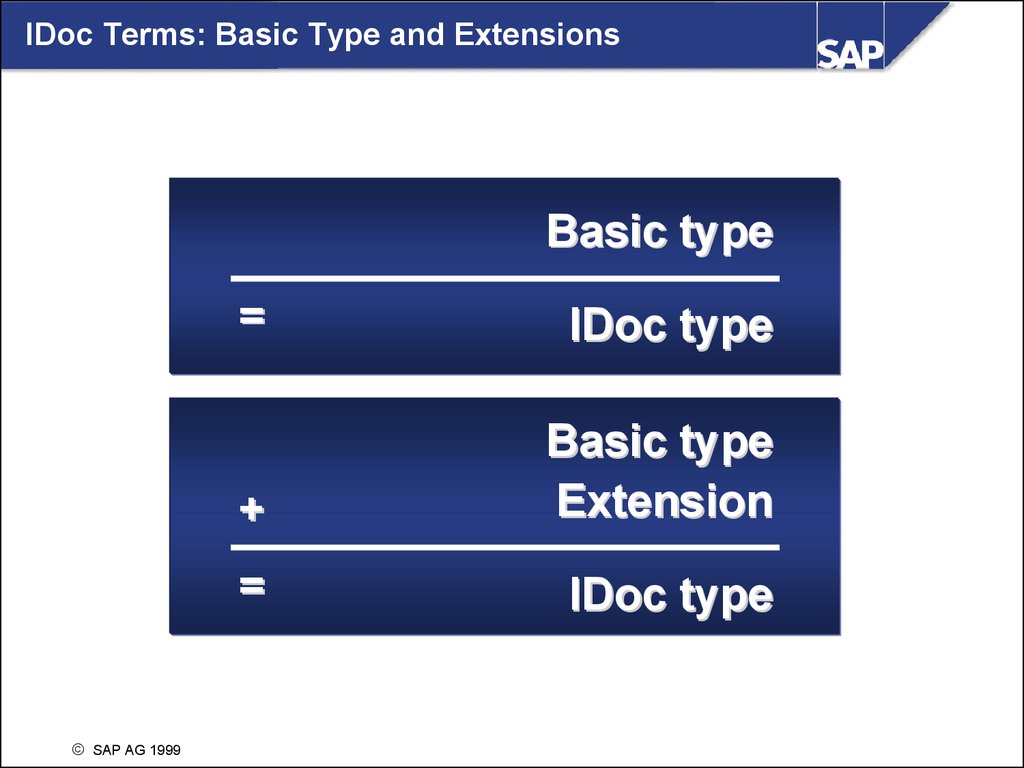
IDoc Terms: Basic Type and ExtensionsBasic type
SAP AG 1999
=
IDoc type
+
Basic type
Extension
=
IDoc type
18.
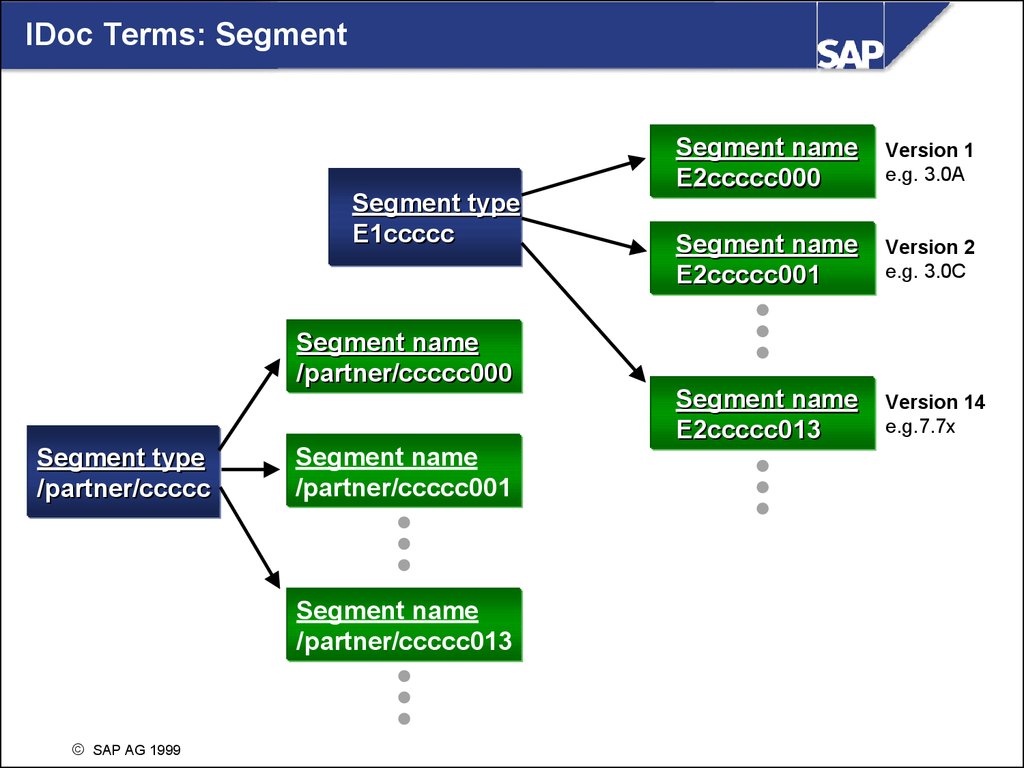
IDoc Terms: SegmentSegment type
E1ccccc
Segment name
E2ccccc000
Version 1
e.g. 3.0A
Segment name
E2ccccc001
Version 2
e.g. 3.0C
Segment name
E2ccccc013
Version 14
e.g.7.7x
Segment name
/partner/ccccc000
Segment type
/partner/ccccc
Segment name
/partner/ccccc001
Segment name
/partner/ccccc013
SAP AG 1999
19.
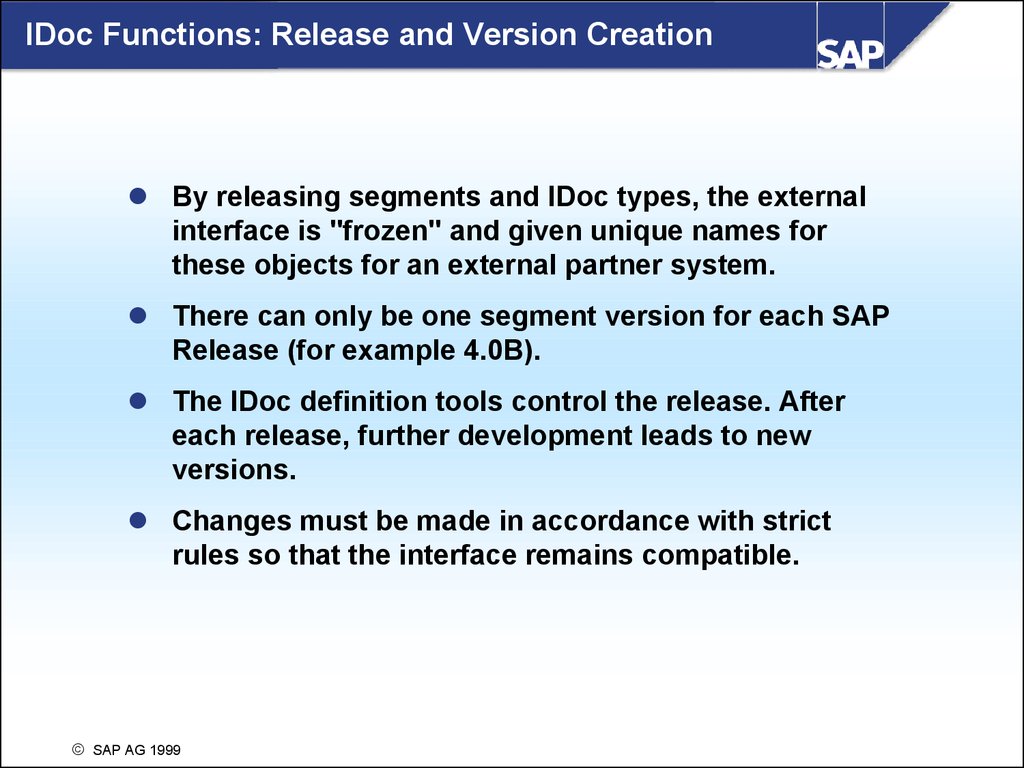
IDoc Functions: Release and Version CreationBy releasing segments and IDoc types, the external
interface is "frozen" and given unique names for
these objects for an external partner system.
There can only be one segment version for each SAP
Release (for example 4.0B).
The IDoc definition tools control the release. After
each release, further development leads to new
versions.
Changes must be made in accordance with strict
rules so that the interface remains compatible.
SAP AG 1999
20.
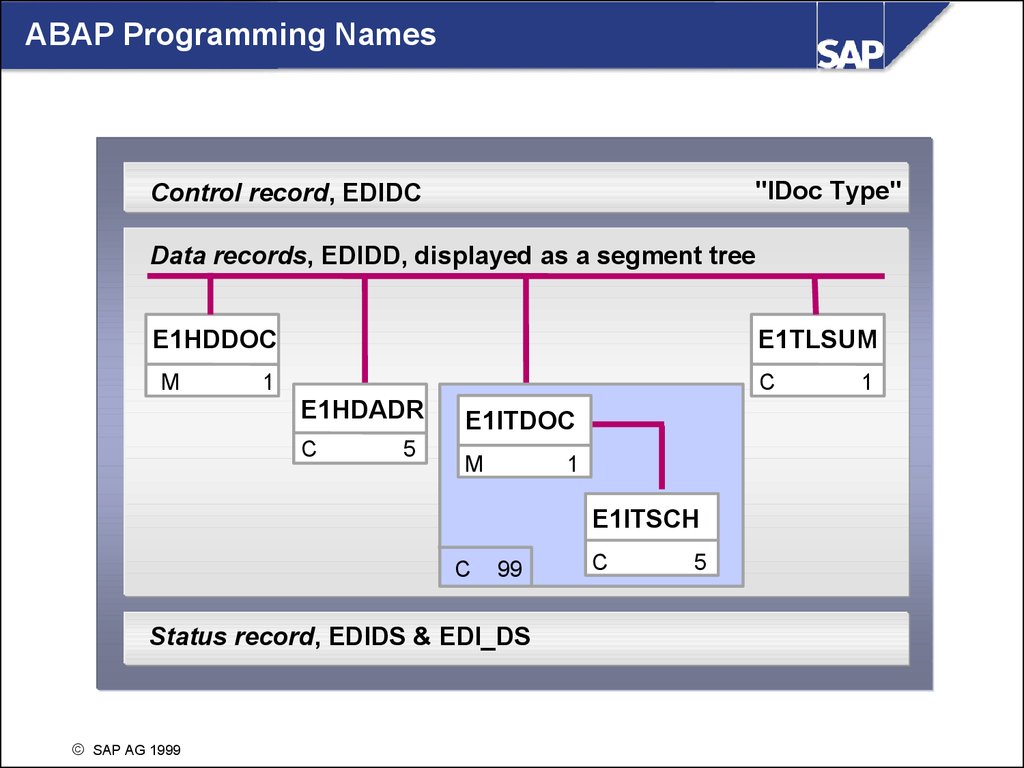
ABAP Programming Names"IDoc Type"
Control record, EDIDC
Data records, EDIDD, displayed as a segment tree
E1HDDOC
M
E1TLSUM
1
C
E1HDADR
C
5
E1ITDOC
Parent
M segment
1
E1ITSCH
E1ITSCH
C
99
Status record, EDIDS & EDI_DS
SAP AG 1999
Child segment
C
5
1
21.
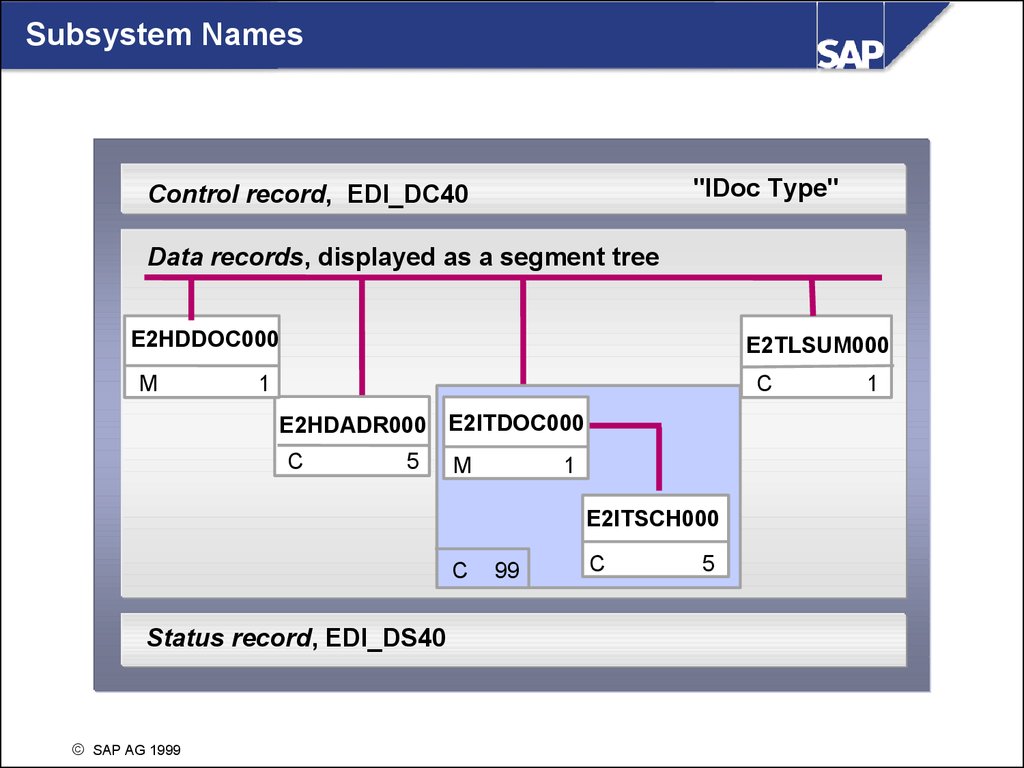
Subsystem Names"IDoc Type"
Control record, EDI_DC40
Data records, displayed as a segment tree
E2HDDOC000
M
E2TLSUM000
1
C
E1ITDOC
E2HDADR000 E2ITDOC000
C
5
Parent segment
M
1
E1ITSCH
E2ITSCH000
C
Status record, EDI_DS40
SAP AG 1999
99
Child segment
C
5
1
22.
23.
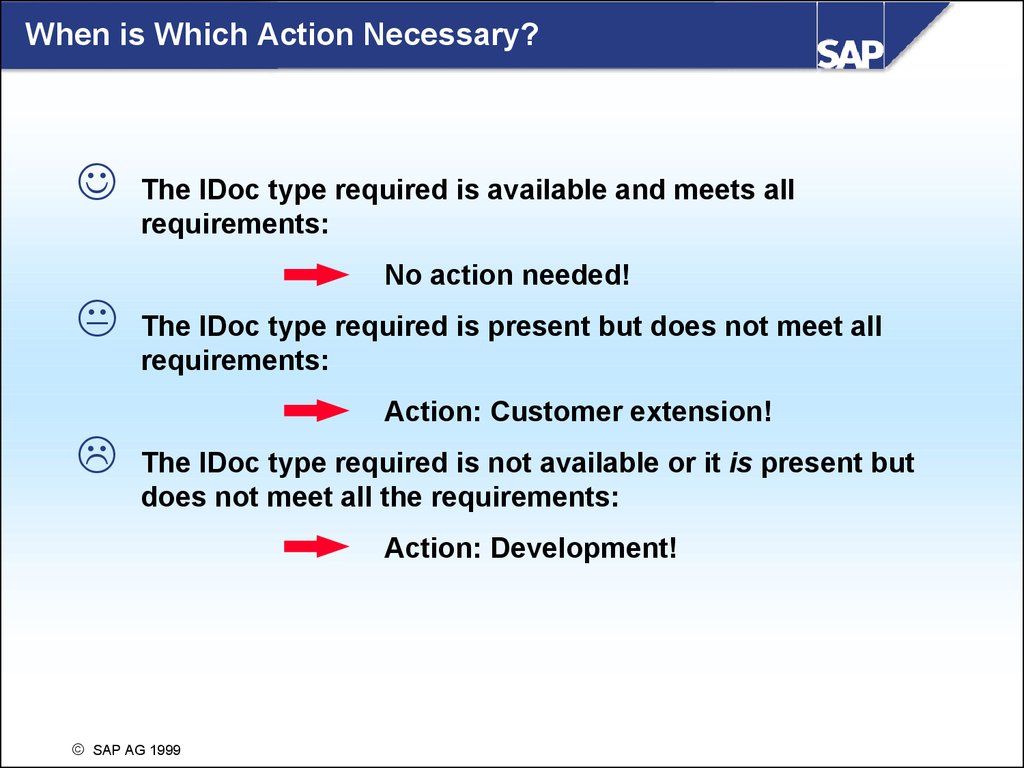
When is Which Action Necessary?The IDoc type required is available and meets all
requirements:
No action needed!
The IDoc type required is present but does not meet all
requirements:
Action: Customer extension!
The IDoc type required is not available or it is present but
does not meet all the requirements:
Action: Development!
SAP AG 1999
24.
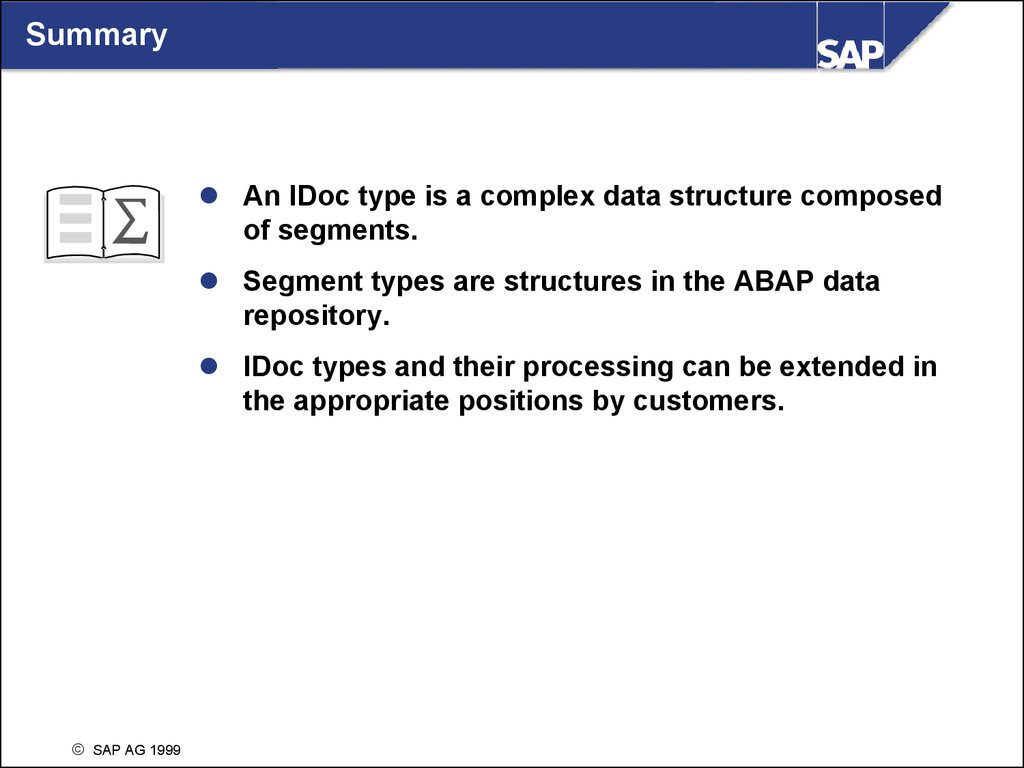
SummaryAn IDoc type is a complex data structure composed
of segments.
Segment types are structures in the ABAP data
repository.
IDoc types and their processing can be extended in
the appropriate positions by customers.
SAP AG 1999
25.
Extension of an IDoc TypeExtension of the data structure
Extension of Outbound Processing
Extension of Inbound Processing
SAP AG 1999
26.
Course ObjectivesCreate IDoc Segment
Extend an IDoc Type
Implement a customer exit in outbound processing
Implement a customer exit in inbound processing
SAP AG 1999
27.
Course Overview Diagram3
Extension of
an IDoc type
Development
environment for
IDoc types
Implementation
SAP AG 1999
Development of
IDoc type
28.
Advantages of Customer EnhancementThe coding provided in the standard system for
processing is used.
Developments and corrections of the coding
delivered in the standard system are therefore
automatically available.
Extension is less time consuming than new
development.
SAP AG 1999
29.
Basic Rules for Customer ExtensionAdditional customer fields are recorded in their own
customer segments.
Customer segments depend on SAP segments
(successor or child relationships).
The processing of customer segments is exclusively
implemented in the customer exits of the coding
provided in the standard system.
SAP AG 1999
30.
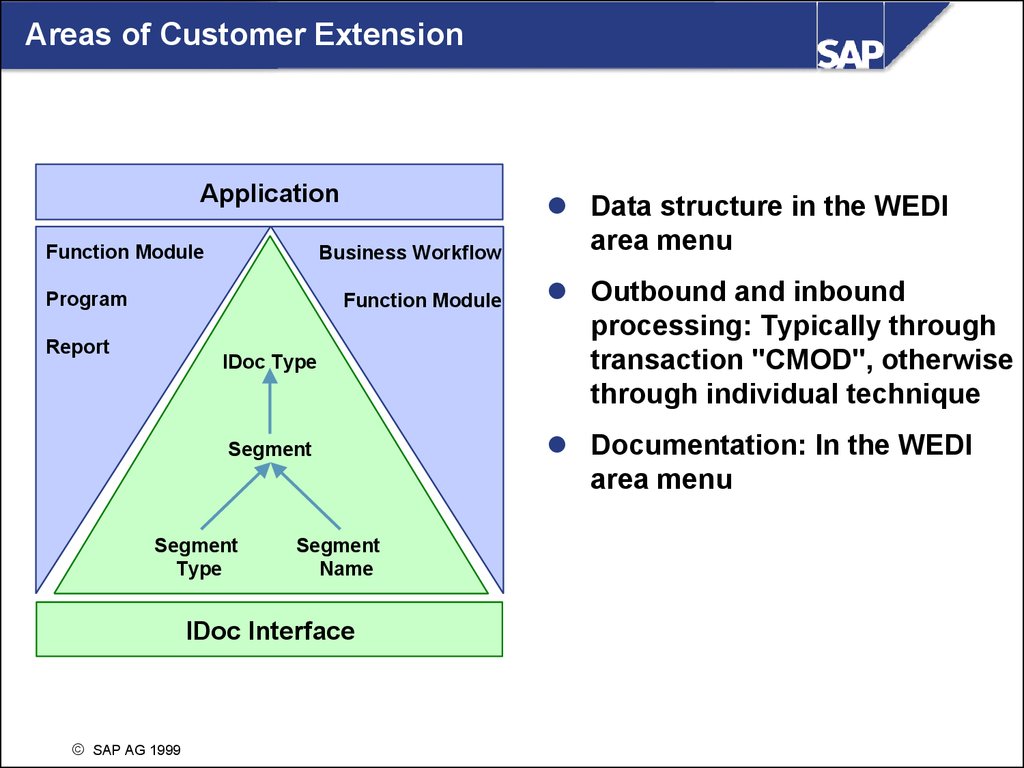
Areas of Customer ExtensionApplication
Function Module
Business Workflow
Program
Function Module
Report
IDoc Type
Segment
Segment
Type
Segment
Name
IDoc Interface
SAP AG 1999
Data structure in the WEDI
area menu
Outbound and inbound
processing: Typically through
transaction "CMOD", otherwise
through individual technique
Documentation: In the WEDI
area menu
31.
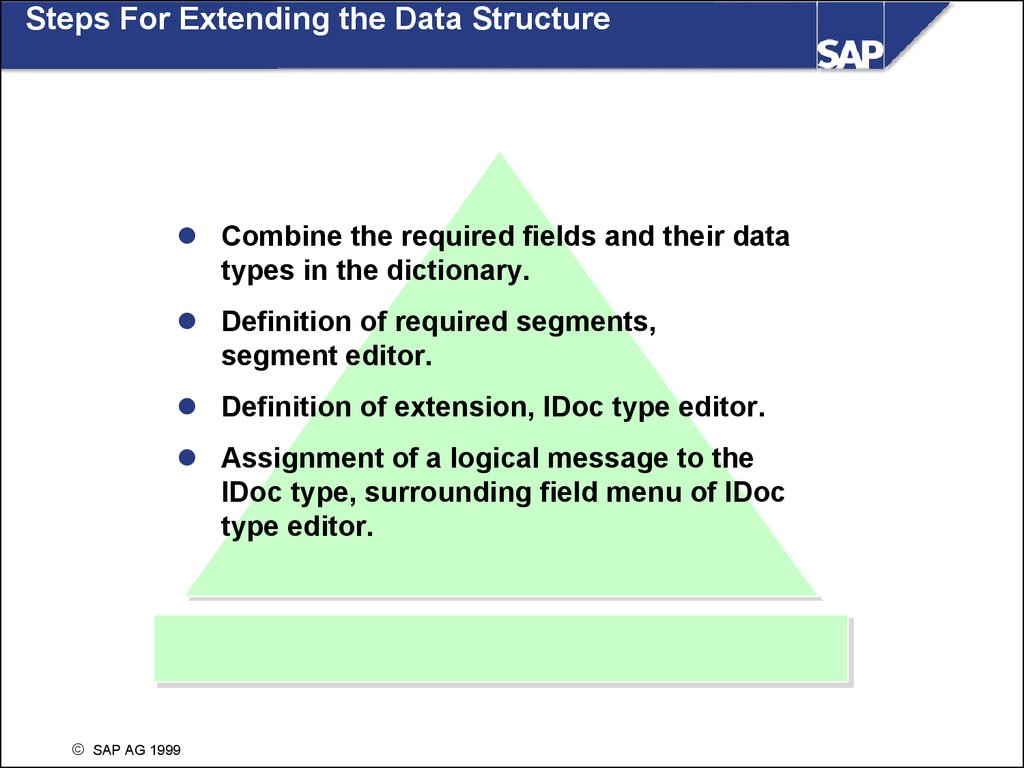
Steps For Extending the Data StructureCombine the required fields and their data
types in the dictionary.
Definition of required segments,
segment editor.
Definition of extension, IDoc type editor.
Assignment of a logical message to the
IDoc type, surrounding field menu of IDoc
type editor.
SAP AG 1999
32.
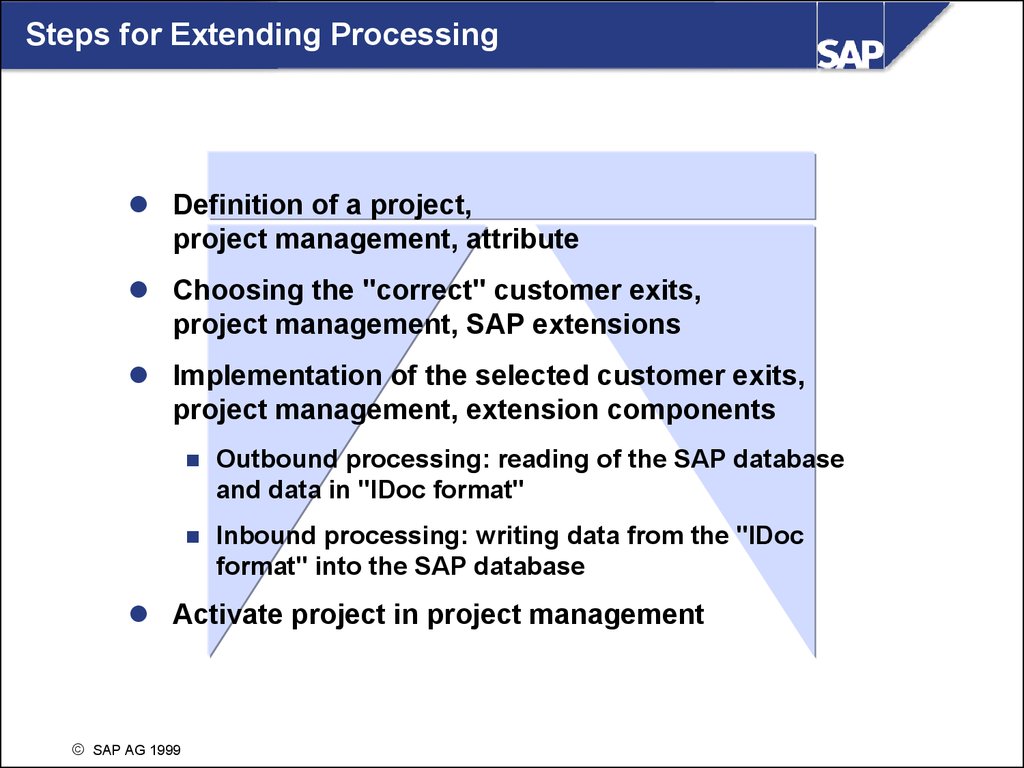
Steps for Extending ProcessingDefinition of a project,
project management, attribute
Choosing the "correct" customer exits,
project management, SAP extensions
Implementation of the selected customer exits,
project management, extension components
Outbound processing: reading of the SAP database
and data in "IDoc format"
Inbound processing: writing data from the "IDoc
format" into the SAP database
Activate project in project management
SAP AG 1999
33.
34.
SummaryAn extension can be limited to processing.
Normally an extension encompasses the data
structure as well as the processing.
Extended data structures can be communicated to
the subsystem by the documentation tools.
SAP AG 1999
35. Erweiterung eines IDoc-Typs: Exercise Data Used in the Exercises
36. Extension of an IDoc Type: Solutions Unit: Extension of an IDoc Type
37.
Development of IDoc TypeDevelopment of the data structure
Processing example
SAP AG 1999
38.
Topic ObjectivesCreate IDoc segments
Develop new IDoc types
Template for IDoc outbound processing
Template for IDoc inbound processing
SAP AG 1999
39.
Course Overview Diagram4
Development of
IDoc type
Extension of
an IDoc type
Development
environment for
IDoc types
Implementation
SAP AG 1999
40.
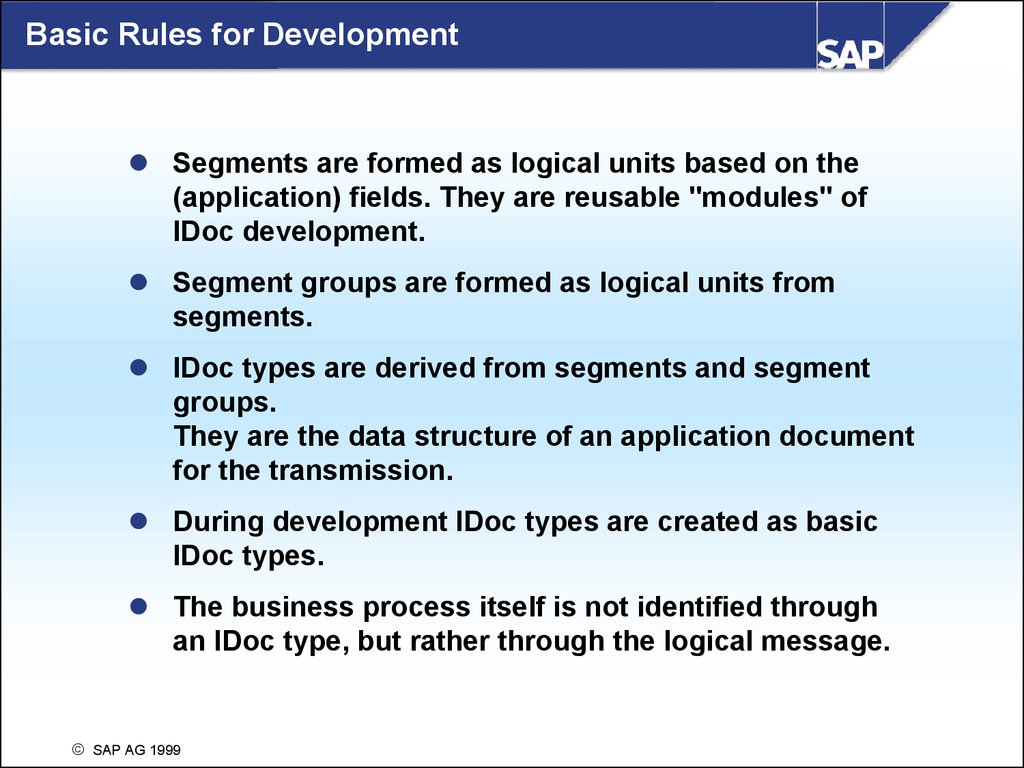
Basic Rules for DevelopmentSegments are formed as logical units based on the
(application) fields. They are reusable "modules" of
IDoc development.
Segment groups are formed as logical units from
segments.
IDoc types are derived from segments and segment
groups.
They are the data structure of an application document
for the transmission.
During development IDoc types are created as basic
IDoc types.
The business process itself is not identified through
an IDoc type, but rather through the logical message.
SAP AG 1999
41.
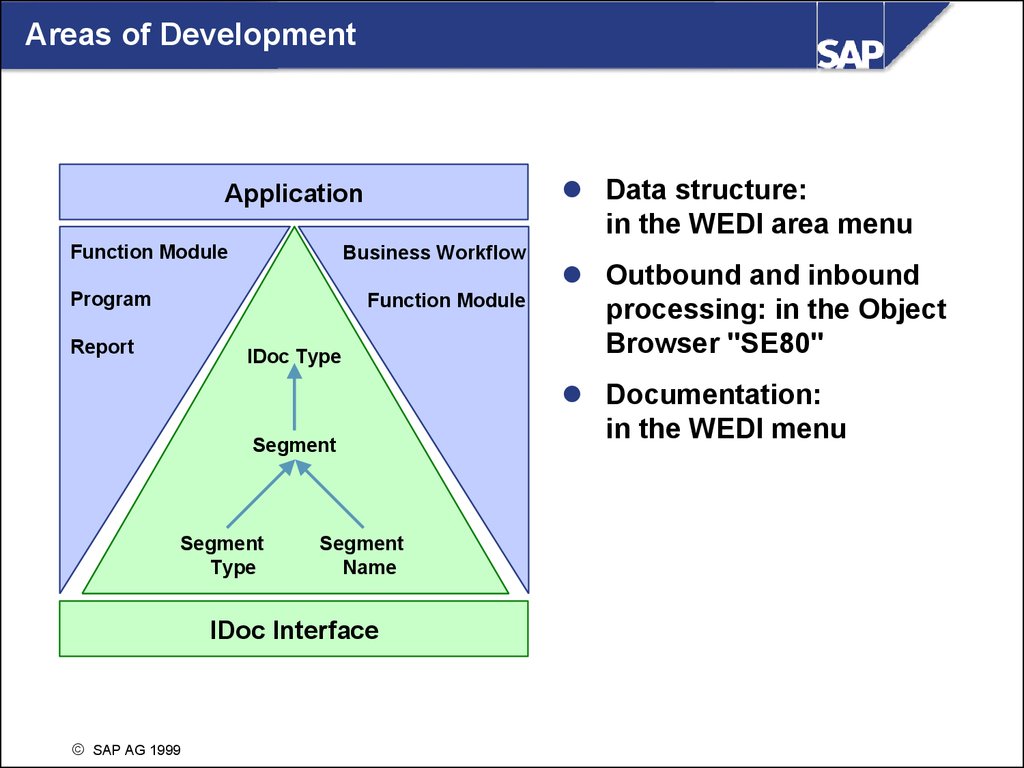
Areas of DevelopmentData structure:
in the WEDI area menu
Application
Function Module
Business Workflow
Program
Function Module
Report
IDoc Type
Segment
Segment
Type
Segment
Name
IDoc Interface
SAP AG 1999
Outbound and inbound
processing: in the Object
Browser "SE80"
Documentation:
in the WEDI menu
42.
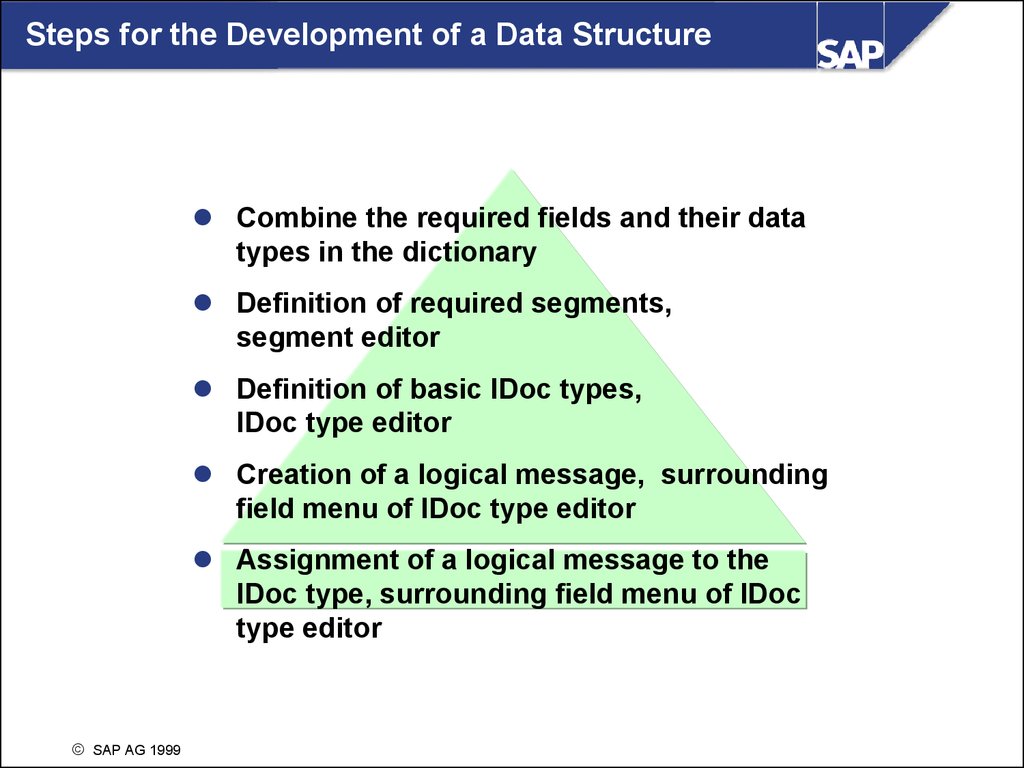
Steps for the Development of a Data StructureCombine the required fields and their data
types in the dictionary
Definition of required segments,
segment editor
Definition of basic IDoc types,
IDoc type editor
Creation of a logical message, surrounding
field menu of IDoc type editor
Assignment of a logical message to the
IDoc type, surrounding field menu of IDoc
type editor
SAP AG 1999
43.
Processing TypesOutbound processing using
Message Control (MC) ?
ALE Interface (FM MASTER_IDOC_DISTRIBUTE)?
Inbound processing using
SAP AG 1999
Business Workflow (single step or multistep task) ?
ALE Interface (function module) ?
44.
Steps for Development of Outbound Processingusing MC
Checking Message Control, that is, the connection
for the message default:
Condition table
Access sequence
Condition types
Procedure
Application
Implementation of a function module that makes
application data available in "IDoc format"
Definition of an outbound process code
SAP AG 1999
45.
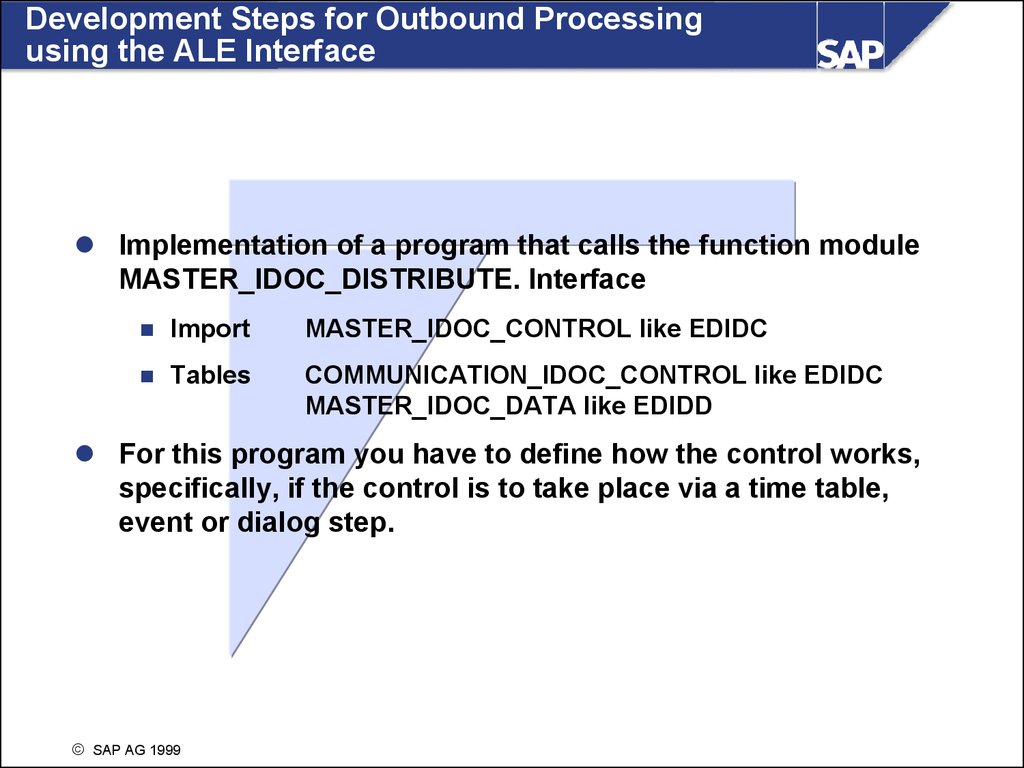
Development Steps for Outbound Processingusing the ALE Interface
Implementation of a program that calls the function module
MASTER_IDOC_DISTRIBUTE. Interface
Import
MASTER_IDOC_CONTROL like EDIDC
Tables
COMMUNICATION_IDOC_CONTROL like EDIDC
MASTER_IDOC_DATA like EDIDD
For this program you have to define how the control works,
specifically, if the control is to take place via a time table,
event or dialog step.
SAP AG 1999
46.
Development Steps of Inbound Processing usingBusiness Workflow
Implementation of a workflow to control inbound
processing
This includes:
Definition of object and method(s) in BOR
Definition of workflow
Definition of inbound process code
SAP AG 1999
47.
Development Steps for Inbound Processing usingALE Interface
Write function module that posts the IDoc as an
application document
Implementation of a workflow to send messages in case
of error. This includes:
Definition of object and method(s) in BOR
Definition of workflow
Maintenance of the characteristics for the function
module for the ALE Call
Allocation of the function module to a logical message
and to an IDoc type for the ALE Call
Definition of an inbound process code and establishing a
connection with the ALE layer
SAP AG 1999
48.
49.
SummaryThe data structure is defined as an IDoc type
Depending on the processing course and direction,
different programming templates can be used
SAP AG 1999
Outbound uses 2 methods:
Message Control and ALE
Inbound uses 2 methods:
Workflow and ALE