Similar presentations:
Cardiovascular diseases
1.
Research adviser : Professor Ablaev N.R2. According to WHO, cardiovascular diseases today occupy fifth place in the structure of global mortality, and, while maintaining
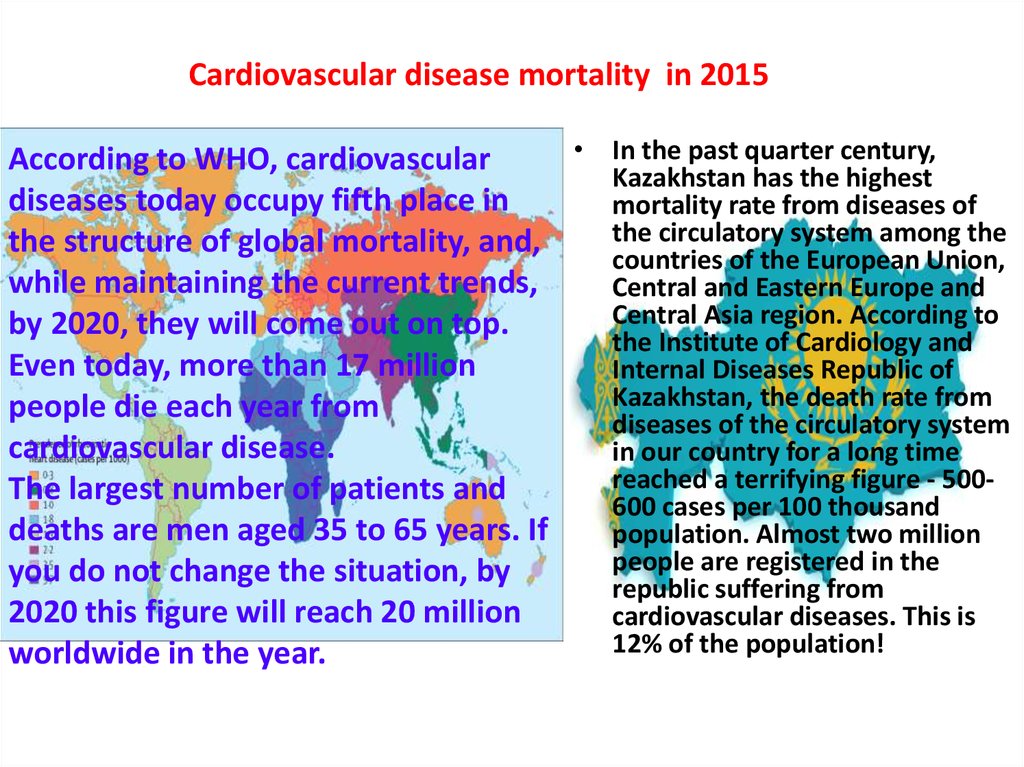
Cardiovascular disease mortality in 2015• In the past quarter century,
According to WHO, cardiovascular
Kazakhstan has the highest
diseases today occupy fifth place in
mortality rate from diseases of
the circulatory system among the
the structure of global mortality, and,
countries of the European Union,
while maintaining the current trends,
Central and Eastern Europe and
Central Asia region. According to
by 2020, they will come out on top.
the Institute of Cardiology and
Even today, more than 17 million
Internal Diseases Republic of
Kazakhstan, the death rate from
people die each year from
diseases of the circulatory system
cardiovascular disease.
in our country for a long time
reached a terrifying figure - 500The largest number of patients and
600 cases per 100 thousand
deaths are men aged 35 to 65 years. If
population. Almost two million
people are registered in the
you do not change the situation, by
republic suffering from
2020 this figure will reach 20 million
cardiovascular diseases. This is
12% of the population!
worldwide in the year.
3.
4.
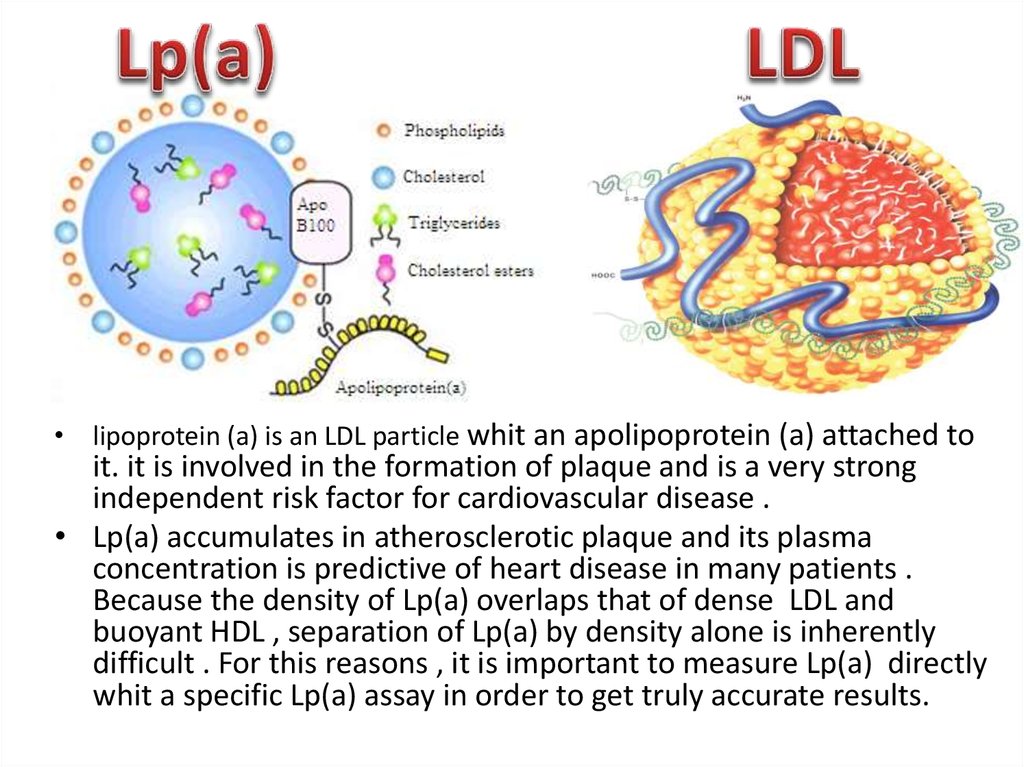
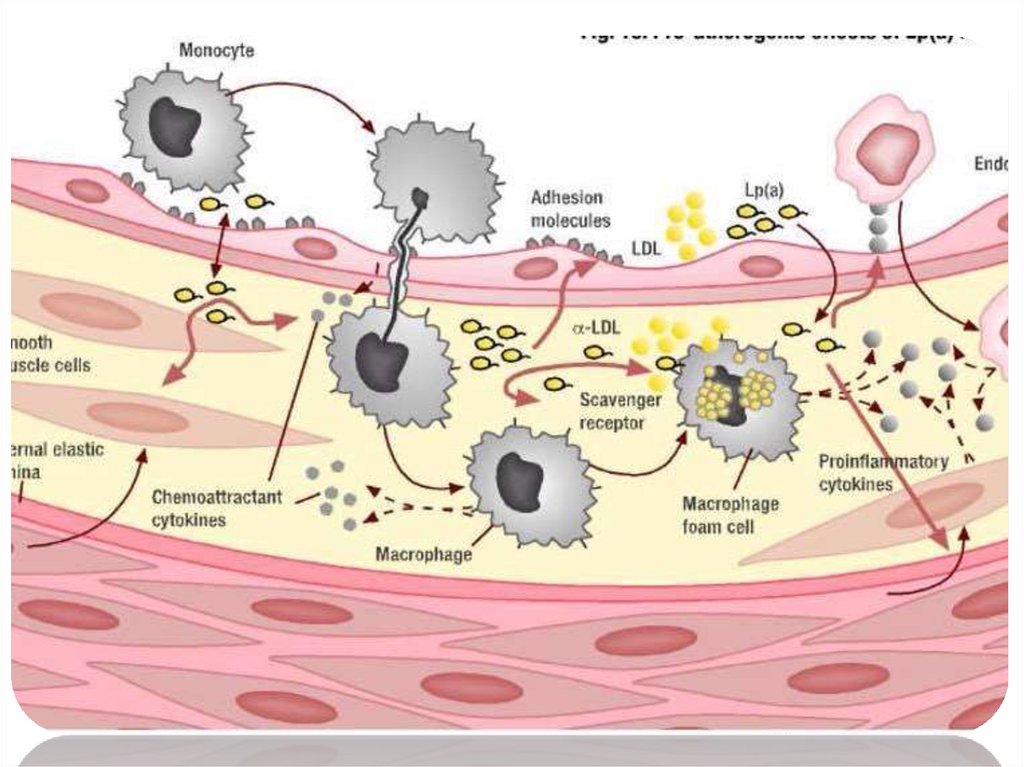
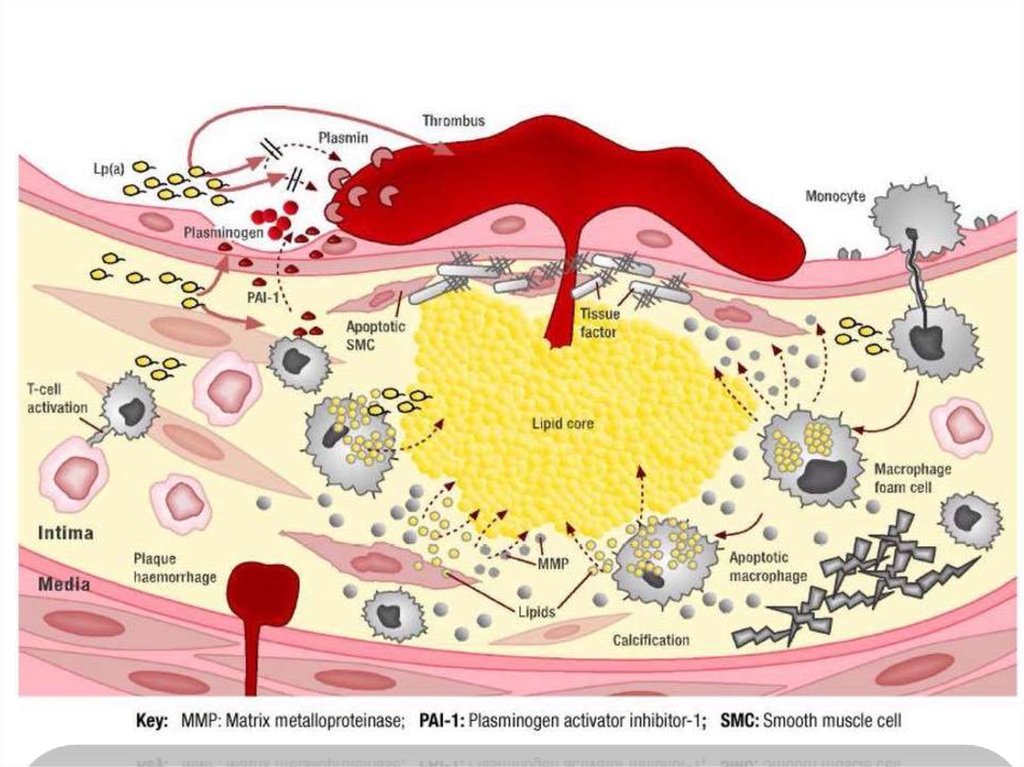
• lipoprotein (a) is an LDL particle whit an apolipoprotein (a) attached toit. it is involved in the formation of plaque and is a very strong
independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease .
• Lp(a) accumulates in atherosclerotic plaque and its plasma
concentration is predictive of heart disease in many patients .
Because the density of Lp(a) overlaps that of dense LDL and
buoyant HDL , separation of Lp(a) by density alone is inherently
difficult . For this reasons , it is important to measure Lp(a) directly
whit a specific Lp(a) assay in order to get truly accurate results.
5.
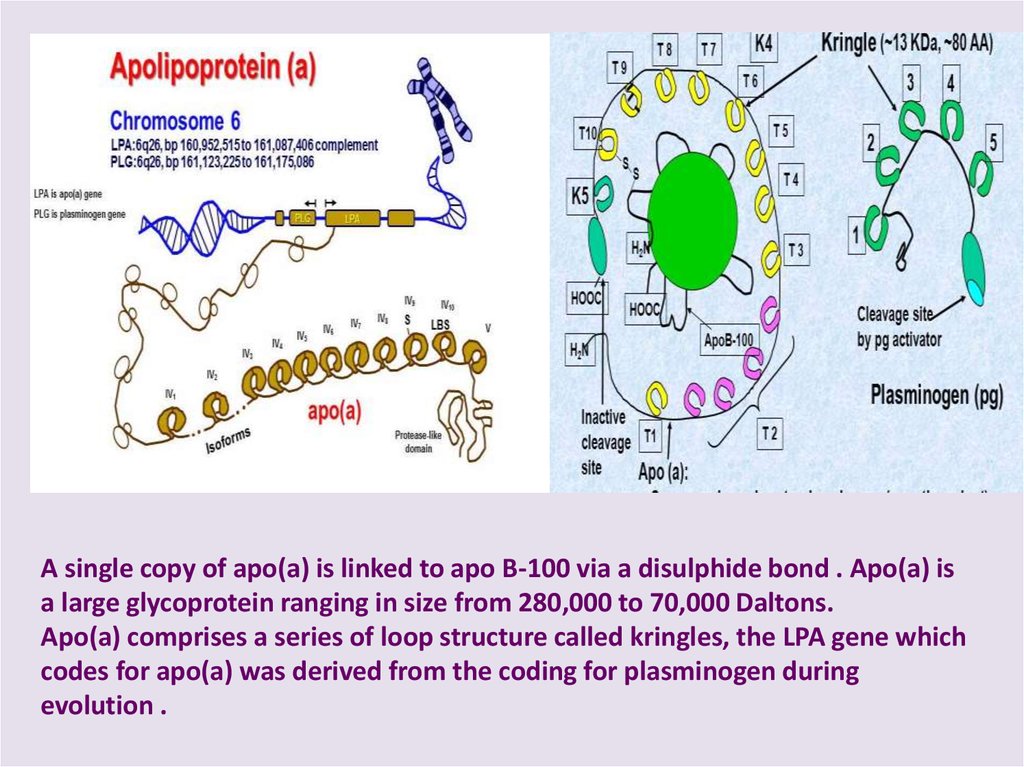
A single copy of apo(a) is linked to apo B-100 via a disulphide bond . Apo(a) isa large glycoprotein ranging in size from 280,000 to 70,000 Daltons.
Apo(a) comprises a series of loop structure called kringles, the LPA gene which
codes for apo(a) was derived from the coding for plasminogen during
evolution .
6.
One in five people has high levels of Lip(a) from birth based on genetic factors theyinherited from their parents, and most don’t know they have it. As high levels of
Lip(a) travel through the bloodstream, it collects in the arteries, leading to gradual
narrowing of the artery that can limit blood supply to the heart, brain, and kidneys
as well as the legs. It can increase the risk of blood clots, heart attack or stroke.
Important facts about Lip(a)
High Lip(a) is not rare. One in five people globally
and 63 million people in the U.S. have high Lip(a)
levels, and most do not know they are at risk.
High Lip(a) is the strongest, single, inherited risk
factor for early coronary artery disease (CAD) and
aortic stenosis, or narrowing of the aorta.
People living with high Lip(a) have a 2-4 times
higher risk of early heart and blood vessel disease
compared to people with normal Lip(a) levels.
High Lip(a) occurs in all ethnic groups, but is more
common among African Americans and South
Asians.
7.
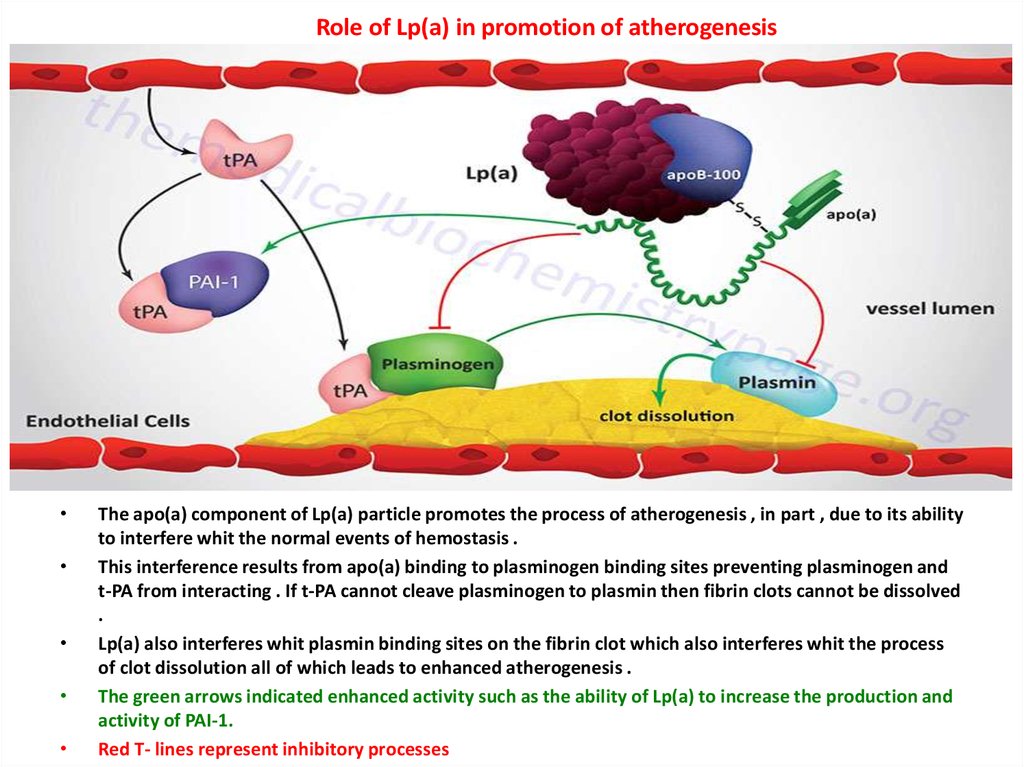
Role of Lp(a) in promotion of atherogenesisThe apo(a) component of Lp(a) particle promotes the process of atherogenesis , in part , due to its ability
to interfere whit the normal events of hemostasis .
This interference results from apo(a) binding to plasminogen binding sites preventing plasminogen and
t-PA from interacting . If t-PA cannot cleave plasminogen to plasmin then fibrin clots cannot be dissolved
.
Lp(a) also interferes whit plasmin binding sites on the fibrin clot which also interferes whit the process
of clot dissolution all of which leads to enhanced atherogenesis .
The green arrows indicated enhanced activity such as the ability of Lp(a) to increase the production and
activity of PAI-1.
Red T- lines represent inhibitory processes
8.
9.
10.
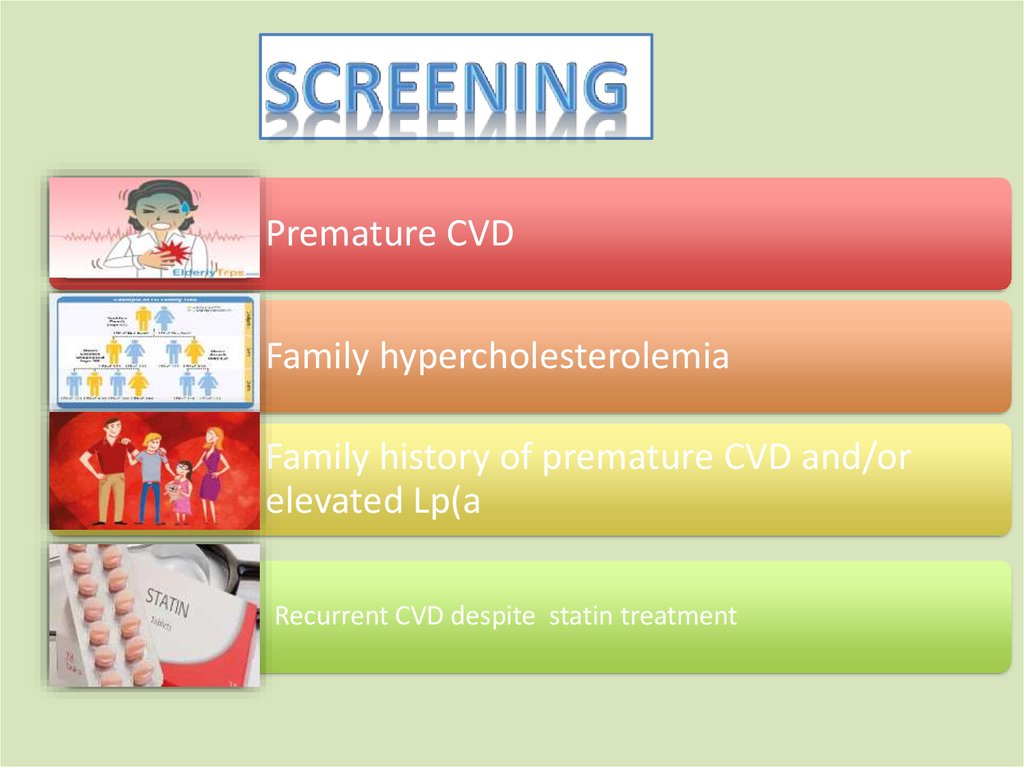
Premature CVDFamily hypercholesterolemia
Family history of premature CVD and/or
elevated Lp(a
Recurrent CVD despite statin treatment
11.
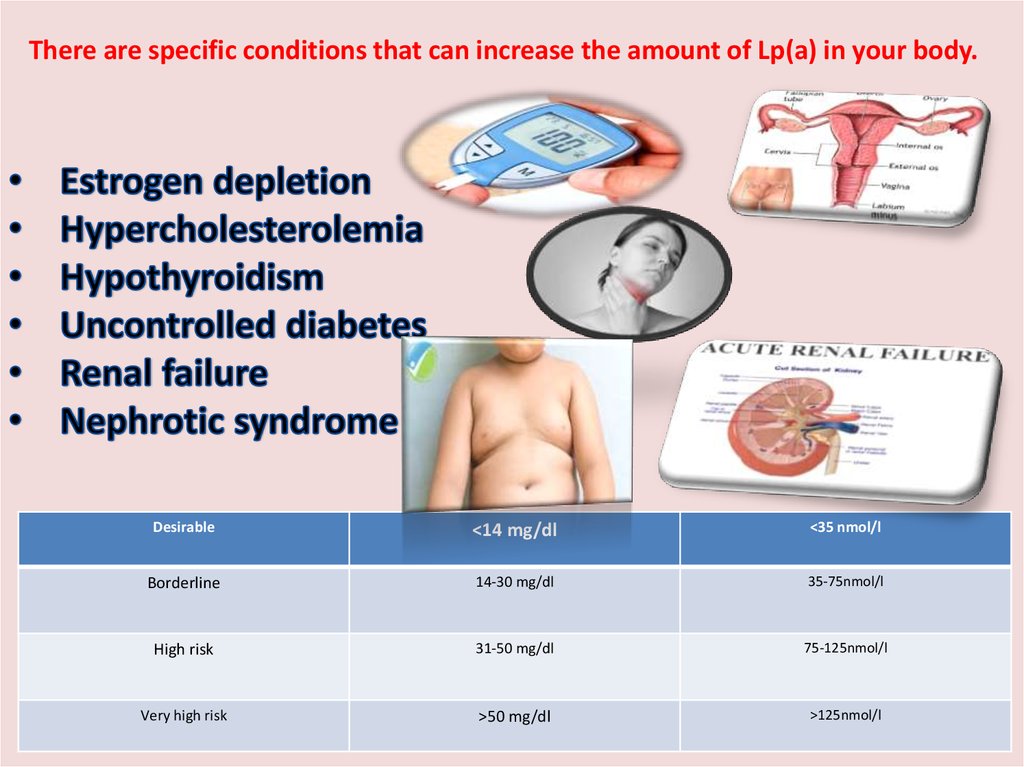
There are specific conditions that can increase the amount of Lp(a) in your body.Desirable
<14 mg/dl
<35 nmol/l
Borderline
14-30 mg/dl
35-75nmol/l
High risk
31-50 mg/dl
75-125nmol/l
Very high risk
>50 mg/dl
>125nmol/l
12.
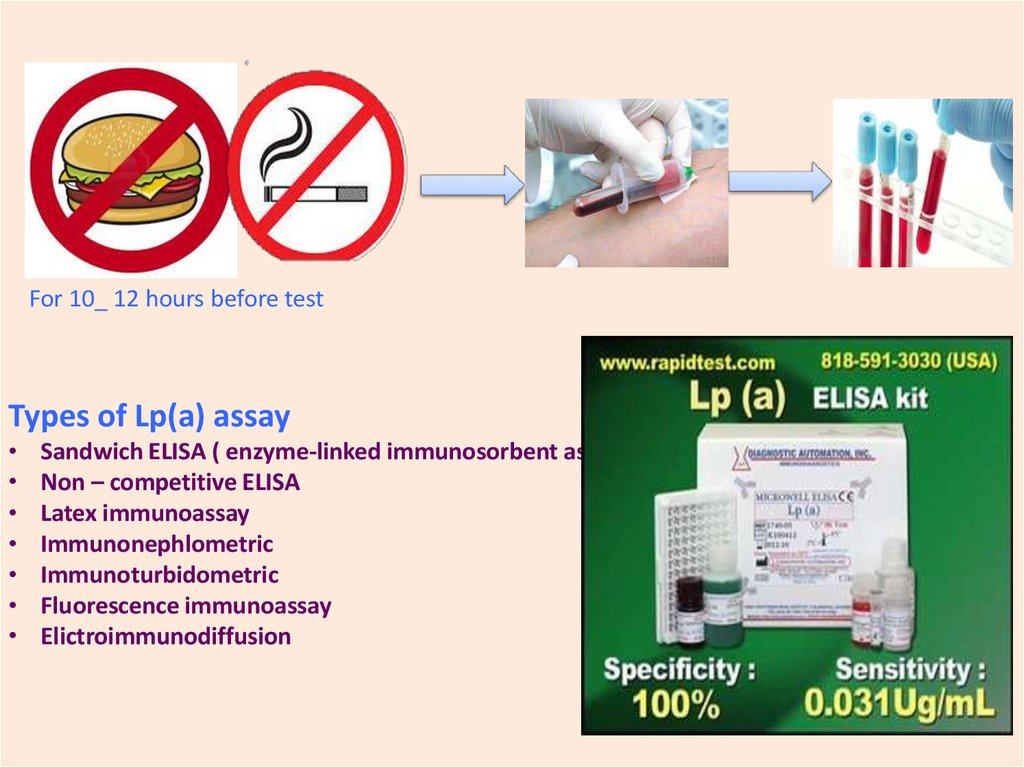
For 10_ 12 hours before testTypes of Lp(a) assay
Sandwich ELISA ( enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Non – competitive ELISA
Latex immunoassay
Immunonephlometric
Immunoturbidometric
Fluorescence immunoassay
Elictroimmunodiffusion



 medicine
medicine english
english