Similar presentations:
Антикризисное управление. (Лекция 1)
1. Anti-crisis Management (Lectures)
Economic and Business DepartmentOmarov Galym Burkitbayevich
PhD, Assistant - professor
1
2.
Current Classes:Management: Spring 2016
Course Objectives:
To develop the student's
understanding of Anti-crisis
Management. To familiarize students
with the principles, methods and ways
of diagnosis of crisis situations.
Development of procedures and
mechanisms to counter the negative
trends in the enterprise and the
consequences of crisis situations,
methods of rehabilitation and
improvement of enterprise
competitiveness.
2
3.
What is the “Crisis”?3
4.
What is the “Crisis”?A translation from Greek: “Crisis” is the solution,
the tipping point
4
5. What is the “Management”?
Mind Map5
6. Course Schedule:
Chapter 1. «The essence of the Anti-crisis management»Chapter 2. «Crises in social and economic development»
Chapter 3. «The system of crisis management»
Chapter 4. «The insolvency of the company: the essence and causes»
Chapter 5. «Diagnosis of the financial condition of the organization.
Evaluation of solvency of the company»
Chapter 6. «The financial rehabilitation of insolvent companies»
Chapter 7.«Anti-crisis marketing strategy»
Chapter 8. «Risks in crisis management»
Chapter 9. «Anti-crisis regulation of the company's situation»
The Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan “On Rehabilitation and Bankruptcy”
Chapter 10. «Basics of enterprise restructuring»
Chapter 11. «Business Engineering Techniques and their application in the
system of crisis management»
Chapter 12. «Foreign experience of crisis management»
Chapter 13. «Anti-crisis management in HR»
Chapter 14. «Basics of Project Management»
Chapter 15. «Emergency Management»
6
7. Chapter 1. The essence of the Anti-crisis management
ISSUESCrisis management (ACM, CM) as a scientific discipline
● The necessity and relevance of ACM
● Life Cycle of organization
● Functions of ACM
● Basic requirements for ACM system
● The basic principles of the ACM
Crises in social and economic development
● Causes of the crisis organization
● Types of changes from the crisis
● Typology of crises of organization
● The emergence and recognition of the crisis
● Evaluation of the crisis in the process of Anti-crisis
management
● Main indicators of early detection of crisis risks
by internal reasons
7
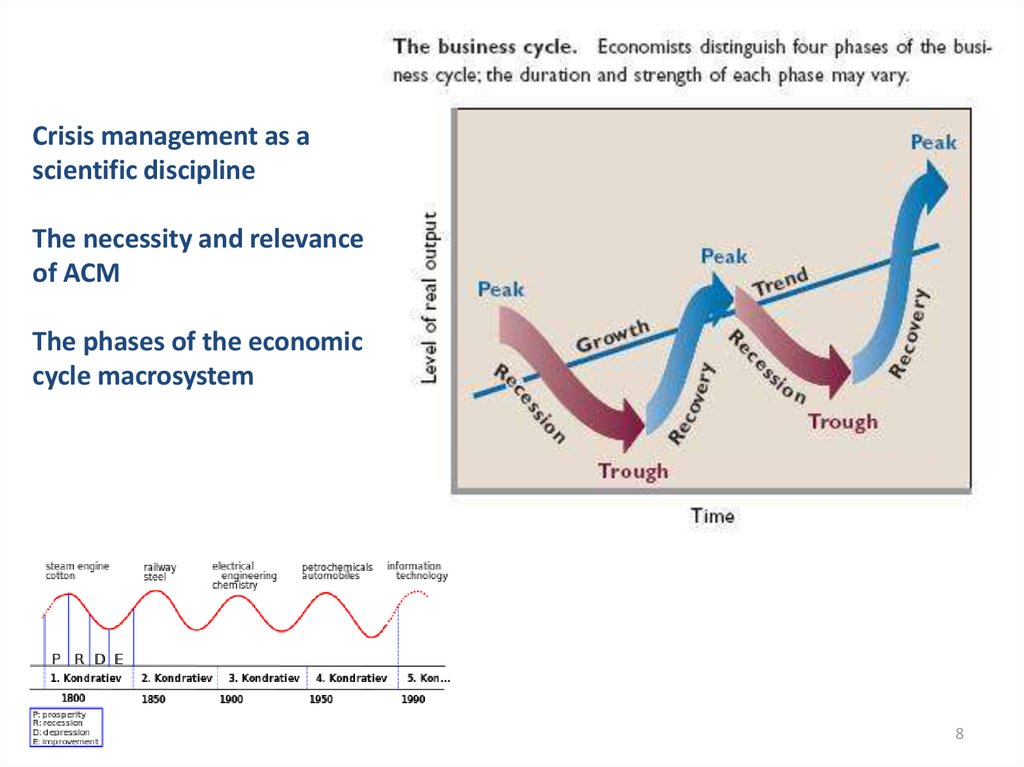
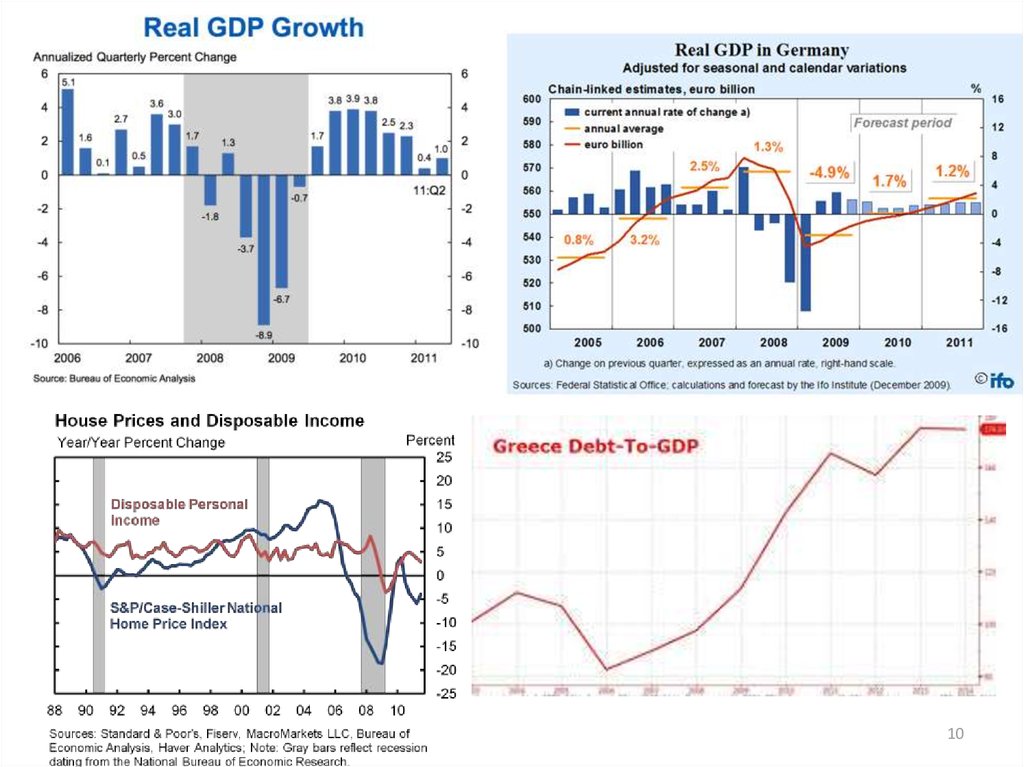
8. Crisis management as a scientific discipline The necessity and relevance of ACM The phases of the economic cycle macrosystem
89.
910.
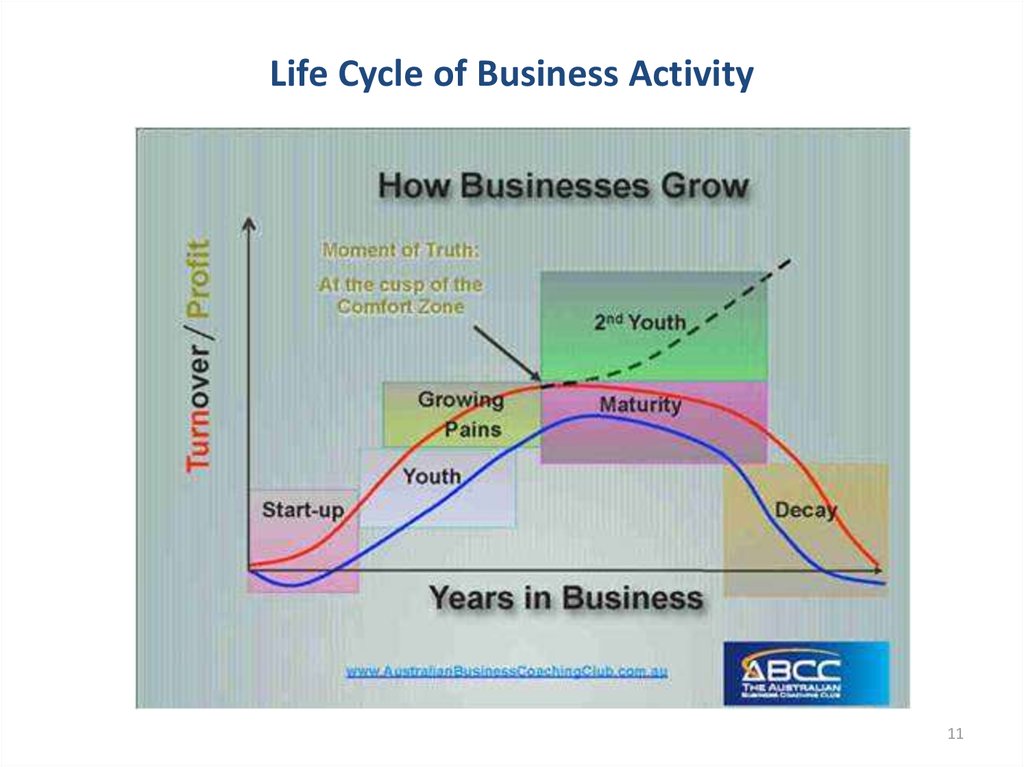
1011. Life Cycle of Business Activity
1112. Разновидности циклов:
1.циклы Кондратьева (Kondratiev waves) —
продолжительностью 40—60 лет, импульсом которых являются
радикальные изменения в технологической базе общественного
производства, его структурная перестройка;
2.
циклы Кузнеца (The Kuznets swing) продолжительностью 20 лет, движущей силой которых выступают
сдвиги в воспроизводственной структуре производства;
3.
циклы Джаглера (The Juglar cycle) - периодичностью 7—11
лет, являющиеся результатом взаимодействия многочисленных
денежно-кредитных факторов;
4.
циклы Китчина (The Kitchin cycle) - продолжающиеся три
— пять лет, порожденные динамикой относительной величины
запасов товарно-материальных ценностей на предприятиях;
5.
частные хозяйственные циклы, охватывающие период от
года до 12 лет и существующие в связи с колебаниями
инвестиционной активности.
12
13. Факторы, обусловливающие цикличность развития предприятий
П. Самуэльсон, книга «Экономика»- денежная теория Хоутри (Hawtrey's Monetary Theory of the Business Cycle),
в которой причина цикличности объясняется сжатием банковского кредита;
- теория нововведений Шумпетера и Хансена (Schumpeter's and Hansen’s
Theory of Innovation,), связывающую зарождение цикла с использованием
нововведений в производстве;
- психологическая теория Пигера, Бэджгота (Psychological Theory of A.Pigou,
Bagehot Walter) и др., рассматривающую цикл как следствие
пессимистических или оптимистических настроений, охватывающих
значительную часть населения;
- теория недопотребления Гобсона, Фостера, Кэтчингса и др. (John
A. Hobson, Emil Lederer, Waddill Catchings and William Foste), усматривающую
причину цикличности в том, что значительная часть дохода распределяется
богатым и бережливым людям, не рискующим инвестировать свой капитал;
- теория чрезмерного инвестирования Хайека, Мизеcа и др.(Mises-Hayek
overinvestment theory), полагающую причиной цикличности неадекватное
инвестирование деятельности предприятий;
- теория солнечных пятен Джевонса, Мура (W.S. Jevons, H.R.Moore) и др.,
которые уверены в том, что волнами в экономике управляют погода и урожай.
13
14. The essence of the Anti-crisis management
• ACM - it is a complex management system to prevent oreliminate negative effects for the business through the use of
the full potential of modern management.
• Important thing in the ACM - providing conditions to prevent
the crisis. With this approach, management mechanism is
directed at eliminating the problems until it received crisis
character.
• The basis of ACM - the triad of "people-product-profit." When
decision of a problem the product anti-crisis marketing comes
to the fore, the essence of which - the transformation of the
buyer's needs in the income of the enterprise.
14
15. Definition by Professor Korotkov E.M.
• Anti-crisis Management - is management, whichdelivered in a certain way foreseeing the danger of
the crisis, the analysis of its symptoms, measures to
reduce the negative effects of the crisis and its use of
factors for further development
• The subject of the ACM are occurring problems in
the social and economic systems, acute
contradictions, the expected and real factors of the
crisis, threatening to their existence or cardinally
reduce the effectiveness of the activity
15
16. The effective ACM covers various aspects of the process
• Assets (liabilities) of the enterprise;• Stages of the business process;
• Programs to protect the property and safety of
the business;
• Personnel;
• Social issues;
• Programs of relations with shareholders;
• Program of information support
16
17. Tasks of ACM
• Ensuring a strong market position and stablesustainable finance;
• Application of the most effective management
tools in solving current problems of the
company;
• Regular and consistent innovation at all levels
of the company.
17
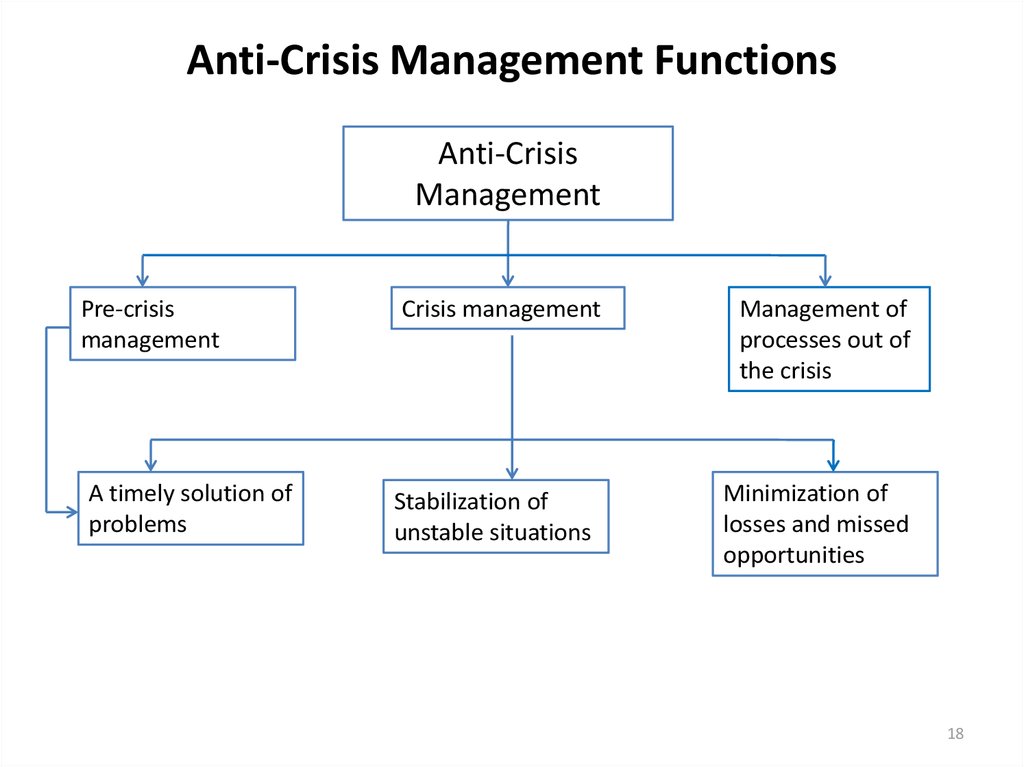
18. Anti-Crisis Management Functions
Anti-CrisisManagement
Pre-crisis
management
A timely solution of
problems
Crisis management
Stabilization of
unstable situations
Management of
processes out of
the crisis
Minimization of
losses and missed
opportunities
18
19. Basic requirements to ACM system
• Flexibility and adaptability• Priority of informal governance
Integration
• Finding the most effective means and methods of
management
• Reduction of centralism for ensuring situational
reaction
• Concentration of efforts for a more efficient use of
the capacity of the enterprise (organization) and
others.
19
20. The basic principles of ACM
• Early diagnosis of the crisis in the enterprise• The timely response to the crisis
• The adequacy of management reaction to the level
of a real threat to the economic development of the
enterprise
• Full mobilization and implementation of the
company's own opportunities to exit from crisis
20
21.
Assignment1 Part. Study the lecture material
Questions of seminars (workshops)
● The necessity and relevance of ACM
● Life Cycle of organization
● Functions of ACM
● Basic requirements for ACM system
● The basic principles of the ACM
2 Part. Assignment
1) Identify eight key industries of Kazakhstan
2) Ranked by their degree of dependence on external crises
3) Provide at least 5 companies in each industry and their products
21

















 management
management








