Similar presentations:
Air transport
1. Slajd 1
TRANSPORTLOTNICZY
AIR TRANSPORT
Imię i nazwisko: Urszula Żugaj
Grupa projektowa: II
Trener: Barbara Frącek
Kompetentny ekonomista i logistyksukces na rynku edukacyjno – zawodowym!
Człowiek – najlepsza inwestycja!
1
2. Slajd 2
Co to są środkitransportu ?
To maszyny transportowe lub istoty żywe, dzięki
którym możliwe
jest przemieszczanie ludzi lub ładunków, czyli transport.
Pod pojęciem transport rozumiemy przewóz ładunków i
pasażerów,
bez względu na to, czy odbywa się on regularnie, czy też nie.
Pojęciem tym nie obejmujemy przekazywania
wiadomości na odległość (telefon, fax, internet, poczta, radio,
telewizja),
co tworzy odrębną grupę zwaną łącznością. Transport
i łączność tworzą razem komunikacje.
Transport odgrywa doniosłą rolę w kształtowaniu
i rozwoju geograficznego podziału pracy pomiędzy
poszczególnymi
regionami, wiążąc je w jedną całość geograficzną.
Szczególne znaczenie ma rejestracja na mapach sieci
i urządzeń transportowych, jak również kierunków
i nasilenia przewozów.
2
Zmiany te odpowiadają w pewnej mierze przemianom
3. Środki transportu dzielą się na :
► środki transportu dalekiego• środki transportu lądowego pojazdy
pojazdy szynowe
pojazdy samochodowe
pojazdy jednośladowe (motocykle, rowery)
• środki transportu wodnego
śródlądowego
morskiego
• środki transportu specjalnego (poduszkowiec,
amfibia)
• środki transportu lotniczego
► środki transportu bliskiego (urządzenia dźwigowo
transportowe)
• urządzenia dźwigowe (dźwignice)
• urządzenia transportowe (wózki i przenośniki
3
4. Transport lotniczy w Polsce
Transport lotniczy obsługuje głównietransport międzynarodowy (zbyt mały
obszar kraju)
Polska utrzymuje regularną komunikację
lotniczą z 54 miastami w 34 państwach
Główny przewoźnik w Polsce to Polskie Linie
Lotnicze "LOT„ ( posiadają one 42 samoloty )
Polskie samoloty są głównie wynajmowane
4
5. Transport lotniczy na świecie
Największą liczbą samolotówdysponuje USA (16770), Kanada
(4490), Wielka Brytania (2642)
W przewozach lotniczych
największe znaczenie mają
transatlantyckie połączenia
pomiędzy Europą Zach. i Ameryką
Pół. USA i Kanadą, z Ameryką
Kompetentny ekonomista i logistykŚrodkową,Południową, Japonią i
sukces na rynku edukacyjno – zawodowym!
Australią.
Człowiek – najlepsza inwestycja!
5
6. Cechy konstrukcyjne samolotów
Ogólne określenie charakterystycznych rozwiązań zastosowanych przybudowie określonego samolotu. Mogą dotyczyć między innymi:
► ilości płatów są to samoloty: jednopłatowe, dwupłatowe,
trójpłatowe,
► umocowania na kadłubie głównego płatu są to samoloty: dolnopłaty,
średniopłaty, górnopłaty;
► ilości zamontowanych silników są to samoloty: jednosilnikowe,
dwusilnikowe, trójsilnikowe, czterosilnikowe, wielosilnikowe;
► ilości kadłubów są to samoloty: jednokadłubowe, dwukadłubowe;
► umocowania płatu są to samoloty: wolnonośne, zastrzałowe;
► rodzaju podwozia są to samoloty: z podwoziem stałym, z podwoziem
chowanym.
► przeznaczenia: towarowe, pasażerskie, cywilne, osobiste, bombowe,
myśliwskie
► sposobu prowadzenia są to samoloty: załogowe, bezzałogowe
6
7. Podział środków transportu lotniczego ze względu na przeznaczenie :
Samoloty pasażerskie,Samoloty towarowe ,
Samoloty wojskowe
7
8. Samoloty pasażerskie
89. Samoloty towarowe
910. Samoloty wojskowe
1011. Największe porty lotnicze na świecie
1112. Porty lotnicze w Polsce
1213. Zalety transportu lotniczego
uważany za najbezpieczniejszy rodzajtransportu (współczynnik wypadków
bardzo mały w stosunku do
samochodów)
szybki czas przelotu
w niewielkim stopniu wpływa na
środowisko
coraz niższe ceny biletów
Punktualność i rytmiczność transportu
Największa prędkość podróżna
13
14. Wady transporty lotniczego
Ryzyko ataków terrorystycznychDuża wrażliwość na warunki klimatyczne
Bardzo wysokie koszty transportu
Ograniczona dostępność przestrzenna
Konieczność wykorzystania usług dowozowo
odwozowych
14
15. What are the means of transport?
What are the means oftransport?
These are machines or people thanks to which/whom relocation of people and cargo is possible. Transport
means carrying cargo and passengers, regardless of whether it takes place on a regular basis, or not.
The concept does not refer to transmission of information by telephone, fax, internet, mail, radio, television,
which create a separate group called means of communications.
Transport plays an important role in shaping and development of the geographical division of labor between
particular regions. Registration of transport devices and equipment, as well as directions and severity of
traffic, on network maps has significant importance.
These changes correspond to economic changes occurring on particular areas.
15
16. The means of transport are divided into :
The means of transport aredivided into :
► Distant transport
• means of land transport vehicles
rail vehicles
motor vehicles
single
track vehicles (motorcycles, bicycles)
• water transport
inland
marine
• special transportation (hovercraft,
amphibious vehicles )
• air transportation
► nearby transport (cranes and
transport equipment)
• lifting equipment (cranes)
• transport equipment (hand
carts and conveyors)
16
17. The means of transport are divided into :
The means of transport aredivided into :
► Distant transport
• means of land transport vehicles
rail vehicles
motor vehicles
single
track vehicles (motorcycles, bicycles)
• water transport
inland
marine
• special transportation (hovercraft,
amphibious vehicles )
• air transportation
► nearby transport (cranes and
transport equipment)
• lifting equipment (cranes)
• transport equipment (hand
carts and conveyors)
17
18. Air transport in Poland
Air transport in PolandAir transport serves mainly international
transport (too small area of the country)
Poland maintains regular air transportation with 54 cities in
34 countries
The main carrier in Poland is Polish Airlines "LOT" (they
have 42 aircraft)
Polish aircraft are mainly leased
18
19. Air transport in the world
Air transport in the worldThe USA has the largest number of aircraft
(16,770), the next is Canada (4490), and the
UK (2642)
In air transport the most important are the
transatlantic links between western Europe and
North America and the U.S.A
and Canada, central America, Japan
and Australia.
19
20. Construction features of aircraft
A general description of typical solutions used in theconstruction of certain aircraft.They can relate to, inter alia:
►the number of wings these are monoplanes and bioplanes
► fastenings of the main wing on the fuselage
►the number of installed engines these
are single, twin, threeengined, fourengined, multiengined
planes
► quantity of fuselages these are: single, doublefuselaged
planes
► attachment of wings
► types of undercarriage these are the planes
with fixed and retractable undercarriage
► purpose: freight, passenger, civil, personal, bomber, fighter
► the way of operating these are manned and unmanned
planes
20
21. Division of means air transport due to the use:
Division of means airtransport due to the use:
Passenger
aeroplanes
Freight
aeroplanes
Military
planes
21
22. Passenger Aeroplanes
2223. Freight Aeroplanes
Freight Aeroplanes23
24. Military planes
Military planes24
25. The largest airports in the world
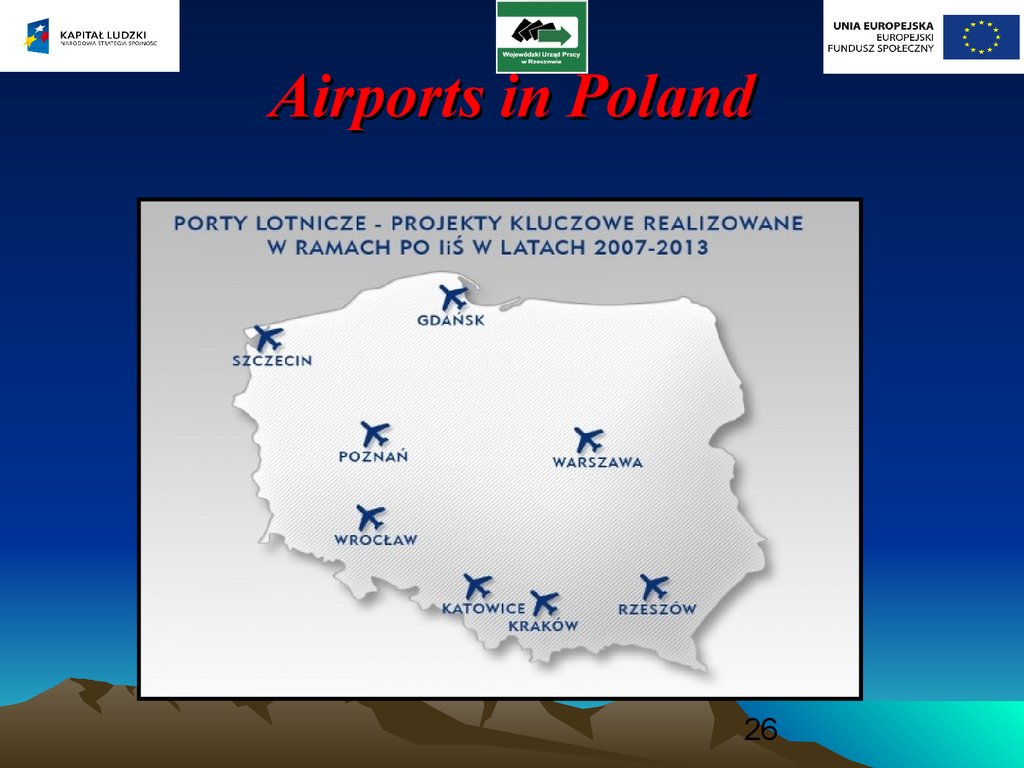
2526. Airports in Poland
Airports in Poland26
27. Advantages of air transport
Advantages of air transportregarded as the safest mode of transport
(the rate of accidents is very small in relation to cars)
fast time of flight
has little effect on the environment
lower and lower fares
punctuality and rhythm of transport
the biggest cruising speed
27
28. Disadvantages of air transport
Disadvantages of air transportthe risk of terrorist attacks
high sensitivity to climatic
conditions
very high transport costs
limited availability of space
necessity of using
ground services
28
29. Slajd 29
Thank you for yourattention =]
29



























 management
management industry
industry








