Similar presentations:
Intro_to_Economics_Demand_Supply_3 (1)
1. Introduction to Economics
Demand & SupplyJanet McCaig
2. The Price Mechanism
• What determines demand?• What determines supply?
• What is the relationship between demand & supply?
3. Law of Demand
• “The quantity of a good demanded per period oftime will fall as price rises and will rise as price falls,
all other things being equal (ceteris paribus)”
• WHY?
4. The Income Effect
• The effect of a change in price on quantity demandedarising from the consumer becoming better or worse
off as a result of the price change.
• People feel poorer the purchasing power of their
income has fallen
5. The Substitution Effect
• The effect of a change in price on quantity ofdemand arising from the consumer switching to or
from alternative (substitute) products
6. The Demand Curve
• A graph showing the relationship between the priceof a good and the quantity of the good demanded
over a given period of time.
• Constructed on the assumption that all other things
remain equal.
7. The Demand Curve
PriceDemand
Quantity Demanded
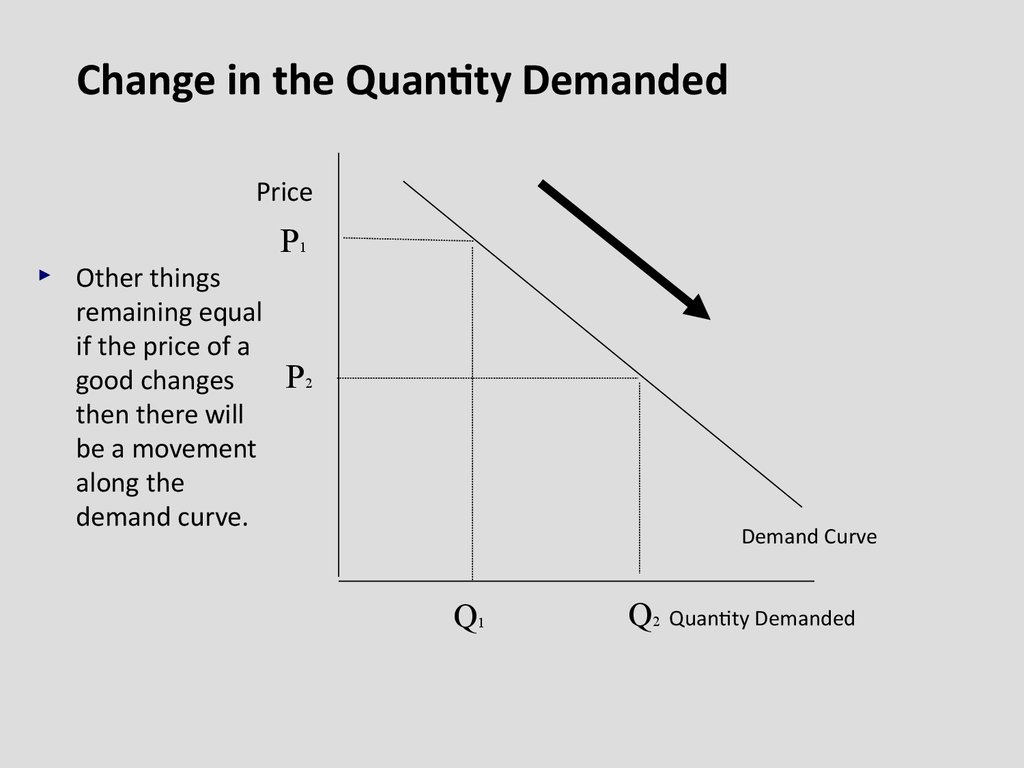
8.
Change in the Quantity DemandedPrice
P1
Other things
remaining equal
if the price of a
good changes
then there will
be a movement
along the
demand curve.
P2
Demand Curve
Q1
Q2 Quantity Demanded
9. Change in Demand
• A shift in the demand curve• If there is a change in one of the other determinants
i.e. income rises a new demand curve needs to be
constructed.
10. Change in Demand
Normal Goods• As income rises the demand for most goods will rise
• Exceptions to this rule Inferior Goods (super market
value ranges)
11. Normal Goods
Demand other factorsTastes
The number and price of substitute goods
The number and price of complementary goods
Income
Distribution of income
Expectations of future price changes
12. Demand other factors
DemandOther things may not always remain equal
Demand determined by other factors
Will cause the pattern of demand to alter
Changes in the demand curve are shown as a shift to either
the right or left of the original demand curve
• A change in demand can cause demand to fall at each and
every price, i.e. a shift to the left
• Or a change in demand can cause demand to increase at each
and every price, i.e. a shift to the right.
13. Demand
Supply• The amount of a good or service a firm wants to sell,
and is able to sell per unit time.
14. Supply
Schedule• Table showing the different quantities of a good that
producers are willing and able to supply at various
prices over a given time period
15. Supply Schedule
Supply Curve• A graph showing the relationship between the price
of a good and the quantity of the good supplied over
a given period of time.
• If the price of a good increases suppliers increase the
quantity supplied.
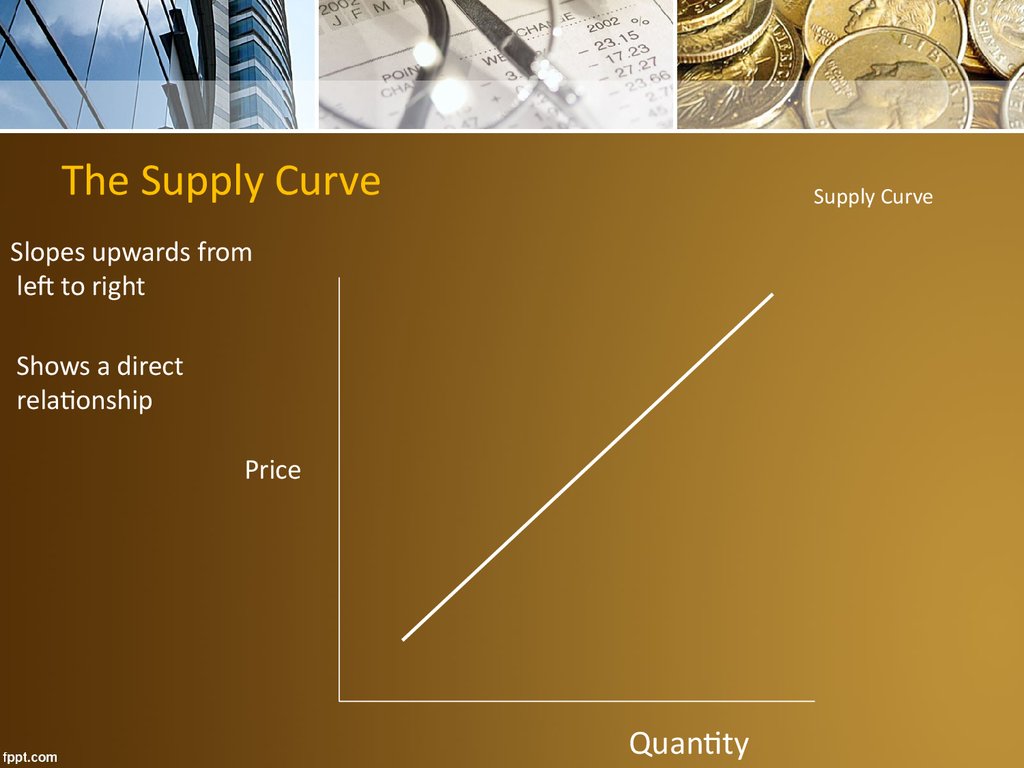
16. Supply Curve
The Supply CurveSupply Curve
Slopes upwards from
left to right
Shows a direct
relationship
Price
Quantity
17. The Supply Curve
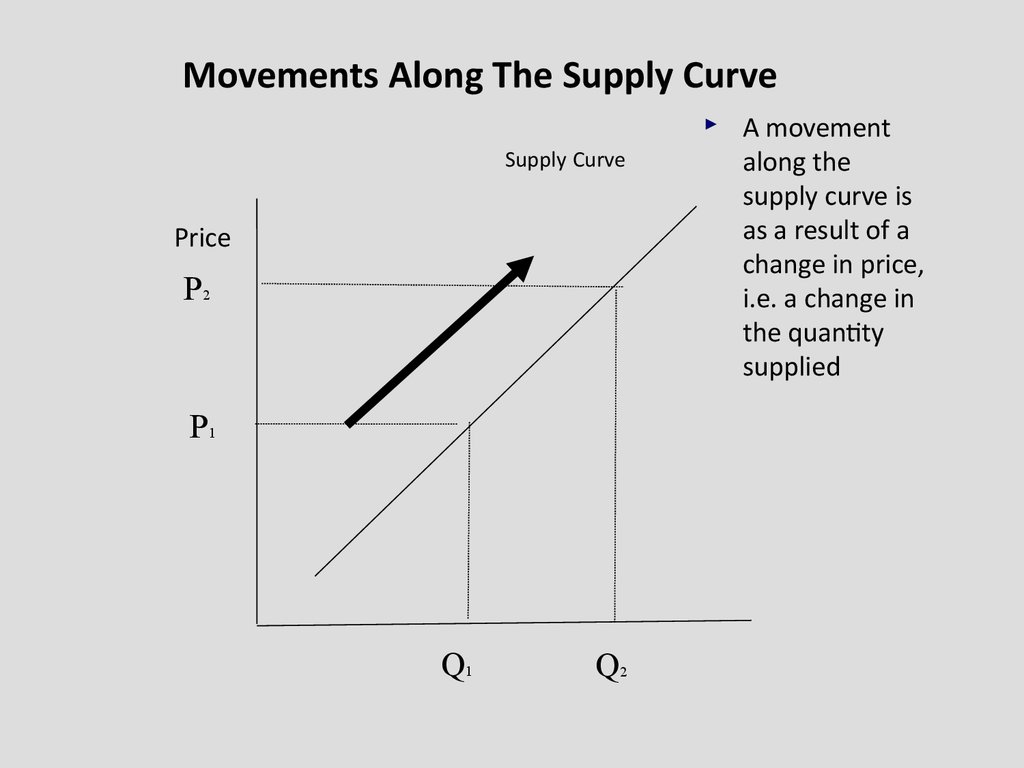
Movements Along The Supply CurveSupply Curve
Price
P2
P1
Q1
Q2
A movement
along the
supply curve is
as a result of a
change in price,
i.e. a change in
the quantity
supplied
18.
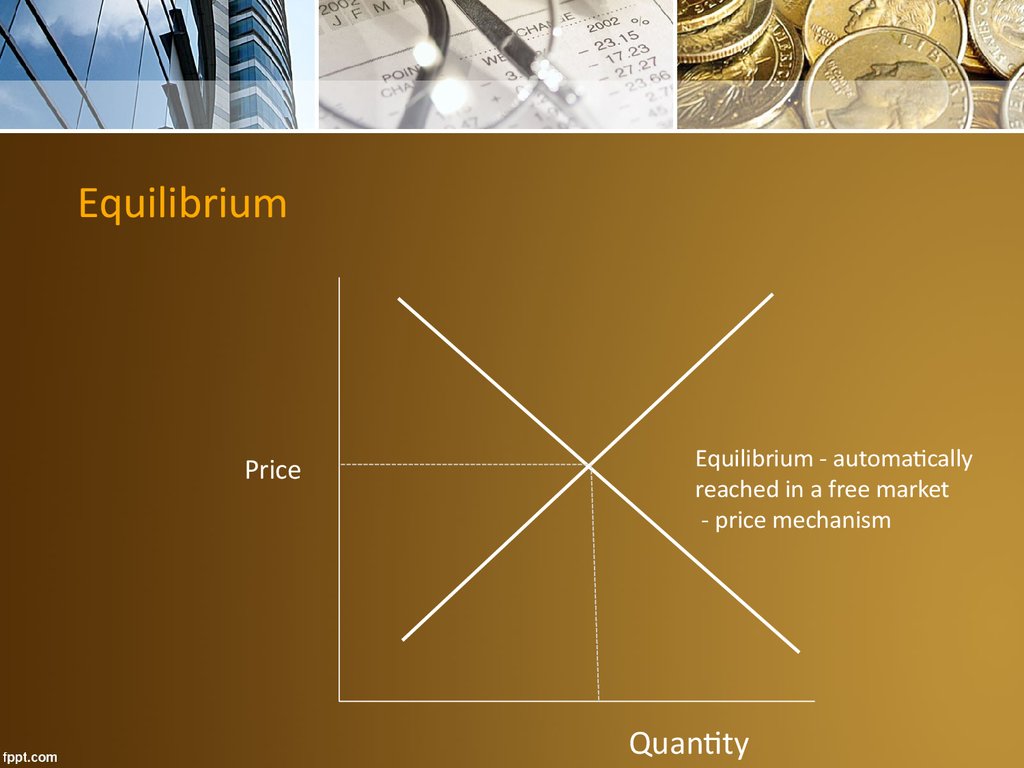
Equilibrium• The point where conflicting interests are balanced
• The amount that demanders are willing to purchase
is the same as the amount suppliers are willing to
supply.
• This point is automatically reached in a free market
through the operation of the price mechanism
19.
EquilibriumPrice
Equilibrium - automatically
reached in a free market
- price mechanism
Quantity
20. Equilibrium
Activities• Pg 11 & 12 students book
















 economics
economics








