Similar presentations:
Historical geography of the United Kingdom. (Lecture 2)
1.
Lecture 2HISTORICAL
GEOGRAPHY OF
THE UNITED
KINGDOM
2.
PLAN1.England.
2.Wales.
3.Scotland.
3.
4.Ireland.5.Oversees
colonies.
6.Decolonisation.
4.
5.
1. England.6.
3000 - 2000 BC Stonehenge was built.7.
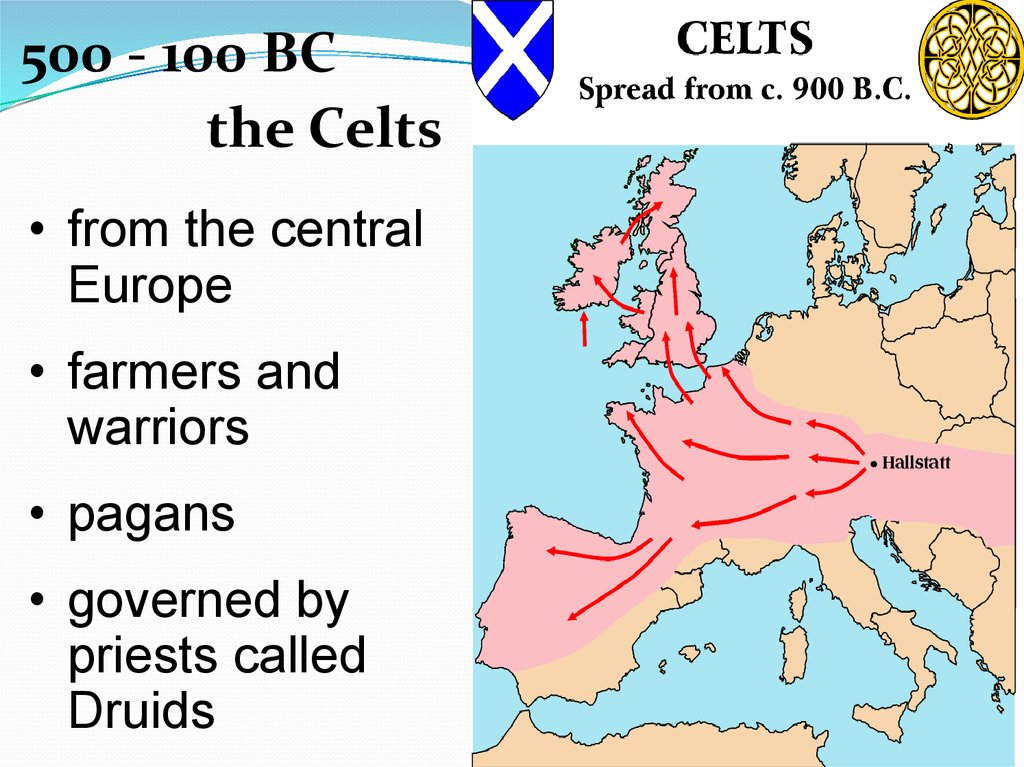
500 - 100 BCthe Celts
• from the central
Europe
• farmers and
warriors
• pagans
• governed by
priests called
Druids
8.
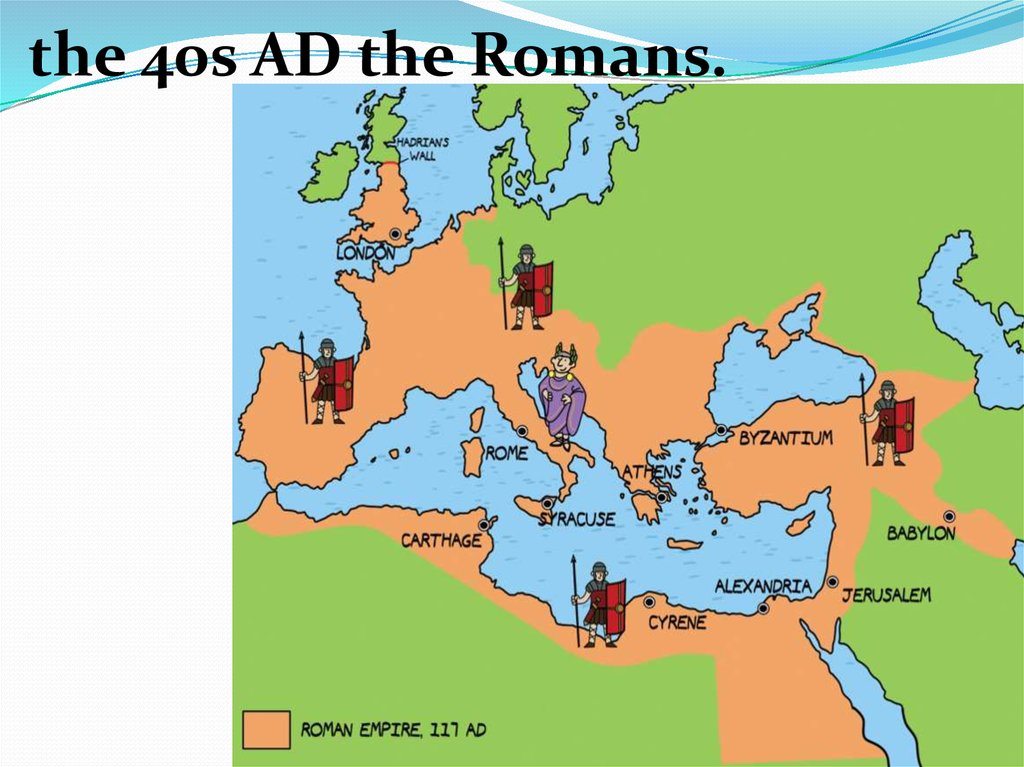
the 40s AD the Romans.9.
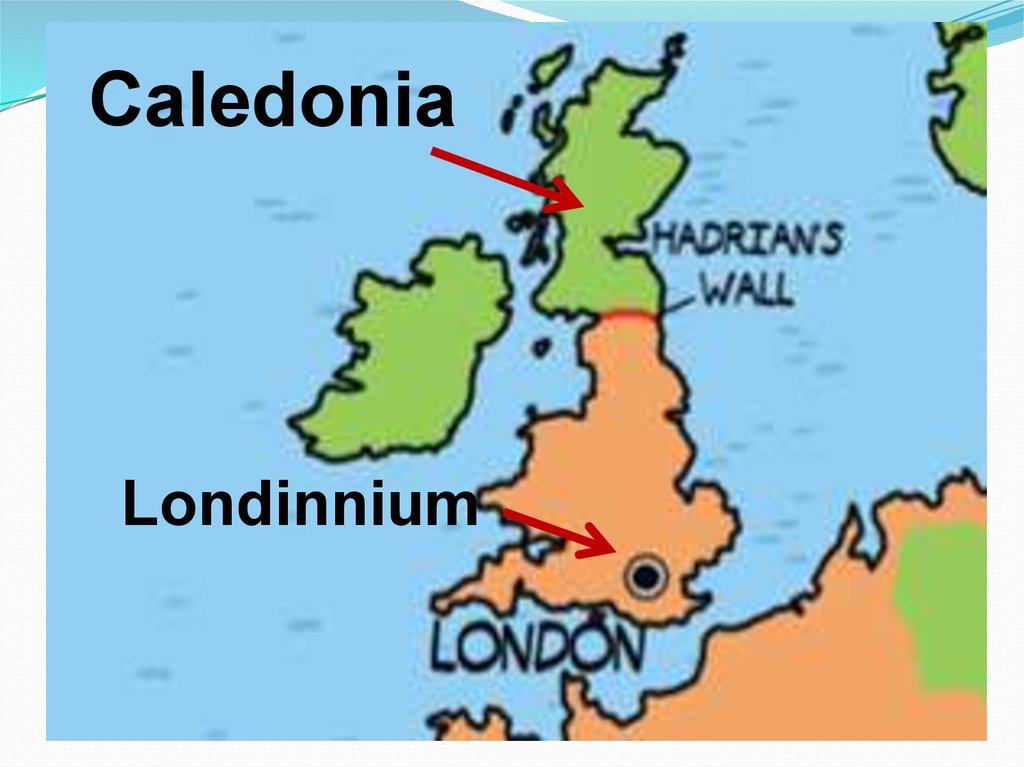
CaledoniaLondinnium
10.
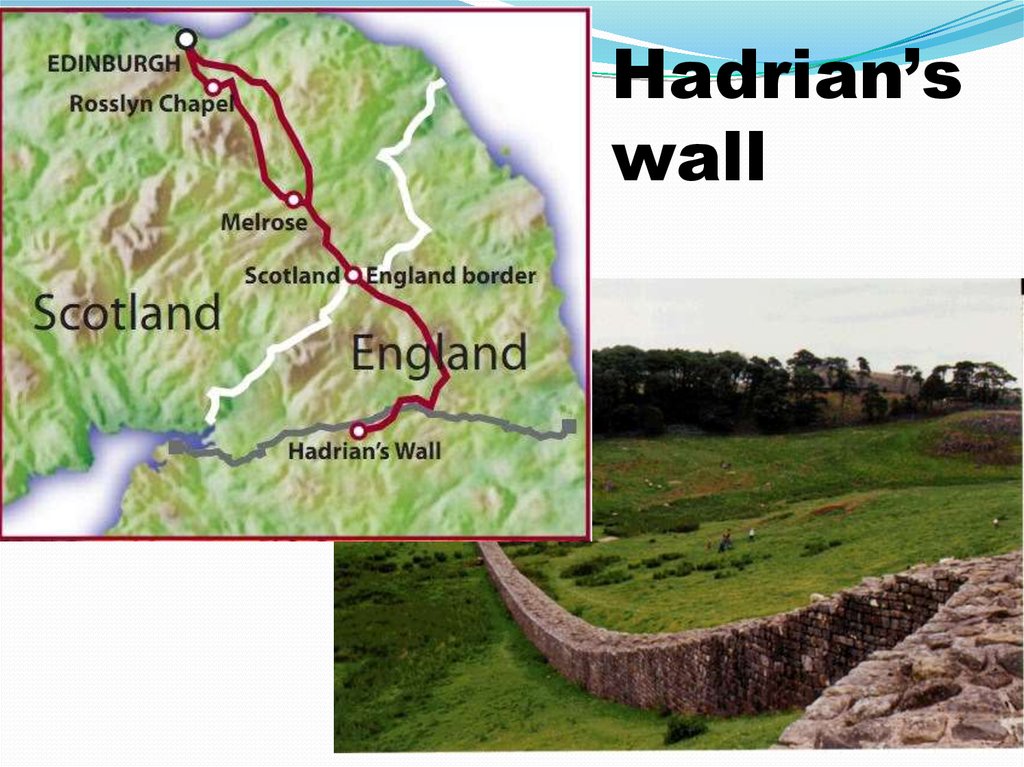
Hadrian’swall
11.
Albionthe white cliffs
of Dover
a Greco-Roman word for the
inhabitants of the islands – “Pretani”,
the Romans called the island
“Britannia”.
12.
Roman influence1) Founded many cities
2)Introduced Christianity
3)Their words survived in
many spheres of life
13.
The Romans unitedthe territories of
modern England and
Wales as one
province!!!
14.
Around 400 ADThe barbaric people
threatened the Roman
Empire
The Romans left the British
Islands
15.
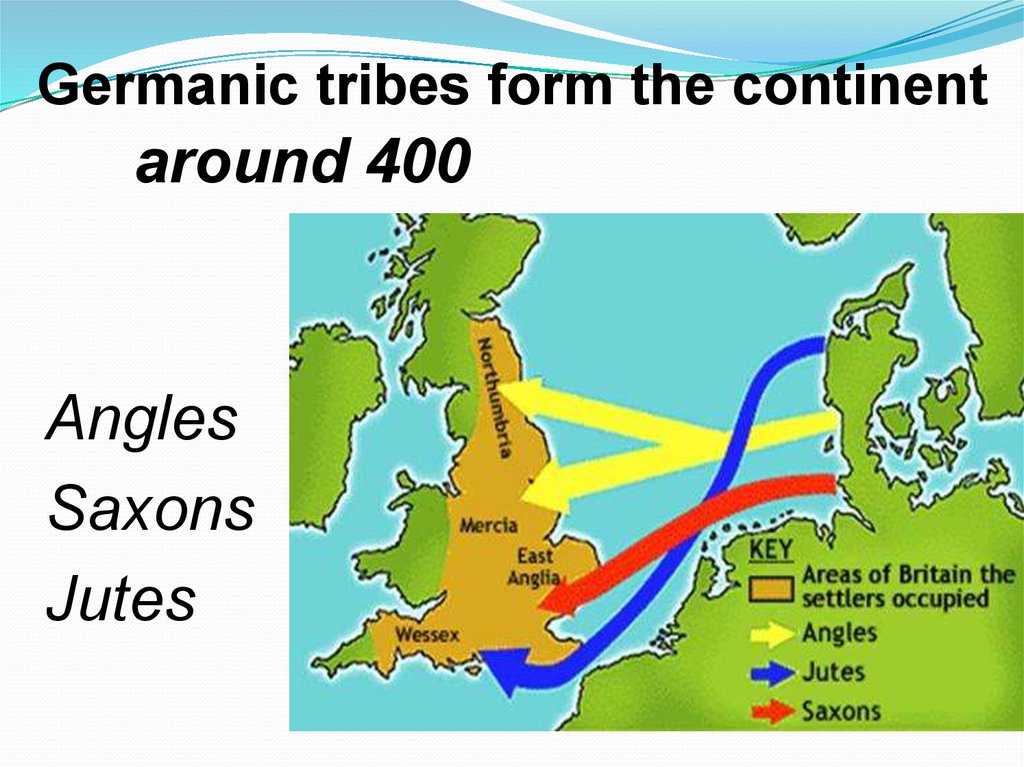
Germanic tribes form the continentaround 400
AD
Angles
Saxons
Jutes
16.
7 Anglo-Saxon KingdomsThe Heptarchy:
• Northumbria
• Mercia
• East Anglia
• Essex
• Wessex
• Kent
• Sussex
17.
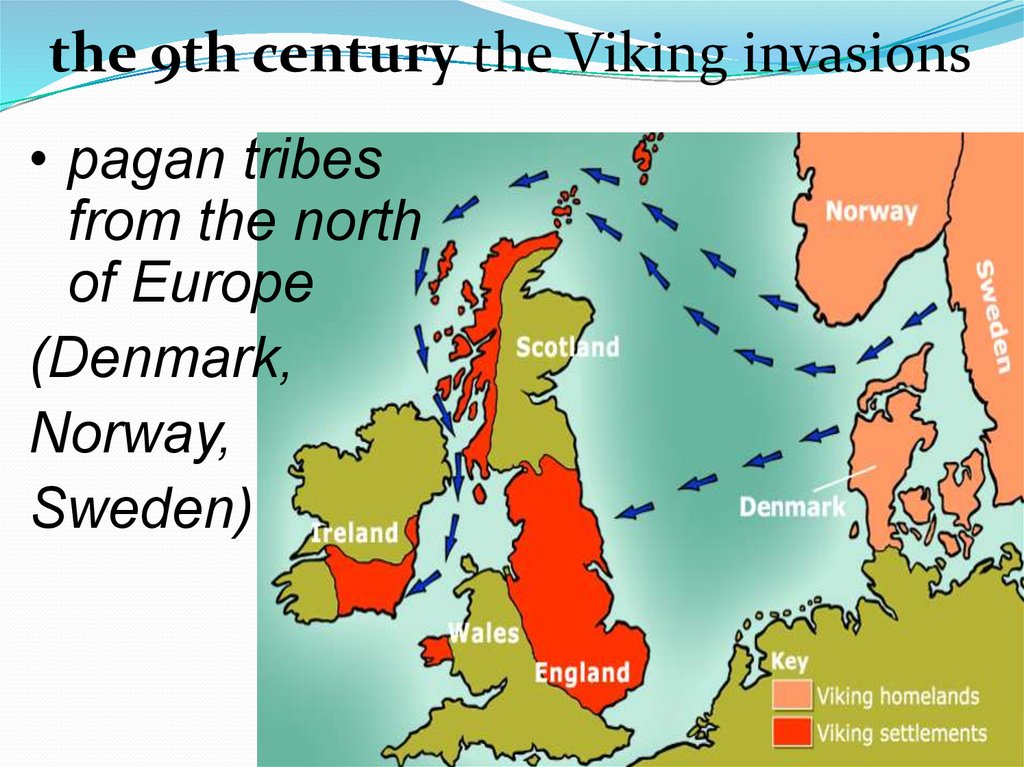
the 9th century the Viking invasions• pagan tribes
from the north
of Europe
(Denmark,
Norway,
Sweden)
18.
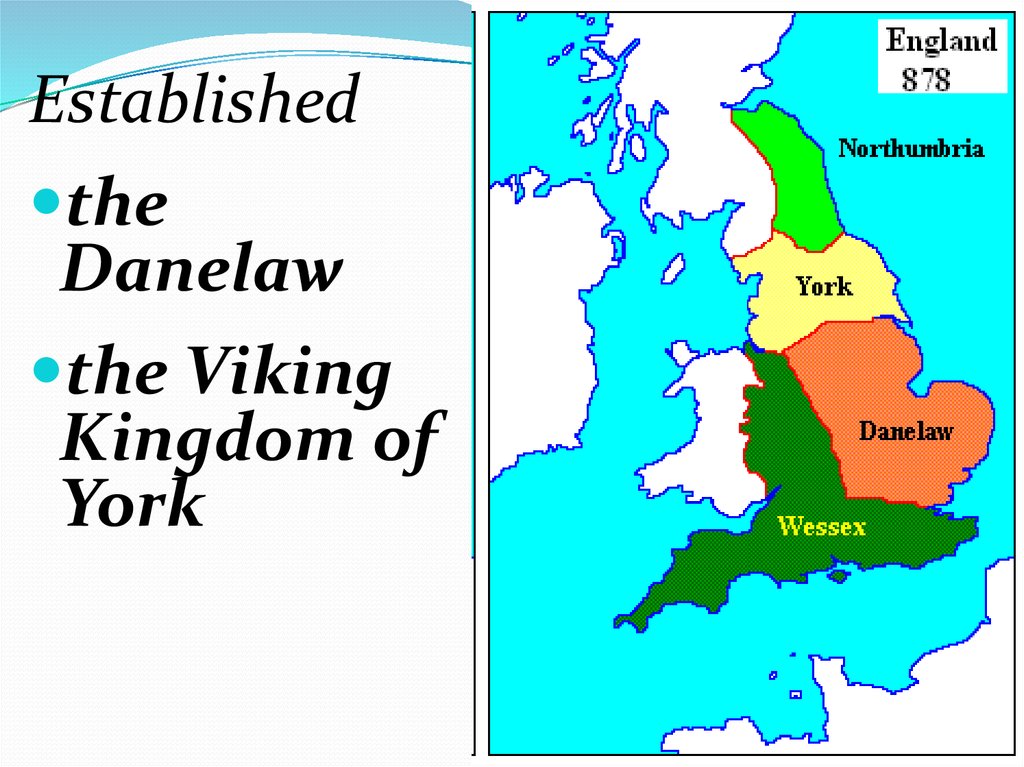
Establishedthe
Danelaw
the Viking
Kingdom of
York
19.
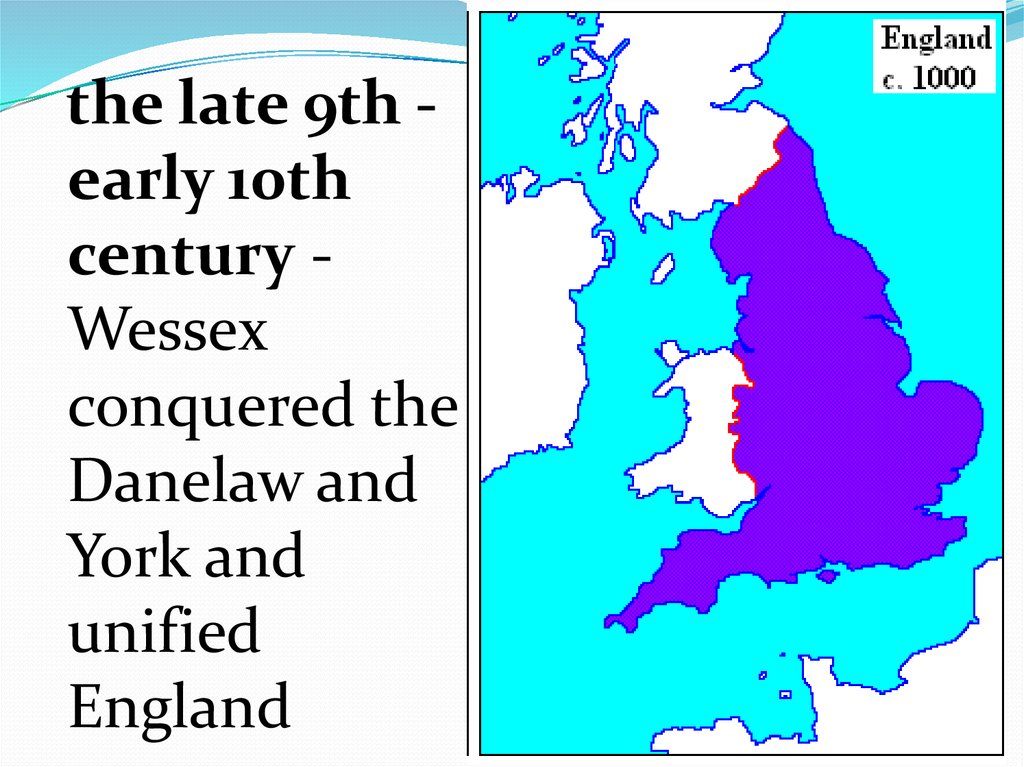
the late 9th early 10thcentury Wessex
conquered the
Danelaw and
York and
unified
England
20.
The dominating tribe –the Saxons (Germanic
people)
Germanic stems in
modern English
21.
the 11th centurythe Norman
invasion
William, Duke of
Normandy
Edward the
Confessor
22.
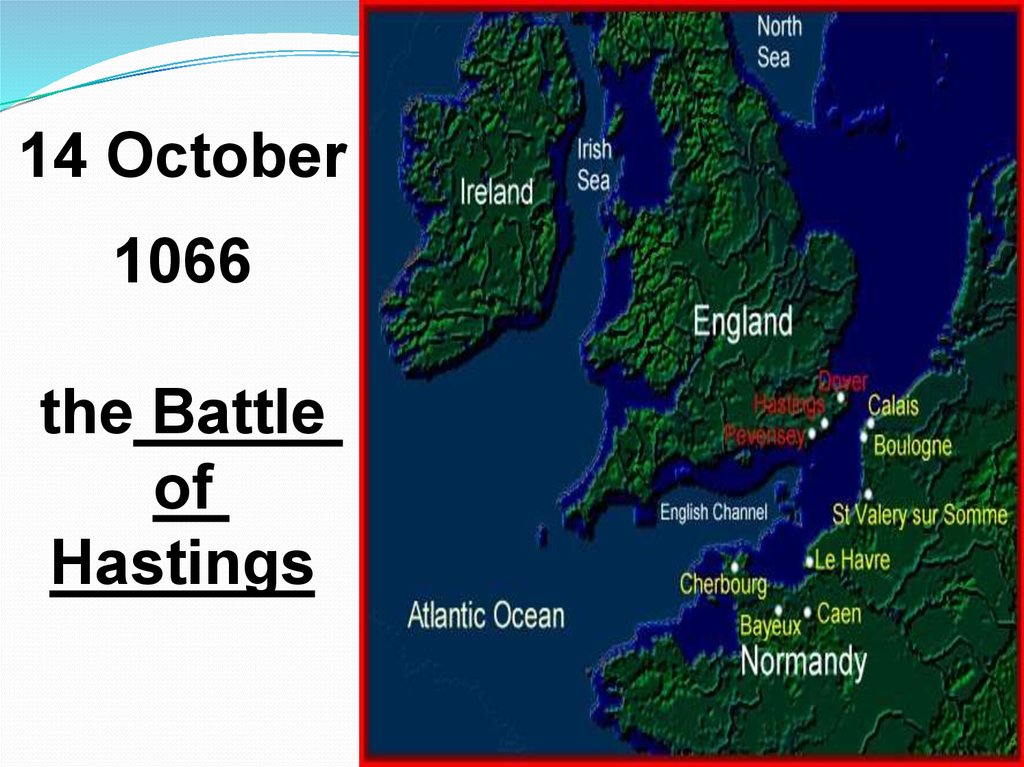
14 October1066
the Battle
of
Hastings
23.
TheNormans
The
Saxons
24.
KingHarold was
killed
His army
lost the
battle
25.
Christmasday 1066
William was
crowned as
king at
Westminster
Abbey.
26.
Norman influence:1) Anglo-Saxon nobility
was replaces by the
Norman nobility.
27.
2) 3 languages:•Norman-French – literature +
nobility
•Latin – the government and the
church
•Anglo-Saxon – common people
28.
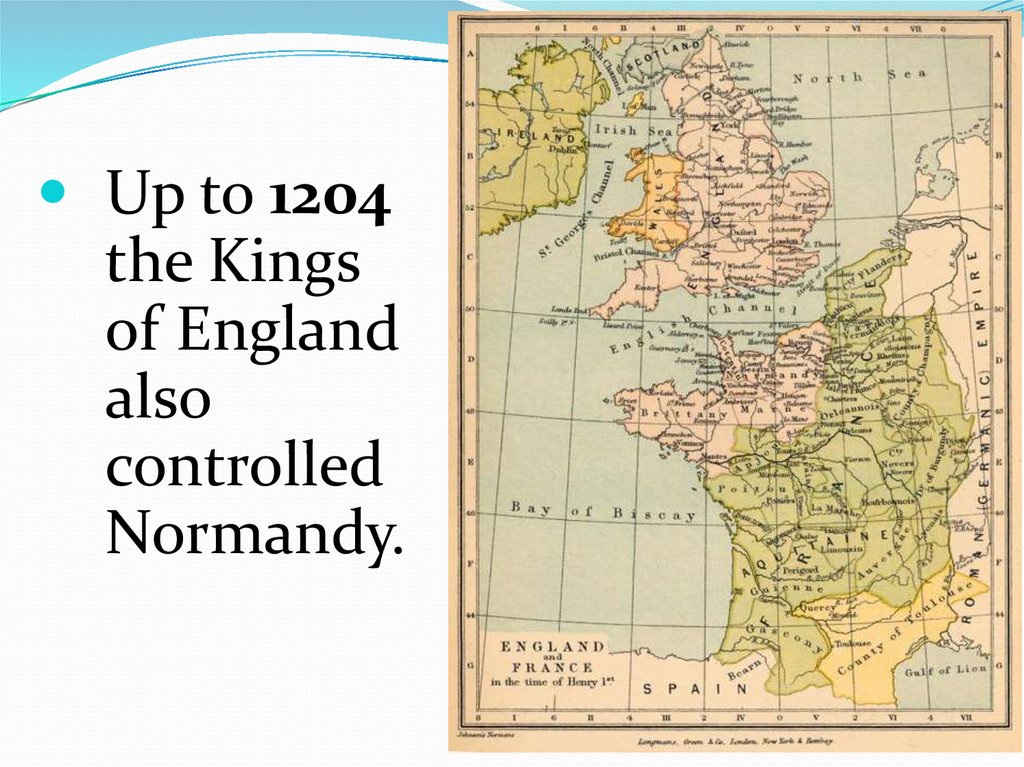
Up to 1204the Kings
of England
also
controlled
Normandy.
29.
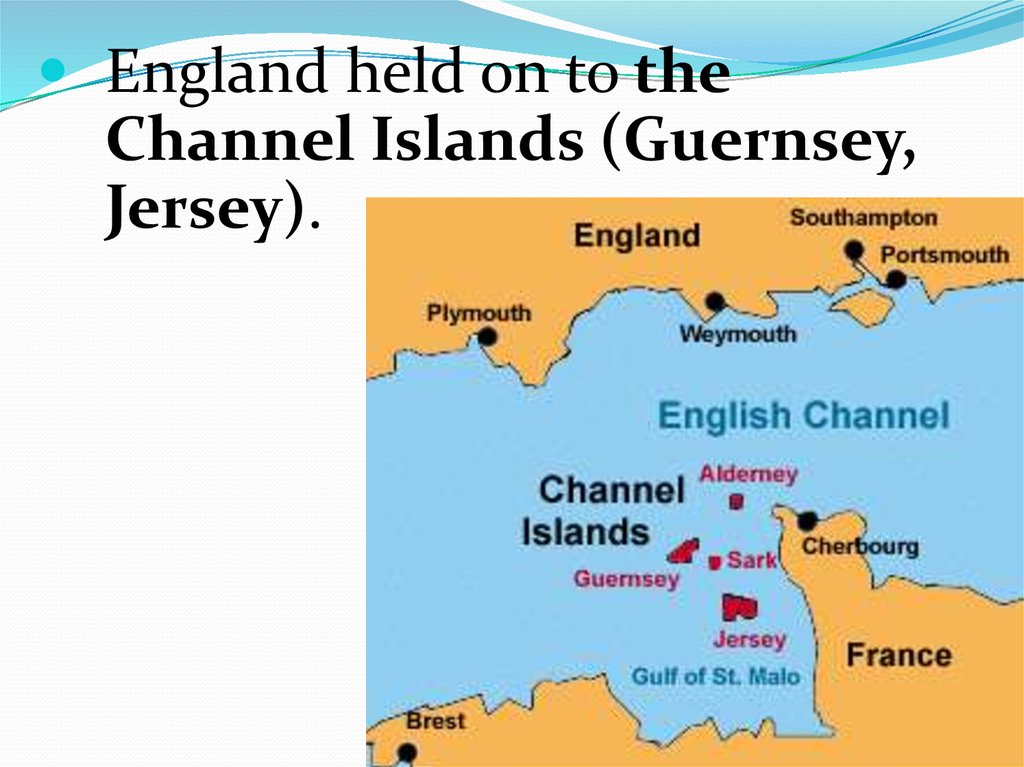
England held on to theChannel Islands (Guernsey,
Jersey).
30.
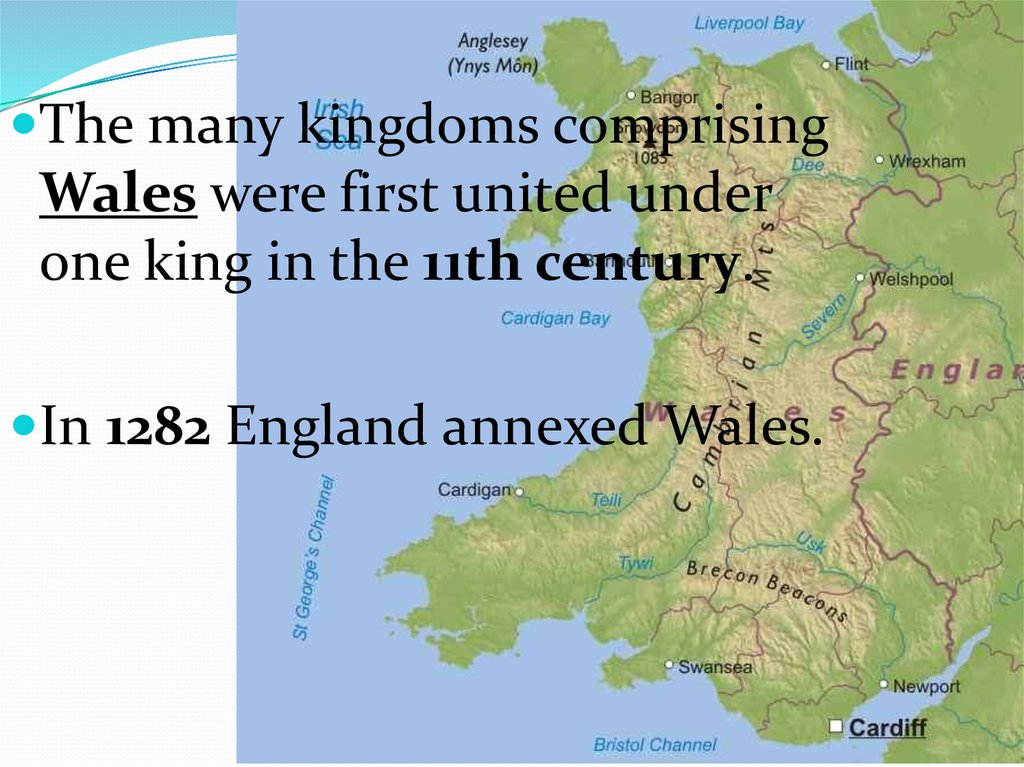
2. Wales.31.
The many kingdoms comprisingWales were first united under
one king in the 11th century.
In 1282 England annexed Wales.
32.
And in 1301 the traditionof heir to English throne
being given the title of
Prince of Wales began.
33.
1455 - 1485 the houses of Lancaster andYork, were fighting for the throne of
England.
The Wars of the Roses
York’s white
rose
Lancaster’s red
rose
34.
in 1485 a relativelyremote Lancastrian
relative, Henry Tudor
defeated the last
Yorkist king Richard III
started the new royal
dynasty, the House of
Tudor (married
Elizabeth of York,
Richard’s niece)
35.
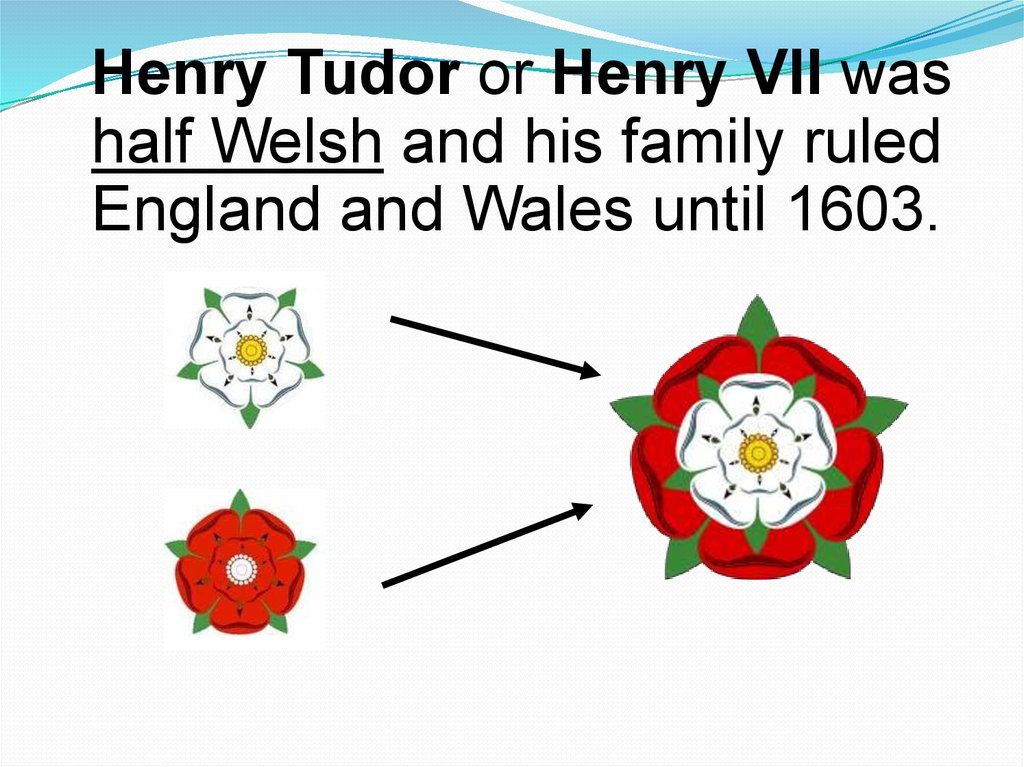
Henry Tudor or Henry VII washalf Welsh and his family ruled
England and Wales until 1603.
36.
1536 the Act of Unionofficially annexed Wales
to England
Welsh law was fully
replaced by English law.
37.
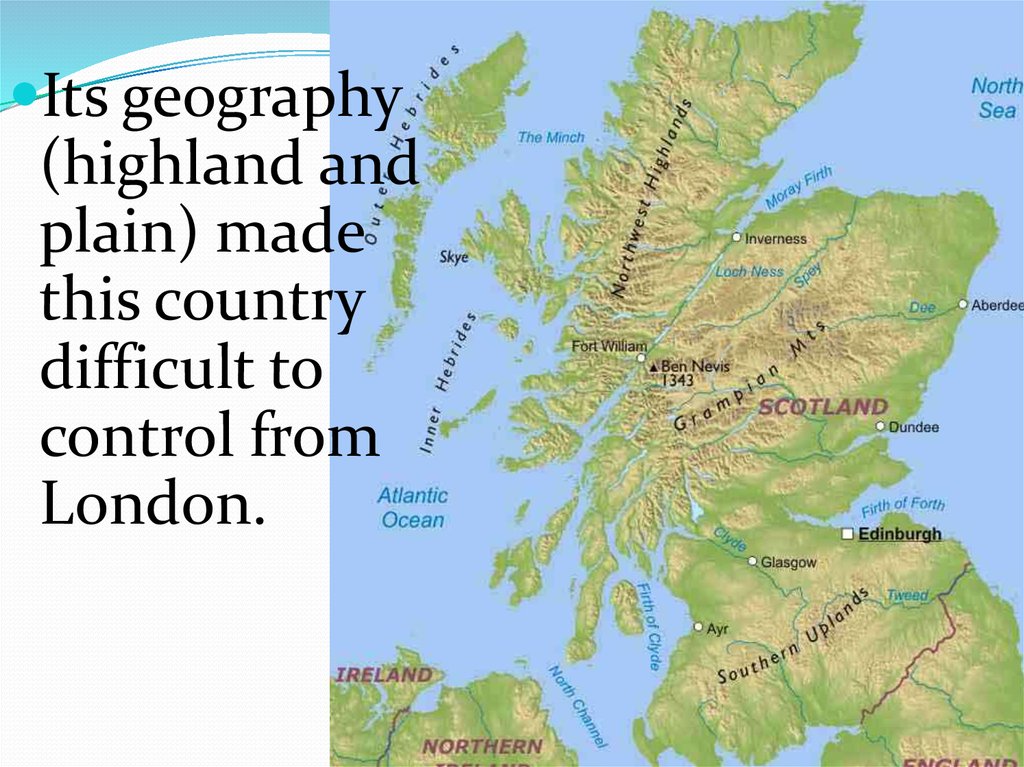
3. Scotland.38.
Its geography(highland and
plain) made
this country
difficult to
control from
London.
39.
Attempts toannex
Scotland led
to national
liberation
uprisings.
40.
In 1296 kingEdward I envaded
Scotland and stole
the Scottish Stone
of Destiny on which
according to the
legend all Scottish
kings must sit.
41.
The Scottishcoronation
stone remained
at Westminster
Abbey until it
was returned to
Scotland in
1996.
42. The
Attemptsto
return
Scottish
The
independence in the 15ht and
th
16 century failed.
Constant conflicts on the
Scottish-English border.
43.
Scotland still had its ownking and queen.
The Scottish royal family, the
Stuarts, were related to the
English royals, the Tudors,
through marriage.
44.
the 16th century Henry VIII6 wives
1491-1547
45.
46. Henry’s reforms:
Conflict with the Pope about hisdivorce
Broke up with the Roman church
Proclaimed himself the Head of the
Church
Started the Anglican church
47.
Henry’s sonEdward VI
1537-1553
48.
Queen Mary I ofEngland.
A Catholic.
Killed a lot
protestants
of
Her sister
Elizabeth I
illegitimate
Bloody Mary
child
She
died
A
Protestant
childless
in
November 1558.
49.
MaryStuart,
queen of ScottsHenry VIII's great
niece.
a constant threat
for Elizabeth’s
throne
accused of
treason, arrested
and beheaded
50.
Elizabeth I diedchildless
in 1603 Mary Stuart's
son, became James I
of England.
•A new dynasty started – the
dynasty of the Stuarts.
51.
A Union of Crowns, a situationwhen England, Scotland and
Ireland were sovereign states, with
one monarch.
52.
Acts of Union of 1707 duringthe reign of the last Stuart
monarch, Queen Anne:
the English and Scottish
parliaments were replaced by a
combined Parliament of Great
Britain;
a full economic union,
replacing the Scottish systems
of currency, taxation and laws
regulating trade.
53.
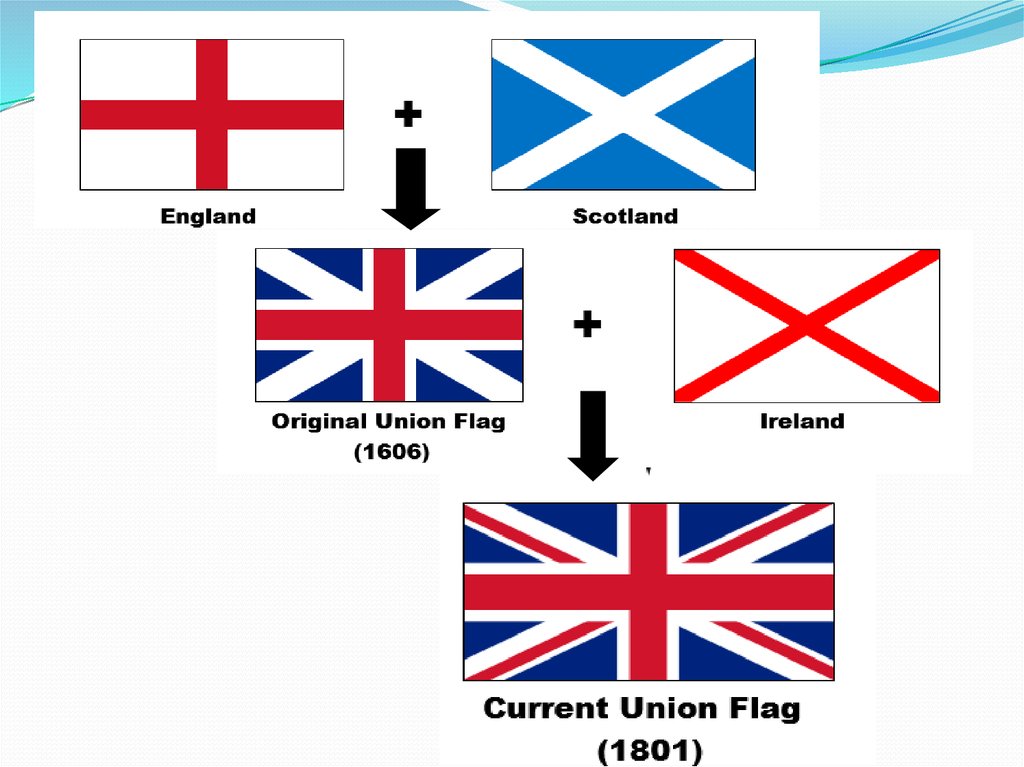
The flag of the Kingdomof Scotland.
The flag of the Kingdom
of England.
Union Flag used in the Kingdom of England from 1606-1707
54.
4. Ireland.55.
In the early 11th century Irelandwas also ruled by one king, Brian
Boru, who was also later killed in
battle.
• In 1171 the English
monarch Henry II
proclaimed himself
Lord of Ireland.
56.
In the 17th centuryIreland was
completely colonized
by the English.
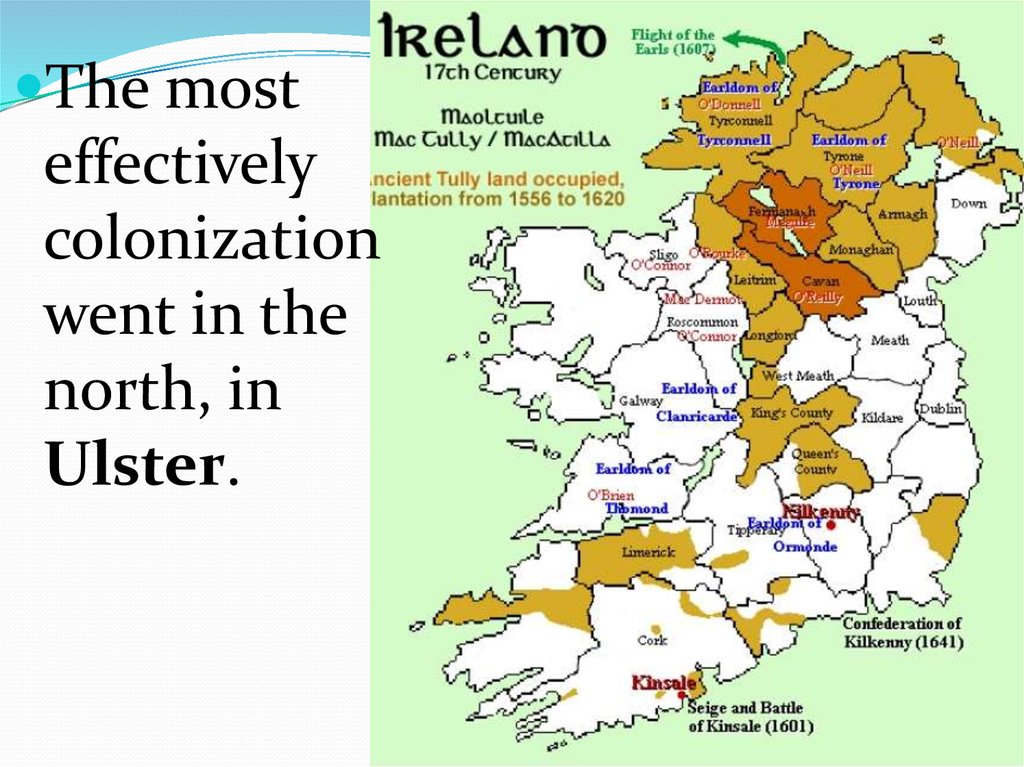
57.
The mosteffectively
colonization
went in the
north, in
Ulster.
58.
In 1801 it merged withthe Kingdom of Great
Britain to form
the United Kingdom of
Great Britain and
Ireland.
59.
60.
At the beginningof the 20th century
Irish liberation
movement achieved
success.
61.
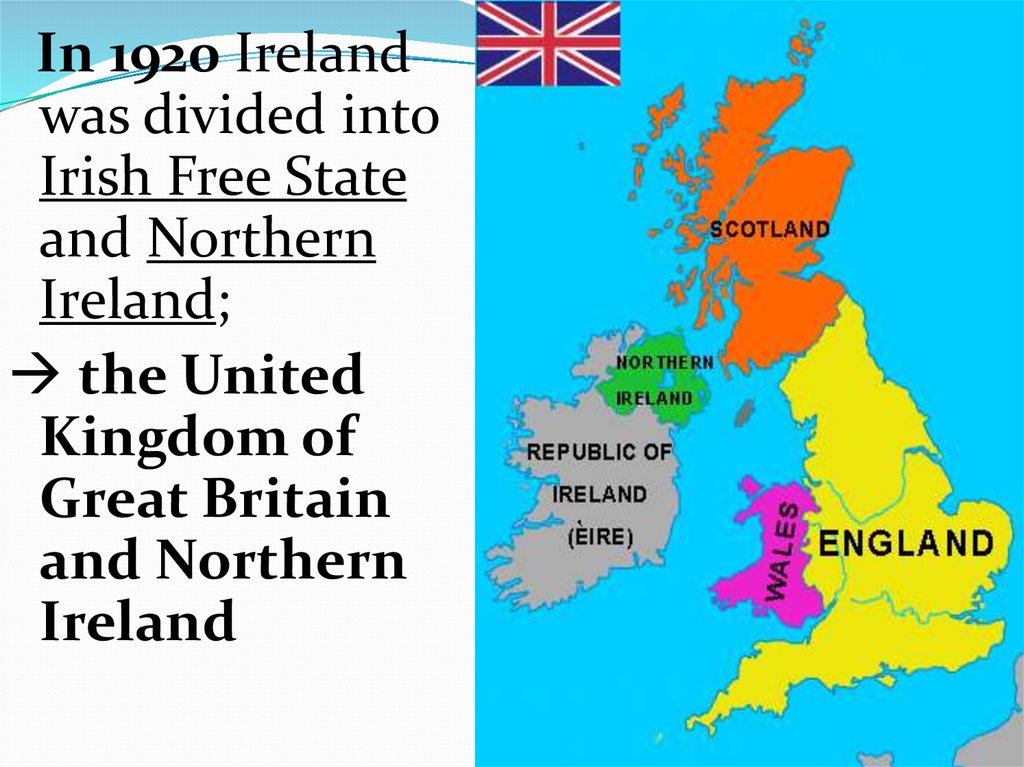
In 1920 Irelandwas divided into
Irish Free State
and Northern
Ireland;
the United
Kingdom of
Great Britain
and Northern
Ireland
62.
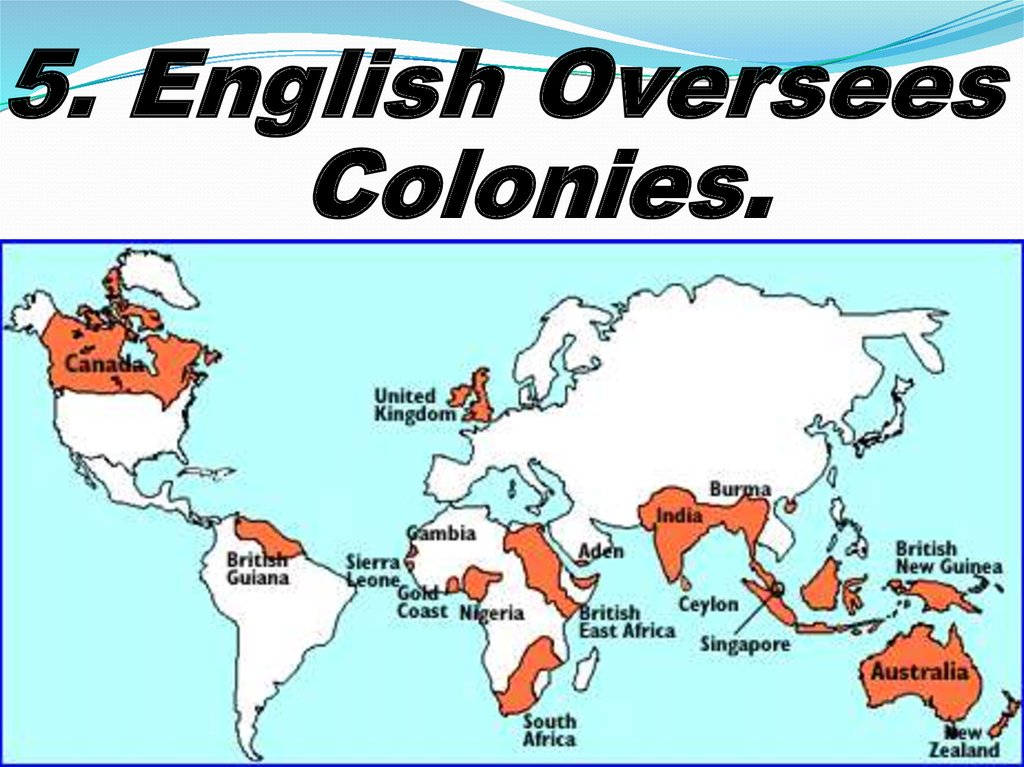
5. English OverseesColonies.
63. North America
64.
1492 Christopher Columbusdiscovered America.
1496 King Henry VII of
England sent British ships to
the new lands.
They reached the coast
of Newfoundland.
65.
The 1580s the 1stEnglish
settlements in
America
In the 18th century
the British
colonies occupied
the territories
along the Atlantic
coast and around
Hudson Bay.
66.
during the 1760s and early 1770srelations between the Thirteen
Colonies and Britain became
increasingly complicated,
the British Parliament tried to
govern and tax American colonists
without their agreement (they
were not represented in the British
Parliament).
67.
Boston TeaParty
December 16, 1773
the Americans revolted
against tea tax and
through all chests of
tea from ships into
Boston Harbor.
68.
The American RevolutionIn response Britain sent the
army to control the colonies and
in 1775 the War for
Independence started.
In 1776, the United States
declared independence.
69. Australia
70.
1606 the westerncoast of Australia
were 1st discovered
by the Dutch and
named New Holland
1770 James Cook
discovered the
eastern coast of
Australia, claimed
the continent for
Britain,
He named it New
South Wales.
71.
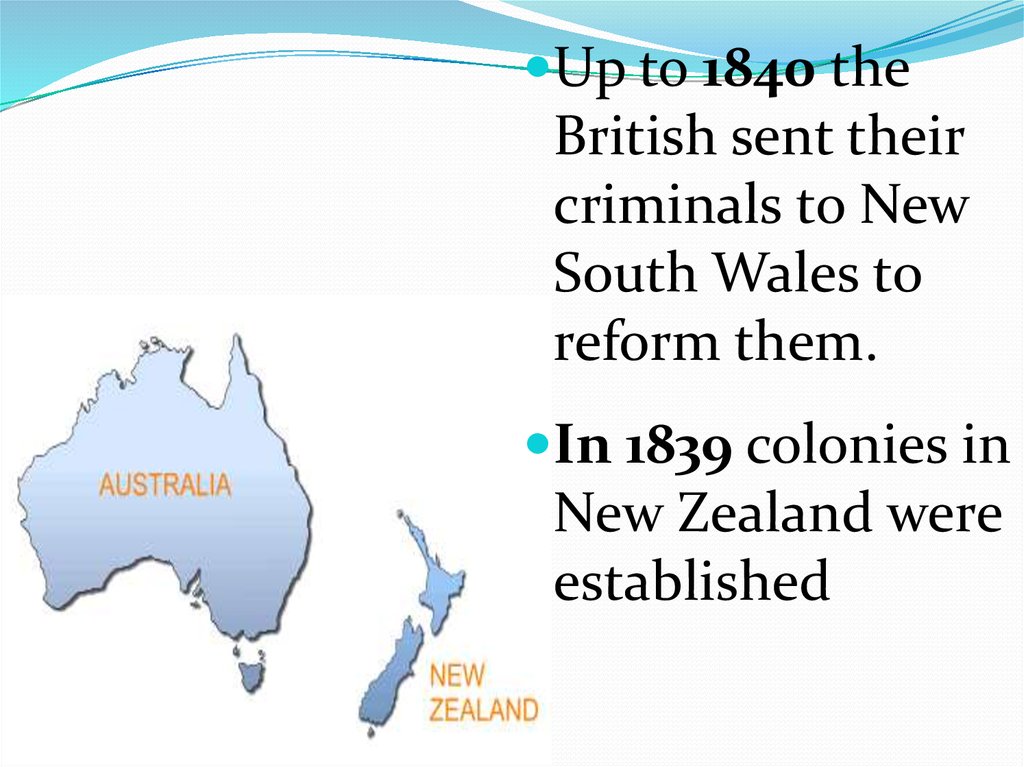
Up to 1840 theBritish sent their
criminals to New
South Wales to
reform them.
In 1839 colonies in
New Zealand were
established
72. India
73.
In 1858 QueenVictoria was
crowned the
Empress of India.
"the Jewel in the
Crown"
74.
1815 - 1914 around26,000,000 km2 of territory
and roughly 400 million
people were added to the
British Empire
75.
76.
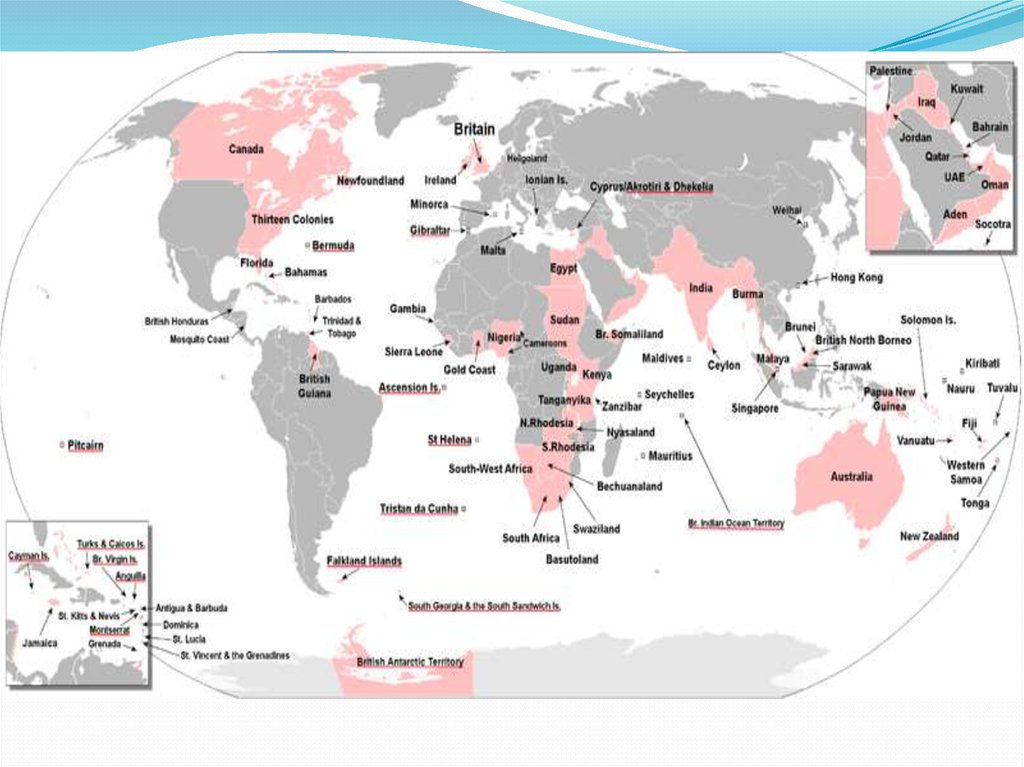
6. Decolonisation.77.
Between 1945 and 1965 most ofthe former British colonies were
given independence.
78.
The number of peopleunder British rule outside
the UK itself fell from
700 million to 5 million,
3 million of whom were in
Hong Kong.
79.
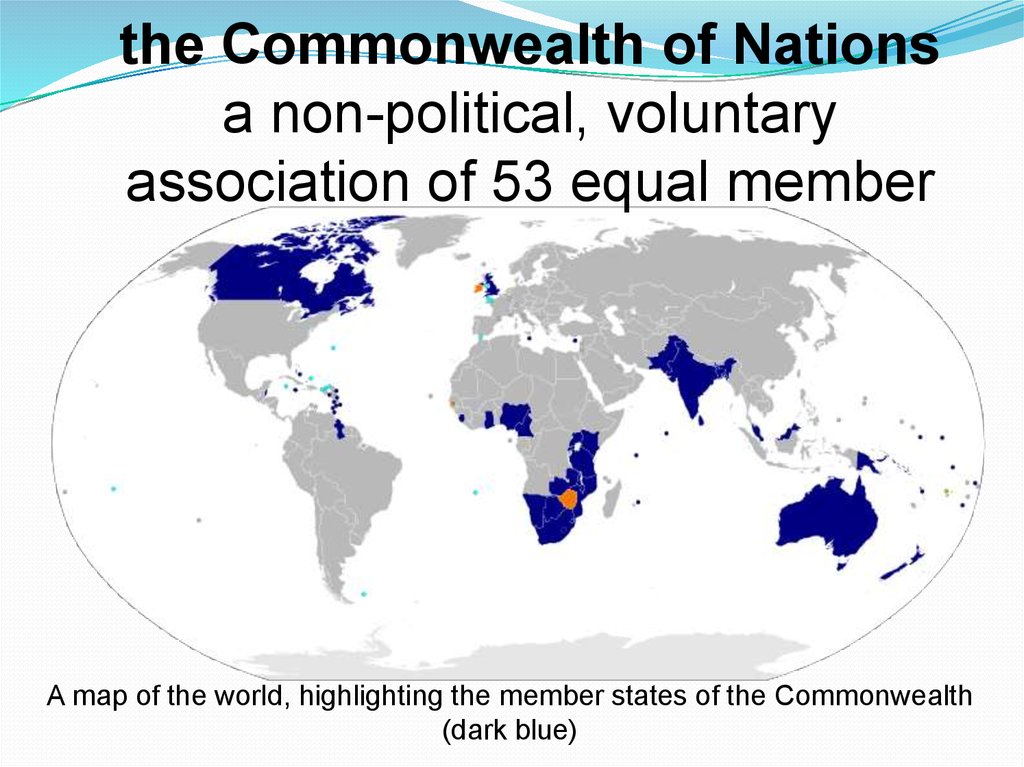
the Commonwealth of Nationsa non-political, voluntary
association of 53 equal member
A map of the world, highlighting the member states of the Commonwealth
(dark blue)
80.
81.
Queen Elizabeth II• the Head of the
Commonwealth
• the monarch of
16 members of the
Commonwealth
(realms)
• Australia,
Canada, Jamaica,
New Zealand, etc.
82.
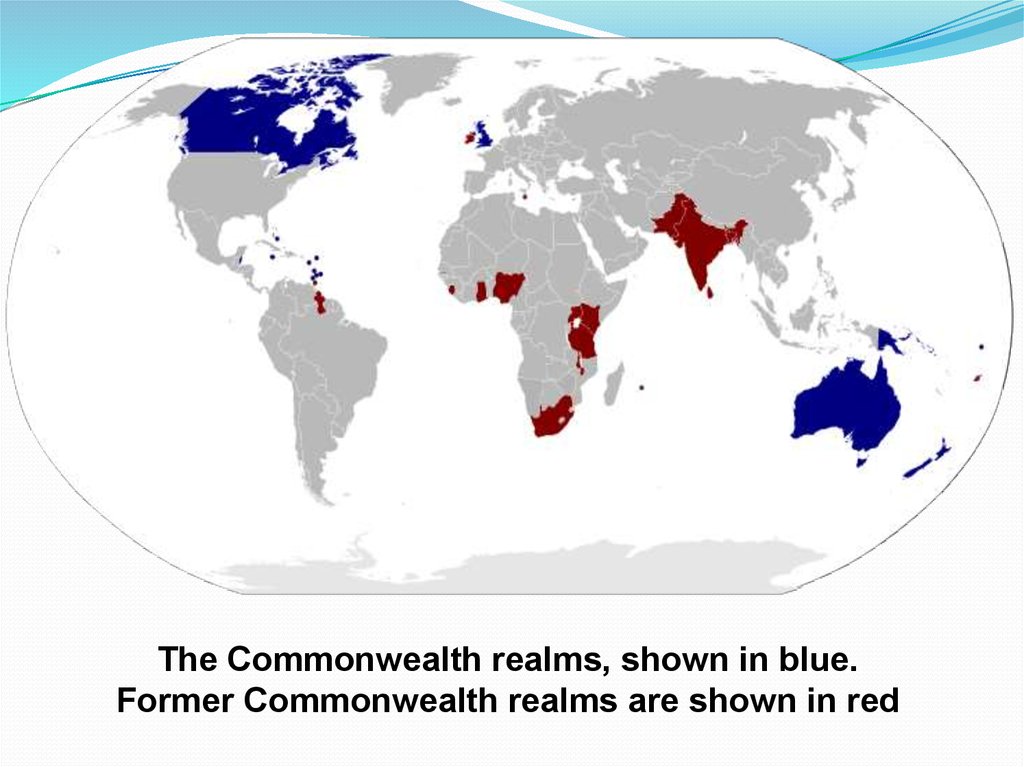
The Commonwealth realms, shown in blue.Former Commonwealth realms are shown in red
83.
The Commonwealth29,958,050 square km (a
quarter of the world land area),
spans all the continents.
population of 2.245 billion, (a
third of the world
population).




























































 history
history geography
geography








