Similar presentations:
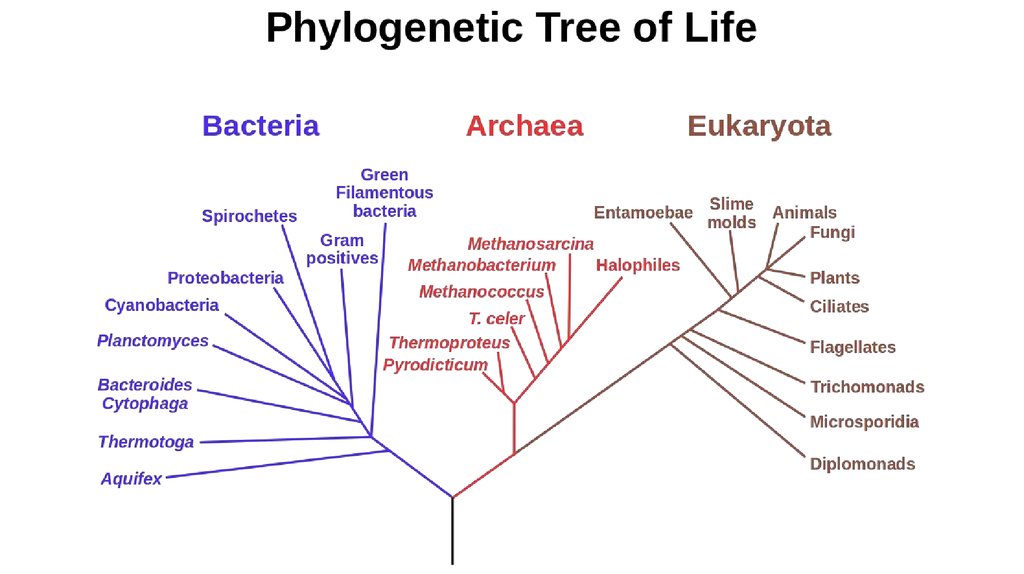
Phylogenetic tree of Life
1.
2. Phylogenetic card (cladogram and phylogenetic tree)
3. Learning objective
•compile and interpret phylogenetic card(cladogram and phylogenetic tree)
4. Success criteria
1. Apply previously obtained knowledgeregarding binominal nomenclature of Carl
Linnaeus.
2. Compare, analyze and find connection
(links) between different taxonomic groups.
3. Constructs and interprets cladograms.
5. Terminology
• Domain Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family GenusSpecies
• Prokaryote Eukaryote
• Animalia Plantae Fungi Bacteria Protista
• Carl Woese and Carl Linnaeus
• Systemics Taxonomy
• Cladistics / cladogram
• Characteristics
• Clade / taxa
• Binominal system
6.
Key WordsGrouping things by similar characteristics
Classification _____________________________________________
Science of grouping
Taxonomy _______________________________________________
Naming of organisms
Nomenclature ____________________________________________
Placing organism in groups
Systematics ______________________________________________
Binomial nomenclature ____________________________________
Each organism has two names:
(1) Language: Latin
(2) Taxa: Genus species
(italics),Genus species or with genus abbreviated - G. species
7.
Key WordsSpecies A group of closely related organisms that are capable of interbreeding
and producing fertile offspring
_______________________________________________________
Two closely related organisms interbreed to produce infertile offspring
-hybrid _____________________________________________________
key that uses observable features to sort organisms
Dichotomous keys A_____________________________________________
leads Statement
______________________________________________________
that leads a paired of contrasting, but mutual, observable features
qualitative Observable characteristics
__________________________________________________
quantitative Characteristics that may be counted or measured.
__________________________________________________
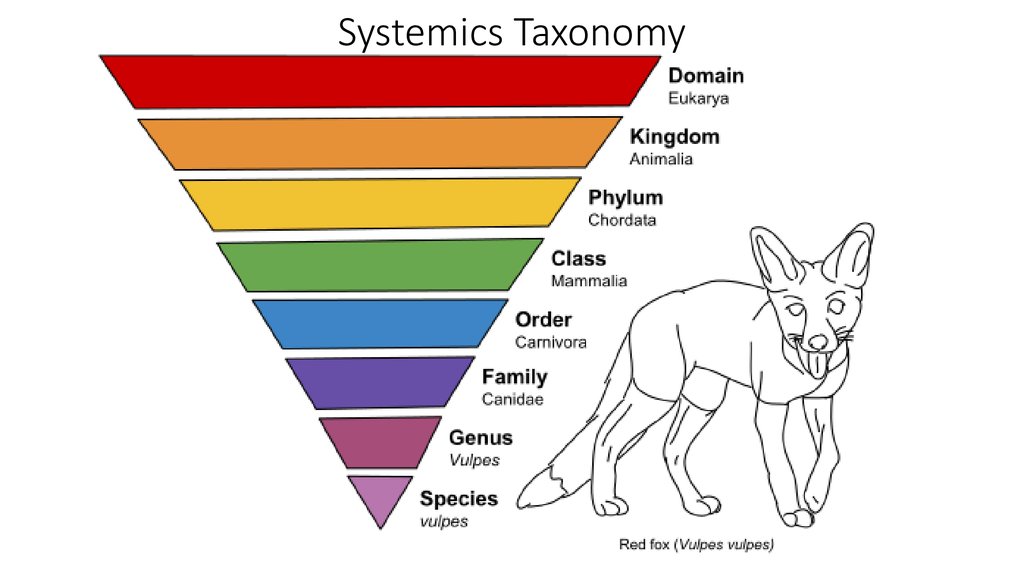
8. Systemics Taxonomy
9.
10. Modern Classification
Linnaeus developed a bettersystem
Binomial Nomenclature
2-name system
Genus and Species
Ex: Homo sapiens
11. Taxon and Classification 1994
1. *Domain least specific or largest taxa2. Kingdom
3. Phylum
4. Class
5. Order
6. Family
7. Genus
most specific or smallest taxa 8. species
A mnemonic to help remember taxon order.
Did King Pedro Come Over For Good soup DKPCOFGs
12.
• Order of classification:• Kingdom Animalia
• Phylum
Choradata
• Class
Mammalia
• Order
Carnivora
• Family
Felidae
• Genus
Lynx
• Species
Lynx rufus
Bobcat
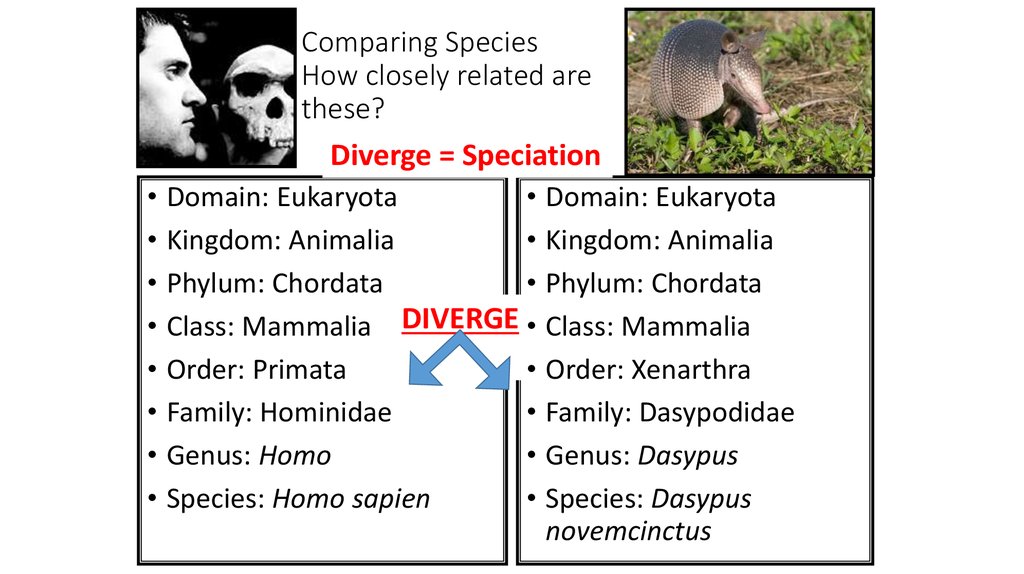
13. Comparing Species How closely related are these?
Diverge = Speciation• Domain: Eukaryota
• Domain: Eukaryota
• Kingdom: Animalia
• Kingdom: Animalia
• Phylum: Chordata
• Phylum: Chordata
• Class: Mammalia DIVERGE • Class: Mammalia
• Order: Primata
• Order: Xenarthra
• Family: Hominidae
• Family: Dasypodidae
• Genus: Homo
• Genus: Dasypus
• Species: Homo sapien
• Species: Dasypus
novemcinctus
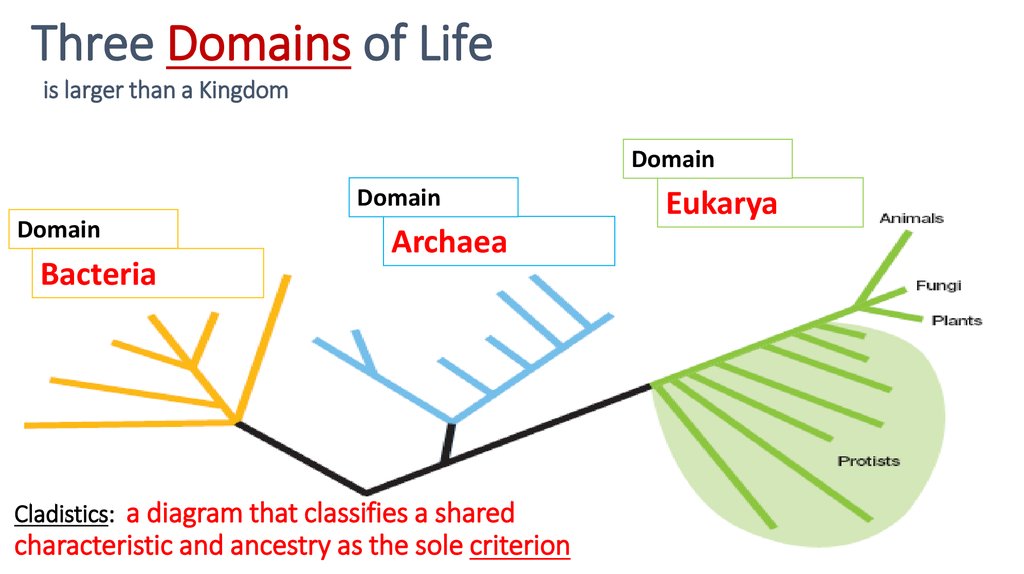
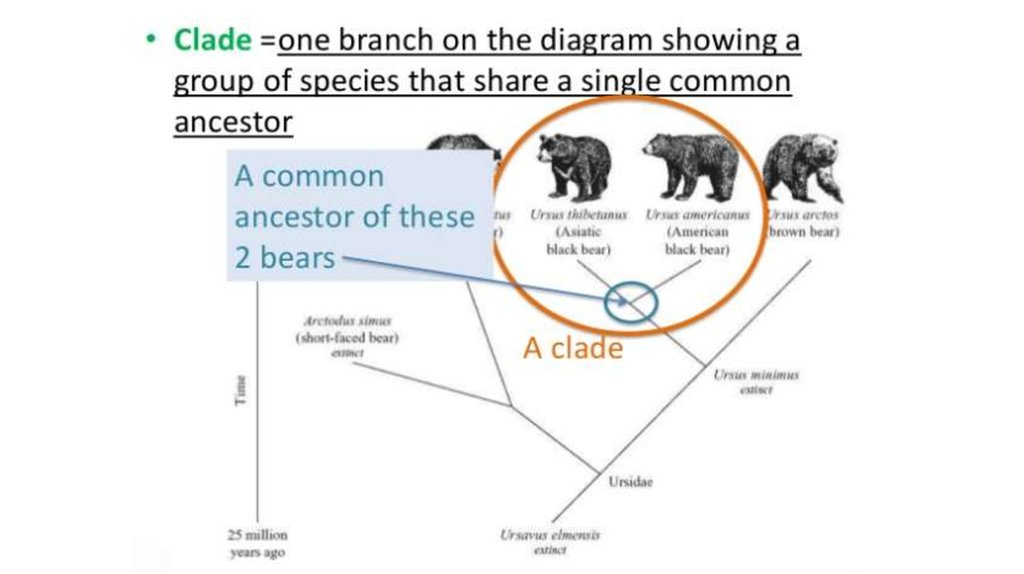
14. Cladistics: a diagram that classifies a shared characteristic and ancestry as the sole criterion
Three Domains of Lifeis larger than a Kingdom
Domain
Domain
Domain
Bacteria
Archaea
Cladistics: a diagram that classifies a shared
characteristic and ancestry as the sole criterion
Eukarya
15. Carl Woese
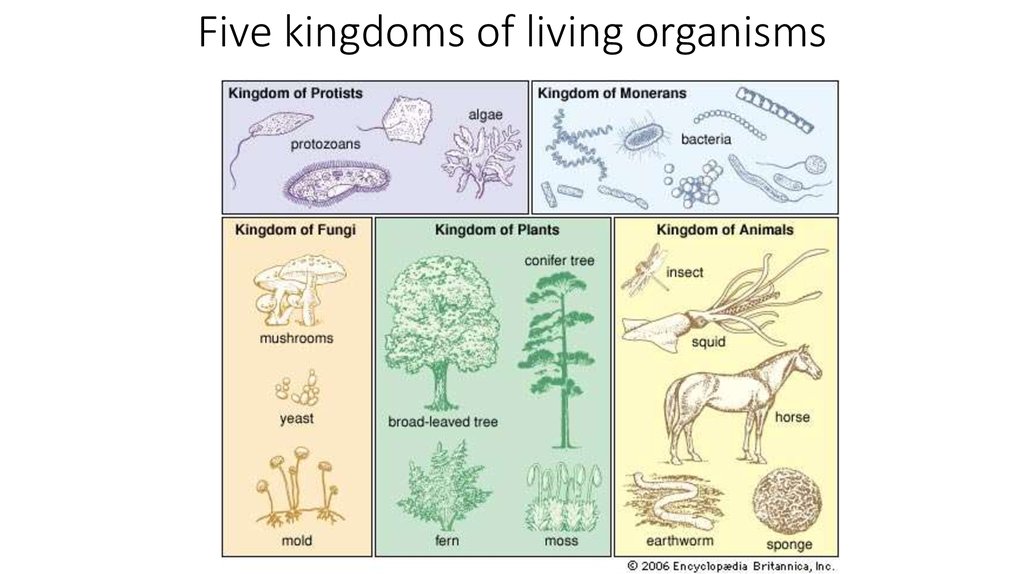
16. Five kingdoms of living organisms
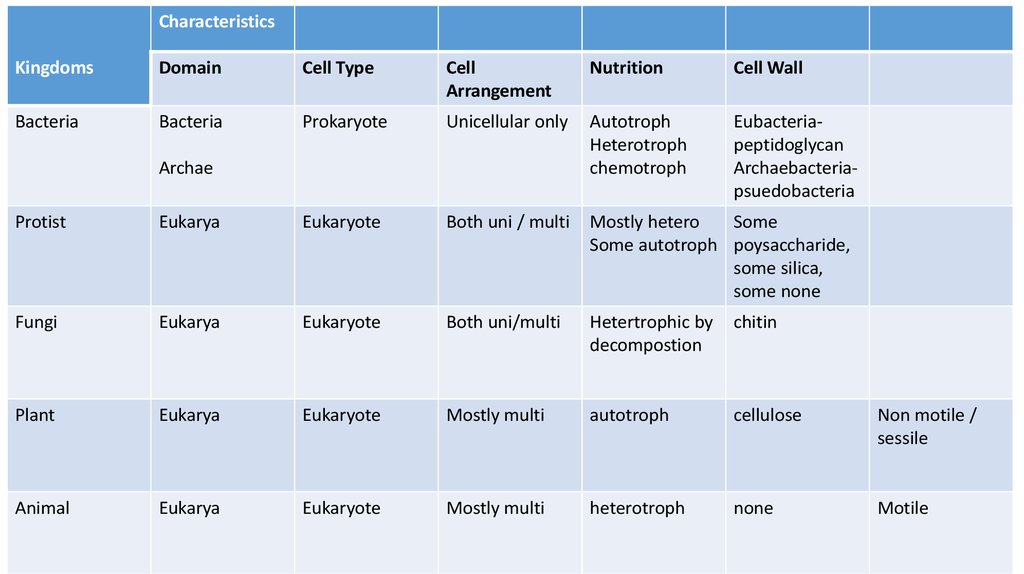
17.
CharacteristicsKingdoms
Domain
Cell Type
Cell
Arrangement
Nutrition
Cell Wall
Bacteria
Bacteria
Prokaryote
Unicellular only
Autotroph
Heterotroph
chemotroph
Eubacteriapeptidoglycan
Archaebacteriapsuedobacteria
Archae
Protist
Eukarya
Eukaryote
Both uni / multi
Mostly hetero
Some
Some autotroph poysaccharide,
some silica,
some none
Fungi
Eukarya
Eukaryote
Both uni/multi
Hetertrophic by
decompostion
chitin
Plant
Eukarya
Eukaryote
Mostly multi
autotroph
cellulose
Non motile /
sessile
Animal
Eukarya
Eukaryote
Mostly multi
heterotroph
none
Motile
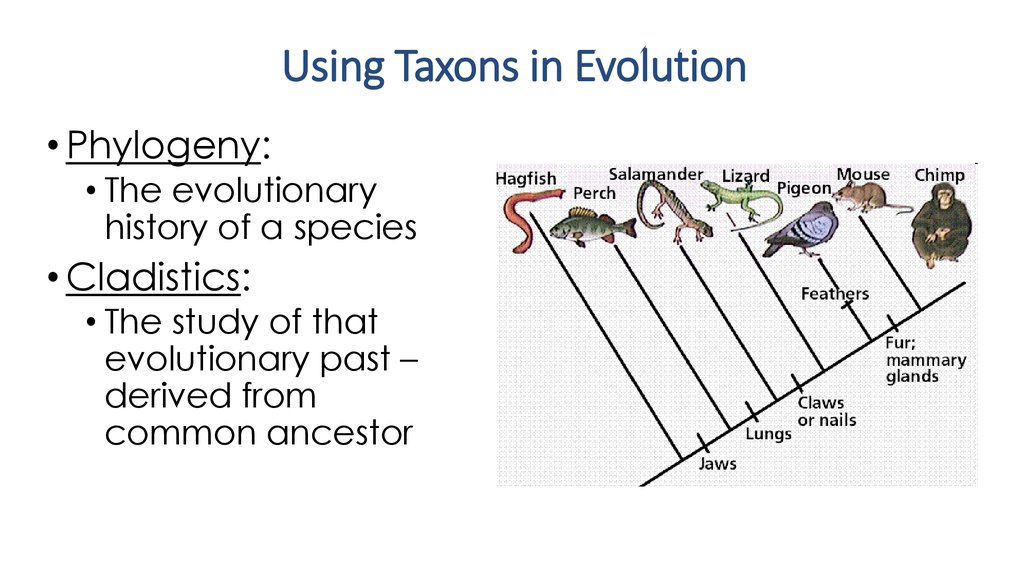
18. Using Taxons in Evolution
• Phylogeny:• The evolutionary
history of a species
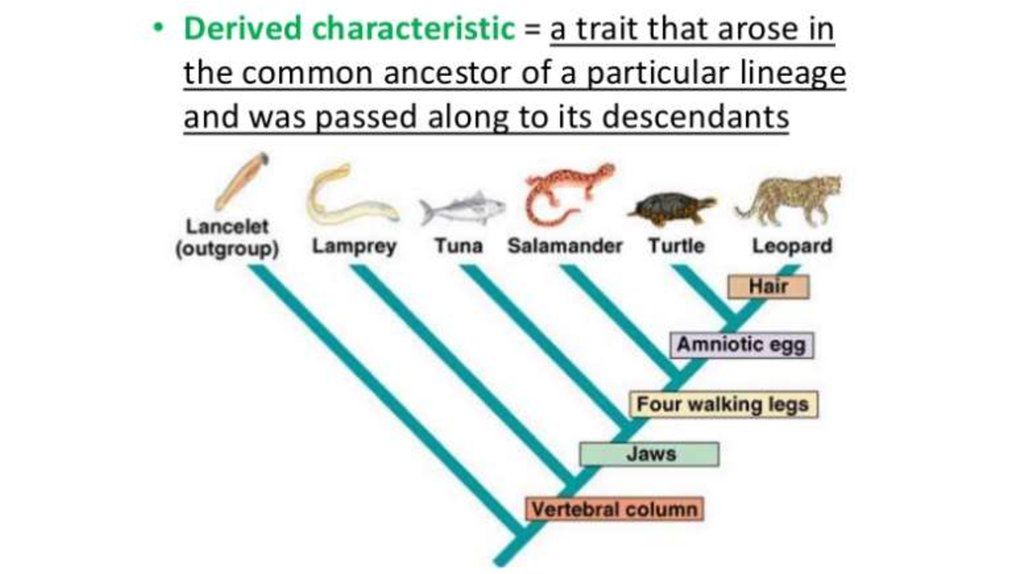
• Cladistics:
• The study of that
evolutionary past –
derived from
common ancestor
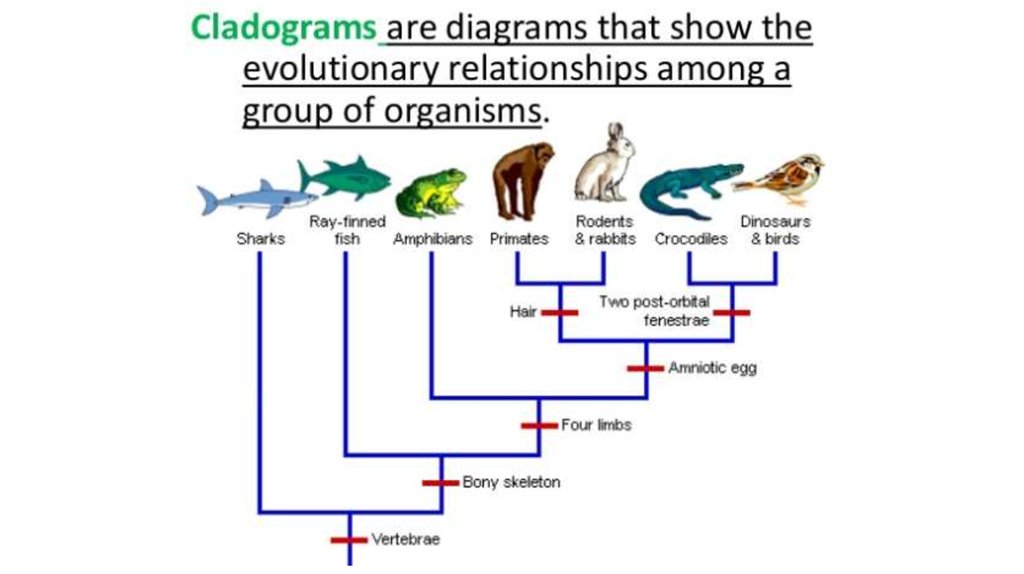
19. Cladograms
•What is a cladogram?•Diagram that depicts evolutionary
relationships among groups
•Based on phylogeny
• AKA: The evolutionary history of a species!
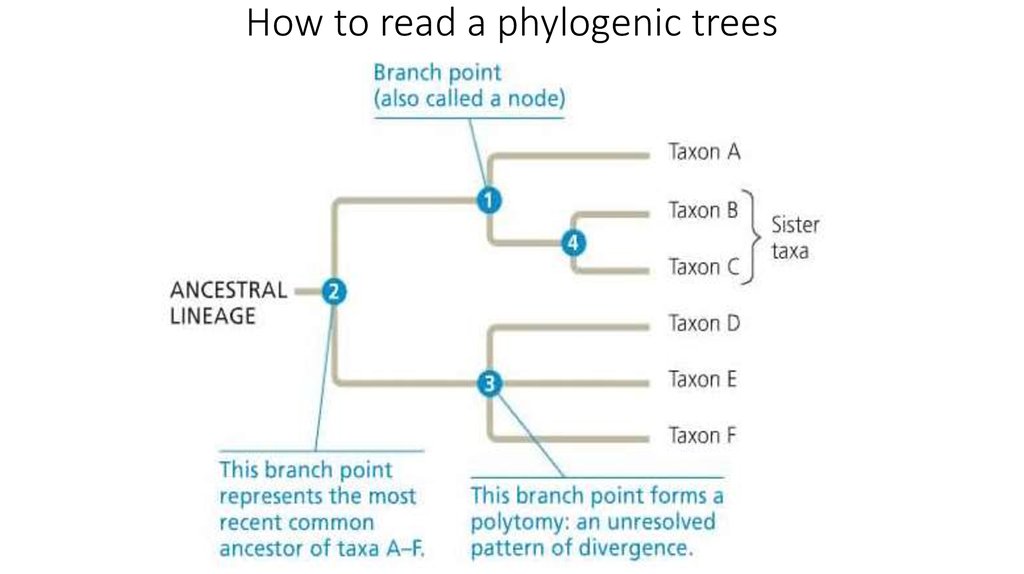
20. How to read a phylogenic trees
21.
22.
23.
24.
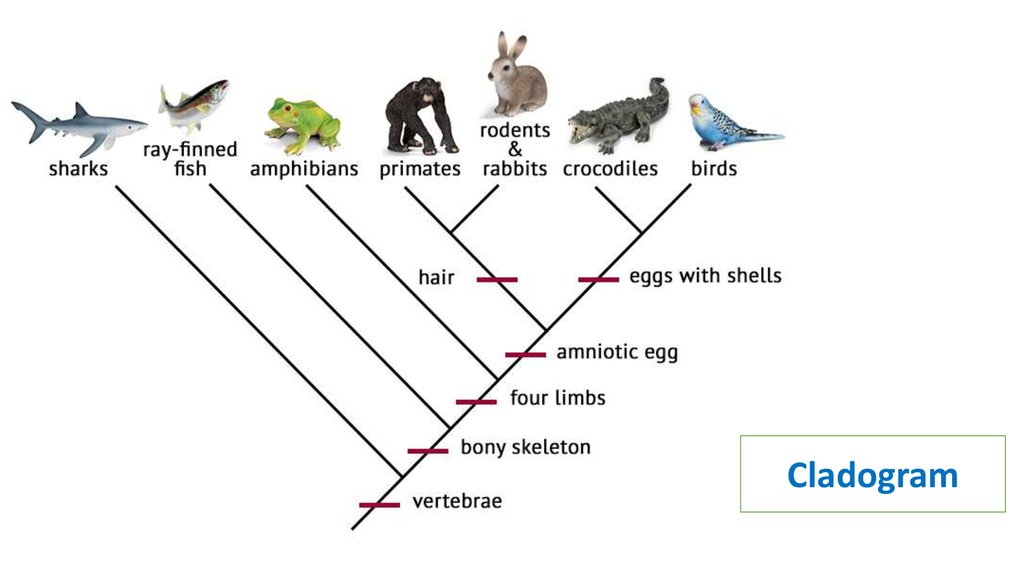
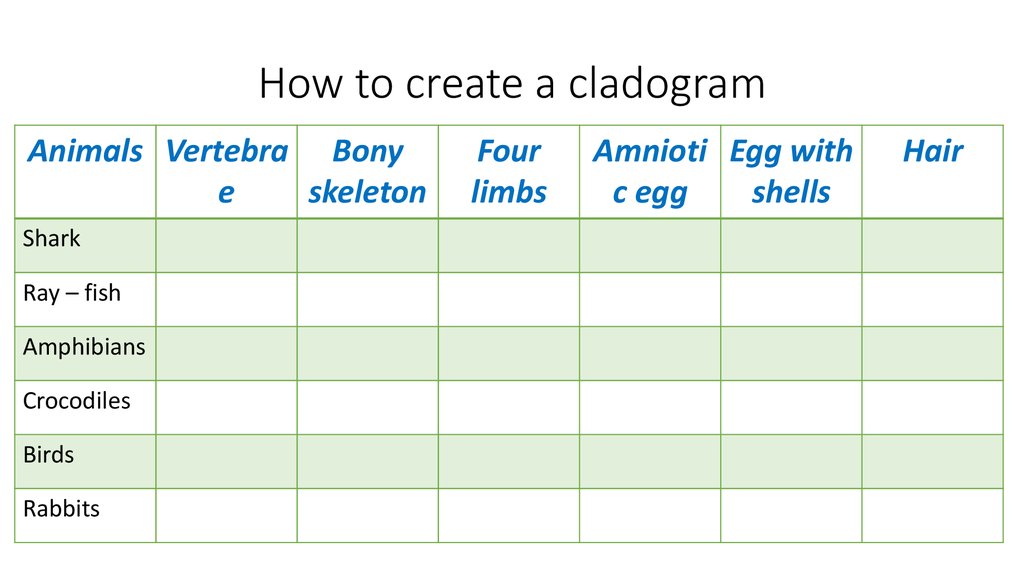
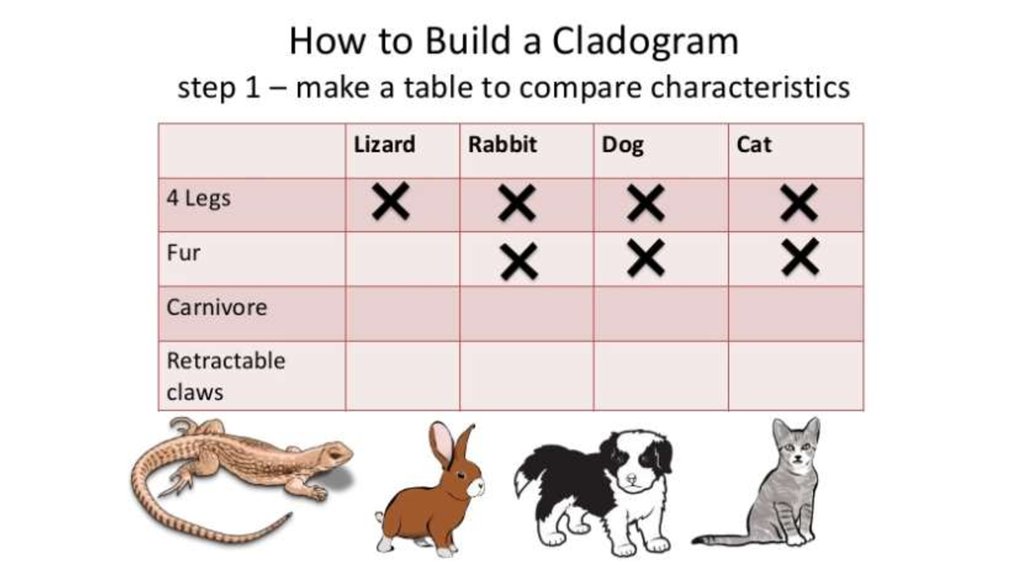
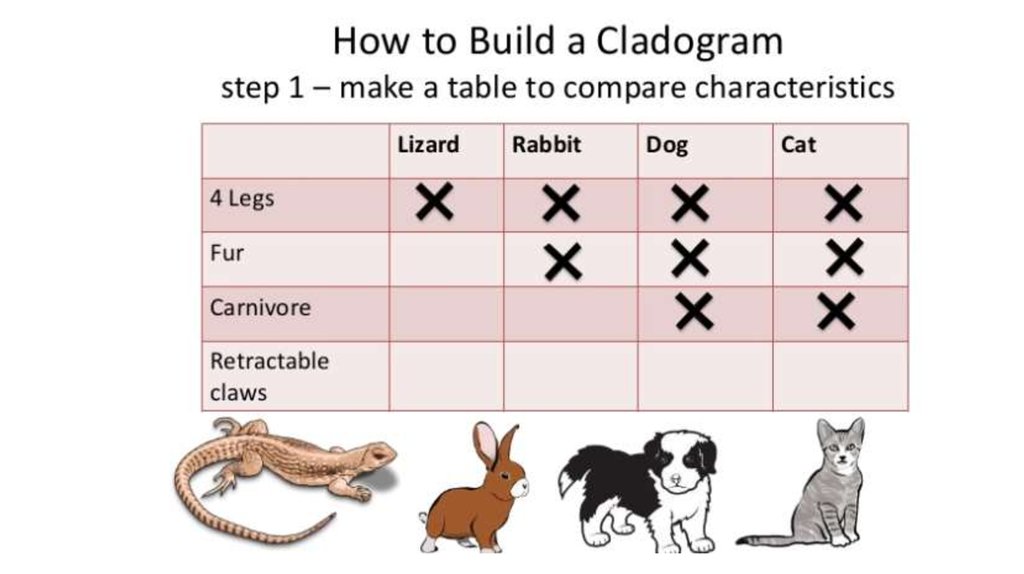
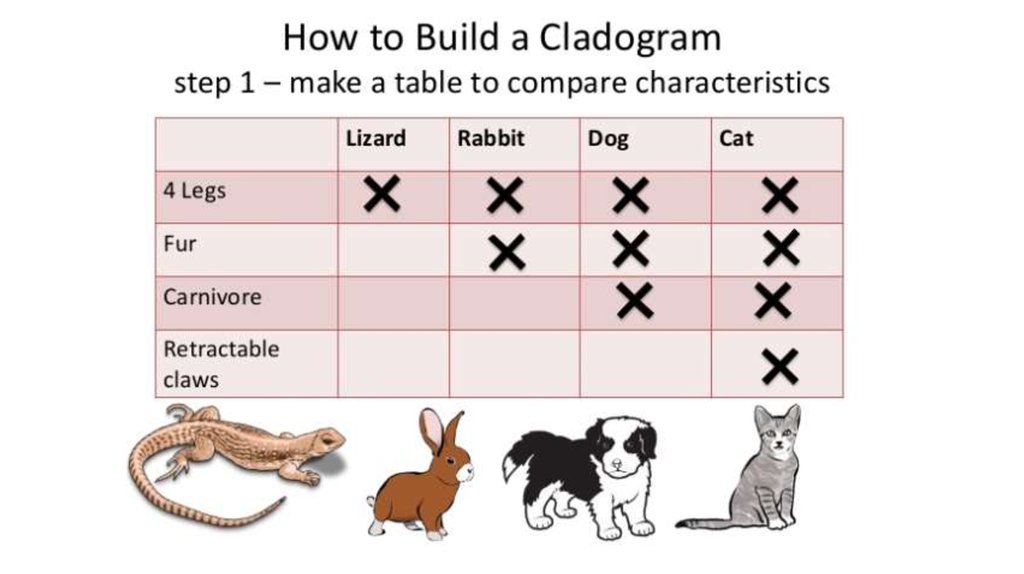
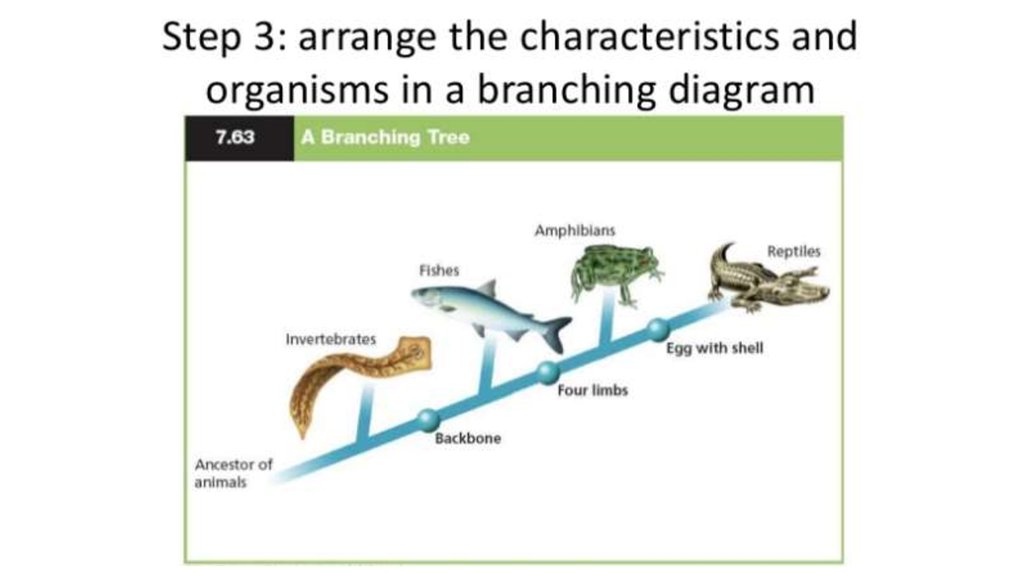
Cladogram25. How to create a cladogram
Animals Vertebra Bonye
skeleton
Shark
Ray – fish
Amphibians
Crocodiles
Birds
Rabbits
Four
limbs
Amnioti Egg with
c egg
shells
Hair
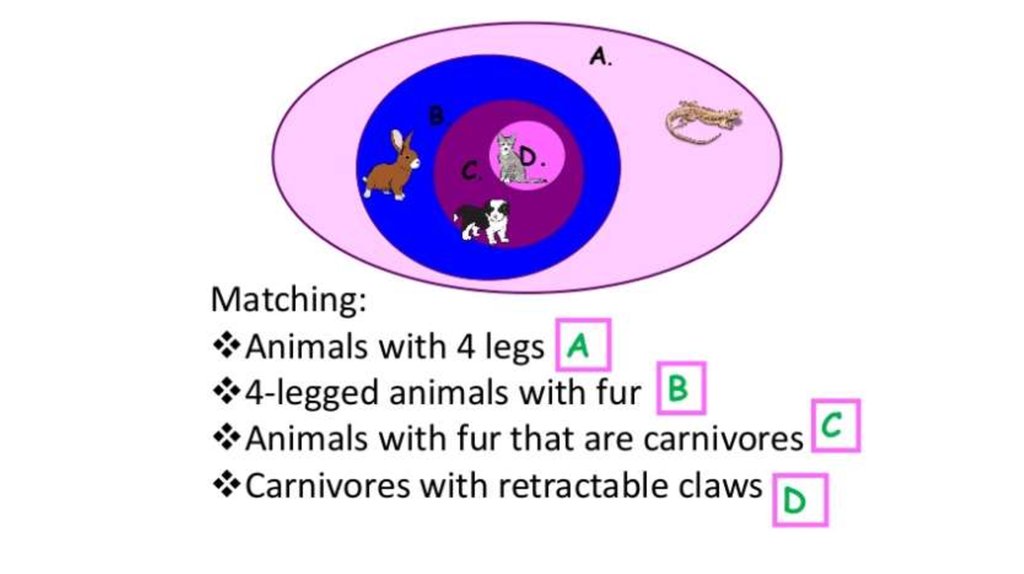
26. Create a Venn diagram
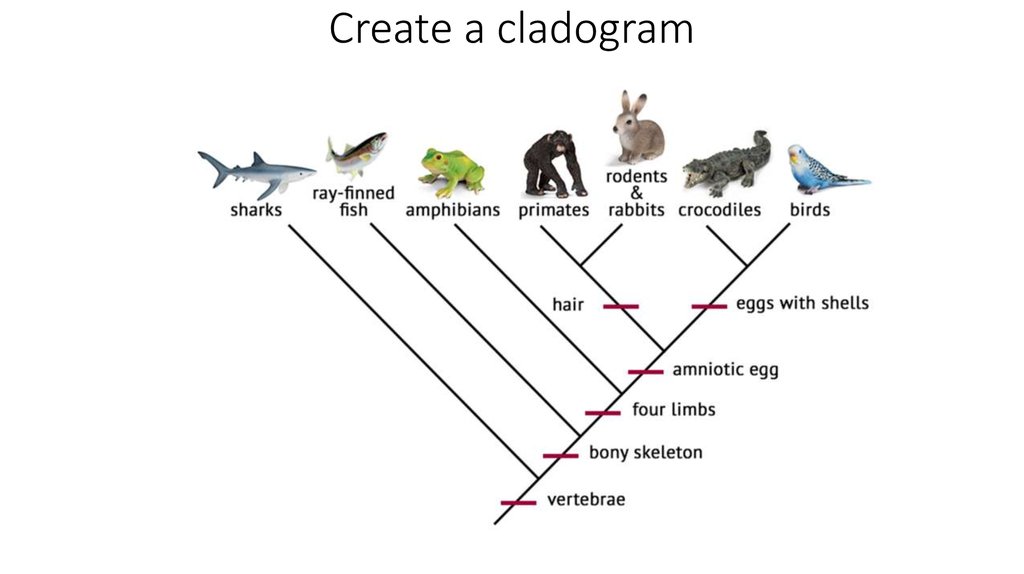
27. Create a cladogram
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34. Success criteria
1. Apply previously obtained knowledgeregarding binominal nomenclature of Carl
Linnaeus.
2. Compare, analyze and find connection
(links) between different taxonomic groups.
3. Constructs and interprets cladograms.
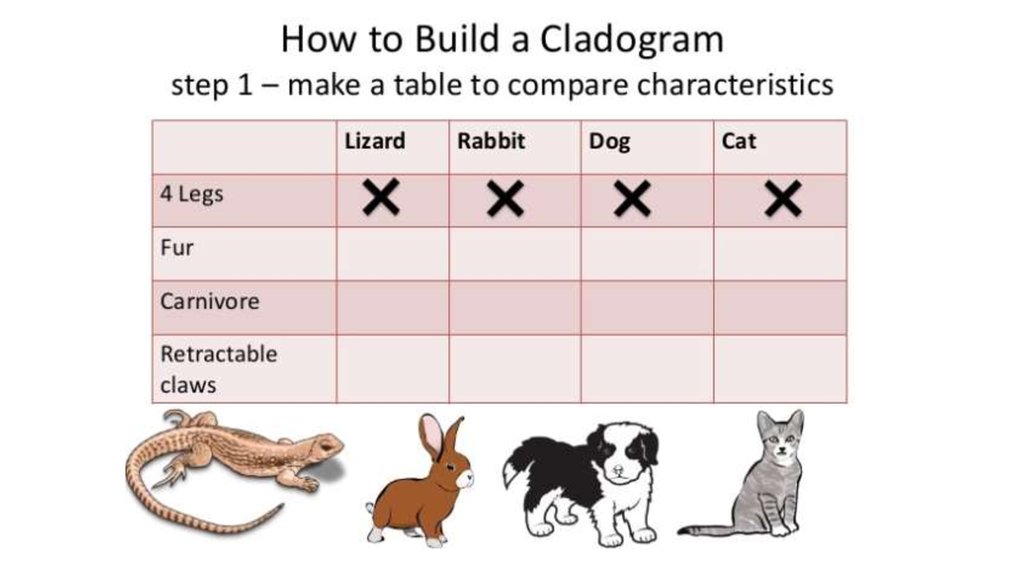
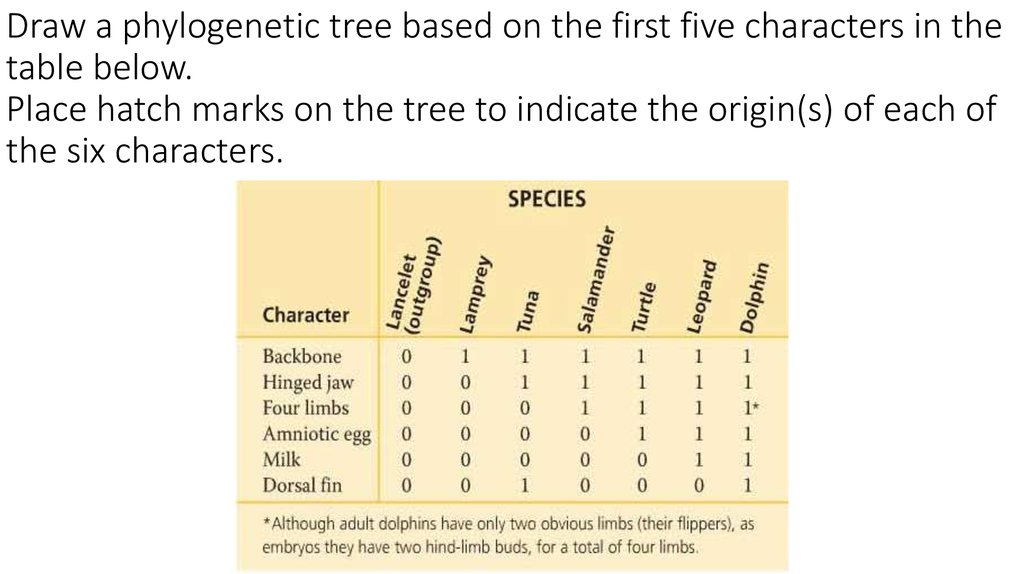
35. Draw a phylogenetic tree based on the first five characters in the table below. Place hatch marks on the tree to indicate the
origin(s) of each ofthe six characters.













 biology
biology








